Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bio - CO 5
Uploaded by
Jae Bert UbisoftOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bio - CO 5
Uploaded by
Jae Bert UbisoftCopyright:
Available Formats
BIOLOGY 01
Course Outcome 5
ENERGY
ENERGY
main forms states
Heat Chemical Electromagnetic Nuclear Mechanical Potential Kinetic
Gravitational Elastic
IMPORTANT TERMS:
Energy – ability to do work (measured in the same unit as work: joules)
Energy Conversions – changes in the form of energy
Heat Energy – produced by friction and cause changes in temperature and phase of any form of matter
Chemical Energy – required to bond atoms together. (Energy is released when bonds are broken)
Electromagnetic – produced in a form of electricity and light.
Nuclear Energy – nucleus is the source of energy and the most concentrated energy. (Fusion and Fission)
Mechanical Energy – performs work
Potential Energy – the capacity to do work or energy that is stored
Kinetic Energy – the energy of motion. Depends on mass and velocity
OXIDATION AND REDUCTION
Important Terms:
Metals – more Cation like, possess positive oxidation number
Non-metals – more Anion like, possess negative oxidation number
GEROA LEORA
Reduction Oxidation
Gain of electron Loss of electron
Non – spontaneous Spontaneous
LAWS OF THERMODYNAMICS
IMPORTANT TERMS:
Thermodynamics – study of energy and its transformation
First Law – energy can be converted from one form to another, but it cannot be created nor destroyed
Second Law – energy cannot be converted without the loss of usable energy
Zeroth Law – thermal equilibrium
Third Law – no entropy
Entropy (S) – measurement of disorder
Enthalpy (H) – total potential energy of a system
Free Energy (G) – the only kind of energy that can do cell work
ATP – ADP CYCLE
Important Terms:
ATP (Adenosine triphosphate) – store and release energy
COMPOSITION
3 Phosphate groups
Ribose, a five carbon sugar
Adenine, a nitrogen-containing organic base
DESCRIPTION
Energy currency of all cells
Type of nucleic acid
Contains high energy phosphate bonds
ADP (Adenosine diphosphate) – energy can be stored by adding another phosphate
ATPase – enzyme that help in hydrolysis (adding H 2O)
ATP Synthase – enzyme that helps ADP turns into ATP
Phosphorylation – reaction in which a phosphate group is transferred to some other compound
NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) – most common acceptor that temporarily stores (G)
NADH – reduced form of NAD+
NADP+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate) – chemically similar to NAD + but has P
NADPH – reduced form of NADP+
CAPTURING LIGHT ENERGY
Important Terms:
Chlorophyll –absorbs blue and red region
Electromagnetic Spectrum – continuous range of radiation
Photons – packets or small particles of energy
Visible Light – electromagnetic spectrum from 380 to 760
Violet has the shortest wavelength and Red has the longest wavelength
Electron Transport Chain – series of proteins in thylakoid membrane
Photolysis – splitting of water
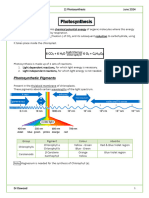
PHOTOSYNTHESIS
(endergonic reaction)
Convert carbon dioxide (CO2) + water (H2O) with the use of photons (light energy)
That will result to the production of organic molecules such as glucose (CH2O) and release oxygen (O2)
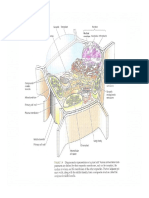
mainly occurs in leaves
Stoma – pores Mesophyll Cells – where photosynthesis occur
where exchange specifically in an organelle called
of gases occur Chloroplast
Stroma Thylakoids
Granum
Grana
Thylakoid Membrane Thylakoid Space or
Chlorophyll Carotenoids Thylakoid Lumen
Porphyrin Hydrocarbon
ring side chain
PHOTOSYNTHESIS REACTION
LIGHT DEPENDENT REACTIONS CARBON FIXATION REACTION
Light reaction Dark reaction
Occurs in thylakoids Occurs in stroma
1. Light energy transfer to chlorophyll 1. Carbon uptake
2. Chlorophyll pass the energy to ETC 2. Carbon Reduction
3. Energized electron may 3. RuBP regeneration
4. Split H2O (photolysis) then release oxygen
forming NADPH or bonds to ADP to form
ATP
5. NADPH and ATP are stored for the use in
the calvin cycle.
You might also like
- 25th International Congress of Pure and Applied Chemistry: Plenary Lectures Presented at the 25th International Congress of Pure and Applied Chemistry, Jerusalem, Israel 6–11 July 1975From Everand25th International Congress of Pure and Applied Chemistry: Plenary Lectures Presented at the 25th International Congress of Pure and Applied Chemistry, Jerusalem, Israel 6–11 July 1975Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Photosynthesis 02-11-02 14Document43 pagesPhotosynthesis 02-11-02 14Soemi BarrientosNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument6 pagesScience ReviewerNathan ArrezaNo ratings yet
- By The End of This Lecture You Will Be Able To:: Light-Dependent Reactions (I.e., Light Reactions)Document35 pagesBy The End of This Lecture You Will Be Able To:: Light-Dependent Reactions (I.e., Light Reactions)Diganta Kr DasNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis ADocument15 pagesPhotosynthesis AJust EllaNo ratings yet
- 2022F PP2 Photosynthesis Light DarkDocument100 pages2022F PP2 Photosynthesis Light Dark啦啦啦啦No ratings yet
- Energy Can Be Transformed From One Form To AnotherDocument35 pagesEnergy Can Be Transformed From One Form To AnotherLatha MahendraNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: B. Carbon Metabolism 1. C3 2. C4 3. CAM C. Factors Regulating The ProcessesDocument94 pagesPhotosynthesis: B. Carbon Metabolism 1. C3 2. C4 3. CAM C. Factors Regulating The ProcessesJonathanNo ratings yet
- Ch. 8 Photosynthesis F17Document70 pagesCh. 8 Photosynthesis F17bae loonaNo ratings yet
- Raven, P. H. Et Al. 1992Document73 pagesRaven, P. H. Et Al. 1992Teflon SlimNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument65 pagesPhotosynthesisVinz Arvhil MatagayNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis 02-11-02 14Document33 pagesPhotosynthesis 02-11-02 14Eanne HavenNo ratings yet
- Ch10 PhotosynthesisDocument23 pagesCh10 Photosynthesiscorygunther6451No ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument29 pagesPhotosynthesisAB CloydNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Notes 20Document19 pagesPhotosynthesis Notes 20Farhadullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Atp Adp CycleDocument34 pagesAtp Adp CycleJepoy dizon Ng Tondo Revengerz gangNo ratings yet
- BCH 223 Assignment 1 2021Document6 pagesBCH 223 Assignment 1 2021Nosibusiso KhaliphaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis - HussDocument43 pagesPhotosynthesis - HussTrish Austria50% (2)
- FotosintezaDocument28 pagesFotosintezaÉvariste GaloisNo ratings yet
- Energy Conservation IN Eukaryotic CellDocument28 pagesEnergy Conservation IN Eukaryotic CellJohn TinambacanNo ratings yet
- By The End of This Lecture You Will Be Able To:: Light-Dependent Reactions (I.e., Light Reactions)Document35 pagesBy The End of This Lecture You Will Be Able To:: Light-Dependent Reactions (I.e., Light Reactions)yu90210No ratings yet
- 3 4 Group 6 Written Report With CommentsDocument7 pages3 4 Group 6 Written Report With CommentsJanine Abiegale PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis 1Document68 pagesPhotosynthesis 1Capili, Princess Jenelle D.No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis LECTUREDocument36 pagesPhotosynthesis LECTUREAnonymous HXLczq3100% (1)
- Photosynthesis Solar Energy Chemical EnergyDocument35 pagesPhotosynthesis Solar Energy Chemical EnergyJennifer GuilarteNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationDocument32 pagesPhotosynthesis and Cellular RespirationDiana HermosuraNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Lect 1Document72 pagesPhotosynthesis Lect 1Nam GonzalesNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument3 pagesPhotosynthesisGustilo, Serj Andreas F.No ratings yet
- 2 Introduction To MetabolismDocument17 pages2 Introduction To MetabolismBryan DellomosNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes Unit TwoDocument158 pagesBiology Notes Unit TwoBlohsh KeenenNo ratings yet
- By The End of This Lecture You Will Be Able To:: Light-Dependent Reactions (I.e., Light Reactions)Document35 pagesBy The End of This Lecture You Will Be Able To:: Light-Dependent Reactions (I.e., Light Reactions)Den Angelica DungoNo ratings yet
- What I Know: Quarter 2 - Module 1 Energy TransformationDocument8 pagesWhat I Know: Quarter 2 - Module 1 Energy TransformationLyka Mae BenitoNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationDocument41 pagesPhotosynthesis and Cellular Respirationjhenjhentot24No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 PhotosynthesisDocument60 pagesChapter 5 Photosynthesisvijaypanwar_2000No ratings yet
- Cellular Energy Resp PhotoDocument85 pagesCellular Energy Resp Photomuhra khaeld salim al abo aldariiNo ratings yet
- 3.2 The Light-Dependent Reaction: PhotosynthesisDocument20 pages3.2 The Light-Dependent Reaction: PhotosynthesisazwelljohnsonNo ratings yet
- Light Reactions and The Calvin CycleDocument24 pagesLight Reactions and The Calvin CycleMay NisperosNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: Powerpoint Lectures ForDocument53 pagesPhotosynthesis: Powerpoint Lectures ForSean JonesNo ratings yet
- Advanced Biology: PhotosynthesisDocument31 pagesAdvanced Biology: Photosynthesiszorbax100% (2)
- Notebook 2ndQDocument7 pagesNotebook 2ndQJohnReyBarnacheaNo ratings yet
- Light Reaction Calvin CycleDocument31 pagesLight Reaction Calvin CycleBianca SuarezNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 101 Module 5Document5 pagesGen Bio 101 Module 5Kyne GasesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 4 Q4Document32 pagesLesson 3 4 Q4Joshua DurogaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 PhotosynthesisDocument41 pagesChapter 2 PhotosynthesisTshering ChodenNo ratings yet
- C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C: Energy Metabolism: PhotosynthesisDocument6 pagesC C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C: Energy Metabolism: PhotosynthesisPatrick JuacallaNo ratings yet
- Reacciones de LuzDocument25 pagesReacciones de LuzAndrés Reinoso SánchezNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis 1Document52 pagesPhotosynthesis 1Ella Mae CelestinoNo ratings yet
- Life 112 PhotosynthesisDocument38 pagesLife 112 Photosynthesiskarabontu35No ratings yet
- Science 3Document66 pagesScience 3Neon True BeldiaNo ratings yet
- CH 2 - PhotosynthesisDocument12 pagesCH 2 - PhotosynthesisnawarakanNo ratings yet
- Bioenergetics and Oxidative PhosphorylationDocument88 pagesBioenergetics and Oxidative PhosphorylationAtif Amin BaigNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis 2Document58 pagesPhotosynthesis 2Jemimah Carmelle DoradoNo ratings yet
- Chapter-4 PhotosynthesisDocument4 pagesChapter-4 Photosynthesiskavitaruby1980No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis EllaDocument42 pagesPhotosynthesis EllaElla AgyeiNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: The Process That Feeds The BiosphereDocument50 pagesPhotosynthesis: The Process That Feeds The BiosphereMicaszen MendozaNo ratings yet
- Light ReactionDocument17 pagesLight Reactionmshtalam.edNo ratings yet
- BSC1005 - Review List - Exam 2Document5 pagesBSC1005 - Review List - Exam 2mystaceeNo ratings yet
- U3 - Study Guide - CELL ENERGYDocument8 pagesU3 - Study Guide - CELL ENERGYJuan CastellanosNo ratings yet
- Light Dependent and Independent ReactionDocument30 pagesLight Dependent and Independent ReactionAsia TundayagNo ratings yet
- Chapter7 Photosynthesisarespiration 281 29Document30 pagesChapter7 Photosynthesisarespiration 281 29NameNo ratings yet
- Math01 - CO 4Document4 pagesMath01 - CO 4Jae Bert UbisoftNo ratings yet
- Bio - CO 4Document5 pagesBio - CO 4Jae Bert UbisoftNo ratings yet
- MATH 01 FormulaDocument3 pagesMATH 01 FormulaJae Bert UbisoftNo ratings yet
- Math04 - CO 4Document1 pageMath04 - CO 4Jae Bert UbisoftNo ratings yet
- Bio - CO 6Document2 pagesBio - CO 6Jae Bert UbisoftNo ratings yet
- 02 Plant EcophysiologyDocument49 pages02 Plant Ecophysiologylam lamNo ratings yet
- Escape Room EDU Teacher InstructionsDocument41 pagesEscape Room EDU Teacher InstructionsNina Romero Ricci100% (1)
- CELLULAR ENERGY-g9Document13 pagesCELLULAR ENERGY-g9Maria RosaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis - WikipediaDocument28 pagesPhotosynthesis - WikipediakamaalNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Worksheet Version 2 SHORT 2018 KEYDocument4 pagesPhotosynthesis Worksheet Version 2 SHORT 2018 KEYRosty Ann GrabilloNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument8 pagesPhotosynthesisvannerrie50% (2)
- Anaerobic RespirationDocument14 pagesAnaerobic RespirationAbegail AcedoNo ratings yet
- Botany XI STBBDocument21 pagesBotany XI STBBHabib U Zaman MemonNo ratings yet
- General Biology - Q2 - Week 2Document23 pagesGeneral Biology - Q2 - Week 2Renard JaenNo ratings yet
- New Zealand Biology Olympiad 2011Document20 pagesNew Zealand Biology Olympiad 2011Science Olympiad BlogNo ratings yet
- Practical 8 MethodDocument1 pagePractical 8 Methodsarah wNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 PPT 2 - Dark and Light ReactionDocument29 pagesQuarter 2 PPT 2 - Dark and Light ReactionKarl Patrick PachecoNo ratings yet
- Exam ReviewDocument12 pagesExam Reviewmadison.cosbyNo ratings yet
- First Quarterly Exam in Science 9Document21 pagesFirst Quarterly Exam in Science 9katherine corveraNo ratings yet
- Biology M4 PhotosynthesisDocument28 pagesBiology M4 Photosynthesisjt50% (2)
- Question Bank On PhotosynthesisDocument11 pagesQuestion Bank On PhotosynthesisSachin KothariNo ratings yet
- Z-Scheme ExplainedDocument19 pagesZ-Scheme ExplainedPiyush ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Command Terms in IB BiologyDocument68 pagesCommand Terms in IB BiologyormattNo ratings yet
- Fatima Laureano-Maravilla - Unit 3 - Photosynthesis ch8Document6 pagesFatima Laureano-Maravilla - Unit 3 - Photosynthesis ch8api-542684299No ratings yet
- Aqa A2 Biology LDRDocument21 pagesAqa A2 Biology LDRjames100% (4)
- 7.1 An Overview of Photosynthesis: - Most of The Energy Used by Almost All Living Cells Ultimately Comes From The SunDocument27 pages7.1 An Overview of Photosynthesis: - Most of The Energy Used by Almost All Living Cells Ultimately Comes From The SunHannah Wynzelle AbanNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 (SHS) : The Two Shades of GreenDocument18 pagesGeneral Biology 1 (SHS) : The Two Shades of GreenLAN soajasNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis WorksheetDocument4 pagesPhotosynthesis WorksheetJustin Marju De VeraNo ratings yet
- BCH 223 Assignment 1 2021Document6 pagesBCH 223 Assignment 1 2021Nosibusiso KhaliphaNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Igcse Biology PhotosynthesisDocument8 pagesEdexcel Igcse Biology PhotosynthesisKamrul Alam MasumNo ratings yet
- Bioenergetics and MetabolismDocument56 pagesBioenergetics and MetabolismAww AddNo ratings yet
- IB Biology 8.3 PhotosynthesisDocument14 pagesIB Biology 8.3 PhotosynthesisDilip Pandurang PattilNo ratings yet
- Crop Science, Same As UPLB ReviewerDocument22 pagesCrop Science, Same As UPLB ReviewerBe Chah94% (53)
- The Process of PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesThe Process of PhotosynthesisIndra WahyudiNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Hhmi BiointeractiveDocument7 pagesPhotosynthesis Hhmi BiointeractivemariaNo ratings yet