Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lecture Notes in Electromagnetic Spectrum and Induction
Uploaded by
AlAr-JohnTienzoTimeniaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lecture Notes in Electromagnetic Spectrum and Induction
Uploaded by
AlAr-JohnTienzoTimeniaCopyright:
Available Formats
Electromagnetic Spectrum
An electromagnetic wave is an alternating electric and magnetic field that moves through space at a speed
of light, 3 x 108 m/s. The various forms of EM waves include radio waves, microwaves, infrared waves, light,
ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays.
EM waves are often classified by frequency in a scheme called the electromagnetic spectrum. The
electromagnetic spectrum extends from the longest wavelengths of radio waves up to the high frequencies
of gamma rays. This arrangement strengthens the inverse relationship between frequency and wavelength,
wavelength and energy, and direct relationship between frequency and energy.
The EM spectrum has many uses: radio waves are used for transmitting radio and television (including
microwave); infrared is seen by many animals (not humans) and is also used in night vision goggles; visible
light is the portion of the spectrum that humans can see; ultraviolet (UV) causes sunburns; X-rays are used
in hospitals to make internal images of the human body; and gamma rays are used in the radiation
treatment of cancer.
EM radiation has practical uses but also poses dangers to living organisms.
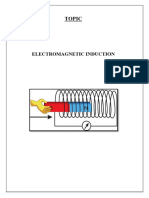
Principle of Electromagnetic Induction in Generator
Modern generators can be attributed to Michael Faraday’s principle of ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION.
Faraday discovered that when a conductor moves in a magnetic field, electrical charges could be created
and directed to create a flow of current.
At its most basic, an electrical generator is nothing more than an electromagnet – moving wire near a
magnet to direct the flow of electricity. It’s similar to how a pump pushes water through a pipe.
It is important to understand that a generator does not actually “create” electrical energy. Instead, it uses the
mechanical energy supplied to it to force the movement of electric charges present in the wire of its
windings through an external electric circuit.
This flow of electric charges constitutes the output electric current supplied by the generator. This
mechanism can be understood by considering the generator to be similar to a water pump, which causes
the flow of water but does not actually create the water flowing through it.
Principle of Electromagnetism in Electric Motor
Danish physicist HANS CHRISTIAN ØRSTED began a new scientific era when he discovered that electricity
and magnetism are linked. He showed by experiment that an electric current flowing through a wire could
move a nearby magnet.
The discovery of ELECTROMAGNETISM set the stage for the eventual development of our modern
technology-based world.
Motors work through the principles of ELECTROMAGNETISM. If you run electricity through a wire, it creates
a magnetic field. If you coil the wire around a rod and run electricity through the wire, it creates a magnetic
field around the rod. One end of the rod will have a north magnetic pole and the other will have a south pole.
Opposite poles attract one another, like poles repel. When you surround that rod with other magnets, the
rod will rotate from the attractive and repulsive forces.
Comparison of Motor and Generator
A motor and generator perform opposite functions, but their fundamental structure is the same. Their
structure is a “coil mounted on an axle within a magnetic field”. An electric motor is used to produce
rotational motion from electrical supply. In a motor, an electric current is passed through the coil. The coil
then creates a magnetic field that interacts with the already existing magnetic field. This interaction forces
the coil to rotate
For a motor, the input energy is electrical energy and the useful output energy is mechanical energy. The
generator is used to produce an electric current from rotational motion (on large scale power stations a
“turbine” is used to provide this rotation). In a generator, the rotation causes the coil to rotate inside the
magnetic field. This induces an alternating current in the coil.
For generator the input energy is mechanical energy and the useful output energy is electrical energy. In
power stations, it is usually the magnet which is attached to the axel and rotates with the coils surrounding
the magnet. However, the end result is the same.
The motor and the generator are almost similar from the construction point of view, as both have stator and
rotor.
The differences between Motor and Generator are as follows:
The motor converts electric energy into mechanical energy, whereas, generator does the opposite.
Electricity is used in the motor, but the generator produces the electricity.
An example of motor is an electric car or bike where electric current is supplied to the machine or device
and it gets converted to mechanical motion and, as a result, the car or bike moves. The example of
generator is that in power stations, the turbine is used as a device which converts mechanical energy from
the force of water falling from the dam to generate electric energy
You might also like
- GeneratorsDocument23 pagesGeneratorsGilvert PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetism SlidesDocument45 pagesElectromagnetism Slideskaushik247No ratings yet
- Research 1Document23 pagesResearch 1John Paul BaquiranNo ratings yet
- ElectromagnetismDocument5 pagesElectromagnetismranaNo ratings yet
- 3-5 Physics Elec MagDocument34 pages3-5 Physics Elec MagPrecious BalgunaNo ratings yet
- ElectromagnetismDocument5 pagesElectromagnetismsusan pajarilloNo ratings yet
- Q2 Module 5 - What's ItDocument6 pagesQ2 Module 5 - What's Itleo markNo ratings yet
- Applications of Electromagnetic InductionDocument6 pagesApplications of Electromagnetic InductionLivombo AveloNo ratings yet
- WiTricity - Wireless Transmission of ElectricityDocument32 pagesWiTricity - Wireless Transmission of ElectricityPawan Kumar100% (2)
- Referat BuzoDocument11 pagesReferat BuzoAnaNo ratings yet
- Nicola Tesla's Principles of the Electric MotorDocument2 pagesNicola Tesla's Principles of the Electric MotorPunal ManalanNo ratings yet
- Motors and Generators SummaryDocument17 pagesMotors and Generators SummaryMNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetism: How Electricity and Magnetism ConnectDocument2 pagesElectromagnetism: How Electricity and Magnetism ConnectAlexà KimNo ratings yet
- Electric Motors and GeneratorsDocument2 pagesElectric Motors and GeneratorsNURSHAHADAH ISMAELNo ratings yet
- ElectromagnetisDocument5 pagesElectromagnetisAachal SinghNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetism 2Document22 pagesElectromagnetism 2abegail chuNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetism: Slide Number DescriptionDocument4 pagesElectromagnetism: Slide Number DescriptionthegaiaprojectNo ratings yet
- Principles of Electromechanical Energy ConversionDocument8 pagesPrinciples of Electromechanical Energy ConversionAxel GayondatoNo ratings yet
- 13.7 Electromagnetism & Its UsesDocument33 pages13.7 Electromagnetism & Its UsesSagar AgrawalNo ratings yet
- AC GeneratorDocument16 pagesAC Generatorsheikhiyad60No ratings yet
- Electric Motor and GeneratorDocument6 pagesElectric Motor and GeneratorJesell JeanNo ratings yet
- Isabela State University: TransformerDocument12 pagesIsabela State University: TransformerChristian Angelo ButacNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetism:: Course Name: Physics For Biologists Course Code: PHY108 Course Instructor: Dr. Md. Shafiqul IslamDocument29 pagesElectromagnetism:: Course Name: Physics For Biologists Course Code: PHY108 Course Instructor: Dr. Md. Shafiqul IslamBushra Altaf ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Car Synopsis: An Introduction to Design and ApplicationsDocument3 pagesElectromagnetic Car Synopsis: An Introduction to Design and ApplicationsyrikkiNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument20 pagesPhysics Projectblah68194No ratings yet
- Mini RomagDocument13 pagesMini Romagranjan1491100% (1)
- Notes in Simple Electric MotorDocument2 pagesNotes in Simple Electric MotorNins SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetism 2: Factors Affecting Induced EMIDocument38 pagesElectromagnetism 2: Factors Affecting Induced EMIChello Marielle San GabrielNo ratings yet
- Rotating Machines Basic ConceptsDocument21 pagesRotating Machines Basic ConceptsArunabh BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- 'ELECTROMAGNETIC WavesDocument2 pages'ELECTROMAGNETIC WavesronaldocuetoNo ratings yet
- What is Electrical Induction? Definitions and PrinciplesDocument3 pagesWhat is Electrical Induction? Definitions and PrinciplesWak Sidek TgKarangNo ratings yet
- How Generators and Motors Work Using ElectromagnetismDocument17 pagesHow Generators and Motors Work Using ElectromagnetismAyla BonitaNo ratings yet
- Generator and MotorDocument19 pagesGenerator and Motortrihandoko1631No ratings yet
- Applications of Electromagnetic InductionDocument6 pagesApplications of Electromagnetic InductionAdeniji OlusegunNo ratings yet
- Electro 3 Finals Task PerformanceDocument23 pagesElectro 3 Finals Task PerformanceJuan Miguel TorresNo ratings yet
- Energy Recycling: Gulshan Kumar Mohit Kumar, Paritosh Vikram, Santosh KumarDocument4 pagesEnergy Recycling: Gulshan Kumar Mohit Kumar, Paritosh Vikram, Santosh KumarMukesh Bharti100% (1)
- Time Varying FieldsDocument14 pagesTime Varying FieldsBishnu gopal DasNo ratings yet
- Motor GeneratorDocument3 pagesMotor GeneratorPrinces JuatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document92 pagesChapter 3tamaramarcuNo ratings yet
- Generator de Curent MagneticDocument12 pagesGenerator de Curent Magnetic77nicu100% (1)
- 1) Hydroelectric DamsDocument9 pages1) Hydroelectric DamsKaren BritanicoNo ratings yet
- Module 1 IntroductionDocument22 pagesModule 1 IntroductionaliyumaidamisaNo ratings yet
- MotorsDocument13 pagesMotorsSandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Eu Module 5Document8 pagesEu Module 5Ezekiel BautistaNo ratings yet
- Assignment Work1Document4 pagesAssignment Work1Osarondor OsarondorNo ratings yet
- AC GeneratorDocument7 pagesAC Generatoraswardi8756No ratings yet
- Electric MotorDocument2 pagesElectric MotorEricNo ratings yet
- Methods To Create Electric Current by Using Magnet-1Document4 pagesMethods To Create Electric Current by Using Magnet-1Niki HiralNo ratings yet
- How Do Electric Motors Work? Physics Books for Kids | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandHow Do Electric Motors Work? Physics Books for Kids | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- GokulDocument20 pagesGokulfunbytesytNo ratings yet
- Gunderson Solid-State Generator Moves Magnetic Flux Without Moving PartsDocument0 pagesGunderson Solid-State Generator Moves Magnetic Flux Without Moving PartsmatijahNo ratings yet
- Generato RS: Prepared By: Ms. Clydine Jethna O. SigueDocument33 pagesGenerato RS: Prepared By: Ms. Clydine Jethna O. SigueChamain MarreroNo ratings yet
- Faradays Law of Electromagnetic InductionDocument6 pagesFaradays Law of Electromagnetic Inductionbas123No ratings yet
- Electric Generator: Generator Is A Device That ConvertsDocument152 pagesElectric Generator: Generator Is A Device That Convertssujiv_sujiv1278No ratings yet
- Apllied PhysicsDocument9 pagesApllied PhysicsM. Qasim ZiaNo ratings yet
- Energy Conversion: 1. Enumerate and Discuss The Different Forms of Energy Conversion. (Site 10 Examples)Document6 pagesEnergy Conversion: 1. Enumerate and Discuss The Different Forms of Energy Conversion. (Site 10 Examples)ooweemgeeNo ratings yet
- ELECTRICITYDocument6 pagesELECTRICITYsamuel rojasNo ratings yet
- The Shocking World of Electricity with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Shocking World of Electricity with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- Physics for Kids : Electricity and Magnetism - Physics 7th Grade | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandPhysics for Kids : Electricity and Magnetism - Physics 7th Grade | Children's Physics BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Problem Set 1Document1 pageProblem Set 1AlAr-JohnTienzoTimeniaNo ratings yet
- Gas Properties and Laws NotesDocument4 pagesGas Properties and Laws NotesAlAr-JohnTienzoTimeniaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions Notes and Problem SetsDocument2 pagesChemical Reactions Notes and Problem SetsAlAr-JohnTienzoTimeniaNo ratings yet
- LCOH - PracRes2Document4 pagesLCOH - PracRes2AlAr-JohnTienzoTimeniaNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1Document1 pageProblem Set 1AlAr-JohnTienzoTimeniaNo ratings yet
- Rendyl Angel BonquinDocument2 pagesRendyl Angel BonquinAlAr-JohnTienzoTimeniaNo ratings yet
- Gas Properties and Laws NotesDocument4 pagesGas Properties and Laws NotesAlAr-JohnTienzoTimeniaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions Notes and Problem SetsDocument2 pagesChemical Reactions Notes and Problem SetsAlAr-JohnTienzoTimeniaNo ratings yet
- Mirrorand Lens Equation ProblemsDocument1 pageMirrorand Lens Equation ProblemsAlAr-JohnTienzoTimeniaNo ratings yet
- (Term 2, Quarter 1) Temperature MonitoringDocument44 pages(Term 2, Quarter 1) Temperature MonitoringAlAr-JohnTienzoTimeniaNo ratings yet
- Forda Tag Booster For The FersonsDocument2 pagesForda Tag Booster For The FersonsAlAr-JohnTienzoTimeniaNo ratings yet
- Name of Participant Barangay Address Contact Number SignatureDocument1 pageName of Participant Barangay Address Contact Number SignatureAlAr-JohnTienzoTimeniaNo ratings yet
- SRHS Alumni Association Membership FormDocument1 pageSRHS Alumni Association Membership FormAlAr-JohnTienzoTimeniaNo ratings yet
- DepEd's Learning Strategies and Modalities for Distance EducationDocument3 pagesDepEd's Learning Strategies and Modalities for Distance EducationAlAr-JohnTienzoTimeniaNo ratings yet
- Why paraphrasing avoids plagiarismDocument3 pagesWhy paraphrasing avoids plagiarismAlAr-JohnTienzoTimeniaNo ratings yet
- Community-Based Disaster Risk Reduction and Management (CBDRRM) Plan TemplateDocument2 pagesCommunity-Based Disaster Risk Reduction and Management (CBDRRM) Plan TemplateAlAr-JohnTienzoTimeniaNo ratings yet
- First-Prelims-HUMSS 5-12Document4 pagesFirst-Prelims-HUMSS 5-12AlAr-JohnTienzoTimeniaNo ratings yet
- Revised Header 2022 MayDocument1 pageRevised Header 2022 MayAlAr-JohnTienzoTimeniaNo ratings yet
- Community-Based Disaster Risk Reduction and Management (CBDRRM) Plan TemplateDocument2 pagesCommunity-Based Disaster Risk Reduction and Management (CBDRRM) Plan TemplateAlAr-JohnTienzoTimenia100% (1)
- Writing Personal Statements For Graduate School: Pat Sokolove, PHDDocument26 pagesWriting Personal Statements For Graduate School: Pat Sokolove, PHDAlAr-JohnTienzoTimeniaNo ratings yet
- Academic DecathlonDocument1 pageAcademic DecathlonAlAr-JohnTienzoTimeniaNo ratings yet
- San Rafael High School Temperature MonitoringDocument25 pagesSan Rafael High School Temperature MonitoringAlAr-JohnTienzoTimeniaNo ratings yet
- Reading Material # 1: The Research ProcessDocument4 pagesReading Material # 1: The Research ProcessAlAr-JohnTienzoTimeniaNo ratings yet
- Reading MaterialDocument4 pagesReading MaterialAlAr-JohnTienzoTimeniaNo ratings yet
- Provided That You Register Your Own Account: NBI Clearance Application (Online Form) (Reference:)Document1 pageProvided That You Register Your Own Account: NBI Clearance Application (Online Form) (Reference:)AlAr-JohnTienzoTimeniaNo ratings yet
- Reading MaterialDocument4 pagesReading MaterialAlAr-JohnTienzoTimeniaNo ratings yet
- Parental ConsentDocument1 pageParental Consentodyson santosNo ratings yet
- SSS Salary Loan DetailsDocument1 pageSSS Salary Loan DetailsAlAr-JohnTienzoTimeniaNo ratings yet
- RibbonetteDocument1 pageRibbonetteAlAr-JohnTienzoTimeniaNo ratings yet
- Motion (Freely Falling Bodies and Projectile Motion) : Course Learning OutcomesDocument9 pagesMotion (Freely Falling Bodies and Projectile Motion) : Course Learning OutcomesYoo JungNo ratings yet
- A Materials Science Guide To Superconductors - and How To Make Them SuperDocument241 pagesA Materials Science Guide To Superconductors - and How To Make Them Superudit Kumar100% (1)
- Ass AsDocument15 pagesAss AsMukesh BishtNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure EssayDocument4 pagesAtomic Structure EssayholliebaldwinnNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics Questions from JEE Main 2021Document6 pagesElectrostatics Questions from JEE Main 2021Narayan HoraNo ratings yet
- Tunable Mid-Infrared Raman Soliton Generation FromDocument7 pagesTunable Mid-Infrared Raman Soliton Generation Fromfaysal.nayan faysal.nayanNo ratings yet
- Lab 9 - Motion of FluidsDocument8 pagesLab 9 - Motion of Fluidsconstantine1106No ratings yet
- Projectile Motion EquationsDocument14 pagesProjectile Motion EquationsBHAGWAN SINGHNo ratings yet
- CLASS XII Physics Preboard Term 2 FinalDocument4 pagesCLASS XII Physics Preboard Term 2 FinalParth SharmaNo ratings yet
- KinematicsDocument52 pagesKinematicsAlyssaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4-9: Bonding in Ceramics and Structure of Ceramics: MM 362 Ceramics and Glasses Spring Semester 2020, FMCE, GIKIDocument70 pagesLecture 4-9: Bonding in Ceramics and Structure of Ceramics: MM 362 Ceramics and Glasses Spring Semester 2020, FMCE, GIKIUsamaNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT 11th 2021-22Document5 pagesEXPERIMENT 11th 2021-22Dolly ParmarNo ratings yet
- Robust Wax Deposition Modeling Incorporating NonDocument4 pagesRobust Wax Deposition Modeling Incorporating Nonabhay.singhNo ratings yet
- +1 CBSE - CHEMISTRY CDF MATERIAL (61-116) .PMD PDFDocument56 pages+1 CBSE - CHEMISTRY CDF MATERIAL (61-116) .PMD PDFcernpaul100% (1)
- Chapter 4 OutlineDocument3 pagesChapter 4 Outlinedill1233No ratings yet
- Light MeasurementHandbookDocument64 pagesLight MeasurementHandbookudummy552No ratings yet
- Target Publications: Board Question Paper: February 2023Document4 pagesTarget Publications: Board Question Paper: February 2023Aditya BadeNo ratings yet
- Quiz No. 1-Unit 1, 2, 3 - KINEMATICS, STATICS, DYNAMICS & ENERGY (SET A) - For StudentsDocument6 pagesQuiz No. 1-Unit 1, 2, 3 - KINEMATICS, STATICS, DYNAMICS & ENERGY (SET A) - For StudentsChristian Nathaniel Ramon Palma100% (1)
- Planck's ConstantDocument5 pagesPlanck's ConstantAparup GhoshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document15 pagesChapter 11John Emmanuel PacresNo ratings yet
- TPH 1Document19 pagesTPH 1ali hadiNo ratings yet
- Attracted To Intermolecular Forces Part A: Frayer Model of Liquids and SolidsDocument6 pagesAttracted To Intermolecular Forces Part A: Frayer Model of Liquids and SolidsGanilyn PoncianoNo ratings yet
- Quantum Groups and Noncommutative Geometry by Yuri I. ManinDocument120 pagesQuantum Groups and Noncommutative Geometry by Yuri I. ManinAmos chenNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 MarkschemeDocument5 pagesTopic 3 MarkschemeGajendraNo ratings yet
- Statistical Mechanics-Module 1Document14 pagesStatistical Mechanics-Module 1Krishna AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Sample Test Questions - Sy 2019-2020 ScienceDocument7 pagesSample Test Questions - Sy 2019-2020 ScienceChitoTabelinaToralbaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 AtomDocument10 pagesModule 2 AtomJaenicaPaulineCristobalNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-03-05 at 12.32.19 AMDocument8 pagesScreenshot 2023-03-05 at 12.32.19 AMAnushka ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Atoms: Chapter - 12Document30 pagesAtoms: Chapter - 12nandani lakhwaniNo ratings yet
- 03 ForceDocument67 pages03 ForcegodiewamuchuNo ratings yet