Professional Documents
Culture Documents
12th Chemistry Syllabus 2022-23
Uploaded by
ram vermaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
12th Chemistry Syllabus 2022-23
Uploaded by
ram vermaCopyright:
Available Formats
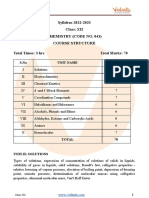
Class- XII
Subject : Chemistry
Syllabus(2022-23)
Month Name of Chapter & Topics Teaching Revision Practical
Book Periods Period
April Chemistry Unit-2 : Solutions 15 2 A (8)
Class 12th 2
May do Unit-3 : Electro Chemistry 10 3 B (8)
8 2 C (6)
June Summer Vacation
July do Unit-4 : Chemical Kinetics 9 2 D (7)
9 2 E (7)
August do Unit-8 : d & f Block 16 6 F (7)
Elements G (7)
September do Unit-9 : Co-ordination 10 3 H (8)
compounds
9 2
October do Unit-10 : Halo Alkanes And 9 1 I (10)
Halo Arenes
Unit-11 : Alcohols 12 2
November do Unit-11: Phenols and Ethers 16 4 J (10)
Unit-12 : Aldehydes, Ketones
December do Unit-12: Carboxylic Acids 8 1 K (8)
Unit-13 : Amines and
Diazonium Salts 10 2
January do Unit-14 : Biomolecules 8 2 K (10)
8 2 Cont.
February Revision of the syllabus
March Exam
Class 12th
Subject-Chemistry
Syllabus(2022-23)
Unit-2: Solution: April Periods-10 Revision-2 Marks-4
Types of solutions, expression of concentration of solution of
solid in liquids, solubility of gases in liquids, (Henry’s law) solid solutions,
colligative properties- relative lowering of vapour pressure, Raoults’s law,
ideal and non Ideal solutions, osmotic pressure, osmosis and it’s applications,
depression of freezing point, elevation of boiling point, determination of
molecular masses using colligative properties, Abnormal molecular masses,
Van’t Hoff- factor, Van’t Hoff equation for colligative properties.
Unit-3: Electrochemistry: May Periods-10 Revision-3 Marks-4
Redox reactions, conductance in electrolytic solutions, specific
and molar conductivity, variation of conductivity with concentration,
Kohlrausch’s law, electrolysis and laws of electrolysis (only elementary
Idea), Electrochemical cell, (construction, representation and working) dry
cell- electrolytic cells, lead accumulator, Ni-cd cell, fuel cell, EMF of a cell,
standard electrode potential, Nernst equation and it’s application to chemical
cells, reference electrode (NHE) Relation between Gibb’s free energy change
and EMF of a cell, Electrochemical series and it’s applications, corrosion
(Rusting of Iron and it’s methods of prevention).
Unit-4: Chemical Kinetics: May Periods-8 Revision-2 Marks-4
Rate of reaction (Average and instantaneous), factors affecting on
the rate of reaction: concentration, temperature, catalyst, order and
molecularity of a reaction; rate law and specific rate constant, Integrated rate
equations and half life (Only for zero and first order reactions), concept of
collision theory (elementary idea, no mathematical treatment), Activation
energy, Arrhenius equation.
June Summer Vacation 1st june to 30th june.
Unit-8: d and f block elements:
September. Periods-10 Revision-3 Marks-5
General introduction, electronic configuration, occurrence and
characteristics of transition metals, general trends in properties of the First
row transition metals- metallic character, atomic size, ionic radii, melting &
boiling point, Ionization enthalpy, oxidation state, colour, formation of
complex compounds, catalytic properties, interstitial compounds, alloy
formation, preparation and properties of K2Cr2O7 and KMnO4 .
Lanthanoids: Electronic configuration, oxidation states, chemical
reactivity and lanthanoid contraction and its consequences.
Actinoids: Electronic configuration, oxidation states and
comparison with lanthanoids.
Unit-9: Coordination compounds:
September. Periods-9 Revision-2 Marks-3
Coordination compounds- Introduction, difference between
Coordination compounds and double salts, liagands, coordination number,
colour, magnetic properties and shapes, IUPAC nomenclature of mono
nuclear Coordination compounds, bonding in complex compounds, Werner’s
theory, VBT and CFT: Structure and stereo isomerism, importance of
Coordination compounds (In qualitative inclusion, extraction of metals and
biological system).
Unit-10: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes:
October Periods-9 Revision- Marks-4
Haloalkanes: Nomenclature, nature of C-X bond
physical and chemical properties, mechanism of substitution reaction,
optical rotation.
Haloarenes: Nature of C-X bond, substitution reaction
(Directive Influence of halogen in monosubstituted compounds only)
Uses and environmental effects of – dichloromethane,
trichloro methane, tetra chloro methane, Iodoform, freons, DDT.
Unit-11: Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers:
October Periods-12 Revision-2 Marks-4
Alcohols: Nomenclature, methods of preparation, physical and
chemical properties (Primary alcohols only), Identification of Primary,
Secondary and Tertiary alcohols, Mechanism of dehydration of alcohols,
uses of alcohol with special reference to ethanol and methanol.
Phenols: Nomenclature, methods of preparation, physical and
chemical properties, acidic nature of phenol, electrophilic
substitution reactions, uses of phenol.
Ethers: Nomenclature, methods of preparation, physical and
chemical properties, uses.
Unit-12: Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic acids:
November Periods-16 Revision-4 Marks-6
Aldehydes and Ketones: Nomenclature, nature of
corbonyl group, methods of preparation of aldehyde & ketones, physical
and chemical properties and mechanism of nucleophilic addition,
reactivity of alpha hydrogen in aldehydes; uses.
Carboxylic acids: Nomenclature, acidic nature, methods of
preparation, physical and chemical properties; uses.
Unit-13: Organic compounds containing Nitrogen:
December Periods-8 Revision-1 Marks-3
Amines: Nomenclature, classification, structure, methods of
preparation, Physical and chemical properties, basic nature of amines.
Identification of primary, secondary and tertiary amines and
uses of amines.
Diazonium salts: Preparation, chemical reaction and importance in
synthetic organic chemistry.
Unit-14: Biomolecules:
Decemberr Periods-10 Revision-2 Marks-3
Carbohydrate: Classification (aldoses and ketoses)
monosaccahrides (glucose and fructose), D-L configuration,
oligosaccharides (sucrose, lactose, maltose), poly saccharides (starch,
cellulose, glycogen) importance.
Proteins: Elementary Idea of amino acids, peptide bond,
polypeptides, proteins, primary, secondary and tertiary and quaternary
structure of proteins. (qualitative Idea only) denaturation of proteins:
enzymes.
Vitamins: Classification and deficiency diseases.
Nucleic acids: DNA and RNA.
You might also like
- C 47 Cdecf 5010707033 Ead 928 e 1 FF 70 HJJBDDocument8 pagesC 47 Cdecf 5010707033 Ead 928 e 1 FF 70 HJJBDMukul RishirajNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 12th Syllabus PDF 2021-22Document7 pagesChemistry 12th Syllabus PDF 2021-22Garima SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- CHEMDocument3 pagesCHEMVardhan AmanapuNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Second-YearDocument5 pagesChemistry Second-YearSantanu DasNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - SrSec - 2023 24 6 9Document4 pagesChemistry - SrSec - 2023 24 6 9k5he06pny2No ratings yet
- CLASS XII (2018-19) Theory: Unit No. Title No. of Periods MarksDocument4 pagesCLASS XII (2018-19) Theory: Unit No. Title No. of Periods MarksPraynshu ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- PHP TV VT XRDocument27 pagesPHP TV VT XRshanedias4828No ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry 20Document15 pages12 Chemistry 20Aranyak NagNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Syllabus 2023 24Document7 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry Syllabus 2023 24IbinNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Chemistry Syllabus 2023-24Document3 pagesClass 12 Chemistry Syllabus 2023-24Rooh KSHIVNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - SrSec - 2023 24 Pages 7 13Document7 pagesChemistry - SrSec - 2023 24 Pages 7 13Mihir MishraNo ratings yet
- XII - Sample Question Paper Paper - 13 - Based On Value Based Question Pattern - 2012-13Document22 pagesXII - Sample Question Paper Paper - 13 - Based On Value Based Question Pattern - 2012-13Sulekha Rani.R.No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Term Wise Chemistry Syllabus 2021-22Document7 pagesCBSE Class 12 Term Wise Chemistry Syllabus 2021-22shivansh gamingNo ratings yet
- 12 2011 Syllabus ChemistryDocument7 pages12 2011 Syllabus Chemistryavpjerk007No ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 10 Sep 2023Document3 pagesAdobe Scan 10 Sep 2023lavyasharma566No ratings yet
- BSE Class 12 Chemsitry List of Important Topics For CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exam 2019 Are Given Below: Unit 1: Solid StateDocument14 pagesBSE Class 12 Chemsitry List of Important Topics For CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exam 2019 Are Given Below: Unit 1: Solid StateSurya RavichandranNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument6 pagesChemistryJmhonishkumarNo ratings yet
- Time: 3 Hours 70 Marks S.No. Title No. of Periods Marks: CLASS XII (2022-23) (THEORY)Document7 pagesTime: 3 Hours 70 Marks S.No. Title No. of Periods Marks: CLASS XII (2022-23) (THEORY)damanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry XiiDocument7 pagesChemistry XiiYash BhardwajNo ratings yet
- CLASS XII (2020-21) (Theory) Total Periods (Theory 98 + Practical 36) Time: 3 Hours 70 Marks Unit No. Title No. of Periods MarksDocument3 pagesCLASS XII (2020-21) (Theory) Total Periods (Theory 98 + Practical 36) Time: 3 Hours 70 Marks Unit No. Title No. of Periods MarksAlok RajNo ratings yet
- ABf 5 y 8 AKOl CKTKS1 HLCWDocument8 pagesABf 5 y 8 AKOl CKTKS1 HLCWdeepakpratap3232No ratings yet
- 12 Syllabus 2024 ChemistryDocument8 pages12 Syllabus 2024 Chemistryharshitaarya740No ratings yet
- Chemistry SyllabusDocument5 pagesChemistry SyllabusDushyant RohillaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry (Theory) (043) Syllabus For Session 2022-23 Class XiiDocument8 pagesChemistry (Theory) (043) Syllabus For Session 2022-23 Class XiiMohit TiwariNo ratings yet
- Unit X Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument8 pagesUnit X Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDeepanshu ChauhanNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Revised Chemistry Syllabus 2020 21Document8 pagesCBSE Class 12 Revised Chemistry Syllabus 2020 21Arsh AhmadNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry SyllabusDocument8 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry SyllabusAwantika ShivhareNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Syllabus 2022 23Document7 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry Syllabus 2022 23KevinNo ratings yet
- C B S E Chemistry - SrSec - 2022-23Document8 pagesC B S E Chemistry - SrSec - 2022-23divyaNo ratings yet
- Subject: Chemistry Code: 34 Class: Second PuDocument8 pagesSubject: Chemistry Code: 34 Class: Second PuDarshan GowdaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 10 Jun 2023Document1 pageAdobe Scan 10 Jun 2023Madhav BhutaniNo ratings yet
- Boards Chemistry Part 1Document128 pagesBoards Chemistry Part 1Ayush RanjaNNo ratings yet
- NEET Chemistry SyllabusDocument13 pagesNEET Chemistry SyllabusNaveen KumarNo ratings yet
- REVISED SR SEC Chemistry 2020 21Document8 pagesREVISED SR SEC Chemistry 2020 21jacobNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY (043) Syllabus For Session 2021-22 Class Xi Term-IDocument7 pagesCHEMISTRY (043) Syllabus For Session 2021-22 Class Xi Term-IM JeevanNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY (Code No. 043) RationaleDocument9 pagesCHEMISTRY (Code No. 043) RationaleYorekeNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument185 pagesChemistryutkarshgourfake8No ratings yet
- Annexure 'I': Syllabus CHEMISTRY (043) CLASS-XII - (2013-14)Document7 pagesAnnexure 'I': Syllabus CHEMISTRY (043) CLASS-XII - (2013-14)Ravi DharawadkarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2021 22Document11 pagesChemistry 2021 22shivam namdevNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument8 pagesChemistrysmalhaar111No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Revised Syllabus 2022Document7 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry Revised Syllabus 2022shrutivashisth95No ratings yet
- Unit 6 - Redox Reactions Student VersionDocument34 pagesUnit 6 - Redox Reactions Student VersionAmadu sallieuNo ratings yet
- Cbse Class 11 Chemistry Syllabus 2019 20Document11 pagesCbse Class 11 Chemistry Syllabus 2019 20Crylia StiaNo ratings yet
- MP Board Class 12 Chemistry SyllabusDocument6 pagesMP Board Class 12 Chemistry SyllabusDNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Term Wise Chemistry Syllabus 2021 22Document6 pagesCBSE Class 11 Term Wise Chemistry Syllabus 2021 22Krish SharmaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Term Wise Chemistry Syllabus 2021 22Document6 pagesCBSE Class 11 Term Wise Chemistry Syllabus 2021 22Krish SharmaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Term Wise Chemistry Syllabus 2021 22Document6 pagesCBSE Class 11 Term Wise Chemistry Syllabus 2021 22Krish SharmaNo ratings yet
- Class XII (Theory) : One Paper Time: 3 Hours 70 Marks Unit No. Title MarksDocument6 pagesClass XII (Theory) : One Paper Time: 3 Hours 70 Marks Unit No. Title MarksjigmeetNo ratings yet
- Subject ChemDocument3 pagesSubject Chemvaishnavisoni32No ratings yet
- Chemistry Syllabus (Chapter Wise Weightage)Document8 pagesChemistry Syllabus (Chapter Wise Weightage)Nandhan AnemNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2 NewnDocument8 pagesChemistry 2 NewnLaxmi JhansiNo ratings yet
- Last Minute Revision - FinalDocument23 pagesLast Minute Revision - Finalsuchetha manjunthaNo ratings yet
- Nanomaterials for Environmental ProtectionFrom EverandNanomaterials for Environmental ProtectionBoris I. KharisovNo ratings yet
- Chemistry SrSec 2022-23Document3 pagesChemistry SrSec 2022-23Afzal MohammedNo ratings yet
- AP Inter 2nd Year Syllabus 2020-21 - CHEMISTRY - IIDocument7 pagesAP Inter 2nd Year Syllabus 2020-21 - CHEMISTRY - IIsonali shaikNo ratings yet
- Chemistry SyllabusDocument10 pagesChemistry SyllabusAnonymous rwUVptzrMNo ratings yet
- Syllabus 12Document28 pagesSyllabus 12Mohini Mohit BatraNo ratings yet
- Let's Review Regents: Chemistry--Physical Setting Revised EditionFrom EverandLet's Review Regents: Chemistry--Physical Setting Revised EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Heaviest Metals: Science and Technology of the Actinides and BeyondFrom EverandThe Heaviest Metals: Science and Technology of the Actinides and BeyondWilliam J. EvansNo ratings yet
- Interviewresult HSTSB PGT Biology PGT SanskritDocument124 pagesInterviewresult HSTSB PGT Biology PGT Sanskritram vermaNo ratings yet
- Datesheet SAT Nov. 2022Document1 pageDatesheet SAT Nov. 2022ram vermaNo ratings yet
- NVS TGT North East Region Result Haryana JobsDocument19 pagesNVS TGT North East Region Result Haryana Jobsram vermaNo ratings yet
- ICHR Recruitment 2023 NotificationDocument3 pagesICHR Recruitment 2023 Notificationram vermaNo ratings yet
- KVS Exam Date Notice 2023 HaryanaJobsDocument1 pageKVS Exam Date Notice 2023 HaryanaJobsram vermaNo ratings yet
- 12th Chemistry Que Paper Design 2022-23Document1 page12th Chemistry Que Paper Design 2022-23ram vermaNo ratings yet