Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Preparing For The Most Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19
Uploaded by
poopOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Preparing For The Most Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19
Uploaded by
poopCopyright:
Available Formats
Comment
Initiation of a new infection control system for the
COVID-19 outbreak
In December, 2019, a group of patients with pneumonia to become familiar with the requirements for infection Lancet Infect Dis 2020
of unknown origin, most of whom had been exposed to control in the negative pressure isolation wards. Herein, Published Online
February 18, 2020
the Huanan seafood wholesale market in Wuhan, China, cameras cover the entire ward except for the privacy https://doi.org/10.1016/
was first reported.1 Using deep sequencing analysis, area. The infection control observer monitors medical S1473-3099(20)30110-9
Chinese authorities identified a new betacoronavirus staff in real time via computer monitors in a separate
(severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; area (figure). The main responsibilities of the observer
SARS-CoV-2) as the cause of the outbreak, and found are to maintain the normal operation of the negative
that SARS-CoV-2 belongs to a clade within the subgenus pressure isolation wards, supervise the implementation
sarbecovirus, orthocoronavirinae subfamily.2 As of of disinfection, ensure a sufficient supply of protective
Feb 10, 2020, the ongoing outbreak of coronavirus materials, arrange specimens for inspection, and relieve
disease 2019 (COVID-19) originating in Wuhan had anxiety of the medical personnel while treating patients.
caused 42 638 confirmed cases and 1016 deaths, The observers pay attention to the medical staff
with 32 provinces and regions of China affected.3 As a not only during their time in the negative pressure
global public health threat, the COVID-19 outbreak has ward, but also during the putting on or taking off of
also raised worldwide public concern, with increasing protective equipment when they enter or leave the
travel-associated cases confirmed in multiple countries, ward. Although the health-care providers have attended
including South Korea, Thailand, Japan, the USA, multiple training sessions and emergency drills, in
Vietnam, and Germany.4–6 operation (especially in high-stress negative pressure
By Feb 10, 2020, Guangdong Second Provincial wards) some steps might be omitted or overlooked,
General Hospital (Guangzhou, Guangdong Province, thus incurring potential exposure to nosocomial
China), as a provincial emergency hospital, had infection. For example, when a nurse helped an elderly
admitted more than 30 confirmed cases of COVID-19 patient pull up a zipper in the negative pressure ward,
and more than 200 suspected cases. Hospital-related the zipper unexpectedly ripped the nurse’s glove. The
transmission of the virus was suspected in up to 29% of nurse became nervous, and anxious to continue her
health-care workers.7 Thus, to try to avoid nosocomial procedures. Discovering this situation on screen, the
infection, the hospital set up an innovative infection- observer immediately soothed the nurse and sent
control system called the observing system, which has
been highly recommended by the frontline medical
staff.8 This innovation originated from the national
emergency medical team in field rescue. Negative
pressure isolation wards, generally the most dangerous
area in the hospital for airborne diseases, are where all
the confirmed cases receive medical care as a standard
practice. Despite multiple preventive procedures, it is
not uncommon that medical personnel in these wards
might not be fully aware of their exposure while caring
for patients; therefore, setting up an infection control
system to provide real-time monitoring and aid for
instant correction is of high importance to minimise
the risk of nosocomial infection. All infection control
observers, appointed by the Department of Infection
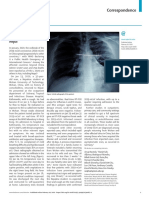
Control and Nursing in Guangdong Second Provincial Figure: An on-duty observer providing instructions to the health-care provider in negative-pressure
General Hospital, have undergone intensive training isolation wards
www.thelancet.com/infection Published online February 18, 2020 https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30110-9 1
Comment
another staff member into the ward to assist. Following Center for Clinical Epidemiology and Methodology (XC, GuoL), and Pulmonary
and Critical Care Medicine (JT, GuaL), Guangdong Second Provincial General
the occupational exposure process, the observer then Hospital, Guangzhou, China; and Department of Health Research Methods,
instructed the nurse to remove her gloves carefully, Evidence, and Impact, McMaster University, Hamilton, ON, Canada (GuoL)
disinfect her hands, and dispose of the ripped gloves. 1 Lu H, Stratton CW, Tang Y-W. Outbreak of pneumonia of unknown etiology
in Wuhan China: the mystery and the miracle. J Med Virol 2020; published
The observer also systematically assessed the risks for online Jan 16. DOI:10.1002/jmv.25678.
the nurse and arranged a quarantine room for medical 2 Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019
novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020; 395: 497–506.
observation to ensure full safety before she was allowed 3 China CDC weekly. National Health Commission Update on
February 11, 2020. http://www.nhc.gov.cn/xcs/yqtb/202002/4a611bc7fa2
to return to the negative pressure ward. 0411f8ba1c8084426c0d4.shtml accessed (Feb 11, 2020).
The observing system, as a proactive infection 4 WHO. Pneumonia of unknown cause–China. 2020. https://www.who.int/
csr/don/05-january-2020-pneumonia-of-unkown-cause-china/en/
control tool, provides immediate prevention against (accessed Jan 5, 2020).
nosocomial infection in negative pressure isolation 5 WHO. Novel coronavirus–China. 2020. https://www.who.int/csr/don/12-
january-2020-novel-coronavirus-china/en/ (accessed Jan 12, 2020).
wards, which offers creative assistance to combat the 6 WHO. IHR emergency committee on novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV).
COVID-19 outbreak. Guangdong Second Provincial 2020. https://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-
statement-on-ihr-emergency-committee-on-novel-coronavirus-(2019-
General Hospital plans to incorporate artificial ncov) (accessed Jan 30, 2020).
intelligence image recognition into the observing 7 Wang D, Hu, B, Hu, C, et al. Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized
patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan,
system, aiming to enhance the sensitivity and accuracy China. JAMA, 2020; published online Feb 7. DOI:10.1001/jama.2020.1585.
8 Guangzhou Daily. A Guangzhou hospital admitted 12 cases of confirmed
of instant detection. Implementing and improving cases, and they created the ‘observing system’. https://pc.gzdaily.cn/
the observing system might be a promising endeavor amucsite/pad/index.html?from=timeline&isappinstalled=0#/
detail/1136795?site4 (accessed Jan 30, 2020).
for controlling nosocomial infection of the COVID-19
outbreak and other acute infectious diseases.
We declare no competing interests.
Xuejiao Chen, Junzhang Tian, Guanming Li, and *Guowei Li
lig28@mcmaster.ca
2 www.thelancet.com/infection Published online February 18, 2020 https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30110-9
You might also like
- Convalescent Plasma As A Potential Therapy For COVID-19: CommentDocument3 pagesConvalescent Plasma As A Potential Therapy For COVID-19: CommentSarahNo ratings yet
- Lancet2019 PDFDocument2 pagesLancet2019 PDFSubhangi NandiNo ratings yet
- Comment: Lancet Infect Dis 2020Document2 pagesComment: Lancet Infect Dis 2020NofiindaNofiINo ratings yet
- Comment: The Lancet-And The Recently Documented Infections inDocument4 pagesComment: The Lancet-And The Recently Documented Infections inmbilotNo ratings yet
- #126 - Zheng 2020Document13 pages#126 - Zheng 2020Adnan SaffiNo ratings yet
- Problem and Advice of Rural Poverty-Alleviation in China Amid The Epidemic of Covid-19 (Victor Mmbengwa and Xiaoshun Qin)Document11 pagesProblem and Advice of Rural Poverty-Alleviation in China Amid The Epidemic of Covid-19 (Victor Mmbengwa and Xiaoshun Qin)Mordecai NdlovuNo ratings yet
- Problem and Advice of Rural Poverty-Alleviation in China Amid The Epidemic of Covid-19Document11 pagesProblem and Advice of Rural Poverty-Alleviation in China Amid The Epidemic of Covid-19Mordecai NdlovuNo ratings yet
- Surgery in Covid-19Document7 pagesSurgery in Covid-19Anonymous VV4iStxLNo ratings yet
- Piis0140673620301859 PDFDocument4 pagesPiis0140673620301859 PDFEnver Facundo Cruz GallegosNo ratings yet
- Protecting Chinese Healthcare Workers While Combating The 2019 Novel CoronavirusDocument2 pagesProtecting Chinese Healthcare Workers While Combating The 2019 Novel CoronaviruschristienNo ratings yet
- Microbes and Infection: Xingchen Pan, David M. Ojcius, Tianyue Gao, Zhongsheng Li, Chunhua Pan, Chungen PanDocument6 pagesMicrobes and Infection: Xingchen Pan, David M. Ojcius, Tianyue Gao, Zhongsheng Li, Chunhua Pan, Chungen PanDavid Adolfo Paez MolinaNo ratings yet
- Novel Coronavirus Is Putting The Whole World On Alert: Journal of Hospital InfectionDocument3 pagesNovel Coronavirus Is Putting The Whole World On Alert: Journal of Hospital Infectionharapan panjaitanNo ratings yet
- LEC ArticleDocument2 pagesLEC ArticleMaria ThereseNo ratings yet
- Covid19 Protecting Healthcare Workers Is A PriorityDocument1 pageCovid19 Protecting Healthcare Workers Is A PriorityAdi Brahmantio' HusodoNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Outbreak in Malaysia: Actions Taken by The Malaysian GovernmentDocument32 pagesCOVID-19 Outbreak in Malaysia: Actions Taken by The Malaysian GovernmentIrfan AzaharNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Infectious Diseases: EditorialDocument3 pagesInternational Journal of Infectious Diseases: EditorialAdrian BeteringheNo ratings yet
- The Role of Masks and Respirator Protection Against Sars-Cov-2Document2 pagesThe Role of Masks and Respirator Protection Against Sars-Cov-2Esther Margaretha YolandaNo ratings yet
- E000759 Full PDFDocument4 pagesE000759 Full PDFValéria CruzNo ratings yet
- Lilliput The Novel Coronavirus - Latest Findings: Bs - Bs - BannerDocument10 pagesLilliput The Novel Coronavirus - Latest Findings: Bs - Bs - BannerSvastitsNo ratings yet
- Covid19 Among Medical Personnel in The Operating RoomDocument1 pageCovid19 Among Medical Personnel in The Operating RoomEduardo Jose Caicedo GomezNo ratings yet
- Correspondence: Zhou Xu, Shu Li, Shen Tian, Hao Li, Ling-Quan KongDocument2 pagesCorrespondence: Zhou Xu, Shu Li, Shen Tian, Hao Li, Ling-Quan KongWiliam Silva CarrilloNo ratings yet
- 1268 2310 1 SMDocument6 pages1268 2310 1 SMHeru Sutanto KNo ratings yet
- Journal Covid-19Document9 pagesJournal Covid-19NURAIN HANIS BINTI ARIFFNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Infectious DiseasesDocument9 pagesInternational Journal of Infectious DiseasesNurfa AliaNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1473309920300670 Main PDFDocument2 pages1 s2.0 S1473309920300670 Main PDFAdilla Shafryantyo PurnomoNo ratings yet
- COVID de La Epidemiologia Al TratamientoDocument21 pagesCOVID de La Epidemiologia Al TratamientoSamuel ToroNo ratings yet
- COVID de La Epidemiologia Al TratamientoDocument21 pagesCOVID de La Epidemiologia Al TratamientoSamuel ToroNo ratings yet
- Cutaneous Manifestations in COVID 19 A First PerspectivDocument2 pagesCutaneous Manifestations in COVID 19 A First PerspectivZihan ZetiraNo ratings yet
- "All About COVID-19": TimelineDocument5 pages"All About COVID-19": TimelineLara Yap AlmaizNo ratings yet
- Covid 2020 ExcelenteDocument21 pagesCovid 2020 ExcelenteLuis Miguel VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- 5protecting Chinese Healthcare Workers While Combating The 2019 Novel CoronavirusDocument4 pages5protecting Chinese Healthcare Workers While Combating The 2019 Novel CoronavirusEduardo Jose Caicedo GomezNo ratings yet
- The Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Pandemic: ReviewDocument8 pagesThe Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Pandemic: Reviewguugle gogleNo ratings yet
- 183-Article Text-698-1-10-20200505Document10 pages183-Article Text-698-1-10-20200505Nailis Sa'adahNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 - El Caso para El Cribado de Trabajadores de La Salud para Prevenir La Transmisión HospitalariaDocument2 pagesCOVID-19 - El Caso para El Cribado de Trabajadores de La Salud para Prevenir La Transmisión HospitalariaLuis Ricardo Soto JimenezNo ratings yet
- Using X Ray Images and Deep Learning For Automated Detection of Coronavirus DiseaseDocument13 pagesUsing X Ray Images and Deep Learning For Automated Detection of Coronavirus DiseasebhattajagdishNo ratings yet
- Quah 2020 - Reorganising The Emergency Department To Manage The COVID-19 OutbreakDocument11 pagesQuah 2020 - Reorganising The Emergency Department To Manage The COVID-19 OutbreakDư Quốc Minh QuânNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1201971220302526 MainDocument3 pages1 s2.0 S1201971220302526 Mainrianda aprizalNo ratings yet
- PIIS1201971220305294Document3 pagesPIIS1201971220305294kristina dewiNo ratings yet
- Full Spectrum of COVID-19 Severity Still Being DepictedDocument1 pageFull Spectrum of COVID-19 Severity Still Being DepictedpoopNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1473309920302267 MainDocument2 pages1 s2.0 S1473309920302267 MainMarlo Jules LagunaNo ratings yet
- MainDocument3 pagesMainmahadabrata21No ratings yet
- The Novel Coronavirus Outbreak in Wuhan, China: Shortreport Open AccessDocument3 pagesThe Novel Coronavirus Outbreak in Wuhan, China: Shortreport Open AccessDelia AndreeaNo ratings yet
- s13063 021 05329 yDocument2 pagess13063 021 05329 ymeth holaNo ratings yet
- Traducir 1 PDFDocument24 pagesTraducir 1 PDFMaritza Escobar MarinNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Pandemic: A New Chapter in The History of Infectious DiseasesDocument2 pagesCOVID-19 Pandemic: A New Chapter in The History of Infectious DiseasesDei Anjelia Nisa Br GintingNo ratings yet
- Sentiment Analysis Tracking of COVID 19 Vaccine Through TweetsDocument9 pagesSentiment Analysis Tracking of COVID 19 Vaccine Through TweetsVishal KhardeNo ratings yet
- Comment: Published March 16, 2020 S0140-6736 (20) 30673-5Document3 pagesComment: Published March 16, 2020 S0140-6736 (20) 30673-5jjmmaarrkk01No ratings yet
- Guide To Forensic Pathology Practice For Death Cases Related To Coronavirus Disease 2019 COVID 19 Trial DraftDocument8 pagesGuide To Forensic Pathology Practice For Death Cases Related To Coronavirus Disease 2019 COVID 19 Trial DraftDavid AlvarezNo ratings yet
- CoronavirusDocument1 pageCoronavirusKenya EspinozaNo ratings yet
- COVID-19: Towards Controlling of A Pandemic: CommentDocument4 pagesCOVID-19: Towards Controlling of A Pandemic: CommentEugenNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0924857920300674 Main PDFDocument9 pages1 s2.0 S0924857920300674 Main PDFFahad AwanNo ratings yet
- Coronavirus (COVID-19) Outbreak: What The Department of Endoscopy Should KnowDocument6 pagesCoronavirus (COVID-19) Outbreak: What The Department of Endoscopy Should KnowswabrijNo ratings yet
- A Weakly-Supervised Framework For COVID-19 Classification and Lesion Localization From Chest CTDocument11 pagesA Weakly-Supervised Framework For COVID-19 Classification and Lesion Localization From Chest CTICRDET 2019No ratings yet
- © The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press For The Infectious Diseases Society ofDocument13 pages© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press For The Infectious Diseases Society ofMastifa HanasitaNo ratings yet
- No 3Document7 pagesNo 37CANTIKA PRAMESWARI HANANTONo ratings yet
- Socio-Economic and Environmental Impacts of COVID-19 Pandemic in Pakistan - An Integrated AnalysisDocument18 pagesSocio-Economic and Environmental Impacts of COVID-19 Pandemic in Pakistan - An Integrated AnalysisShahzad MirzaNo ratings yet
- Guidance for COVID-19: Prevention, Control, Diagnosis and ManagementFrom EverandGuidance for COVID-19: Prevention, Control, Diagnosis and ManagementNo ratings yet
- Classification of COVID 19 Individuals Using Adaptive Neuro Fuzzy Inference SystemDocument15 pagesClassification of COVID 19 Individuals Using Adaptive Neuro Fuzzy Inference Systemosman turanNo ratings yet
- Management of Pregnant Women Infected With COVID-19: CommentDocument2 pagesManagement of Pregnant Women Infected With COVID-19: CommentMelisa Arroyo GuarinNo ratings yet
- Travel Medicine and Infectious Disease: CorrespondenceDocument3 pagesTravel Medicine and Infectious Disease: CorrespondenceanomNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Medico-Legal IssuesDocument27 pagesChapter 5 - Medico-Legal IssuesLalita A/P AnbarasenNo ratings yet
- Barton Et Whitehead (1969) - The Gaslight PhenomenonDocument3 pagesBarton Et Whitehead (1969) - The Gaslight Phenomenonhsanches21No ratings yet
- Primary Health CareDocument35 pagesPrimary Health CarenchlrysNo ratings yet
- Ayed LAMA Medical 2009Document7 pagesAyed LAMA Medical 2009RizaNo ratings yet
- Construction Today MagazineDocument1 pageConstruction Today MagazineSchofield MediaNo ratings yet
- WONCA2013 - Book of Abstracts PDFDocument830 pagesWONCA2013 - Book of Abstracts PDFBruno ZanchettaNo ratings yet
- PACIS-Amani Medical Insurance-BrochureDocument15 pagesPACIS-Amani Medical Insurance-BrochureNjeri AsiahNo ratings yet
- NCM103 - Chapter Test PDFDocument4 pagesNCM103 - Chapter Test PDFFrancine Dominique CollantesNo ratings yet
- 14-047430-047775-Plaintiff Bundle of Authorities ErrorDocument206 pages14-047430-047775-Plaintiff Bundle of Authorities ErrorFarah Najeehah ZolkalpliNo ratings yet
- MIS Review of Related LiteratureDocument5 pagesMIS Review of Related LiteraturePatrick Jalos100% (1)
- SOP For Accident Incident Investigation and ReportingDocument10 pagesSOP For Accident Incident Investigation and ReportingShreedhar100% (4)
- Abbreviations Used in KSPCB WebsiteDocument4 pagesAbbreviations Used in KSPCB WebsiteamarendrakamatNo ratings yet
- Secondary Level Health Care FacilitiesDocument6 pagesSecondary Level Health Care FacilitiesTheo LomioNo ratings yet
- History IGCSE Medicine Sample - Florence NightingaleDocument2 pagesHistory IGCSE Medicine Sample - Florence NightingaleMariam AhmedNo ratings yet
- National Rural Telemedicine Network For India - MoHFWDocument30 pagesNational Rural Telemedicine Network For India - MoHFWHemprasad BadgujarNo ratings yet
- Patient SafetyDocument258 pagesPatient SafetycosommakNo ratings yet
- Hospital Desktop Study FinalDocument49 pagesHospital Desktop Study Final052 Deepak Narala0% (1)
- Fourth BASICbsc NursingDocument40 pagesFourth BASICbsc Nursingshubham rathodNo ratings yet
- Asm Charitable Super Specialty Hospital and Medical CollegeDocument20 pagesAsm Charitable Super Specialty Hospital and Medical CollegeTripurari KumarNo ratings yet
- Nursing EssayDocument11 pagesNursing Essayapi-255976823100% (1)
- Shouldice Hospitals CanadaDocument21 pagesShouldice Hospitals CanadaNeel KapoorNo ratings yet
- City Limits Magazine, November 1998 IssueDocument40 pagesCity Limits Magazine, November 1998 IssueCity Limits (New York)No ratings yet
- Clin ToxDocument2,979 pagesClin Toxhabeebpapa75% (4)
- NLF - Ending An American Tragedy 2009Document8 pagesNLF - Ending An American Tragedy 2009ttcoffeyNo ratings yet
- Sops Hospital Survey: Language: EnglishDocument6 pagesSops Hospital Survey: Language: EnglishNoviyanti LindaNo ratings yet
- Hospital DesignDocument2 pagesHospital DesignVipulParashar0% (1)
- UNICEF Sri Lanka Humanitarian Situation Report No. 3 (Economic Crisis 2022), 31 December 2022Document11 pagesUNICEF Sri Lanka Humanitarian Situation Report No. 3 (Economic Crisis 2022), 31 December 2022Ada DeranaNo ratings yet
- NABH Guidelines PDFDocument71 pagesNABH Guidelines PDFAshish kumarNo ratings yet
- Tertiary HospitalDocument3 pagesTertiary HospitalDarlene AmbrocioNo ratings yet
- EHSTG-Volume IDocument425 pagesEHSTG-Volume Imelkamu100% (1)