Professional Documents
Culture Documents
12 Cranial Nerves Functions
Uploaded by
Chn Pobadora0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views4 pagesOriginal Title
Cranial Nerves Transes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views4 pages12 Cranial Nerves Functions
Uploaded by
Chn PobadoraCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
CRANIAL NERVES
Nervous System Motor (Output)
Sensory Neuron – in Branchial Motor (BM) – originating from the branchial
Interneuron – processing (CNS) arch (muscles of mastication and facial expression)
Motor Neuron – out Somatic Motor (SM) – originating from the somatic
Visceral Motor (VM) – for internal organs (glands like
salivary, lacrimal glands etc)
12 pairs of cranial nerves
III to XII attached to the brain stem
Their cell bodies form nuclei in the brain stem
The first cell body of sensory nerves lies outside CNS
(form ganglia)
Sensory (Input)
Special Sensation (SS)
Hearing
Vision
Taste
Smell
Visceral Sensation (VS)
breathlessness during exercise, immediate satiation of
hunger and thirst, bladder fullness, and rectal fullness
blood pressure and chemical composition of the blood
General Sensation (GS)
Touch
Pain
Temperature
Vibration
Proprioception/Kinesthesia - the sense that lets us
perceive the location, movement, and action of parts of
the body
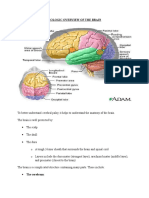
Processing (CNS)
For Cranial Nerves
The primary place where interneuron process information is
in the brain stem
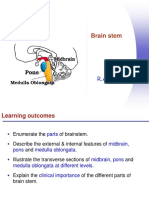
Midbrain
Pons
Medulla Oblongata
Brainstem Cranial Nerve Nuclei
Somatic
Branchial
Visceral
The 12 Cranial Nerves and Their Functions (cont’d.)
(I) Olfactory: smell
(II) Optic: sight
(III) Oculomotor: movement of eyeball, constriction of pupil
(IV) Trochlear: movement of eyeball
(V) Trigeminal: chewing, sensations in teeth
(VI) Abducens: movement of eyeball
(VII) Facial: facial expression, taste, tear and salivary glands
(VIII) Vestibulocochlear: equilibrium, hearing
(IX) Glossopharyngeal: swallowing, taste, salivary glands
(X) Vagus: certain muscle movements, sensory impulses
(XI) Accessory: swallowing, head movement
(XII) Hypoglossal: swallowing, speech
Special Senses
The Sense of Smell
Molecules in air dissolve in nasal mucus
Bipolar sensory neurons transfer chemical impulse
Olfactory bulbs receive impulse
Impulse sent to olfactory cortex
Odor variety dependent on brain interpretation
The Sense of Hearing and Equilibrium
Outer ear
Auricle: external, visible, flexible part
External auditory meatus
----------Lined with hair and ceruminous glands
The Sense of Taste Tympanic membrane: vibrates in response to sound
Taste buds on tongue, palate, and pharynx
Taste bud cell types
-Exterior capsule: epithelial cells
-Interior: taste cells
Taste depends on chemicals dissolved in saliva
Taste influenced by olfactory sensations
The Sense of Sight
Eyes protected by eyelids and eyelashes
Tears
-Lubricate the eyes
-Contain bacteriolytic lysozyme enzyme
-Contain salt and gamma globulin
Middle ear
Auditory ossicles: malleus, incus, and stapes
Openings: oval and round windows
Eustachian tube: equalizes pressure
Inner ear
Cochlea: hearing
Equilibrium
--------Static: vestibule
--------Kinetic: semicircular canals
CRANIAL NERVES
You might also like
- Cranial Nerve Function(s) of Cranial Nerve: EyesightDocument3 pagesCranial Nerve Function(s) of Cranial Nerve: EyesightElle Ricab EnimesNo ratings yet
- The Peripheral Nervous SystemDocument80 pagesThe Peripheral Nervous SystemDanitra B AlexanderNo ratings yet
- I Olfactory Nerve Anterior Olfactory Nucleus Transmits The Sense of SmellDocument4 pagesI Olfactory Nerve Anterior Olfactory Nucleus Transmits The Sense of SmellalvinNo ratings yet
- Si 9Document1 pageSi 9ray72roNo ratings yet
- Crohn's DiseaseDocument20 pagesCrohn's DiseaseTiffany AdriasNo ratings yet
- Jizhong Du-6: Centre of The SpineDocument1 pageJizhong Du-6: Centre of The SpineBDI92No ratings yet
- Psoas AbscessDocument17 pagesPsoas AbscessYasinta HelenNo ratings yet
- SP 21Document1 pageSP 21ray72roNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination 6Document95 pagesPhysical Examination 6Си Йи ФуNo ratings yet
- Tianquan P-2: Heavenly SpringDocument1 pageTianquan P-2: Heavenly Springray72roNo ratings yet
- SJ 4Document1 pageSJ 4ray72roNo ratings yet
- All PatternDocument4 pagesAll PatternManas BramheNo ratings yet
- BL-10 (2014 - 08 - 31 04 - 35 - 54 Utc)Document2 pagesBL-10 (2014 - 08 - 31 04 - 35 - 54 Utc)Juan Gabriel CunhaNo ratings yet
- Meridian LimpaDocument23 pagesMeridian LimpaHilyatul ilmi Al mufidahNo ratings yet
- Liv 11Document1 pageLiv 11ray72roNo ratings yet
- The Conception Vessel 1Document4 pagesThe Conception Vessel 1ray72roNo ratings yet
- Thieves Booklet v12 Issuu Flat 2016Document16 pagesThieves Booklet v12 Issuu Flat 2016api-251091141No ratings yet
- Bell's Palsy: Submitted By: Twinkle Singh & Kinjalika VarmaDocument34 pagesBell's Palsy: Submitted By: Twinkle Singh & Kinjalika Varmatwinklestar1396No ratings yet
- BL 43Document2 pagesBL 43BDI92No ratings yet
- Lu 9Document2 pagesLu 9ray72roNo ratings yet
- Acute Exacerbation Bronchial AsthmaDocument21 pagesAcute Exacerbation Bronchial AsthmaChekNatrahNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal Failure: Dr. Ibrahiem SaeedDocument81 pagesChronic Renal Failure: Dr. Ibrahiem SaeedUzma KhanNo ratings yet
- Understanding a Patient with SplenomegalyDocument24 pagesUnderstanding a Patient with SplenomegalyWasswaNo ratings yet
- Meridian+System+ +Extra+PDFDocument4 pagesMeridian+System+ +Extra+PDFnotsomarvelouslifeNo ratings yet
- Lu 7Document3 pagesLu 7ray72roNo ratings yet
- Jianshi P-5: Intermediate MessengerDocument2 pagesJianshi P-5: Intermediate Messengerray72roNo ratings yet
- Lu 2Document1 pageLu 2ray72roNo ratings yet
- Pericardium Meridian PDFDocument1 pagePericardium Meridian PDFrinkyNo ratings yet
- SP 8Document2 pagesSP 8ray72roNo ratings yet
- ST 12Document1 pageST 12ray72roNo ratings yet
- Lu 1Document2 pagesLu 1ray72roNo ratings yet
- Si 3Document2 pagesSi 3a_steri_x2000No ratings yet
- Relation Between Respiratory Rate and HeDocument4 pagesRelation Between Respiratory Rate and HeMuhammad Naufal NoorrachmanNo ratings yet
- Quze P-3: Marsh at The CrookDocument2 pagesQuze P-3: Marsh at The Crookray72roNo ratings yet
- Spine Exam Lecture - Shaffer 2006Document65 pagesSpine Exam Lecture - Shaffer 2006মোহাম্মদ আবীরNo ratings yet
- An Acupuncture Approach to Improved Breast HealthDocument1 pageAn Acupuncture Approach to Improved Breast HealthmnaturaisNo ratings yet
- BL 30Document1 pageBL 30BDI92No ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Spinal Cord: Dr. Eyad M. HusseinDocument41 pagesAnatomy of The Spinal Cord: Dr. Eyad M. Husseinأمال داود100% (1)
- Lu 10Document2 pagesLu 10ray72roNo ratings yet
- Facialpain 150204113108 Conversion Gate01Document51 pagesFacialpain 150204113108 Conversion Gate01Muhammad IrfanNo ratings yet
- Test II-3.indd PDFDocument1 pageTest II-3.indd PDFKika HadjNo ratings yet
- 28 הדפקיםDocument7 pages28 הדפקיםTom Fleischer100% (1)
- Daling P-7: Great MoundDocument3 pagesDaling P-7: Great Moundray72roNo ratings yet
- Acup Amenorrhea PDFDocument15 pagesAcup Amenorrhea PDFRonyNo ratings yet
- Tianfu Lu-3: Palace of HeavenDocument2 pagesTianfu Lu-3: Palace of Heavenray72roNo ratings yet
- Ren 3Document2 pagesRen 3ray72ro100% (1)
- BL 36Document1 pageBL 36BDI92No ratings yet
- Ren Mai - Conception Vessel The Sea of YinDocument18 pagesRen Mai - Conception Vessel The Sea of YinCarleta StanNo ratings yet
- Tongue color and shape guide to health imbalancesDocument5 pagesTongue color and shape guide to health imbalancesElizabeth Durkee NeilNo ratings yet
- BL 18Document2 pagesBL 18BDI92No ratings yet
- Acupuntura y MenopausiaDocument10 pagesAcupuntura y MenopausiajesussalvadorsuazaNo ratings yet
- Acupressure Points To Stay FitDocument6 pagesAcupressure Points To Stay FitWafaa Abdel AzizNo ratings yet
- Meditation Map1Document1 pageMeditation Map1koravNo ratings yet
- Acupressure Points To Improve Fertility in WomenDocument6 pagesAcupressure Points To Improve Fertility in WomenNikunj GuptaNo ratings yet
- Ren 22Document2 pagesRen 22ray72roNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Taste: Taste Receptor Cells, Taste Buds and Taste NervesDocument4 pagesPhysiology of Taste: Taste Receptor Cells, Taste Buds and Taste NerveskeerpngNo ratings yet
- Friday 2-2-2018 Multiple MyelomaDocument20 pagesFriday 2-2-2018 Multiple MyelomaJefri SusantoNo ratings yet
- Taichong Liv-3: Great RushingDocument4 pagesTaichong Liv-3: Great Rushingray72roNo ratings yet
- ST 11 PDFDocument1 pageST 11 PDFsorinNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3 Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument49 pagesChapter - 3 Autonomic Nervous SystemjarssooNo ratings yet
- Higher Center - Dr. BarbonDocument5 pagesHigher Center - Dr. BarbonMelissa SalayogNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Palsy AnatomyDocument5 pagesCerebral Palsy AnatomyIoana irimiaNo ratings yet
- Medical Terminology 2Document20 pagesMedical Terminology 2khererer11No ratings yet
- Nervous System Anatomy and FunctionsDocument30 pagesNervous System Anatomy and FunctionsRenjith Moorikkaran MNo ratings yet
- The Normal Anterior Inferior Cerebellar ArteryDocument19 pagesThe Normal Anterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery16fernandoNo ratings yet
- Prime Centric Therapy Clinic: Special Topic Report March 23, 2023 I. Cerebrovascular Accident (CVA) II. ReferencesDocument19 pagesPrime Centric Therapy Clinic: Special Topic Report March 23, 2023 I. Cerebrovascular Accident (CVA) II. ReferencesKRYSTEL CAMILLE ESCANONo ratings yet
- Download ebook Essentials Of Modern Neuroscience Lange Pdf full chapter pdfDocument67 pagesDownload ebook Essentials Of Modern Neuroscience Lange Pdf full chapter pdfsusie.plack633100% (25)
- Neurologic Care NursingDocument439 pagesNeurologic Care NursingKirk08No ratings yet
- All PSY Notes (Slides)Document66 pagesAll PSY Notes (Slides)JessicaWuNo ratings yet
- Manual of Neurologic TherapeuticsDocument534 pagesManual of Neurologic TherapeuticsDefault User100% (1)
- AnaphyDocument8 pagesAnaphyCELLINA CLARISSE DE LEONNo ratings yet
- Amyotrophic Lateral SclerosisDocument37 pagesAmyotrophic Lateral SclerosisBisma MalikNo ratings yet
- TALIBDocument578 pagesTALIBnazeefNo ratings yet
- Long COVID or Post-Acute Sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC) - An Overview of Biological Factors That May Contribute To Persistent SymptomsDocument24 pagesLong COVID or Post-Acute Sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC) - An Overview of Biological Factors That May Contribute To Persistent SymptomsRicardo Pariona LlanosNo ratings yet
- Wawa - Sistem Saraf PusatDocument38 pagesWawa - Sistem Saraf PusatnuhaNo ratings yet
- Case Study Onhead InjuryDocument32 pagesCase Study Onhead InjurySaroj Kumar BeheraNo ratings yet
- Report TextDocument5 pagesReport TextJuniorzSunshinersNo ratings yet
- ComaDocument13 pagesComaMamoon J. MehdiNo ratings yet
- SKDIDocument22 pagesSKDIFakhrunnisak UunNo ratings yet
- 1.7 Introduction To Neuroanatomy PDFDocument80 pages1.7 Introduction To Neuroanatomy PDFCarina SuarezNo ratings yet
- 3 Nervous SystemDocument33 pages3 Nervous SystemSusan ZhaoNo ratings yet
- 22 - Brain Stem (Neu)Document64 pages22 - Brain Stem (Neu)checkmate100% (3)
- Psy 432 - NeuroanatomyDocument16 pagesPsy 432 - NeuroanatomyMikaela Gabrielle MalinisNo ratings yet
- The Central Nervous SystemDocument41 pagesThe Central Nervous Systemhijrah nafeerNo ratings yet
- Brain Thesis StatementDocument5 pagesBrain Thesis Statementzyxnlmikd100% (2)
- Anatomy OspeDocument42 pagesAnatomy OspeSamson Owoetomo100% (1)
- Kdigo Aki GuidelineDocument187 pagesKdigo Aki GuidelineGoghuladheeiwy ChandranNo ratings yet
- LP 1.2 in PhysioBio PsychologyDocument11 pagesLP 1.2 in PhysioBio PsychologyWayne GodioNo ratings yet
- NervousSystem enDocument164 pagesNervousSystem ennikolaNo ratings yet
- Neurological Assessment Guide for Respiratory CareDocument33 pagesNeurological Assessment Guide for Respiratory CareArifurRahman100% (1)