Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Betacoronavirus Conserved Open Reading Frame La/b
Betacoronavirus Conserved Open Reading Frame La/b
Uploaded by
yayasan alhidayah bello0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageBased on molecular characterization and phylogenetic analysis, SARS-CoV-2 is a distinct betacoronavirus belonging to the subgenus Sarbecovirus. It is most closely related to bat SARS-related coronaviruses, with 89% nucleotide identity. SARS-CoV-2 shares 80% identity with the original SARS-CoV and 82% identity with human SARS-CoV strains. However, it only shares 51.8% identity with MERS-related coronaviruses. The evidence suggests SARS-CoV-2 originated in bats and was transmitted to humans, potentially with other intermediate hosts.
Original Description:
Original Title
7424
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentBased on molecular characterization and phylogenetic analysis, SARS-CoV-2 is a distinct betacoronavirus belonging to the subgenus Sarbecovirus. It is most closely related to bat SARS-related coronaviruses, with 89% nucleotide identity. SARS-CoV-2 shares 80% identity with the original SARS-CoV and 82% identity with human SARS-CoV strains. However, it only shares 51.8% identity with MERS-related coronaviruses. The evidence suggests SARS-CoV-2 originated in bats and was transmitted to humans, potentially with other intermediate hosts.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageBetacoronavirus Conserved Open Reading Frame La/b
Betacoronavirus Conserved Open Reading Frame La/b
Uploaded by
yayasan alhidayah belloBased on molecular characterization and phylogenetic analysis, SARS-CoV-2 is a distinct betacoronavirus belonging to the subgenus Sarbecovirus. It is most closely related to bat SARS-related coronaviruses, with 89% nucleotide identity. SARS-CoV-2 shares 80% identity with the original SARS-CoV and 82% identity with human SARS-CoV strains. However, it only shares 51.8% identity with MERS-related coronaviruses. The evidence suggests SARS-CoV-2 originated in bats and was transmitted to humans, potentially with other intermediate hosts.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
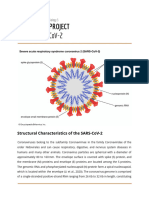
Based on molecular characterization, SARS-
CoV-2 is considered a new Betacoronavirus
belonging to the subgenus Sarbecovirus (3). A few
other critical zoonotic viruses (MERS-related CoV
and SARS-related CoV) belong to the same genus.
However, SARS-CoV-2 was identified as a distinct
virus based on the percent identity with other
Betacoronavirus; conserved open reading frame la/b
(ORF1a/b) is below 90% identity (3). An overall
80% nucleotide identity was observed between
SARS-CoV-2 and the original SARS-CoV, along
with 89% identity with ZC45 and ZXC21 SARS-
related CoVs of bats (2, 31, 36). In addition, 82%
identity has been observed between SARS-CoV-2
and human SARS-CoV Tor2 and human SARS-CoV
BJ01 2003 (31). A sequence identity of only 51.8%
was observed between MERS-related CoV and the
recently emerged SARS-CoV-2 (37). Phylogenetic
analysis of the structural genes also revealed that
SARS-CoV-2 is closer to bat SARS-related CoV.
Therefore, SARS-CoV-2 might have originated from
bats, while other amplifier hosts might have played a
role in disease transmission to humans (31). Of note,
the other two zoonotic CoVs (MERS-related CoV
and SARS-related CoV) also originated from bats
(38, 39). Nevertheless, for SARS and MERS, civet
You might also like
- The 2nd Yan ReportDocument33 pagesThe 2nd Yan ReportRaheem Kassam100% (13)
- The Yan ReportDocument26 pagesThe Yan ReportZerohedge96% (117)
- Img 0201Document1 pageImg 0201yayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- Curbio Current-BiologyDocument22 pagesCurbio Current-BiologyM Abdurrahman ArNo ratings yet
- Img 8167Document1 pageImg 8167Muhammad FahmiNo ratings yet
- El Origen Del Covid19Document5 pagesEl Origen Del Covid19Herrera NataliaNo ratings yet
- Probable Pangolin Origin of Sars-Cov-2 Associated With The Covid-19 OutbreakDocument13 pagesProbable Pangolin Origin of Sars-Cov-2 Associated With The Covid-19 OutbreaksantilesolNo ratings yet
- SARS-CoV-2 GeneticsDocument9 pagesSARS-CoV-2 GeneticsAlexandra GarridoNo ratings yet
- Img 8289Document1 pageImg 8289garudaNo ratings yet
- SARS CoV 2Document5 pagesSARS CoV 2José Guadalupe Pinedo MuñozNo ratings yet
- 986c09ca-d494-4a7c-a65b-9eec9c0a06b8 (1)Document24 pages986c09ca-d494-4a7c-a65b-9eec9c0a06b8 (1)SahalS MNo ratings yet
- CovDocument31 pagesCovMichelle “Ellie” TiongsonNo ratings yet
- Rañola Micro-Para Covid-19 PrelimsDocument6 pagesRañola Micro-Para Covid-19 PrelimsAndrey Mary RanolaNo ratings yet
- Probable Pangolin Origin of Sars-Cov-2 Associated With The Covid-19 OutbreakDocument9 pagesProbable Pangolin Origin of Sars-Cov-2 Associated With The Covid-19 OutbreakLeandro RodríguezNo ratings yet
- ApossibleoriginforSARS-CoV-2 200520 UpdatedDocument14 pagesApossibleoriginforSARS-CoV-2 200520 UpdatedKrešimir PavelićNo ratings yet
- The Proximal Origin of Sars-Cov-2Document16 pagesThe Proximal Origin of Sars-Cov-2perete69No ratings yet
- Wetransfer - ProjectDocument40 pagesWetransfer - ProjectĐinh ThắngNo ratings yet
- Nuevo Coronavirus en MurcielagosDocument22 pagesNuevo Coronavirus en MurcielagosCarlos Vinicio Chiluisa GuachoNo ratings yet
- CoronavirusDocument12 pagesCoronavirusZubair GhouriNo ratings yet
- The Genetic Structure of Sars-Cov-2 Does Not Rule Out A Laboratory OriginDocument9 pagesThe Genetic Structure of Sars-Cov-2 Does Not Rule Out A Laboratory OriginNicholas SchmittNo ratings yet
- SARS-CoV-2 and Covid19 Lecture 3Document4 pagesSARS-CoV-2 and Covid19 Lecture 3Aishwarya SinghNo ratings yet
- Boni Et Al. 2020. Evolutionary Origins of The SARS-CoV-2 PDFDocument17 pagesBoni Et Al. 2020. Evolutionary Origins of The SARS-CoV-2 PDFDiego Mauri99No ratings yet
- Virology: Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2Document1 pageVirology: Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2Sadhak AarushNo ratings yet
- Current Understanding of An Emerging Coronavirus UsingDocument11 pagesCurrent Understanding of An Emerging Coronavirus UsinganselmoNo ratings yet
- Kang-A Selective Sweep in The Spike Gene Has Driven SARS-CoV-2 Human Adaptation-2021-CellDocument15 pagesKang-A Selective Sweep in The Spike Gene Has Driven SARS-CoV-2 Human Adaptation-2021-CellSimón Villegas VelásquezNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy-2020-Martinez-AAC.00399-20.fullDocument18 pagesAntimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy-2020-Martinez-AAC.00399-20.fullBasilio Papuico RomeroNo ratings yet
- The Yan ReportDocument27 pagesThe Yan ReportAndrea MartinezNo ratings yet
- The Proximal Origin of SARS-CoV-2Document9 pagesThe Proximal Origin of SARS-CoV-2sylodhiNo ratings yet
- Evolutionary Distance of SARS-CoV-2 and Bat Coronaviruses Studied Under The NIHsupported Research Grant To EcoHealth AllianceDocument3 pagesEvolutionary Distance of SARS-CoV-2 and Bat Coronaviruses Studied Under The NIHsupported Research Grant To EcoHealth AllianceAl StatiliusNo ratings yet
- Sars-Cov-2 Genetics: Key Findings For Public HealthDocument2 pagesSars-Cov-2 Genetics: Key Findings For Public HealthRishabh SachanNo ratings yet
- Project 1 (1 100 Page)Document47 pagesProject 1 (1 100 Page)haleem ullah khanNo ratings yet
- Nature 12711Document16 pagesNature 12711Ruby Rey Rueda de AguilarNo ratings yet
- Intro Mpro HighlightedDocument26 pagesIntro Mpro HighlightedTifah InternationalNo ratings yet
- ACE-2 em Cães e GatosDocument10 pagesACE-2 em Cães e GatosExpedito MaiaNo ratings yet
- SARS CoV-2Document26 pagesSARS CoV-2Bahadır MüftüoğluNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Gain of FunctionDocument5 pagesCOVID-19 Gain of FunctionRed Cloud ShamanNo ratings yet
- SARS-CoV-2 and Covid19 Lecture 3 - 2Document5 pagesSARS-CoV-2 and Covid19 Lecture 3 - 2Aishwarya SinghNo ratings yet
- Specific Primer Design For Accurate Detection of Sars-Cov-2 Using Deep LearningDocument17 pagesSpecific Primer Design For Accurate Detection of Sars-Cov-2 Using Deep LearningHasna Mirda AmazanNo ratings yet
- Caractere VirologiaueDocument29 pagesCaractere Virologiauehind el hamriNo ratings yet
- Sars-Cov-2: Phylogenetic Status, Mutations and Therapeutic Research Based On Spike ProteinDocument10 pagesSars-Cov-2: Phylogenetic Status, Mutations and Therapeutic Research Based On Spike ProteinArley GutarraNo ratings yet
- Project 1Document64 pagesProject 1haleem ullah khanNo ratings yet
- SARS CoV2Document14 pagesSARS CoV2Zubair GhouriNo ratings yet
- s41586 021 03493 4 KomprimiertDocument36 pagess41586 021 03493 4 KomprimiertKrešimir PavelićNo ratings yet
- Coronavirus3 PDFDocument28 pagesCoronavirus3 PDFWilmar David Medina MadridNo ratings yet
- Sars-Cov-2: Camazotz 'S Curse: SciencedirectDocument6 pagesSars-Cov-2: Camazotz 'S Curse: SciencedirectautomationenggNo ratings yet
- 60 Iamges To One Word FileDocument58 pages60 Iamges To One Word FileAbdul Ahad ShafiqiNo ratings yet
- 5 SARS CoV 2 Is An Robot BioweaponDocument28 pages5 SARS CoV 2 Is An Robot BioweaponChristopher William LeeNo ratings yet
- Ren 2008Document9 pagesRen 2008William VenegasNo ratings yet
- Endonuclease Fingerprint Indicates A Synthetic Origin of SARS-CoV-2 (Oct. 2022)Document17 pagesEndonuclease Fingerprint Indicates A Synthetic Origin of SARS-CoV-2 (Oct. 2022)Pierre SchlaederNo ratings yet
- Dholariya2021 Article NotableAndEmergingVariantsOfSADocument8 pagesDholariya2021 Article NotableAndEmergingVariantsOfSAA.R MaheshNo ratings yet
- Chemical Biology: SARS-CoV-2Document9 pagesChemical Biology: SARS-CoV-2Eliakim InsongNo ratings yet
- Journal Pre-Proof: Clinical Microbiology and InfectionDocument23 pagesJournal Pre-Proof: Clinical Microbiology and Infectionsameer sahaanNo ratings yet
- Full PDFDocument8 pagesFull PDFYad Mohammad NazaryNo ratings yet
- TrialDocument1 pageTrialHaina HadjialiNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 LEGACY: SARS-CoV-2 clinical trials, vaccines trials and bioethicsFrom EverandCOVID-19 LEGACY: SARS-CoV-2 clinical trials, vaccines trials and bioethicsNo ratings yet
- Img 0194Document1 pageImg 0194yayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- Img 0186Document1 pageImg 0186yayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- Img 0178Document1 pageImg 0178yayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- Img 0142Document1 pageImg 0142yayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- Img 0182Document1 pageImg 0182yayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- Img 0193Document1 pageImg 0193yayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- Betacoronavirus Gammacoronavirus and Deltacoronavirus MainlyDocument1 pageBetacoronavirus Gammacoronavirus and Deltacoronavirus Mainlyyayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- Img 0196Document1 pageImg 0196yayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- Img 0127Document1 pageImg 0127yayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- Img 0163Document1 pageImg 0163yayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- Ig 2 Sars-Cov-2 Virus StructureDocument1 pageIg 2 Sars-Cov-2 Virus Structureyayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- Img 0128Document1 pageImg 0128yayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- Img 0155Document1 pageImg 0155yayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- 7433Document1 page7433yayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- 7427Document1 page7427yayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- Therapeutics and DrugsDocument1 pageTherapeutics and Drugsyayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- 7432Document1 page7432yayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- 7440Document1 page7440yayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- 7431Document1 page7431yayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- 7459Document1 page7459yayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- 7438Document1 page7438yayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- 7455Document1 page7455yayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- 7443Document1 page7443yayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- 7451Document1 page7451yayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- 7444Document1 page7444yayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- 7460Document1 page7460yayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- 7461Document1 page7461yayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- Coronaviwses in Animals and Zoonotic Links-A Brief ViewpointDocument1 pageCoronaviwses in Animals and Zoonotic Links-A Brief Viewpointyayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet
- 7466Document1 page7466yayasan alhidayah belloNo ratings yet