Professional Documents
Culture Documents
7463
7463
Uploaded by
yayasan alhidayah bello0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageSevere COVID-19 patients are treated with oxygen therapy and may require mechanical ventilation if their respiratory condition worsens or does not respond to oxygen therapy. Therapeutic agents for COVID-19 can block virus entry into cells, block viral replication, or attenuate the exaggerated immune response. Anti-inflammatory treatments using drugs like glucocorticoids or cytokine inhibitors should only be given to COVID-19 patients after analyzing the risks and benefits.
Original Description:
Original Title
7463(1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSevere COVID-19 patients are treated with oxygen therapy and may require mechanical ventilation if their respiratory condition worsens or does not respond to oxygen therapy. Therapeutic agents for COVID-19 can block virus entry into cells, block viral replication, or attenuate the exaggerated immune response. Anti-inflammatory treatments using drugs like glucocorticoids or cytokine inhibitors should only be given to COVID-19 patients after analyzing the risks and benefits.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 page7463
7463
Uploaded by
yayasan alhidayah belloSevere COVID-19 patients are treated with oxygen therapy and may require mechanical ventilation if their respiratory condition worsens or does not respond to oxygen therapy. Therapeutic agents for COVID-19 can block virus entry into cells, block viral replication, or attenuate the exaggerated immune response. Anti-inflammatory treatments using drugs like glucocorticoids or cytokine inhibitors should only be given to COVID-19 patients after analyzing the risks and benefits.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
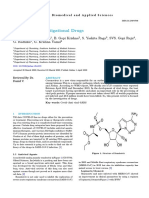
COVID-19 patients showing severe signs are
treated symptomatically along with oxygen therapy.
In such cases where the patients progress toward
respiratory failure and become refractory to oxygen
therapy, mechanical ventilation is necessitated. The
COVID-19-induced septic shock can be managed by
providing adequate hemodynamic support (299).
Several classes of drugs are currently being
evaluated for their potential therapeutic action
against SARS-CoV-2. Therapeutic agents that have
anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity can be broadly classified
into three categories: drugs that block virus entry
into the host cell, drugs that block viral replication as
well as its survival within the host cell, and drugs
that attenuate the exaggerated host immune response
(300). An inflammatory cytokine storm is commonly
seen in critically ill COVID-19 patients. Hence, they
may benefit from the use of timely anti-inflammation
treatment. Anti-inflammatory therapy using drugs
like glucocorticoids, cytokine inhibitors, JAK
inhibitors, and chloroquine/hydroxychloroquine
should be done only after analyzing the risk/benefit
ratio in COVID-19 patients (301). There have not
been any studies concerning the application of
nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) to
COVID-19-infected patients. However, reasonable
pieces of evidence are available that link NSAID
You might also like
- Communication: Multidrug Treatment For COVID-19Document3 pagesCommunication: Multidrug Treatment For COVID-19احمد عرفاتNo ratings yet
- IMG - 0221 (20 Files Merged)Document33 pagesIMG - 0221 (20 Files Merged)Eurica CabilunaNo ratings yet
- Journal Homepage: - : IntroductionDocument11 pagesJournal Homepage: - : IntroductionIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Corticosteroids For COVID 19, Worth It or Not? 2Document10 pagesCorticosteroids For COVID 19, Worth It or Not? 2sigit sigitNo ratings yet
- Cells: Thymoquinone: A Tie-Breaker in Sars-Cov2-Infected Cancer Patients?Document29 pagesCells: Thymoquinone: A Tie-Breaker in Sars-Cov2-Infected Cancer Patients?Yoni LinggaNo ratings yet
- Immunosuppressive Drugs and COVID-19: A ReviewDocument20 pagesImmunosuppressive Drugs and COVID-19: A ReviewCristie SumbillaNo ratings yet
- The Development ofDocument13 pagesThe Development ofGaspar PonceNo ratings yet
- Inmunoterapia Dirigida Al Huésped de Infecciones Virales y BacterianasDocument13 pagesInmunoterapia Dirigida Al Huésped de Infecciones Virales y BacterianasLis PariNo ratings yet
- Empirical TreatmentDocument12 pagesEmpirical TreatmentAbdelghani MILIANINo ratings yet
- Treatment of Psoriasis Unburdened by Fear During SARS CoV2 MenaceDocument5 pagesTreatment of Psoriasis Unburdened by Fear During SARS CoV2 MenaceDora TimisNo ratings yet
- Safety and Adverse Reaction of Therapeutic Antibodies Against Sars-Cov-2Document26 pagesSafety and Adverse Reaction of Therapeutic Antibodies Against Sars-Cov-2preeti yadavNo ratings yet
- Covid TreatmentDocument10 pagesCovid TreatmentkanazNo ratings yet
- Pharmaco Immunomodulatory Therapy in COVID 19Document26 pagesPharmaco Immunomodulatory Therapy in COVID 19Daniel PratamaNo ratings yet
- Montelukast in COVID-4Document6 pagesMontelukast in COVID-4Golam JILANI Mahbubay AlamNo ratings yet
- Mesenchymal Stem Cell Immunomodulation and Regeneration TherapeuticsDocument13 pagesMesenchymal Stem Cell Immunomodulation and Regeneration TherapeuticswiwiNo ratings yet
- Molecules: Can Natural Polyphenols Help in Reducing Cytokine Storm in COVID-19 Patients?Document14 pagesMolecules: Can Natural Polyphenols Help in Reducing Cytokine Storm in COVID-19 Patients?Sammy HolidayNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Community-Acquired Pneumonia in Adults in The Outpatient SettingDocument19 pagesTreatment of Community-Acquired Pneumonia in Adults in The Outpatient SettingDylanNo ratings yet
- Gopalaswamy y Subbian - 2021 - Corticosteroids For COVID-19 Therapy Potential ImDocument18 pagesGopalaswamy y Subbian - 2021 - Corticosteroids For COVID-19 Therapy Potential ImOsmar SulcaNo ratings yet
- Immunopharmacological Perspective On Zinc in SARS-CoV-2 InfectionDocument16 pagesImmunopharmacological Perspective On Zinc in SARS-CoV-2 InfectionW CnNo ratings yet
- Jara2022 Article AutoimmunePost-COVIDVaccineSynDocument7 pagesJara2022 Article AutoimmunePost-COVIDVaccineSynJoão Paulo CarneiroNo ratings yet
- Wrotek2021Document10 pagesWrotek2021Laura Alejandra Torres CanchalaNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Community-Acquired Pneumonia in Adults Who Require HospitalizationDocument79 pagesTreatment of Community-Acquired Pneumonia in Adults Who Require Hospitalizationmayteveronica1000No ratings yet
- Name: Athena Dianne B. Aguillon Block: 2-NgDocument3 pagesName: Athena Dianne B. Aguillon Block: 2-NgATHENA DIANNE BARON AGUILLONNo ratings yet
- Biomed 2Document28 pagesBiomed 2HernanVelardeNo ratings yet
- Montelukast in COVIDDocument7 pagesMontelukast in COVIDGolam JILANI Mahbubay AlamNo ratings yet
- Review Article Mesenchymal Stem Cells and COVID-19: Cure, Prevention, and VaccinationDocument12 pagesReview Article Mesenchymal Stem Cells and COVID-19: Cure, Prevention, and VaccinationBala BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Refrat TBDocument15 pagesRefrat TBAndika TatagNo ratings yet
- Improve On DexamethasoneDocument9 pagesImprove On DexamethasoneZac IngNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Community-Acquired Pneumonia in Adults Who Require Hospitalization - UpToDateDocument80 pagesTreatment of Community-Acquired Pneumonia in Adults Who Require Hospitalization - UpToDateTran Thai Huynh NgocNo ratings yet
- Micronutrients As Immunomodulatory Tools For COVID-19 ManagementDocument10 pagesMicronutrients As Immunomodulatory Tools For COVID-19 ManagementPavan MujawdiyaNo ratings yet
- Sistem Kekebalan Sebagai Target Terapi SARS-CoV-2 Tinjauan Sistematis Imunoterapi Terkini Untuk COVID-19Document14 pagesSistem Kekebalan Sebagai Target Terapi SARS-CoV-2 Tinjauan Sistematis Imunoterapi Terkini Untuk COVID-19PSPPA 06No ratings yet
- Math A Guide To Managing The HospitalizedDocument43 pagesMath A Guide To Managing The HospitalizedAjla SalihovicNo ratings yet
- (2020) Potential Cytoprotective Activity of Ozone Therapy in SARS-CoV-2COVID-19Document12 pages(2020) Potential Cytoprotective Activity of Ozone Therapy in SARS-CoV-2COVID-19Vu TranNo ratings yet
- Main 9Document11 pagesMain 9Eltohn JohnNo ratings yet
- MelatoninDocument11 pagesMelatoninSalvatore BiundoNo ratings yet
- Nutraceutical Effects On Covid 19Document35 pagesNutraceutical Effects On Covid 19Tikendra SinghNo ratings yet
- 1Document79 pages1Umar Ali RajaNo ratings yet
- Banerjee Et Al 2020Document5 pagesBanerjee Et Al 2020Alex RomeroNo ratings yet
- ASA COVID 19 Ebook PDFDocument18 pagesASA COVID 19 Ebook PDFAnt Son MINo ratings yet
- Treatment of Community-Acquired Pneumonia - UpToDateDocument45 pagesTreatment of Community-Acquired Pneumonia - UpToDateEjaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- Anti Corona Drugs and VaccineDocument13 pagesAnti Corona Drugs and VaccineImran KhanNo ratings yet
- Temi 9 1760145Document3 pagesTemi 9 1760145Arns Dyt RifNo ratings yet
- Tropicalmed 05 00112 v4Document22 pagesTropicalmed 05 00112 v4IchaNo ratings yet
- TCMDocument10 pagesTCM1122GNo ratings yet
- Curcumin As A Potential Target For COVIDDocument10 pagesCurcumin As A Potential Target For COVIDPathirage Kamal PereraNo ratings yet
- Antioxidante Covid PDFDocument6 pagesAntioxidante Covid PDFTays AndradeNo ratings yet
- Covid UpdateDocument5 pagesCovid UpdateAndreea PostolacheNo ratings yet
- 218-Article Text-349-1-10-20200401 PDFDocument3 pages218-Article Text-349-1-10-20200401 PDFLeonardo de SouzaNo ratings yet
- Nosocomial Infections Associated To COVID-19 in The IntensiveDocument8 pagesNosocomial Infections Associated To COVID-19 in The Intensivenanang hidayatullohNo ratings yet
- Vol 28 2 2020 10Document14 pagesVol 28 2 2020 10Nanang SupriyantoNo ratings yet
- Are Promising Mechanisms of Hydroxychloroquine Abolish COVID-19 Activity? A Review StudyDocument5 pagesAre Promising Mechanisms of Hydroxychloroquine Abolish COVID-19 Activity? A Review StudyAbdulsalamNo ratings yet
- SV2021123101Document21 pagesSV2021123101AniAliciaOrtizCastleNo ratings yet
- Convalescent PlasmaDocument42 pagesConvalescent PlasmaOlaniyi John OlajideNo ratings yet
- Autoimmunity Reviews: SciencedirectDocument9 pagesAutoimmunity Reviews: SciencedirectetienNo ratings yet
- Editorial: COVID-19: An Unexpected Indication For Anti-Rheumatic Therapies?Document4 pagesEditorial: COVID-19: An Unexpected Indication For Anti-Rheumatic Therapies?dayuseed001No ratings yet
- Journal Pre-Proof: International Journal of Antimicrobial AgentsDocument13 pagesJournal Pre-Proof: International Journal of Antimicrobial Agentssameer sahaanNo ratings yet
- Rheumatology: Implications of COVID 19 in Pediatric RheumatologyDocument21 pagesRheumatology: Implications of COVID 19 in Pediatric RheumatologyLaira VillalobosNo ratings yet
- De-Escalation of Antibiotic Therapy and Culture Positivity in COVID-19 Patients With PneumoniaDocument5 pagesDe-Escalation of Antibiotic Therapy and Culture Positivity in COVID-19 Patients With PneumoniaTebby OkothNo ratings yet
- FullDocument2 pagesFullyuri goitiaNo ratings yet
- Img 0194Document1 pageImg 0194yayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- Img 0186Document1 pageImg 0186yayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- Img 0193Document1 pageImg 0193yayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- Img 0196Document1 pageImg 0196yayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- Img 0142Document1 pageImg 0142yayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- Img 0155Document1 pageImg 0155yayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- Img 0182Document1 pageImg 0182yayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- Img 0178Document1 pageImg 0178yayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- Img 0201Document1 pageImg 0201yayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- Img 0127Document1 pageImg 0127yayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- Img 0163Document1 pageImg 0163yayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- 7431Document1 page7431yayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- Betacoronavirus Conserved Open Reading Frame La/bDocument1 pageBetacoronavirus Conserved Open Reading Frame La/byayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- 7433Document1 page7433yayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- Betacoronavirus Gammacoronavirus and Deltacoronavirus MainlyDocument1 pageBetacoronavirus Gammacoronavirus and Deltacoronavirus Mainlyyayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- Ig 2 Sars-Cov-2 Virus StructureDocument1 pageIg 2 Sars-Cov-2 Virus Structureyayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- 7427Document1 page7427yayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- Img 0128Document1 pageImg 0128yayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- Therapeutics and DrugsDocument1 pageTherapeutics and Drugsyayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- 7432Document1 page7432yayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- 7451Document1 page7451yayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- 7440Document1 page7440yayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- 7444Document1 page7444yayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- 7443Document1 page7443yayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- 7438Document1 page7438yayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- 7455Document1 page7455yayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- 7459Document1 page7459yayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- 7460Document1 page7460yayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- 7466Document1 page7466yayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- Coronaviwses in Animals and Zoonotic Links-A Brief ViewpointDocument1 pageCoronaviwses in Animals and Zoonotic Links-A Brief Viewpointyayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet