Professional Documents
Culture Documents
General Purpose FS Special Purpose FS
Uploaded by
Kylie CortezOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
General Purpose FS Special Purpose FS
Uploaded by
Kylie CortezCopyright:
Available Formats
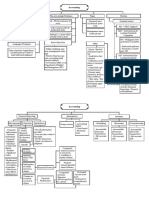
Financial Accounting and Reporting
Financial accounting – financial position, results of operation || Financial
Corporation report
– at least – FS + other SEC
5 (stockholders),
useful info Cooperative – 15 or more (members), CDA
Accounting
AAA – process Types of business activities
AICPA – art Service – offer service
ASC – service activity Merchandising/Trading – buy and sell
Manufacturing – raw materials to finished
Types of accounting information
Quantitative – numbers, units
Accounting concepts and principles
Qualitative – words, notes
(Ideas and procedures that guide accountants)
Financial – money
Separate entity concept – owner’s transaction
Users of accounting information diff. from entity’s
Historical cost – record purchase at purchase
Internal – directly involved in management
price
External – for investment and credit decisions
Going concern – entity to continue || Liquidating
General Purpose FS Special Purpose FS concern – entity intends to end
-for external users -for internal users Matching – some cost initially recognized as
-common needs -specific needs assets until recognition of related revenue
-by financial accounting -by management Accrual basis – record in period where it
accounting occurred/when earned or incurred || Cash basis –
Objectives of financial reporting… record when cash is affected
1. Provide info on economic resources, claims, Prudence – degree of caution
and changes on resources Time Period – using reporting periods
2. Provide info for assessing management (calendar/fiscal, interim can be
stewardship month/quarter/semiannually)
Fields and branches of accounting Stable monetary unit – inflation ignored
Public Accounting – professional services for Materiality concept – record if it affects decision
fee Cost-benefit – cost should not exceed benefits
o External auditing – independent
Full disclosure – disclose important matters
evaluation || PSA (Philippine Standard
Consistency – same treatments
on Auditing)
Accounting Standards
o Tax Services, Management Advisory
Philippine Financial Reporting Standards
Services
(PFRS)
Private Accounting – employed in privates / o PFRS, PAS, Interpretations
NGO
o Issued by FRSC (standard-setting body
o Financial accounting – PFRS/PAS
in Philippines)
o Cost accounting
o Patterned from IFRS by IASB
o Tax accounting – NIRC (National
Generally Accepted Accounting Principles
Internal Revenue Code)
(GAAP)
o Management accounting
Qualitative characteristics of useful financial info
o Internal auditing Fundamental – makes info useful
Government Accounting - disposition of public Relevance – can affect decision
funds || NGAS (National Government o Predictive value – predictions about outcome
Accounting System) o Confirmatory value – confirm predictions
Accounting Education o Materiality – entity-specific
Accounting Research
Faithful representation – factual
Forms of business organizations
o Completeness – necessary info
Sole proprietorship – one owner (sole
o Neutrality – without bias
proprietor), DTI
o Free from error - in description/process
Partnership – 2 or more (partners), SEC
Enhancing – supports fundamentals o Check equality and detect errors
Comparability – identify similarities/differences 5. Adjusting Entries
Verifiability – reach same agreement o Update accounts (accruals, depreciation,
Timeliness – available in time bad debts, deferrals)
Understandability – clear and concise *accruals – recognize uncollected/unpaid income and
Accounting Equation expense
Assets = Liabilities + Equity (+ Income – Expense) *deferrals – postpone recognition advanced
Income – Expense = Profit/Loss collections/prepayments
Major Accounts: >advance collections – liability/income method
Balance sheet accounts/Real accounts >prepayments – asset/expense method
Assets – economic resources you control 6. Adjusted Trial Balance / Worksheet
Liabilities – obligations >analytical device to gather data
Legal – from contract, law >cross-footing – add/sub amounts horizontally
Constructive – expected responsibilities >footing – add/sub amounts vertically
Equity – capital, net assets, net worth 7. Financial Statements
Income statement accounts/Nominal accounts o Balance sheet (FS) – info on assets,
Income – increase in economic benefits; +assets, -liab liabilities, and equity
Expenses – decrease in econ benefits; -assets, +liab o Income statement – profit/loss
DEBIT (VALUE CREDIT (VALUE o Statement of comprehensive income –
RECEIVED) PARTED) other income and expense not in profit
EXPENSES LIABILITIES and loss
ASSETS INCOME o Statement of changes in equity
DRAWINGS CAPITAL o Statement of cash flows – assess ability
Account – record of increase/decrease in items
to generate income, pay obligations
Contra accounts – deduction to related account i. Operating activities – creates
Adjunct account – addition to related account income/expense
Chart of accounts – list of all accounts used by business ii. Investing activities – PPE,
Book of accounts loans, lending (long term)
Journal – book of original entries iii. Financing activities – obtain
o Special – similar transactions cash on investors, providing
o General – transactions not in special ROI, debt financing
Ledger – book of secondary/final entries 8. Closing Entries
o General – accounts in trial balance o Zero out nominal accounts including
o Subsidiary – w/balances of accounts drawings
9. Post-closing Trial Balance
Double-entry system 10. Reversing Entries
Transactions should have a debit and credit o Receivables and payables
Concepts: Accounting in Merchandising Business
Duality – two-fold effect Inventory – goods for resale
Equilibrium – equal debits and credits Perpetual – continuous record
Accounting Cycle Periodic – physical count
1. Identifying and Analyzing Gross profit = Net sales – COGS
o Accountable events from source Net sales = Total sales – sales returns and discounts
documents COGS = Beginning inventory + net purchases – ending
2. Journalizing Net purchases = Purchases + freight in – purchase
o Record accountable events returns and discounts
chronologically; entries can be
simple/compound
3. Posting
o Classify effects of transaction to ledger
4. Unadjusted Trial Balance
SAMPLE
(Sample problems)
1.
a. account PROBLEMS
It is the basic storage of information in accounting
b. journal c. memory card d. USB
2. The term “record” is most synonymous with
a. identifying b. journalizing c. posting d. communicating
3. Sole proprietorship is registered with
a. DTI b. SEC c. CDA d. all of these
4. Under the accrual basis of accounting, a business records a sale
a. When sale occurs b. when sale price is collected c. a or b, as an accounting policy choice
5. Which of the following is least likely to be a source of an accounting concept?
a. The standards b. the conceptual framework c. general acceptance d. laws by congress
6. Which of the following is not correct?
a. Assets = Liabilities = Equity + Income – Expense
b. Assets – Liabilities = Equity + Income – Expense
c. Assets + Expense = Liabilities + Equity + Income
d. Assets = Liabilities + Equity – Income + Expense
7. An expense could not possibly result
a. In a decrease in equity b. from an increase in assets c. from an increase in liabilities d. from
decrease in assets
8.
You might also like
- 3 Financial Reporting and Analysis MMDocument29 pages3 Financial Reporting and Analysis MMAishwarya BansalNo ratings yet
- Cfas NotesDocument3 pagesCfas NotesUyara LeisbergNo ratings yet
- Introductuion To AccountsDocument4 pagesIntroductuion To AccountsJoanne CrysantherNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 NotesDocument3 pagesMODULE 1 NotesJoshua AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Cfas Reviewer Chapter 1 5 CompressDocument5 pagesCfas Reviewer Chapter 1 5 CompressabetomelyprincessNo ratings yet
- Finalized Mod 1&2 ReviewerDocument4 pagesFinalized Mod 1&2 ReviewerJoshua AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Intro To FA Jan2018Document33 pagesLecture 1 Intro To FA Jan2018IssacNo ratings yet
- CFA1 FRA Revision HHD 2020.10.23Document62 pagesCFA1 FRA Revision HHD 2020.10.23Hà Thúy VyNo ratings yet
- ACFAR ReviewDocument39 pagesACFAR ReviewYza IgartaNo ratings yet
- Financial Reporting M20: TutorialDocument37 pagesFinancial Reporting M20: TutorialrandomNo ratings yet
- Far ReviewerDocument12 pagesFar ReviewerAndrew Gino CruzNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2: Transaction Analysis & Financial Statements: ACCT10001 Accounting Reports and AnalysisDocument21 pagesLecture 2: Transaction Analysis & Financial Statements: ACCT10001 Accounting Reports and AnalysisBáchHợpNo ratings yet
- 11 ABM ReviewerDocument8 pages11 ABM ReviewerJonwel OcampoNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Framework and Accounting StandarsDocument12 pagesConceptual Framework and Accounting StandarsMarifel AldacaNo ratings yet
- Fabm1 - Reviewer: AccountingDocument7 pagesFabm1 - Reviewer: AccountingBaluyut, Kenneth Christian O.No ratings yet
- Foundation FA S1Document18 pagesFoundation FA S1narmadaNo ratings yet
- Far 1-2Document3 pagesFar 1-2Marjorie UrbinoNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Framework and Accounting StandardsDocument3 pagesConceptual Framework and Accounting StandardsGenena QuitasolNo ratings yet
- Accounting FOR ManagementDocument63 pagesAccounting FOR ManagementAnonymous 1ClGHbiT0JNo ratings yet
- Summary ReviewerDocument3 pagesSummary ReviewerJohn Aries MiranoNo ratings yet
- Nature of AccountingDocument39 pagesNature of AccountinghotpokerchipsNo ratings yet
- Accounting: Scope of Practice of AccountancyDocument6 pagesAccounting: Scope of Practice of AccountancyKl HumiwatNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Framework and Accounting Standards Guide QuestionsDocument3 pagesConceptual Framework and Accounting Standards Guide QuestionsAngel heheNo ratings yet
- AFM - Session 1Document5 pagesAFM - Session 1PRASHANT ARORANo ratings yet
- BFAR ReviewerDocument11 pagesBFAR Reviewergyurijoss.ulfindo.cvtNo ratings yet
- FM 10 - Dr. Cedric Val Naranjo, CPADocument5 pagesFM 10 - Dr. Cedric Val Naranjo, CPARichielen Navarro RabayaNo ratings yet
- 11 ABM ReviewerDocument8 pages11 ABM ReviewerDriz DepositarNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Framework and Accounting StandardsDocument3 pagesConceptual Framework and Accounting StandardsGenena QuitasolNo ratings yet
- CAPE Accounting Unit 1 Module 1 The Nature and Scope of AccountingDocument11 pagesCAPE Accounting Unit 1 Module 1 The Nature and Scope of AccountingRhea Lee Ross100% (1)
- Introduction To Financial AccountingDocument64 pagesIntroduction To Financial AccountingAnonymous HumanNo ratings yet
- Abm 1 TransesDocument2 pagesAbm 1 TransesYanch SanchezNo ratings yet
- For With God, Nothing Shall Be Impossible. (Luke 1:37) : Accounting ReviewerDocument7 pagesFor With God, Nothing Shall Be Impossible. (Luke 1:37) : Accounting ReviewerDebbie Grace Latiban LinazaNo ratings yet
- Basic Accounting Concepts and PrinciplesDocument16 pagesBasic Accounting Concepts and PrinciplesRenmar CruzNo ratings yet
- OBLICON Definition of TermsDocument9 pagesOBLICON Definition of TermsKimmy ShawwyNo ratings yet
- Financial Analysis and Reporting Introduction CourseDocument2 pagesFinancial Analysis and Reporting Introduction CourseRamjie MercadoNo ratings yet
- CFAS Chapter 1 The Accountancy ProfessionDocument1 pageCFAS Chapter 1 The Accountancy ProfessionKaren CaelNo ratings yet
- Topic Outline For Topic 1 Introduction To Cost Accounting and Cost Information SystemsDocument9 pagesTopic Outline For Topic 1 Introduction To Cost Accounting and Cost Information SystemsJuliana BalbuenaNo ratings yet
- LS 1 - ACCOUNTING AND ITS ENVIRONMENT Part 2Document53 pagesLS 1 - ACCOUNTING AND ITS ENVIRONMENT Part 2Danielle Angel Malana100% (1)
- Financial AccountingDocument8 pagesFinancial AccountingKetan ThakkarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Cost & Management AccountingDocument30 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Cost & Management AccountingJiajia MoxNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting and Reporting: Exchange Non-Reciprocal TransferDocument14 pagesFinancial Accounting and Reporting: Exchange Non-Reciprocal TransferMa. Cristy BroncateNo ratings yet
- Fabmlt 1Document3 pagesFabmlt 1lemonNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Accounting 3Document10 pagesIntermediate Accounting 3Hannaniah PabicoNo ratings yet
- 1 AccountingDocument25 pages1 AccountingSaltanat ShamovaNo ratings yet
- AD1101 AY15 - 16 Sem 1 Lecture 1Document21 pagesAD1101 AY15 - 16 Sem 1 Lecture 1weeeeeshNo ratings yet
- Basic AccountingDocument15 pagesBasic AccountingShellalyn RigonNo ratings yet
- ICAI Jan 30 2016Document34 pagesICAI Jan 30 2016Devasish ParmarNo ratings yet
- On CFS FFSDocument31 pagesOn CFS FFSShirsendu MondolNo ratings yet
- CFAS (Review) - Summary CFAS (Review) - Summary: Accounting (Far Eastern University) Accounting (Far Eastern University)Document6 pagesCFAS (Review) - Summary CFAS (Review) - Summary: Accounting (Far Eastern University) Accounting (Far Eastern University)jaymz esperatNo ratings yet
- Introduction To AccountingDocument32 pagesIntroduction To AccountingRaj RajputNo ratings yet
- BoA CPA Board Syllabus MappingDocument27 pagesBoA CPA Board Syllabus MappingTrisha Monique VillaNo ratings yet
- Abo 1Document3 pagesAbo 1Shane Ivory ClaudioNo ratings yet
- Accounting Concept Maps 5Document18 pagesAccounting Concept Maps 5Ashley Levy San Pedro100% (1)
- Foundation FA S1 - LecturerDocument24 pagesFoundation FA S1 - LecturernarmadaNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting NotesDocument7 pagesFinancial Accounting NotesGan JessieNo ratings yet
- TO Accounting: Dr. Ritika BhatiaDocument35 pagesTO Accounting: Dr. Ritika BhatiaRahul Rajendra Kumar BanyalNo ratings yet
- Financial AccountingDocument110 pagesFinancial AccountingMayara CabralNo ratings yet
- ACCOUNTINGDocument6 pagesACCOUNTINGFe VhieNo ratings yet
- An Introduction to Business Accounting for ManagersFrom EverandAn Introduction to Business Accounting for ManagersRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Summary: Financial Intelligence: Review and Analysis of Berman and Knight's BookFrom EverandSummary: Financial Intelligence: Review and Analysis of Berman and Knight's BookNo ratings yet
- Esri Course CatalogDocument44 pagesEsri Course CatalogMelvin MagbanuaNo ratings yet
- How To Calculate Roi To Justify A ProjectDocument4 pagesHow To Calculate Roi To Justify A Projectsinta AgtrianasariNo ratings yet
- SYBBA Finance ProjectDocument10 pagesSYBBA Finance ProjectJanki PatilNo ratings yet
- Business Report - 2 (GODIGIT Bank)Document10 pagesBusiness Report - 2 (GODIGIT Bank)Rahul100% (1)
- AWS To Azure Services Comparison High Level PDFDocument28 pagesAWS To Azure Services Comparison High Level PDFBhavanesh AsarNo ratings yet
- Benelite Process For Upgradation of IllemniteDocument6 pagesBenelite Process For Upgradation of Illemnitemadangk100% (1)
- Random Walk Model of ConsumptionDocument22 pagesRandom Walk Model of Consumptionshahid_hussain_41100% (1)
- GSIS TEMPLATE Fire Insurance Application Form (TRAD)Document3 pagesGSIS TEMPLATE Fire Insurance Application Form (TRAD)Ronan MaquidatoNo ratings yet
- CV - Bhupendra SinghDocument3 pagesCV - Bhupendra SinghTejas LakhaniNo ratings yet
- Strategic Cost Management: AssignmentDocument2 pagesStrategic Cost Management: AssignmentPranai MehtaNo ratings yet
- Types of Directors and Other Managerial Personnel in A CompanyDocument14 pagesTypes of Directors and Other Managerial Personnel in A CompanyKamal NaraniyaNo ratings yet
- JD For Workday HCM Functional ConsultantDocument2 pagesJD For Workday HCM Functional ConsultantDevdutt Singh100% (1)
- CENECO Vs Secretary of DOLEDocument2 pagesCENECO Vs Secretary of DOLEJanno SangalangNo ratings yet
- Commerce: Pearson Edexcel International GCSEDocument16 pagesCommerce: Pearson Edexcel International GCSEAbdul Kader OniNo ratings yet
- Google Inc.: Bmde Case SubmissionDocument6 pagesGoogle Inc.: Bmde Case SubmissionKeshavNo ratings yet
- Business Finance Lecture 1Document19 pagesBusiness Finance Lecture 1arabella joy gabitoNo ratings yet
- ITM Power Annual Report 2021Document104 pagesITM Power Annual Report 2021Jose LopezNo ratings yet
- Memorandum of Association OF Rehbar FoundationDocument14 pagesMemorandum of Association OF Rehbar FoundationAyaz ManiNo ratings yet
- International Business 1st Edition Ebook PDFDocument41 pagesInternational Business 1st Edition Ebook PDFmilagros.ehrhardt872100% (35)
- Morning: BriefDocument50 pagesMorning: BriefvnaliniNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: 1. in The Audit of The Heats Corporation's Financial Statements at December 31, 2005, TheDocument5 pagesThis Study Resource Was: 1. in The Audit of The Heats Corporation's Financial Statements at December 31, 2005, TheIvy BautistaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 POM 2020Document5 pagesChapter 1 POM 2020Hà MintNo ratings yet
- Canada Case Study Edited - EditedDocument4 pagesCanada Case Study Edited - EditedTalvir SinghNo ratings yet
- Jobs in AndalusiaDocument10 pagesJobs in AndalusiaSonia Sánchez BarrancoNo ratings yet
- CMR Technologies DriveDocument4 pagesCMR Technologies DriveHunter UnitedNo ratings yet
- Accounting EquationnnnDocument9 pagesAccounting Equationnnnshrestha.aryxnNo ratings yet
- Od428020695557784100 1Document1 pageOd428020695557784100 1Rájñîsh MôñdālNo ratings yet
- Consolidation, Joinder, Cross-Claims, Multiparty and Multicontract Arbitrations - Recent ICC ExperienceDocument9 pagesConsolidation, Joinder, Cross-Claims, Multiparty and Multicontract Arbitrations - Recent ICC ExperienceTuputamadreNo ratings yet
- Exporting HeadphoneDocument5 pagesExporting HeadphoneNguyễn Huyền100% (1)
- Advanced Trading ICO Due DilligenceDocument29 pagesAdvanced Trading ICO Due DilligenceciciyNo ratings yet