Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lent
Uploaded by
Lexter Fallo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
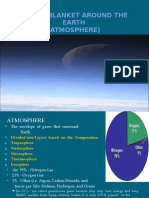
14 views1 pageThe atmosphere is divided into five layers - the troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere and exosphere. The troposphere extends from the Earth's surface to around 15 km high, containing around 75-80% of the atmosphere's mass. Temperatures decrease with height in the troposphere. The stratosphere sits above the troposphere, extending from 15-50 km high where temperatures increase with height due to ozone absorbing UV light. Above this is the mesosphere from 50-85 km high where temperatures decrease with height to a low of -90°C. The thermosphere extends from 85-600 km high where temperatures again increase with height due to solar radiation.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe atmosphere is divided into five layers - the troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere and exosphere. The troposphere extends from the Earth's surface to around 15 km high, containing around 75-80% of the atmosphere's mass. Temperatures decrease with height in the troposphere. The stratosphere sits above the troposphere, extending from 15-50 km high where temperatures increase with height due to ozone absorbing UV light. Above this is the mesosphere from 50-85 km high where temperatures decrease with height to a low of -90°C. The thermosphere extends from 85-600 km high where temperatures again increase with height due to solar radiation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views1 pageLent
Uploaded by
Lexter FalloThe atmosphere is divided into five layers - the troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere and exosphere. The troposphere extends from the Earth's surface to around 15 km high, containing around 75-80% of the atmosphere's mass. Temperatures decrease with height in the troposphere. The stratosphere sits above the troposphere, extending from 15-50 km high where temperatures increase with height due to ozone absorbing UV light. Above this is the mesosphere from 50-85 km high where temperatures decrease with height to a low of -90°C. The thermosphere extends from 85-600 km high where temperatures again increase with height due to solar radiation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
The
atmosphere is divided into five different layers, based on temperature. The layer closest to Earth’s
troposphere
surface is th1e , reaching from about seven and 15 kilometers (five to 10 miles)
from the surface. The trop22223osphere is thickest at the equator, and much thinner at the North and
South Poles. The majority of the mass of the entire atmosphere is contained in the troposphere—
between approximately 75 and 80 percent. Most of the water vapor in the atmosphere, along with dust
and ash particles, are found in the troposphere—explaining why most of Earth’s clouds are located in
this layer. Temperatures in the troposphere decrease with altitude.
The stratosphere is the next layer up from Earth’s surface. It reaches
from the top of the troposphere, which is called the tropopause, to an altitude
of approximately 50 kilometers (30 miles). Temperatures in
the stratosphere increase with altitude. A high concentration of ozone, a
molecule composed of three atoms of oxygen, makes up the ozone
layer of the stratosphere. This ozone absorbs some of the incoming solar
radiation, shielding life on Earth from potentially harmful ultraviolet (UV)
light, and is responsible for the temperature increase in altitude.
The top of the stratosphere is called the stratopause. Above
that is the mesosphere, which reaches as far as about 85
kilometers (53 miles) above Earth’s surface. Temperatures
decrease in the mesosphere with altitude. In fact, the
coldest temperatures in the atmosphere are near the top of
the mesosphere—about -90°C (-130°F). The atmosphere is
thin here, but still thick enough so that meteors will burn
up as they pass through the mesosphere—creating what
we see as “shooting stars.” The upper boundary of
the mesosphere is called the mesopause.
The thermosphere is located above the mesopause and
reaches out to around 600 kilometers (372 miles). Not
much is known about the thermosphere except that
temperatures increase with altitude. Solar radiation makes
the upper regions of the thermosphere very hot, reaching
temperatures as high as 2,000°C (3,600°F).
You might also like
- A Giant Shield : A Study of the Atmosphere - Weather Books for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksFrom EverandA Giant Shield : A Study of the Atmosphere - Weather Books for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksNo ratings yet
- LentDocument1 pageLentLexter FalloNo ratings yet
- LentDocument2 pagesLentLexter FalloNo ratings yet
- Troposphere: MesosphereDocument2 pagesTroposphere: MesosphereLexter FalloNo ratings yet
- RelapseDocument2 pagesRelapseLexter FalloNo ratings yet
- Unit - 2 Global WarmingDocument10 pagesUnit - 2 Global WarmingVamsi ReddyNo ratings yet
- RelapseDocument2 pagesRelapseLexter FalloNo ratings yet
- DecomposeDocument2 pagesDecomposeLexter FalloNo ratings yet
- DecomposeDocument2 pagesDecomposeLexter FalloNo ratings yet
- DecomposeDocument2 pagesDecomposeLexter FalloNo ratings yet
- DecomposeDocument2 pagesDecomposeLexter FalloNo ratings yet
- Geographic AtmosphereDocument2 pagesGeographic AtmosphereLexter FalloNo ratings yet
- RelapseDocument2 pagesRelapseLexter FalloNo ratings yet
- RelapseDocument2 pagesRelapseLexter FalloNo ratings yet
- NecrosisDocument2 pagesNecrosisLexter FalloNo ratings yet
- Justine Hazel Rivera Atmosphere - 20230911 - 000728 - 0000Document8 pagesJustine Hazel Rivera Atmosphere - 20230911 - 000728 - 0000Justine Hazel RiveraNo ratings yet
- Geographic AtmosphereDocument2 pagesGeographic AtmosphereLexter FalloNo ratings yet
- L WorksheetsatmosphereDocument7 pagesL WorksheetsatmosphereMEENA PEREZNo ratings yet
- Atmosphere: CollectionDocument6 pagesAtmosphere: CollectionJacob AgboNo ratings yet
- LayersDocument3 pagesLayersRajas MudafaleNo ratings yet
- The Composition of The Earth's AtmosphereDocument81 pagesThe Composition of The Earth's AtmosphereChristie Joy BuctonNo ratings yet
- Layers of The Earth's AtmospherDocument4 pagesLayers of The Earth's AtmospherBem PladeroNo ratings yet
- Exosphere: Take It To The MAX!Document2 pagesExosphere: Take It To The MAX!Mohammad ParkerNo ratings yet
- Layers of The Atmosphere NotesDocument3 pagesLayers of The Atmosphere NotesJustin Marc RagpaNo ratings yet
- Layers of AtmosphereDocument2 pagesLayers of AtmosphereSumaiya ImamNo ratings yet
- 8 Done Layers of AtmosphereDocument2 pages8 Done Layers of AtmosphereSumaiya ImamNo ratings yet
- A Cozy Blanket Around The Earth (Atmosphere)Document9 pagesA Cozy Blanket Around The Earth (Atmosphere)Xandrei AravellaNo ratings yet
- ExosphereDocument3 pagesExosphereneilonlinedealsNo ratings yet
- Layers of Earth's Atmosphere: TroposphereDocument4 pagesLayers of Earth's Atmosphere: TroposphereCarlos EduardoNo ratings yet
- UNIT-2 (Atmosphere& Its Components)Document22 pagesUNIT-2 (Atmosphere& Its Components)arcoromaruchi629No ratings yet
- ReportchemDocument11 pagesReportchemCARIG IVANNE ALDRICHNo ratings yet
- Structure of The AtmosphereDocument2 pagesStructure of The AtmosphereIlham Husain BhatNo ratings yet
- 3) The Earth Is Divided Into Various Layer Namely As Shown Below. Briefly Explain With Sketch Describe Each OneDocument5 pages3) The Earth Is Divided Into Various Layer Namely As Shown Below. Briefly Explain With Sketch Describe Each OneMuhammad MimHa MimDalNo ratings yet
- Atmosphere LayersDocument15 pagesAtmosphere LayersVidhyaNo ratings yet
- Group 3. ESDocument3 pagesGroup 3. ESreynalene inanodNo ratings yet
- Es Assign 2Document1 pageEs Assign 2Jimlord GarciaNo ratings yet
- Q4 W3 Layers of The AtmosphereDocument1 pageQ4 W3 Layers of The AtmosphereRona Lynn CelesteNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 ENV103Document16 pagesLecture 3 ENV103FarehinNo ratings yet
- Eslam Ahmed PresentationDocument9 pagesEslam Ahmed PresentationEslam A. ElabbassiNo ratings yet
- Atmosphere: Composition & StructureDocument5 pagesAtmosphere: Composition & StructureSrishti kashyapNo ratings yet
- Chemistry HomeworkDocument2 pagesChemistry Homeworkbabyprincess_khaingNo ratings yet
- Gases in The AtmosphereDocument3 pagesGases in The AtmosphereJamie Deviànts KiznaiverNo ratings yet
- Stratification: Earth's Atmosphere Lower 4 Layers of The Atmosphere in 3 Dimensions As Seen Diagonally FromDocument7 pagesStratification: Earth's Atmosphere Lower 4 Layers of The Atmosphere in 3 Dimensions As Seen Diagonally FromJordan MosesNo ratings yet
- Structure of AtmosphereDocument4 pagesStructure of AtmosphereAju 99GamingNo ratings yet
- Atmosphere of EarthDocument10 pagesAtmosphere of EarthDen Mark AlbayNo ratings yet
- The Different Layers of The AtmosphereDocument2 pagesThe Different Layers of The AtmosphereBryan Culqui MejîaNo ratings yet
- Layers of The Atmosphere - G6 Lesson NotesDocument3 pagesLayers of The Atmosphere - G6 Lesson NotesJung Ahn HongNo ratings yet
- Layers of The AtmosphereDocument3 pagesLayers of The Atmospheredonimonsz87No ratings yet
- What Is The AtmosphereDocument6 pagesWhat Is The AtmosphereKabir PachecoNo ratings yet
- Define Atmosphere.: TroposphereDocument2 pagesDefine Atmosphere.: TroposphereJhune Dominique GalangNo ratings yet
- Environment and Orbital MechanicsDocument27 pagesEnvironment and Orbital MechanicsSmilindNo ratings yet
- Layers of AtmosphereDocument4 pagesLayers of AtmosphereAj sathesNo ratings yet
- Layers of The AtmosphereDocument23 pagesLayers of The AtmosphereChristopher Philip0% (1)
- Traits of Each Layers The EarthDocument3 pagesTraits of Each Layers The EarthmaryaniNo ratings yet
- Iloilo State College of Fisheries School of Graduate Studies Barotac Nuevo, IloiloDocument7 pagesIloilo State College of Fisheries School of Graduate Studies Barotac Nuevo, IloiloGold P. TabuadaNo ratings yet
- AtmosphereDocument7 pagesAtmospheremachuchla09No ratings yet
- AtmosphereDocument12 pagesAtmospheresuvarna27No ratings yet
- What Are The Layers of Earth's Atmosphere and Layers CompositionDocument3 pagesWhat Are The Layers of Earth's Atmosphere and Layers CompositionThrecia RotaNo ratings yet
- MeteorologyDocument2 pagesMeteorologyMar Jerome TomasNo ratings yet
- Atmosphere 101Document9 pagesAtmosphere 101Howard Duck100% (1)
- PropertyDocument2 pagesPropertyLexter FalloNo ratings yet
- EtymologyDocument2 pagesEtymologyLexter FalloNo ratings yet
- EarthDocument1 pageEarthLexter FalloNo ratings yet
- RelapseDocument2 pagesRelapseLexter FalloNo ratings yet
- EarthquakesDocument1 pageEarthquakesLexter FalloNo ratings yet
- EtymologyDocument2 pagesEtymologyLexter FalloNo ratings yet
- RelapseDocument2 pagesRelapseLexter FalloNo ratings yet
- EarthquakesDocument1 pageEarthquakesLexter FalloNo ratings yet
- RelapseDocument2 pagesRelapseLexter FalloNo ratings yet
- PropertyDocument2 pagesPropertyLexter FalloNo ratings yet
- DecomposeDocument2 pagesDecomposeLexter FalloNo ratings yet
- What Are The Possible Consequences of Receiving Stolen PropertyDocument2 pagesWhat Are The Possible Consequences of Receiving Stolen PropertyLexter FalloNo ratings yet
- DecomposeDocument2 pagesDecomposeLexter FalloNo ratings yet
- What Are The Possible Consequences of Receiving Stolen PropertyDocument2 pagesWhat Are The Possible Consequences of Receiving Stolen PropertyLexter FalloNo ratings yet
- DecomposeDocument2 pagesDecomposeLexter FalloNo ratings yet
- Geographic AtmosphereDocument2 pagesGeographic AtmosphereLexter FalloNo ratings yet
- NecrosisDocument2 pagesNecrosisLexter FalloNo ratings yet
- DecomposeDocument2 pagesDecomposeLexter FalloNo ratings yet
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldFrom EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (597)
- The Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorFrom EverandThe Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (138)
- Alex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessFrom EverandAlex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessNo ratings yet
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (812)
- World of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsFrom EverandWorld of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (223)
- When You Find Out the World Is Against You: And Other Funny Memories About Awful MomentsFrom EverandWhen You Find Out the World Is Against You: And Other Funny Memories About Awful MomentsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (13)
- Braiding Sweetgrass: Indigenous Wisdom, Scientific Knowledge and the Teachings of PlantsFrom EverandBraiding Sweetgrass: Indigenous Wisdom, Scientific Knowledge and the Teachings of PlantsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (1424)
- Fire Season: Field Notes from a Wilderness LookoutFrom EverandFire Season: Field Notes from a Wilderness LookoutRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (142)
- Remnants of Ancient Life: The New Science of Old FossilsFrom EverandRemnants of Ancient Life: The New Science of Old FossilsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (3)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildFrom EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)
- Come Back, Como: Winning the Heart of a Reluctant DogFrom EverandCome Back, Como: Winning the Heart of a Reluctant DogRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (10)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (35)
- Darwin's Doubt: The Explosive Origin of Animal Life and the Case for Intelligent DesignFrom EverandDarwin's Doubt: The Explosive Origin of Animal Life and the Case for Intelligent DesignRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (19)
- Spoiled Rotten America: Outrages of Everyday LifeFrom EverandSpoiled Rotten America: Outrages of Everyday LifeRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (19)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- The Soul of an Octopus: A Surprising Exploration into the Wonder of ConsciousnessFrom EverandThe Soul of an Octopus: A Surprising Exploration into the Wonder of ConsciousnessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (254)
- The Hidden Life of Trees: What They Feel, How They CommunicateFrom EverandThe Hidden Life of Trees: What They Feel, How They CommunicateRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1003)
- Why Fish Don't Exist: A Story of Loss, Love, and the Hidden Order of LifeFrom EverandWhy Fish Don't Exist: A Story of Loss, Love, and the Hidden Order of LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (699)
- The Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsFrom EverandThe Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (65)
- Eels: An Exploration, from New Zealand to the Sargasso, of the World's Most Mysterious FishFrom EverandEels: An Exploration, from New Zealand to the Sargasso, of the World's Most Mysterious FishRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (30)