Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Properties of Soil
Uploaded by
Humberto Moreno0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageSoils can be divided into fractions based on grain size, such as separating a soil sample using a 4.75-mm sieve into fractions finer and coarser than 4.75-mm. The fraction finer than 4.75-mm is called the control fraction while the fraction coarser is the oversize. Different upper size limits are used for evaluating soils, as the largest particles can affect workability, with important limits including the 4.75-mm used to divide soils for construction and earthwork control.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSoils can be divided into fractions based on grain size, such as separating a soil sample using a 4.75-mm sieve into fractions finer and coarser than 4.75-mm. The fraction finer than 4.75-mm is called the control fraction while the fraction coarser is the oversize. Different upper size limits are used for evaluating soils, as the largest particles can affect workability, with important limits including the 4.75-mm used to divide soils for construction and earthwork control.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageProperties of Soil
Uploaded by
Humberto MorenoSoils can be divided into fractions based on grain size, such as separating a soil sample using a 4.75-mm sieve into fractions finer and coarser than 4.75-mm. The fraction finer than 4.75-mm is called the control fraction while the fraction coarser is the oversize. Different upper size limits are used for evaluating soils, as the largest particles can affect workability, with important limits including the 4.75-mm used to divide soils for construction and earthwork control.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
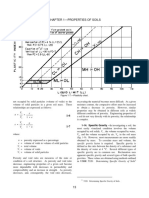
CHAPTER 1—PROPERTIES OF SOILS
Figure 1-4.—Gradation plot.
A soil sample may be divided into parts&called A number of different upper-size limits are frequently used
fractions&based on grain size. For example, in construction in appraising soils. The workability of a soil is often
control of earthwork, soil is frequently divided into two affected appreciably by the largest soil particles present.
fractions using the U.S.A. Standard 4.75-mm sieve (No. 4). Important upper-size limits for various applications are:
The fraction finer than the 4.75-mm sieve (the minus
4.75-mm fraction) is called the control fraction, and the
fraction coarser than the 4.75-mm sieve (the plus 4.75-
mm fraction) is called the oversize.
You might also like
- Soil Works For Road ConstructionDocument40 pagesSoil Works For Road ConstructionYaseen YousafNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 1. Identification of Soil (Visual-Manual Method)Document4 pagesLaboratory 1. Identification of Soil (Visual-Manual Method)Dean Albert ArnejoNo ratings yet
- Density Test of SoilDocument12 pagesDensity Test of SoilJessa LatosaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 Soil CompactionDocument24 pagesChapter-3 Soil CompactionYedenekachew NigussieNo ratings yet
- AmorDocument3 pagesAmorMIKI RULOMANo ratings yet
- Soil ClassificationDocument40 pagesSoil ClassificationSyed Mobashir HassanNo ratings yet
- Soil Stabilization and CompactionDocument8 pagesSoil Stabilization and CompactionaulaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document33 pagesChapter 3siskoo habteNo ratings yet
- Dayuday Lab01Document7 pagesDayuday Lab01Guhan DayudayNo ratings yet
- النظريDocument3 pagesالنظريAhmed Atef KeshkNo ratings yet
- Sieve AnalysisDocument12 pagesSieve AnalysisRitesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Ge Presentation 1Document13 pagesGe Presentation 1Samuel EsparteroNo ratings yet
- Methods of Soil CompactionDocument4 pagesMethods of Soil CompactionLyka Isabel TanNo ratings yet
- Engineering Classification of SoilDocument40 pagesEngineering Classification of Soilhany seifNo ratings yet
- AM780-prim. TillageDocument52 pagesAM780-prim. Tillagegilbert domingoNo ratings yet
- He Module IIIDocument25 pagesHe Module IIIDheeraj KumarNo ratings yet
- ANALISIS DATA Kualitatih KuantitatifDocument12 pagesANALISIS DATA Kualitatih KuantitatifjanurtpatNo ratings yet
- Astm 2Document1 pageAstm 2zeeshanNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Geotechnical Engineering BSRE 1st 23 24Document36 pagesModule 4 Geotechnical Engineering BSRE 1st 23 24calebjohnf0512No ratings yet
- Lec. 1 Subgrade SoilDocument56 pagesLec. 1 Subgrade SoilCarvajal015No ratings yet
- Lecture 03 Particle Size DistributionDocument42 pagesLecture 03 Particle Size Distributionmuhammad asimNo ratings yet
- Grain Size Distribution of Soil by Sieve AnalysisDocument10 pagesGrain Size Distribution of Soil by Sieve AnalysisJasbir SinghNo ratings yet
- D2488 - Description and Identification of Soils (Visual-Manual Procedure) PDFDocument11 pagesD2488 - Description and Identification of Soils (Visual-Manual Procedure) PDFNachoNo ratings yet
- 1 Soil MechanicsDocument113 pages1 Soil MechanicsAysheshim BahruNo ratings yet
- Abdalrhman Ali: Engineering Technical Baghdad Department of Building and ConstructionDocument4 pagesAbdalrhman Ali: Engineering Technical Baghdad Department of Building and ConstructionAbdurrahman AliNo ratings yet
- Ai8211-Crop & Husbandry Lab ManualDocument47 pagesAi8211-Crop & Husbandry Lab Manualpa ndiNo ratings yet
- Fine and Coarse AggregatesDocument4 pagesFine and Coarse AggregatesOwais Munir Owais MunirNo ratings yet
- Compacion and Diff Types of Comp Action EquipmentDocument16 pagesCompacion and Diff Types of Comp Action EquipmentAtish KumarNo ratings yet
- Secondary Tillage Equipment: HarrowsDocument13 pagesSecondary Tillage Equipment: HarrowsYendis SamsonNo ratings yet
- BRE - LArge Diameter PLTDocument5 pagesBRE - LArge Diameter PLTAegrine100% (1)
- Soil ClassificationDocument47 pagesSoil ClassificationEr VenkatNo ratings yet
- Mix Design by DOE - 1Document20 pagesMix Design by DOE - 1Nalubega Mary GloriaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Soil+ClassificationDocument66 pagesLecture 5 Soil+ClassificationBruhNo ratings yet
- Partical Size AnalysisDocument12 pagesPartical Size AnalysisAhmed Mohamed Ismail 183-47-859No ratings yet
- SoilDocument151 pagesSoilSubrat DashNo ratings yet
- Geotech 2 Particle Size Distribution.Document23 pagesGeotech 2 Particle Size Distribution.Regine OlayaNo ratings yet
- Standard-Installation 3Document1 pageStandard-Installation 3Alshamllaa RD AlirsalNo ratings yet
- Ce512 - Geotechnical Engineering Presentation 1Document13 pagesCe512 - Geotechnical Engineering Presentation 1Samuel EsparteroNo ratings yet
- Ce1305 - Foundation EngineeringDocument12 pagesCe1305 - Foundation Engineeringsaamy100% (2)
- Laboratory Compaction Characteristics of Soil Using Standard Effort (12 400 FT-LBF/FT (600 KN-M/M) )Document13 pagesLaboratory Compaction Characteristics of Soil Using Standard Effort (12 400 FT-LBF/FT (600 KN-M/M) )grats_singcoNo ratings yet
- 2-Highway Materials NewDocument8 pages2-Highway Materials Newhamid shahNo ratings yet
- Highway: Construction Materials, Equipments and Practice HDocument44 pagesHighway: Construction Materials, Equipments and Practice Hnurul hidayatiNo ratings yet
- Construction Technology: Earthmoving TechnologiesDocument77 pagesConstruction Technology: Earthmoving TechnologiesMelad S MasriNo ratings yet
- Dhanalakshmi College of Engineering, Chennai Department of Civil Engineering 2 Mark Questions With Answers Ce6502 - Foundation EngineeringDocument10 pagesDhanalakshmi College of Engineering, Chennai Department of Civil Engineering 2 Mark Questions With Answers Ce6502 - Foundation EngineeringDr J Logeshwari Asst. Prof., CIVIL Veltech, ChennaiNo ratings yet
- Presentationgroupageoteknik 150320092112 Conversion Gate01Document89 pagesPresentationgroupageoteknik 150320092112 Conversion Gate01Paradise BirdNo ratings yet
- Ground Improvement TechniquesDocument74 pagesGround Improvement TechniquesNishanthan RavinNo ratings yet
- Final Report Disk MillDocument10 pagesFinal Report Disk MillMuhammad Irfan MalikNo ratings yet
- HE Mod3@AzDOCUMENTS - inDocument57 pagesHE Mod3@AzDOCUMENTS - inMANASA.M.PNo ratings yet
- Practically Incompressible When DenseDocument5 pagesPractically Incompressible When DensehaileyyyNo ratings yet
- 2.highway MaterialsDocument44 pages2.highway MaterialsmikaillianaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report TemplateDocument15 pagesLab Report TemplateChristine Mae TinapayNo ratings yet
- Soil PreparationFrom EverandSoil PreparationNo ratings yet
- Properties of Soil 2Document1 pageProperties of Soil 2Humberto MorenoNo ratings yet
- Tabla de Maximo Contenido de ClorurosDocument1 pageTabla de Maximo Contenido de ClorurosHumberto MorenoNo ratings yet
- Relationship Between Air Water and Solids in A Soil MassDocument1 pageRelationship Between Air Water and Solids in A Soil MassHumberto MorenoNo ratings yet
- In Control CUSUM Chart Process Mean Example 1Document1 pageIn Control CUSUM Chart Process Mean Example 1Humberto MorenoNo ratings yet
- Phases of A Soil-Water SystemDocument1 pagePhases of A Soil-Water SystemHumberto MorenoNo ratings yet
- Extension of Workability TimeDocument1 pageExtension of Workability TimeHumberto MorenoNo ratings yet
- Level 2 Master Format Numbers Div 07Document1 pageLevel 2 Master Format Numbers Div 07Humberto MorenoNo ratings yet
- In Control CUSUM Chart Example 1Document1 pageIn Control CUSUM Chart Example 1Humberto MorenoNo ratings yet
- In Control CUSUM Chart Additional FormattingDocument1 pageIn Control CUSUM Chart Additional FormattingHumberto MorenoNo ratings yet
- In Control CUSUM Chart Process Mean ExampleDocument1 pageIn Control CUSUM Chart Process Mean ExampleHumberto MorenoNo ratings yet
- Level 2 Master Format Numbers Div 09Document1 pageLevel 2 Master Format Numbers Div 09Humberto MorenoNo ratings yet
- Level 2 Master Format NumbersDocument1 pageLevel 2 Master Format NumbersHumberto MorenoNo ratings yet
- Level 2 Master Format Numbers Div 02Document1 pageLevel 2 Master Format Numbers Div 02Humberto MorenoNo ratings yet
- Level 2 Master Format Numbers Div 04Document1 pageLevel 2 Master Format Numbers Div 04Humberto MorenoNo ratings yet