100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote) 3K views6 pagesKeratometer Booklet
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content,
claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online on Scribd
- Keratometer Overview
- Parts of the Keratometer and Their Functions
- Setup of Keratometer
- Step by Step Procedure
Seep’ Gaiage Gpisianty Program
Procedues and Gadelnes Reference Gude
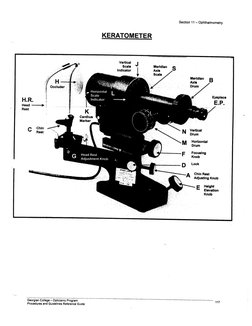
KERATOMETER
ey
rere
Section 11 ~ Ophthaimometry
Moridian
aa B
“7
‘Eyepiece
EP.
Drum
Horizontal
Drum
Focusing
knob
Lock
Chin Rest
‘Adjusting Knob
Hott
E Elevation
ob
co�Contact Lens Dispensing 1 2.4
Theory Workbook
Unit 02: Instrumentation
Module: 2.1: Keratometer
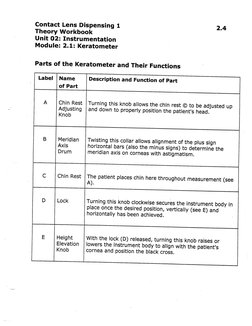
Parts of the Keratometer and Their Functions
Label | Name Description and Function of Part
of Part
A Chin Rest | Turning this knob allows the chin rest © to be adjusted up
Adjusting | and down to properly position the patient's head.
Knob
B Meridian | Twisting this collar allows alignment of the plus sign
Axis horizontal bars (also the minus signs) to determine the
Drum meridian axis on corneas with astigmatism.
Cc Chin Rest | The patient places chin here throughout measurement (see
A).
D_ | Lock Turning this knob clockwise secures the instrument body in
place once the desired position, vertically (see E) and
horizontally has been achieved.
E Height With the lock (D) released, turning this knob raises or
Elevation | lowers the instrument body to align with the patient's
Knob cornea and position the black cross,�Contact Lens Dispensing 1 2.5
Theory Workbook
Unit 02: Instrumentation
Module: 2.1: Keratometer
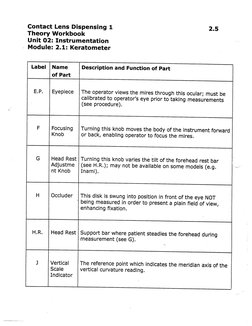
Label |Name _| Description and Function of Part
of Part
E.P. | Eyepiece |The operator views the mires through this ocular; must be
calibrated to operator's eye prior to taking measurements
(see procedure).
F | Focusing | Turning this knob moves the body of the instrument forward
Knob or back, enabling operator to focus the mires.
G | Head Rest | Turning this knob varies the tilt of the forehead rest bar
Adjustme | (see H.R.); may not be available on some models (e.g.
nt Knob | Inami).
H_ | Occluder | This disk is swung into position in front of the eye NOT
| being measured in order to present a plain field of view,
enhancing fixation.
H.R. | Head Rest | Support bar where patient steadies the forehead during
measurement (see G).
J | Vertical | The reference point which indicates the meridian axis of the
Scale vertical curvature reading.
Indicator�Contact Lens Dispensing 1 2.6
Theory Workbook
Unit 02: Instrumentation
Module: 2.1: Keratometer
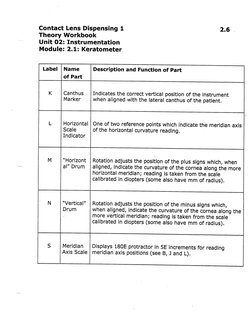
Label | Name Description and Function of Part
of Part
K | Canthus | Indicates the correct vertical position of the instrument
Marker when aligned with the lateral canthus of the patient.
Z Horizontal | One of two reference points which indicate the meridian axis
Scale of the horizontal curvature reading.
Indicator
M “Horizont | Rotation adjusts the position of the plus signs which, when
al” Drum | aligned, indicate the curvature of the cornea along the more
horizontal meridian; reading is taken from the scale
calibrated in diopters (some also have mm of radius).
N “Vertical” | Rotation adjusts the position of the minus signs which,
Drum when aligned, indicate the curvature of the cornea along the
more vertical meridian; reading is taken from the scale
calibrated in diopters (some also have mm of radius).
s Meridian | Displays 180E protractor in 5E'increments for reading
Axis Scale | meridian axis positions (see B, ) and L).�BwNe
SET UP OF KERATOMETER
Disinfect the chin rest and forehead rest of the Keratometer
Ask patient to remove eyeglasses or contact lenses
Focus the eyepiece by turning clockwise as far as you can counter clockwise
Place a piece of paper in front of the instrument and focus the eyepiece until the reticle
is in focus by turning the eyepiece clockwise
‘Adjust the patients chair and the instrument to a comfortable position for both the
patient and the examiner.
Unlock the instrument controls
Instruct the patient to place his chin in the chin rest and forehead against the headrest.
Raise or lower the chin rest until the canthus marker is even with the patients outer
canthus
Adjust the headrest to be slightly above the patients eyebrow.�STEP BY STEP PROCEDURE
1. From the outside of the instrument align the barrel with the patients right eye by raising
or lowering the instrument and by moving it to the left or right until a reflection of the
mires is seen on the patients cornea
2. Instruct the patient to look at the reflection of their eye inside the Keratometer
3. Look into the keratometer and refine the alignment of the image of the mires
4, Focus the mires and adjust the instrument so that the reticle is centered in the lower
right mire
5. Lock the instrument in place. This is necessary on to keep the instrument from moving
around
6. Adjust the horizontal and vertical power wheels until the mires are close ( you should
have only 3 mires).
7. To locate the two principle meridians of the patients cornea rotate the horizontal wheel
until the horizontal spurs are consistant( beside each other}
8. Adjust the horizontal wheel until the horizontal spurs cross over or overlap to create
one
9. Adjust the vertical wheel until the vertical mires overlap If there is corneal astigmatism
matching the mires in both meridians together will not be possible without rotating the
drum to change the axis
10. During this procedure you will have to realign and focus the mires to keep the reticle in
the center of the bottom right mire
11. The quality of the mires will indicate the integrity of the cornea
12. Repeat this procedure with the left eye