Professional Documents
Culture Documents
410ufrep - FST 4 CE ESE 2023 Pre Test Series
410ufrep - FST 4 CE ESE 2023 Pre Test Series
Uploaded by
Krishna Prints0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views33 pagesOriginal Title
410ufrep_FST-4-CE-ESE-2023-Pre-Test-Series
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views33 pages410ufrep - FST 4 CE ESE 2023 Pre Test Series
410ufrep - FST 4 CE ESE 2023 Pre Test Series
Uploaded by
Krishna PrintsCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 33
etre
MADE EAs
Test centres Deh Hyderabad, Bhopal, Jaipur Lucknow, Bhubaneswar Pune Kolkata, Pana
1) PVE Te cli) fa V1 Test 20
CLASSROOM TEST SERIES Nan aati est
Full Syllabus Test 4: Paper-II
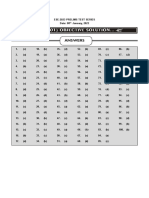
1 (d) 26. (d) 51. (d) 76. (d) 101. (a) 126. (c)
2 (d) 27. (a) 52. (b) 77. (a) 102. (c) 127. (e)
3. () 28. (b) 53. (b) 78. (a) 103. (a) 128. (d)
4 6) 54. (b) 79. (a) 104. (9) 129, (
5. (b) 30. (a) 55. (d) 80. (d) 105. (c) 130. (c)
6. (a) 31. () 56. (0) 81. (b) 106. (a) 131. (a)
7. (a) 32. (a) 57. (b) 82. (a) 107. (c) 132. (c)
8. (b) 33. (o) 58. (c) 83. (b) 108. (b) 133. (a)
9. (d) 34. () 59. (a) 84. (d) 109. (c) 134, (a)
10. (b) 35. (b) 60. (d) 85. (d) 110. (b) 135. (d)
11. (b) 36. (0) 61. (0) 86. (c) 111. (a) 136. (b)
12. (b) 37. (a) 62. (d) 87. (d) 112. (c) 137. (b)
13. (a) 38. (d) 63. (b) 88. (d) 113. (b) 138. (c)
4. (9) 39. () 64. (b) 89. (b) 114. (c) 139. (d)
15. (0) 40. (c) 65. (b) 90. (b) 115. (©) 140. (d)
16. (c) 41. (b) 66. (a) 91. (d) 116. (a) 141. (e)
17. (b) 42. (b) 67. () 92. (d) 117. (d) 142. (c)
18. (d) 43. (b) 68. (a) 93. (a) 118. (0) 143. (a)
19. (d) 44. (d) 69. (0) 94, (b) 119. (a) 144, (a)
20. (c) 45. (b) 70. (a) 95. (b) 120. (a) 145. (c)
21. (¢) 46. (0) 71. (b) 96. (c) 121. (d) 146. (a)
22. (b) 47. (0) 72. (b) 97. (a) 122. (a) 147. (0)
23. (b) 48. (a) 73. (a) 98. (c) 123. (c) 148. (d)
24. (b) 49. (d) 74. () 99. (d) 124. (d) 149. (d)
25. (co) 50. (a) 75. (a) 100. (a) 125. (a) 150. (a)
24
ESE 2023 Prelims Exam « Classroom Test Series MADE EASY
Ds
ILED EXPLANATIONS
(4)
Mango is found almost everywhere in India. The wood from this tree is of inferior quality. This
has a lot of sap and moisture. It is a relatively cheap quality of timber. It is used for making low
quality doors and windows and in packaging industries.
Note:
Deodar: These trees found in the Himalayan region are straight and tall with short branches.
Timber from these trees has well defined grains and is very strong, This timber is used for
railway sleepers, bridges and piles.
‘al: This is found in the foot hills of Himalayas. This provides a very good variety of timber. It is
hard, coarse grained, heavy and durable. It is used for bridges, piles, railway sleepers. Since it is
very hard and difficult to work, it is not suited for ornamental work.
‘Teak: This is very popular in South India. It provides a strong durable timber with a dark brown
colour. It is light and can be easily worked. It can take fine polish. It is a very valuable and costly
variety of timber. It is used for furniture, radio and television cabinets and decorative pieces of
works,
Shisham: This is found generally in Central India, Punjab and Uttar Pradesh. These trees are
found on the road sides generally. It is coarse grained and heavy and strong, This timber is very
satisfactory for making furniture. It is also used for piles, cart wheels, railway sleepers.
Kail: This is found in the Himalayas. It is hard, durable and coarse grained, It is used for furniture,
railway sleepers.
Sisso: This is found in Maharashtra, Bengal, Punjab and Uttar Pradesh. Timber from this tree is
strong and durable. It has a reddish brown colour. It is used for making furniture.
(a)
Knot is an assembly of roots of small branches. A knot breaks the continuity of fibres, causing
reduction of strength.
©)
Bethell’s process (creosoting): Creosote oil is the best preservative which can destroy the wood
attacking fungi. Creosote oil is obtained by distillation of coal tar. Well seasoned timber is dried
for 24 hours and is kept in an air chamber. The air is exhausted and creosote is pumped into the
chamber at a pressure of 0.8 N/mm? to 1 N/mm? at 50°C for a duration of 90 minutes. After this,
the timber is removed out of the chamber.
)
Refer Table 2 (common types of bonds for brick work and situations of their use) of IS 2212 : 1991
Brick works - Code of practice
(a)
The edge of a good brick should be sharp.
scoot MADE EASY wowmadeeasyin
Civil Engineering | Test20 25
10.
(a)
Harmful ingredients of in brick earth:
1. Excess of lime: Excess of lime results in melting of bricks and bricks will lose their shape.
2. Iron pyrites Presence of iron pyrites will produce crystallization of bricks leading to
disintegration during burning.
3. Alkalies Alkalies act as flux. Excess of alkalies results in the melting of the clay and the bricks
will lose their moulded shape. Alkalies absorb moisture from the surroundings producing
efflorescence in the bricks. This results in a powdery precipitate on the bricks, affecting their
appearance,
4, Pebbles: Mixing the clay will be affected by the presence of pebbles, gravel, grit etc. They
produce pores in bricks making them weak,
5. Organic matter and vegetation: Organic matter assists in burning. If organic matter present
is not fully burnt, then it will result in pores in bricks rendering them weak.
+ Plutonic rocks are formed when magma solidifies at great depths below the earth’s surface.
+ Hypabyssal rocks are formed when magma solidifies at small depths below the earth’s surface.
+ When an igneous intrusion has a surface area more than 100 square km, then it is called as a
batholith. A batholith which generally has a dome like extension into rocks above is called a
cupola. There are also downward projections of the rock into a batholith called roof pendants.
Hydraulic lime
Fat lime
1. This is eblained by calcination of raw lime stone
containing impurities like silica, alumina and
ionoxide
2. This lime slakes slowly. Minimal heats evolved.
whileslaking very slow
5. ‘This lime does not absorb carbon dioxide, The
slaking process continuous for a very long
period and absorbs moisture from the
atmosphere.
‘Thisisobtained by calcination of pure limestone.
This lime slakes very vigorously with water
givingoutalotof heat witha hissing sound,
This lime when exposed to the atmosphere,
absorbs carbon dioxide in the presence of
moisture and becomes an inert cazbonate losing
thecementing properties,
4, Thislimedoesnot undergo sheinking,
“This lime shzinks andalsocracksasit dries,
(b)
5, This cansetevenin the absence of air.
6, This is most suitable where strength is required.
Thisis notsuitable for white wash work,
‘Thislime needs the presence ofcarbon dioxide to
set
This does not provide strength. This is most
suitable or plaster work and white washing,
For plastering walls to prevent weathering, 1:3 or 1: 4 mortar is used.
For masonry work at super structure, 1:3 or 1:4 is used.
For masonry work at sub structure, 1: 5 or 1: 6 is used.
For pointing work, 1: 1 or 1:2 mortar may be used.
wwwmadeeasyin
26
ESE 2023 Prelims Exam « Classroom Test Series MADE EASY
11.
12.
13.
(b)
With fine ground cement, workability is increased, especially in harsh mixes, making the concrete
more cohesive and decreasing the tendency of segregation. A coarse ground cement reduces
stickiness.
)
Degree of workability for different placing conditions:
Placing conditions Degree of workability | Slump (mm)
lndingconerete shallow setons;pavementusing | Very ow Note
power
Maw concrete lighlyranfored sectors in dab Tow Bo
beams, walls, columns, floors, hand placed
pavements, canal lining strip footings
Ficavly reinforced sections in slabs, beams, walls, Medium 50-100
columns
Slip from work pumped concrete Medium 75-100
| Trench il insite piling | High 100-150
Tremieconcrete Very igh Note2
Note 1: In the ‘very low’ category of workability where strict control is necessary, for example
pavement quality concrete, measurement of workability in terms of compacting factor will be
more appropriate than slump value and a value of compaction factor of 0.75 to 0.80 is suggested.
Note 2: In the ‘very high’ category of workability, measurement of workability by determination
of flow value will be the most appropriate
(a)
+ Table vibrator: It is commonly used for vibrating concrete cubes. It is mostly adopted in the
laboratories and in making small but precise prefabricated RCC members
+ Internal vibrator: Also called needle vibrator, immersion vibrator or poker vibrator. Useful
in the case of mass concrete works like construction of dam.
+ Form vibrator: Used for concreting columns, thin walls or in the casting of precast units. This,
method of vibrating concrete is particularly useful and adopted where reinforcement, lateral
ties and spacers interfere too much with the internal vibrator.
+ Surface vibrator or Screed board vibrator: Mostly, floor slabs and roof slabs are so thin that
internal vibrator or any other type of vibrator cannot be easily employed. In such cases, the
surface vibrator can be effectively used.
In modern construction practices like vacuum dewatering technique, or slip-form paving
technique, the use of screed board vibrators are a common feature.
ccorot MADE ERSY wowmadeeasyin
MADE EASY Civil Engineering | Test20 27
4. (0)
At any section
whose radius vector makes an angle ‘6’ with OB,
BM = PR - PR (1 - cos ®)
= PReos @
M?ds _7P?R? cos? @(Rd8)
us Serf 2EL
PREG
- cos? 0-8
° O° OE 4
PPR? ¥( 1400820
= = aS ae
USEF i( 2 )
PPR [| sin20P°
oer le]
PPR? PP aR®
= 0)-(0+0)
gey (+9)-0+0)] =
y au _ Par?
~ Vertical deflection of load, 8= S5-=—Frr
15. (0)
20KN/m
>
EM_ = 0 (right side of C)
= 50x10 = Hx4
> H = 125kN
At any section ‘x’ from A or B
4h 4x4
ye pada) = px2Q0-x)
(20-2)
ccorot MADE EASY wwwmadeeasyin
28 ESE 2023 Prelims Exam « Classroom Test Series MADE EASY
At any section distant ‘x’ from B, the bending moment is given by
1
M, = 50x=125x.x(20-2)
e125 x(20-a)
= 50x - 100x + 5x?
Ox + 53?
For condition of maximum bending moment,
0 x 5 + 5(25) = -125 KN-m
16.
A M, i
M,b(3a—l)
My =
My 1a0 1204 8) _ \60kNem
180% 4(3 x26)
M, = SOX8C%2°9) og kNm
hs @
30x47
M,. = 57 =~40 KN-m
30x48
My = =+40 kN-m
Ma 2
Joint | Member | Relative stiffness | Total relative stiffness | DF.
B BA fia 2
ou 3 5
2
Be 13 3
an 5
ccorot MADE ERSY wowmadeeasyin
MADE EASY Civil Engineering | Test20 29
inn 0
104m spun
> q ) s24nim
tol
fbn ale am af Sonn 164000
ae Ul
44+51=95 kN
17. (b)
f
a ra 2
14 in pe 6m»
1 i 1 1 1
Pol PY '
toe a ir '
1 048 — 1
poe ~
r4
8-x 6
> 3x = 16-2
> 5x = 16
> x=32m
0.48+2.4 0.48+24
Maximum bending moment = | ——*
92408224 cashso
2
= AREA 69.24 4.8)%50- 576 kNem
vo MADE EASY wwwmadeeasyin
30 ESE 2023 Prelims Exam + Classroom Test Series MADE EASY
18. (d)
For cantilever beam, stiffness is,
-
Now the cantilever beam and spring k, are acting in parallel
ky = ith,
(15 105) + (7.5 x 108
This combination (Le. k,) isin series with ky
a4 1
kK, > 9108" 3x10"
= Ky, = 225% 105 N/m
This combination (ie, k,) isin parallel with k, and k,
k, = (2.25 +446) x 10° N/m = 12.25 x 108 N/m
Natural frequency, fee 12. 25x10" 112.2510" =70 rad/see
vw. ()
Refer IS $00 : 2007 Clause 10.2.5 (Tacking fasteners)
20.)
Refer IS 800 : 2007, Clause 10.5.1.1 (End returns), 10.1.2 (Lap joint), 10.5.5 (Intermittent welds)
2. (b)
“Angie | 60° 90°] 91° 100°] 101-106 07 333° 14° 120"
k | om | os | oo | os | om
23. (b)
There will be only torsional shear and no direct shear stress.
r= V50? +50* = 50J2 mm
Shear force in bolt ‘A’ is given by
é
B= MM 50210502 59-2 17678 KN #1768 KN
zr 4x (502)
24. (b)
Refer IS 800 : 2007, Clause 8.6.1 (Minimum web thickness)
Also Refer Clause 8.6.1.2 (Compression flange buckling requirement)
23. ©)
Applied shear force = 180 kN
Factored shear force = 1.5 x 180 = 270 kN
0.6V,, = 0.6 x 300 = 180 kN
ccorot MADE ERSY wowmadeeasyin
MADE EASY Civil Engineering | Test20 31
Since, 270 KN > 180 KN = High shear case
2 2
(2-1) = (223) = 0.64
Vy 300
26. (a)
When the angles are not tack-riveted, both the angles will act individually.
Aye = 2A, + kA]
3Ay 3(600) __ 1800
3A, +A, 3(600) +900 2700 3
B
where,
Ane = 2[50 <50%
2, Centrifugal collectors including cyclone collectors oe
and dynamic precipitator 25 30-90%
3. Wetscrubbers ofcollectors including spray towers >10 <80%
4, Cyclonicscrubbers >25 <80%
5. Venturiscrubbers 5 .
(Alsoused for gaseous pollutants) 705 <9
6, Hlectrostaie precipitator >1 95-99%
17. abricfilters <1 >99%
wowmadeeasyin
MADE EASY Civil Engineering | Test20 33
3. ©)
P
aotee( PF)
where, P, = 20uPa
.
a0iogy[ 22} 140 decibel
a.)
Specific yield: Volume of water drained by gravity per unit volume of aquifer.
Specific retention: Volume of water retained against gravity per unit volume of aquifer.
Storativity / Specific storage / Coefficient of storage: Volume of water drained from aquifer (by
any means i.e., not only by gravity) per unit volume of aquifer.
In case of unconfined aquifer, specific storage is equal to specific yield.
In case of confined aquifer, water is drained because of compression of aquifer and expansion of
water. Hence incase of confined aquifer specific storage is defined as volume of water released
from unit volume of aquifer per unit decline in piezometric head.
Specific capacity: Discharge obtained per unit area per unit drawdown of a well. The performance
of a well is measured by its specific capacity.
35. (b)
r 03m
2 7
\ (03) x3.6x10 asxi0
F310" 3000x3600
From the table, W(u) = 21.5323
Q 314x107
Drawdown, r = 2-xw(u) = —314%107 94 5993 -17.94
gat “1 = Baraat =
36.)
A geological formation which is highly porous and permeable > Aquifer
A geological formation through which only seepage is possible and thus the yield is insufficient
compared to an aquifer > Aquitard
‘A geological formation which is highly porous but impermeable + Aquiclude
scoot MADE EASY wwwmadeeasyin
34 ESE 2023 Prelims Exam « Classroom Test Series MADE EASY
38. (a)
Valve Function Testi of ftalation
Sluice /gate/shut | Regulates the ow of water trough | Placed at ery, ext and summit of
siteawe the pipe by dividing the mainline | the pressure conduit where, the
into! several sections. (Used fr | prestuelsow
isolate)
Airvletvale | Torslensetheairpresore Trowided at he sommit pont on
tpareamotgatevaee
‘ivi 7 Allows air into the eaten to | Provided onthe downstream side
Sdmitance valve |” preveravacuum cgatevalve,
+ eed where gravity flow is
requied tough pipeline
Gheckvalve7 | Allows watertofowinonedirecion | Provided on dalivary and waction
Retux/ now | only Sidcot pump
rerumingvatee
Sxourvalve/ [Avoids sediment accumulation | Provided atthe dead end of he
Bow-off/ Drain | removessandstete ‘ipelincand alow eel point
7 Washes valve
Pressure rele! | Toveduce waterhammerpressurein | Usually provided in smal pipelines.
valve pee
%.
Water borne diseases:
eee Disease
Bacteria | Typhoid cholera, dysentery
a)
Protozoa "Amocbie dysentery, gastroenteritis
Helminths | Worms
Jaundice (Hepatitis) — leads to
Virus inflammation of liver
Polio Poliomyelitis)
* Asbestos cement sewers are not strong enough to bear heavy compressive load.
+ They are susceptible to hydrogen sulphide corrosion at crown,
+ Due to these drawbacks, they are used as verticals or to carry less foul sewage from kitchen
and bathroom.
wowmadeeasyin
MADE EASY Civil Engineering | Test20 35
41. (b)
Year| Population | Increase in population (x)
1970 25000
1980) 27000 2000
1990 33000 6000
2000 40000 7000)
2010 5000 5000
Total 720000
20000
Average increase per decade (x) = —j—=5000
P, = 45000 + 3(5000) = 60000
42. (b)
(H+ 750, + 6CO, + 3H,
240
Theoretical oxygen demand = [5-x25=76.92 mg/lit
43. (b)
Piezometric head = 2+2=15m
1
= Pn 5-3=12m
Y
Let the area of floor be A. So, by force balance,
Weight of floor + Weight of water = Uplift force
> (EXAKGXY,) +QX AY) = 127, %A
> (xQ+2= 2
10
=
=
4. (a)
Volume of water actually stored in the root zone = 10 x 10* x 0.1 = 10! m?
Volume of water supplied = 6 x 8 x 3600 = 172800 m?
Volume of water actually stored in the root zone
Volume of water delivered to the field
108
Field application efficiency
x100=5.79%
scoot MADE EASY wwwmadeeasyin
36
ESE 2023 Prelims Exam « Classroom Test Series
MADE EASY
45. (b)
Base period =
100 days
Water is required at an average interval of 20 days.
Number of waterings required
Total depth of water required each
Total depth of water
Hence, delta for wheat
46.
47.
P @
2p —{ le—2P 27
bronze =
48. (a)
49. (a)
Buckling load =
F
v2
= F
© 300
> Srronze
100
20
Sem
5x5=25cm
25cm
time
Prrax toe) S82
Prax too (L + tan? at)
oft)
24x3=3.6N/mm?
2 R R
4 Lop sp
2P
goo = 005?
3? oop
2P
F599 7 0.0083?
> Gy,
(e+HeyE
1-y?
(04x10 +0.35 x 0.310) x 110x 10"
1-0.35"
Leap
3.3 MPa
wowmadeeasyin
Civil Engineering | Test20 37
50. (a)
51 (a)
Now,
52. (b)
Radius of Mohr's circle
. (ameamy, ta
“a 2
600,
ATy=AT, |
ae
AT, = ty + Aaa, =Ala y
ad = a(tx) (AT,) at st
a8 = (ds) [ans + Ata ATs a + | -e- |
—ar,
8- Jats[aty 4 Ata ATy
Ts
ae
B= GATT (ATs ATs)
o
2
E
L
[AT +47]
* (AT, +AT, |
T
2Agt
80 x 30 = 2400 mm?
T ___960x10°
At 2x2400%100
scoot MADE EASY
wwwmadeeasyin
ESE 2023 Prelims Exam « Classroom Test Series MADE EASY
2
b 6y2
200 me
300 men 5
50mm
Test oes
PM
Snax = At Z
= 240x108 |, 240% 10° x50x6 = 444=3Mp,
* 200%300 "200x307 SS MNS
Soin =
Spin = Oand thus whole column section is under compression
scoot MADE EASY wowmadeeasyin
MADE EASY Civil Engineering | Test20 39
Stress diagram,
200 mm
300 mm
200 mm
°
8 x 16
300 ~ 200 7 ~~ 3 MPa
56. (0)
MP, ML 3MP
w=
2EI ” ET 2EL
RD? _ 8RP
Deflection at C due to M, 8. =
Deflection at C due to prop, 8: =
SEI SET
But 3. = 8 (Compatibility condition)
= 3MP _ sR
2Er SEI
9M
= Re og
57, (b)
=M, = 0
sai 2x1000+400 3
= Rox5 $00 r000} a 24 PACE OP
> $oc1s0033 [242] =700%3%28
= Re = 1560.N
(400+ 1000) <3 1560 = 540
58. (0)
as
el
>
scoot MADE EASY wowmadeeasy.in
40 ESE 2023 Prelims Exam « Classroom Test Series MADE EASY
59. (a)
Using conjugate beam method:
Real beam BMD:
Conjugate beam:
60. (a)
S|
+
sit
scoot MADE EASY wowmadeeasyin
MADE EASY Civil Engineering | Test20 41
62.
63.
64.
66.
(d)
3 = Pauia’ Vimmersed * Se
‘As the block is dropped, the effective acceleration due to gravity is constant (g). The density of
fluid also remains same (p).
Thus, the buoyant force acting on it will also remain same.
(b)
ae
2-3
ox
Also, u = e+ 38y 46
ay
oy
w, = 3@-a)=0
(b)
Gradient of a scalar function gives a vector quantity but potential function is scalar quantity.
Velocity can be written as gradient of potential function (scalar function).
Velocity = Vo
If 6 = 2x + Sy is a potential function, then it must satisfy Laplace equation
6 = 2x +5y
Lana BO.
Sem Zand Se =O
and 2 =o
Fo Fo
Laplace equation: Priay 7°
(b)
de
‘ (3)
= <= vp x10!
> + = 18x 10+ 1260 x 10'Pa
> = 22.68 kPa
(@)
For rotational flow, Bernoulli's equation cannot be applied on two different streamlines.
scoot MADE EASY wwwmadeeasyin
42 ESE 2023 Prelims Exam « Classroom Test Series MADE EASY
67.)
Peeneratea = YQ(H - hy)
10 x3 x (28) = 840 kW
Protracted = 750 KW
Premaining ~ 840 - 750 = 90 KW
90x10"
Residual head = oO Jo000x3 m
68. (a)
1 iy
B= cLafeaa
Conservation of discharge bey
ax(Bx1) = Juda —
Es |
= wxB = Ju(dyxt) co
5
B y 2
. axe = fiigdy
® Unit thickness
2
= TXB = thy X>
> a
B
= B
69. (co)
alk
300’ 30
Slope = Vertical distance
‘9PS * “Horizontal distance
1
30
J
300
70. (a)
Stoke's equation, F = 3nDuV,,
where, F = longitudinal force on sphere
D = diameter of sphere
= viscosity of fluid
ccorot MADE ERSY wowmadeeasyin
MADE EASY Civil Engineering | Test20 43
7. (b)
f f
Ty 4
J pv’
2?
5 Bt 8x50 _
pV? 1000x 2?
72. (b)
Conditions favouring boundary layer separation:
1. Positive pressure gradient
2. Negative velocity gradient
73. (a)
Designing, tendering and construction fall under project phase.
73. (a)
Contract consists of
1. contract drawings
2. general conditions of contract
3. special conditions of contract
4, agreement
5. specification
6. bill of quantities (if applicable)
76. (a)
+ Forward pass technique calculates earliest start time of an activity.
* Backward pass technique chooses minimum of all latest occurrence times at any node.
7. (a)
Scraper : Purposes -— Site stripping
Levelling
}— Loading
|— Hauling
| Discharging
n—m+1
ei
2
cme -1+ |
78. (d)
aa +7)
2
4
1000{ 4 | = 400
ccorot MADE EASY wwwmadeeasyin
44
ESE 2023 Prelims Exam « Classroom Test Series MADE EASY
79.
80.
81.
82.
84,
(a)
Safety indices:
1, Frequency rate
2, Severity rate
3. Incidence rate
4, Experience modification rate
5. Loss ratio
6. Workmen’s compensation claim frequency index
(a
Z P
0 50%
1 | 843%
2 | 72%
)
Critical path is 1 - 2-3 - 4 and the project duration 13 days
0.9)
oo) 5 03,13)
Fy = (TP) ~ (Slack),
= (3-4-7) -0=2 days
@
During updating, activities and their inter-relationship is maintained, It means activities can neither
be added nor be deleted from the network,
After project updating, project duration as well as critical path may change.
(a)
Mode
Expected time
Most likely time (occurring most of the time)
scoot MADE EASY wowmadeeasyin
MADE EASY Civil Engineering | Test20 45
Optimistic time
Pessimistic time
85. (a)
RF (wrong scale)
BR (correc scale) “Measured length
Correct length =
1
= 500.200 = 400 m
1000
86.)
Only systematic errors follow some well-defined mathematical or physical law or system.
87. (a)
Ey) = + 16450
Eyyq = 3.296
Eyy = + 1.9650
Eys5 = £26
Fy, = +36
89. (b)
©
“
A
aay
3
Included angle = 360° - [90° ~ 60° 30" + 90° + 35° 30")
360° - [155°] = 205°
90. (b)
AH
SL 0.5 = 118x x15 4
E
> E = 44.25 kg/cm?
102. (c)
* WBM, WMM (wet mix macadam) and soil aggregate mixes belongs to granular base course.
104. (c)
15xL+5 15x104+5
Optimum cycle time (C,) Tq ¥yg) 1=(020+0A0)~ 50
Ya
Now, =4[C)-L)
[0-1]
92 150-10] = 13.33
06
G
Percentage of time for which there is flow on road A = 4.x 100 =
0
ccorot MADE EASY wwwmadeeasyin
48 ESE 2023 Prelims Exam « Classroom Test Series MADE EASY
105. (0)
+ Bitumen is obtained from fractional distillation of petroleums.
+ Ductility of bitumen is measured at 27°C.
106. (a)
Stress developed due to wheel load at interior is given by,
0.316P 1
8,= S- [s108 (} 1 o«|
0.316%4500[ 5. (90 >
= | 4log| — ]+ 1.069 | = 32 ks
5)? [ (Z)- | wien
108. (b)
Traffic capacity and traffic volume have same units
109. ()
Relative density (J,) =
= 1350-1200 109 = 41.67%
1350-990,
ob Dessiption
O15 Very loose
15-38 Loose
356 Median
5-85 Dense
35100 Very dene
110. (b)
Hydraulic gradient () =
[TH], = [TH], +i-Z
« szisens-as9.m
-25=35m
(H.-H,
= 883-3 5.33
111. (a)
* Coulomb's theory assumes wedge failure.
+ Itis not preferred for passive earth pressure analysis.
scoot MADE EASY wowmadeeasyin
MADE EASY Civil Engineering | Test20 49
m2
Ultimate load carrying capacity of piles
3 x 5500 = 16500 kN
CG, NLA, ta, Ay
Load carrying capacity of single pile
100 9x F X05? +05%80%05%Rx1 =805 kN
Agog 7205221
Number of piles required
113. (b)
+ Inside clearance should be low.
+ Area ratio should be less than 20%.
14. (©)
Final volume —Initial volume
Free swell (%) = 100
= 1810 100 65%
100
For Illite, possible range is 30% to 80%.
116. (a)
pA 585-450
‘AG, 700-600
4 q = Aly 745-545
an op 500
A =AB
A_ 04
= A= 3 pgp 702
a7. (a)
R, = (p- 1) * 1000
(1.015 - 1) x 1000 =
RG
yn = 1000~ 6-1 499
Now, wn = 100VS=1x
v
15 26
1000 2 =
Feo} x 100 = 34.82%
1000
118. (©)
+ Shape factor is ratio of number of flow channels to number of equipotential channels.
+ Shape of flow field is square for isotropic medium and rectangle or curvilinear for non-
isotropic medium,
scoot MADE EASY wwwmadeeasyin
50 ESE 2023 Prelims Exam « Classroom Test Series MADE EASY
119. (a)
The soil which has maximum plasticity index (I,) will have maximum amount of clay.
Soil A Ip = 054-024 = 03
Soil B I, = 047 - 0.21 = 0.26
Soil C Ip = 041 - 0.16 = 0.25
Soil D I, = 0.50 - 0.23 = 0.27
120. (a)
+ The contact pressure distributions under a rigid footing on a cohesionless soil would be
maximum at centre and zero at the edges. The distribution is close to parabolic,
+ The bearing capacity of footing not always gets affected by the location of ground water
table.
a2. (a)
s-w
Minimum depth of ballast (0) = “3
ap = S28
"2
= $= 65cm
322. (a)
The gate capacity for single gate is,
c= ——_1
Weighted service time
1 4
T4SKI5+055x50 ~ 155A min Bate
Capacity of all gates (C) = G, x Number of gate
4
= aXe
= 031 aircraft/min = 18 aircraft/hour
123.
Energy head transferred to runner
Hydraulic efficiency Water head
36
= 7
2 os
Overall efficiency, n, = ny, * 1,
0.9 « 0.857 = 0.77
Water power, P = n, 7QH
45 x10°
= x10" Loam’,
> 2 o77x4ax1P x10
ccorot MADE ERSY wowmadeeasyin
MADE EASY Civil Engineering | Test20 51
124, (a)
Average depth of flow
Effective depth of flow
30mm
Average depth of flow - Losses
30 - 0.25 x 2* 10 = 25 mm
Peak flow for flood hydrograph = 220 m/sec
Peak flow for direct runoff hydrograph = 220 ~ 20 = 200 m?/sec
Peak flow for DRH
Peak flow for unit hydropraph = Gactve depth of ow a)
= — 200-80 m°/see
25x10
+ Prism storage: It is the volume that would exist if the uniform flow occurred at the down
stream depth.
+ Wedge storage: It is the volume formed between the actual water surface profile and surface
parallel to bed of channel.
Wedge storage
Prism storage
126.
The rainfall data are arranged in descending order:
Rainfall Order
1 1
10 2
93 3
8 4
85 5
3 6
7 7
6 8
As per Weibull’s method,
Reta gr = N#d_S#1
‘eturn period, 7, = “>= =~
Risk = 1-[1- PP
al
scoot MADE EASY wwwmadeeasyin
52
ESE 2023 Prelims Exam « Classroom Test Series MADE EASY
127.
128.
129.
130.
131.
©)
+ The maximum area of reinforcement (including both tension and compression reinforcement)
shall not exceed 0.04 b.D.
+ Minimum shear reinforcement in the form of stirrups shall be provided such that;
Ag 04
bs, * O87f,
For FeAl, 2» 04 _
or Realy BS, > 087x415
> A, 2 0.00118,
(a)
For single HYSD bar is compression,
$x 087 fy
= 32.239
Wty XL6x125
Fora bundle of four bars in contact, the development length of each bar shall be that for individual
bar increased by 33 percent.
Ly = 1.33 x 32.239 = 436
(b)
Refer IS 1343 - 1980, Clause 19.6.1.1.(b)
©
My tim = 0:36 fig BX tim 1d ~ O42 24 id
For severe condition, dg = D-45 mm
50 - 45 mm = 405 mm
For Fe500, My tim = 0-133 fp Bd?
(0.133 x 20 x 200 x (405)? x 10 kNm
87.26 kN-m = 87 kN-m
(a)
Side face reinforcement is provided when beam depth exceeds 750 mm.
The total area of such reinforcement shall not be less than 0.1 percent of the web area and shall be
distributed equally on both the faces.
TAgliae = 01% of Bx D
= 91,350 x800 = 280 mm?
00
280
Reinforcement on each side = “5° = 140 mm?
ccorot MADE ERSY wowmadeeasyin
MADE EASY Civil Engineering | Test20 53
133.
134,
135.
136.
137.
(a)
wxP 4x6
8
Stress at bottom fiber at working load = 0 N/mm? (Given)
Stress corresponding to cracking at the bottom fiber = 5 N/mm?
Extra moment required to develop this stress = 5 x 18 x 105
9% 10° N-mm = 9 kN-m
18 +9=27KN-m
Cracking moment _ 27
Working moment 18
=18kN-m
Maximum working moment
Cracking moment
Load factor against cracking
(a)
Loss due to creep in steel = @f,-m
where, m = Modular ratio
-5
Ee
(a)
Total area of steel in longer direction = L, x Ay
= (Agron = 5-4 * 900 = 4860 mm?
(As)oat _ 4860
Total number of 16 mm ¢ bars for full length ('t,) = = =25 nos,
Fxg? =x (16)?
4 4
Number of bars in central band (11) = mp x—2
(4)
B
= =19,66=20
(b)
For axial loading;
P, = 045 fA, +067 f, Ay
= 1800 * 10° = 0.45 * 20 x [300 * 350 ~ A,.] + 0.67 x 415 x A.
= Ag = 3177.8 mm?= 3178 mm?
o
Cracks get developed when tensile stresses and strains are caused during shrinkage due to
restraint. Thus shrinkage cause tension cracks.
scoot MADE EASY wwwmadeeasyin
54 ESE 2023 Prelims Exam + Classroom Test Series MADE EASY
138. (0)
The temperature contrast causes convection and air cools adiabatically to from the shape of the
cloud which finally bursts into thunderstorm,
139. (a)
Self compacting concrete exerts high pressure on the from-work and accordingly while casting
the rate of casting has to be slow.
140. (a)
False setting: Water of crystallization of gypsum (CaSO,2H,O) vapourizes either partially or
completely during manufacturing of cement. Hence when water is added in cement, it first reacts
with gypsum to fulfill its water deficiency, during which it hardness and gives impression of false
setting of cement. It can be removed by adding extra water.
Flash setting: It occurs due to more C, A and less gypsum, After flash setting, remixing is not
possible.
mu. ©
Viscous damping introduces a damping force which varies linearly with the relative velocity and
the differential equation of motion becomes linear. On the otherhand, the damping force in
Coulomb's damping is assumed to be constant and independent of relative velocity. Due to this
resulting differential equation of motion becomes non-linear.
m2. (9)
Triangular section is the most inefficient cross-section, because most of area lies near plastic
neutral axis and thus plastic section modulus (z,) is less
145. (9)
200015200520 (30422)
¥ (Grom bottom) = 3003030030
Distance of neutral axis from the junction of flange and web
= 975-30 = 67.5 mm
ccorot MADE ERSY wowmadeeasyin
MADE EASY Civil Engineering | Test20 55
146. f@)
At critical condition,
U7. (0)
Project crashing is applied on critical activities with lowest cost slopes along a critical path.
148. (a)
IRC suggested that the maximum volume of traffic of 3000 veh/hr entering from all legs of the
rotary intersection can be handled efficiently.
149. (a)
At the same void ratio desiccated clay is stronger than saturated clay. During drying due to rise
in temperature, tension develops in pore water and effective stress increases
0000
vo MADE EASY wowmadeeasy.in
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5814)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- 1703491779Document3 pages1703491779Krishna PrintsNo ratings yet
- Mis Unit 5 NotesDocument8 pagesMis Unit 5 NotesKrishna PrintsNo ratings yet
- 1703664053Document355 pages1703664053Krishna PrintsNo ratings yet
- 1703491568Document3 pages1703491568Krishna PrintsNo ratings yet
- CONCLUSION-WPS OfficeDocument1 pageCONCLUSION-WPS OfficeKrishna PrintsNo ratings yet
- 1703491257Document2 pages1703491257Krishna PrintsNo ratings yet
- 1703491508Document4 pages1703491508Krishna PrintsNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Operating SystemDocument24 pagesIntroduction of Operating SystemKrishna PrintsNo ratings yet
- 1701337797Document3 pages1701337797Krishna PrintsNo ratings yet
- Pts 2024 B4b5b5alt l1 Test 8 QP EngDocument18 pagesPts 2024 B4b5b5alt l1 Test 8 QP EngKrishna PrintsNo ratings yet
- 1703491327Document2 pages1703491327Krishna PrintsNo ratings yet
- MergedDocument59 pagesMergedKrishna PrintsNo ratings yet
- 1701337951Document2 pages1701337951Krishna PrintsNo ratings yet
- 1701337781Document3 pages1701337781Krishna PrintsNo ratings yet
- 1701337773Document3 pages1701337773Krishna PrintsNo ratings yet
- 1701338026Document3 pages1701338026Krishna PrintsNo ratings yet
- 1701337899Document7 pages1701337899Krishna PrintsNo ratings yet
- PTS 2024 Preparatory Test 15 QP EngDocument10 pagesPTS 2024 Preparatory Test 15 QP EngKrishna PrintsNo ratings yet
- PTS 2024 Preparatory Test 14 Solutions EngDocument23 pagesPTS 2024 Preparatory Test 14 Solutions EngKrishna PrintsNo ratings yet
- 1701337685Document3 pages1701337685Krishna PrintsNo ratings yet
- 04 Viniam 030212Document2 pages04 Viniam 030212Krishna PrintsNo ratings yet
- PTS 2024 Preparatory Test 16 QP EngDocument10 pagesPTS 2024 Preparatory Test 16 QP EngKrishna PrintsNo ratings yet
- 414ufrep GS FST 5 ESE 2023 Pre TestDocument14 pages414ufrep GS FST 5 ESE 2023 Pre TestKrishna PrintsNo ratings yet
- Module Exercise 1 - RotationDocument22 pagesModule Exercise 1 - RotationKrishna PrintsNo ratings yet
- PTS 2024 Preparatory Test 13 QP EngDocument9 pagesPTS 2024 Preparatory Test 13 QP EngKrishna PrintsNo ratings yet
- Module Exercise 3 - RotationDocument5 pagesModule Exercise 3 - RotationKrishna PrintsNo ratings yet
- PTS 2024 Preparatory Test 14 QP EngDocument9 pagesPTS 2024 Preparatory Test 14 QP EngKrishna PrintsNo ratings yet
- GSFLT-01 Solution-1673161403363Document9 pagesGSFLT-01 Solution-1673161403363Krishna PrintsNo ratings yet
- Ies Master: Ese-2023 Prelims Test Series PAPER-I (FLT-01)Document12 pagesIes Master: Ese-2023 Prelims Test Series PAPER-I (FLT-01)Krishna PrintsNo ratings yet
- 406ufrep FST 3 ESE 2023 Test SeriesDocument14 pages406ufrep FST 3 ESE 2023 Test SeriesKrishna PrintsNo ratings yet