Professional Documents
Culture Documents
HW #3
Uploaded by
Ali KhubbakhtOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
HW #3
Uploaded by
Ali KhubbakhtCopyright:
Available Formats
Advance Metal Cutting Peiman Mosaddegh HW # 3
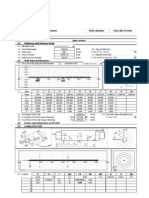
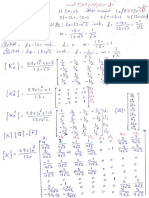
1 – Determine the shear angle in Oblique cutting can be obtained by following equation (Altintas
book Eq. 2.56) by assuming that the shear velocity is collinear with shear force:
2- A set of orthogonal cutting test are conducted to identify the shear angle,
average friction coefficient, and shear stress of P20 mold steel that has a hardness
of 34Rc. The cutting conditions and measured forces and chip thicknesses are
given in below table. The cutting tool was an S10 grade plunge turning tool with a
zero rake angle. The width of cut (i.e. width of disk) was b=5 mm, and the cutting
speed was V=240 m/min.
A) Evaluate the cutting coefficient, Ktc, and Kfc [N/mm^2] and edge forces
constants Kte and Kfe [N/mm] by linear regression of the measured force.
B) Evaluate the shear angle, shear stress, and average friction coefficient for
each test, and express them as a empirical function of uncut chip thickness
to form an orthogonal cutting database.
C) Predict the cutting force coefficient, Ktc, and Kfc [N/mm^2] using
empirically expressed shear angle, shear stress, and average friction
coefficient and compare them against the values identified from
mechanistic linear regression of the forces.
D) Evaluate the shear strain and strain rate for each test at the primary shear
zone.
c(mm) Ft(N) Ff(N) hc(mm)
0.02 350 290 0.06
0.03 480 350 0.058
0.04 590 400 0.074
0.05 690 440 0.083
0.06 790 480 0.102
0.07 890 505 0.116
0.08 980 540 0.131
You might also like
- HW1 ReportDocument3 pagesHW1 ReportAbdul Ahad100% (1)
- DIL-Column CalculationsDocument2 pagesDIL-Column Calculationsabu taherNo ratings yet
- Rectangular Column CalculationsDocument1 pageRectangular Column CalculationsSharif UddinNo ratings yet
- Rectangular Colum CalculationDocument1 pageRectangular Colum Calculationmikeme 4realNo ratings yet
- MItcal - Ejemplo de ClaseDocument102 pagesMItcal - Ejemplo de ClasedaagiraldogoNo ratings yet
- Rectangular Column CalculationsDocument1 pageRectangular Column CalculationsWilliamray PabloNo ratings yet
- RCC Column Calc Good MahfuzDocument1 pageRCC Column Calc Good Mahfuzkim lokNo ratings yet
- Rectangular Column CalculationsDocument1 pageRectangular Column Calculationsabu taherNo ratings yet
- Rectangular Column CalculationsDocument1 pageRectangular Column CalculationsLeonardo DamschiNo ratings yet
- Rectangular Column CalculationsDocument1 pageRectangular Column CalculationsInter GalacticNo ratings yet
- Rectangular Column CalculationsDocument1 pageRectangular Column Calculationsguiulfo tafurNo ratings yet
- Rectangular Column CalculationsDocument1 pageRectangular Column CalculationsRennie Dourado PlateroNo ratings yet
- Rectangular Column CalculationsDocument1 pageRectangular Column CalculationsakshaykhaireNo ratings yet
- Rectangular Column CalculationsDocument1 pageRectangular Column CalculationsRafael GarciaNo ratings yet
- COLCALCDocument1 pageCOLCALCahmedhusseinkamelNo ratings yet
- Rectangular Column CalculationsDocument1 pageRectangular Column CalculationsM ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Rectangular Column CalculationsDocument1 pageRectangular Column CalculationsEduardo LopezNo ratings yet
- Rectangular Column CalculationsDocument1 pageRectangular Column Calculationspmali2100% (1)
- Short Column AnalysisDocument1 pageShort Column Analysisrelu59No ratings yet
- Rectangular Column CalculationsDocument1 pageRectangular Column CalculationsPlas FabilloNo ratings yet
- ColumnDocument1 pageColumnAnil kumar RNo ratings yet
- Rectangular Column CalculationsDocument1 pageRectangular Column CalculationsTomasiNo ratings yet
- Rectangular Column CalculationsDocument1 pageRectangular Column CalculationsKen Roldan DiamanteNo ratings yet
- Corrected - Gear - 9 Teeth - ContactAnalysisDocument10 pagesCorrected - Gear - 9 Teeth - ContactAnalysiskarthikeyan NNo ratings yet
- Mechanical PrinciplesDocument46 pagesMechanical PrinciplesHarshini Premachandra0% (1)
- Drive Shaft CalculationDocument106 pagesDrive Shaft CalculationMustu AkolawalaNo ratings yet
- Jarak Antar Sengkang: Panjang Sloof - Jumlah Lebar Kolom Sepanjang Sloof 2Document6 pagesJarak Antar Sengkang: Panjang Sloof - Jumlah Lebar Kolom Sepanjang Sloof 2farhanNo ratings yet
- Shaft Design and CalculationDocument4 pagesShaft Design and CalculationHugo Mario Ariza PalacioNo ratings yet
- M.E. 3300 Lab Memo: Table 1. Data TableDocument4 pagesM.E. 3300 Lab Memo: Table 1. Data TableJan YsNo ratings yet
- COLUMN CALC Very Very Good MahfuzDocument1 pageCOLUMN CALC Very Very Good MahfuzHAITHAM ALINo ratings yet
- COLUMN CALC Very Very Good MahfuzDocument1 pageCOLUMN CALC Very Very Good MahfuzARAVINDNo ratings yet
- Rectangular Column Calculations Equally Spaced Reinf. On PerimeterDocument1 pageRectangular Column Calculations Equally Spaced Reinf. On PerimeterARAVINDNo ratings yet
- Sap DesignDocument1 pageSap DesignReza ErmawanNo ratings yet
- COLUMN CALC Very Very GoodDocument1 pageCOLUMN CALC Very Very Goodmostafiz18jun2007No ratings yet
- Winch Brake Test Form - WBTDocument3 pagesWinch Brake Test Form - WBTΝικόλαος Συρακούλας0% (1)
- Mechanical Operations (CH31007 and CH21205) Assignment: InstructionsDocument5 pagesMechanical Operations (CH31007 and CH21205) Assignment: InstructionsHarsh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Torsion Report PDFDocument31 pagesTorsion Report PDFSheikh BajunaidNo ratings yet
- College of Engineering Department of Architectural and Civil Engineering Foundation Engineering, I - CVEN 330 - Fall 2019 - L02Document4 pagesCollege of Engineering Department of Architectural and Civil Engineering Foundation Engineering, I - CVEN 330 - Fall 2019 - L02أحمد العمريNo ratings yet
- SAPDesign MB12Document1 pageSAPDesign MB12mrnaeem76No ratings yet
- Astm A 615Document2 pagesAstm A 615dana setiawanNo ratings yet
- Secant Pile ReinforcementDocument8 pagesSecant Pile ReinforcementghansaNo ratings yet
- Spreadsheet For Estimation of Machining Forces and Power Requirements - End Milling OperationsDocument7 pagesSpreadsheet For Estimation of Machining Forces and Power Requirements - End Milling OperationsMuhammad Ghiyats MukminNo ratings yet
- Shaft CalculationDocument4 pagesShaft Calculationksangeeth2000No ratings yet
- Blade DesignDocument2 pagesBlade Designtpa1962No ratings yet
- BladedesignDocument2 pagesBladedesigndiogenesrobertoNo ratings yet
- Asset-V1 CornellX+ENGR2000X+2T2016+Type@Asset+Block@F-1 Engine Model Calculations Non-Proprietyary Non-ITAR Rev2Document26 pagesAsset-V1 CornellX+ENGR2000X+2T2016+Type@Asset+Block@F-1 Engine Model Calculations Non-Proprietyary Non-ITAR Rev2salehmashrur 98No ratings yet
- Junming 2018 IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 317 012006Document7 pagesJunming 2018 IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 317 012006Ankit ShrivastwaNo ratings yet
- Duct Weight 28Document16 pagesDuct Weight 28STANDARD EDUCATION ACADEMY M.E.P CENTERNo ratings yet
- Rectangular Column CalculationsDocument2 pagesRectangular Column CalculationsMopao JojoNo ratings yet
- NIS Bearing Units Catalogue PDFDocument162 pagesNIS Bearing Units Catalogue PDFMunkhnasan MonaNo ratings yet
- Aerial Bundle Conductor Abc CableDocument1 pageAerial Bundle Conductor Abc CableBrianNo ratings yet
- Fastener Size Tables - MechaniCalcDocument14 pagesFastener Size Tables - MechaniCalcperdhana2000No ratings yet
- Appendix A Thickness of Base MetalDocument24 pagesAppendix A Thickness of Base MetalSaylittle PrayerNo ratings yet
- HCC4522B HCF4522B: Programmable BCD Divider-By-N CounterDocument6 pagesHCC4522B HCF4522B: Programmable BCD Divider-By-N CounterGoodLookingPirateNo ratings yet
- Surface Roughness Conversion Chart Tables - Engineers EdgeDocument10 pagesSurface Roughness Conversion Chart Tables - Engineers Edgejames.anitNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering DepartmentDocument2 pagesMechanical Engineering DepartmentArjit Goswami100% (1)
- Deflection in BimetalDocument4 pagesDeflection in BimetalRoisin ClearNo ratings yet
- Tugas Dinstruk - 2Document12 pagesTugas Dinstruk - 2Alek SusandiNo ratings yet
- Critical Load On StrutDocument5 pagesCritical Load On StrutelhammeNo ratings yet
- Tool Machinery Frames Comparison WeldedDocument6 pagesTool Machinery Frames Comparison WeldedAli KhubbakhtNo ratings yet
- Ebook Tapping Away Guide To Tapping and Threading Xometry SuppliesDocument19 pagesEbook Tapping Away Guide To Tapping and Threading Xometry SuppliesAli KhubbakhtNo ratings yet
- 23213Document16 pages23213Ali KhubbakhtNo ratings yet
- Hardinge Super Precision Turning EbookDocument13 pagesHardinge Super Precision Turning EbookAli KhubbakhtNo ratings yet
- Mech 421Document8 pagesMech 421Ali KhubbakhtNo ratings yet
- Kang 2019Document25 pagesKang 2019Ali KhubbakhtNo ratings yet
- P8.3 Consider Temperature in The Chip, Neglecting Heat Conducted Through The Tool. Refer ToDocument3 pagesP8.3 Consider Temperature in The Chip, Neglecting Heat Conducted Through The Tool. Refer ToAli KhubbakhtNo ratings yet
- FEMS4Document6 pagesFEMS4Ali KhubbakhtNo ratings yet
- Mayer 2019Document25 pagesMayer 2019Ali KhubbakhtNo ratings yet
- HW14Document2 pagesHW14Ali KhubbakhtNo ratings yet
- Presentation-Control AutomaticDocument43 pagesPresentation-Control AutomaticAli KhubbakhtNo ratings yet
- Developments in Machine Tool Spindle Technology: March 2021Document10 pagesDevelopments in Machine Tool Spindle Technology: March 2021Ali KhubbakhtNo ratings yet