0% found this document useful (0 votes)
812 views2 pagesTrigonometry Reviewer
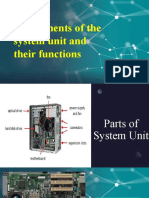
The document defines the six trigonometric functions - sine, cosine, tangent, cosecant, secant, and cotangent - using the ratios of sides of a right triangle. It provides examples of calculating each function using a right triangle where angle A is the angle of reference and a, b, and c are the opposite, adjacent, and hypotenuse sides respectively.
Uploaded by
Kate Megan ApuliCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
812 views2 pagesTrigonometry Reviewer
The document defines the six trigonometric functions - sine, cosine, tangent, cosecant, secant, and cotangent - using the ratios of sides of a right triangle. It provides examples of calculating each function using a right triangle where angle A is the angle of reference and a, b, and c are the opposite, adjacent, and hypotenuse sides respectively.
Uploaded by
Kate Megan ApuliCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd