Professional Documents
Culture Documents
AGR 116 - Lecture 1
Uploaded by
Bhavani Bava0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views6 pagesThis document provides a classification of different types of crops based on several factors such as life cycle, economic use, botany, seasons, and climate. It discusses key classifications including annual, biennial, and perennial crops; cereals, millets, pulses, oilseeds, sugar crops, fiber crops, fodder crops, spices, medicinal plants, beverages, and green manure crops. Specific examples are given for different crop types classified under each system. The economic uses and products obtained from different crops are also outlined.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides a classification of different types of crops based on several factors such as life cycle, economic use, botany, seasons, and climate. It discusses key classifications including annual, biennial, and perennial crops; cereals, millets, pulses, oilseeds, sugar crops, fiber crops, fodder crops, spices, medicinal plants, beverages, and green manure crops. Specific examples are given for different crop types classified under each system. The economic uses and products obtained from different crops are also outlined.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views6 pagesAGR 116 - Lecture 1
Uploaded by
Bhavani BavaThis document provides a classification of different types of crops based on several factors such as life cycle, economic use, botany, seasons, and climate. It discusses key classifications including annual, biennial, and perennial crops; cereals, millets, pulses, oilseeds, sugar crops, fiber crops, fodder crops, spices, medicinal plants, beverages, and green manure crops. Specific examples are given for different crop types classified under each system. The economic uses and products obtained from different crops are also outlined.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
LECTURE 1.
CLASSIFICATION OF CROPS AND THEIR ECONOMICS
Crops
In general crop is an organism grown or harvested for obtaining yield.
Agronomically crop is a plant cultivated for economic purpose.
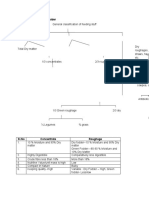
Classification of crops
Crops do not belongs any particular portion of the plant kingdom. Several crops are
alike with respect to ontology, morphology, anatomy, physiology and requirement of
particular type of ecology at different stages of their growth and development. Classification
is done to generalize similar crop plants as a class for better understanding of them.
Classification types used in crops
1. Based on ontogeny (Life cycle)
2. Based on economic use (Agronomic)
3. Based on botany (Scientific classification)
4. Based on seasons
5. Based on climate
1. Based on ontogeny (life cycle)
a) Annual crops
Crop plants that complete life cycle within a season for year. They produce seed and
die within the season.
Example: wheat, rice, maize, mustard.
b) Biennial crops
Plants that have life span of two consecutive seasons or years. First years/ season
these plants have purely vegetative growth usually confined to rosette of leaves. The tap root
is often fleshy and serves as a food storage organ. During the second year / season they
produce flower stocks from the crown and after producing seeds the plants die
Example: sugar beet, beet root, cabbage, radish, carrot, etc.
c) Perennial crops
They live for three or more years. They may be seed bearing or non-seed bearing.
Example: Napier fodder grass, coconut
2. Based economic use (Agronomic)
This classification is based on use of crop plants and their products. This is an
important classification as for as agronomy is concerned.
a. Cereals: Cereals are cultivated grasses grown for their edible starchy grains (one seeded
fruit - caryopsis). Larger grains used as staple food. Cereal derived from word ‘ceres’ which
denotes as goddess who was believed as the giver of grains by Romans.
Example
Rice - Oryza sativa
Wheat - Triticum aestivum
Bread wheat - T. vulgare
Macaroni wheat - T. durum
Emmer wheat - T. dicocum
Dwarf wheat - T. sphaerococcum
Maize - Zea mays
Barley - Hordeum vulgare
Rye - Secale cereale
Oats - Avena sativa
Cereal grain contains 60% to 70% starch and are excellent energy rich foods for humans.
In almost every country and region, cereals provide the staple food. In the world as a
whole, only 5% of starchy staple food comes from root crops (mainly cassava, potato, and
yams, depending on climate), whereas the rest is from cereal.
Cereals are an excellent source of fat soluble vitamin E, which is an essential antioxidant.
Whole cereal grains contain 20% to 30% of the daily requirements of the minerals
selenium, calcium, zinc, and copper.
b. Millets: Small grained cereals - staple food in drier regions of the developing countries are
called millets. They are also annual grasses of the group cereals. But they are grown in lesser
area or less important area whose productivity and economics are also less important. These
are also staple food for people of poor countries. In India pearl millet is a staple food in
Rajasthan
Types
1. Major millets
2. Minor millets
1. Major millets
1. Sorghum / Jowar / Cholam - Sorghum bicolor
2. Pearl Millet / Bajra / cumbu - Pennisetum typhoides
3. Finger millet or ragi - Eleusine coracona
2. Minor millets (Nutri-cereals)
1. Fox tail millet / Thenai - Setaria italica
2. Little millet / Samai - Panicum miliare
3. Common millet / Panivaraugu - Panicum miliaceum
4. Barnyard millet / Kudiraivali - Echinchloa colona var frumentaceae
5. Kodomillet / Varagu - Paspalum scrobiculatum
Staple, human food
Grains from ear heads or panicle is the economically used part
All the minor millets – panicle
Sorghum, cumbu – ear heads
Used after ‘dehusking’
Flour is used for making many delicious food items
Mostly used as fodder crops
c. Pulses
Seeds of leguminous plants used as food, dhal rich in protein
Pod containing grain is the economic portion
Pulses preferred for protein rich value
Are also economic important in cropping system
Green manure, High value cattle feed
Green pods used as vegetables, e.g., cowpea, lablab
Seed coat of pulses are nutritious cattle feed
The wastes or stalk is called the ‘Haulm’ or ‘Stover’
1. Red gram - Cajanus cajan
2. Black gram - Vigna mungo
3. Green gram - Vigna radiata
4. Cowpea - Vigna unguiculata
5. Bengal gram - Cicer arietinum
6. Horse gram - Macrotyloma uniflorum
7. Lentil - Lens esculentus
8. Soybean - Glycine max
9. Peas or garden pea - Pisum sativum
10. Garden bean - Lablab purpureus
11. Lathyrus / Kesari - Lathyrus sativus
d. Oil seeds: Those crops which are rich in fatty acid are cultivated for the production of
vegetable oil. They are used either for edible or industrial or medicinal purposes.
1. Groundnut or peanut - Arachis hypogeae
2. Sesamum or gingelly - Sesamum indicum
3. Sunflower - Helianthus annuus
4. Castor - Ricinus communis
5. Linseed or flax - Linum usitatissimum
6. Niger - Guizotia abyssinia
7. Safflower - Carthamus tinctorius
8. Rapeseed & Mustard
Brown or Indian Mustard - Brassica juncea
Sarson - Brassica sp.
Groundnut
Pod is economic portion
50% oil content
Edible oil/ cooking oil
Haulm is a cattle feed
It also has manure value
The shell has fuel value, it is used for soil amendment. It is a bed material in the
poultry forms
Oil cake – cattle feed and manure value.
Oil is used for production of vanaspathi and soap making
Gingelly
Cooking oil
Economic parts – seeds in the pod
Gingelly cake is a cattle feed
Whereas capsule and stalk are used for composting / burning purpose
Castor
Seed (kernal) contain oil
Medicinal and industrial oil
Mainly aviation industries use this lubricating purpose
Castor cake is a concentrated organic manure
The shell and stalk is used for fuel purpose
Mustard
Edible oil
Seeds are the economic portion
Cake is a cattle feed
Safflower and Sunflower
Unsaturated fatty acids used for heart patients
Cooking oil
Cake is a cattle feed
Also organic material
Decorticated manure
Niger
Seed is the economic portion
It is used in soap making, paint, varnish & light lubricant
Industrial crop
Linseed
Oil extracted from seeds used in paints and varnishes
e. Sugar crops
Crops cultivated for sugar.
Juice extracted from stem used for jaggery or sugar
Number of by products like Molasses, bagasse, pressmud
Molasses used for alcohol and yeast formation
Bagasse for paper making and fuel
Pressmud used for soil amendment
Trash (green leaf + dry foliage) – the waste is used for cattle feed
Sugar beet – Tuber for extraction of sugar , Tubers and tops are used as a fodder for cattle
feed
Example
1. Sugarcane - Saccharum officinarum
2. Sugar beet - Beta vulgaris
f. Fibre crops
Plants grown for their fibre yield.
Different kinds of fibre,
i) seed fibre – cotton,
ii) Stem/bast fibre – jute, mesta,
iii) leaf fibre – agave, pineapple.
Cotton
Important fibre crop in the world, garment purpose, Seed for cattle feed, Oil is
edible
Epidermal hairs of seed coats is the economic portion
Lint (kappas – seed) has industrial value (fibre)
Stalk is of fuel nature
Jute, Sunhemp, Mesta
The fibre obtained from stems is used for gunny bags, ropes
Stem itself is used as fuel
Sun hemp – stem fibre and green manure crop
Example
Cotton
Karunganni cotton - Gossypium arborium
Uppam cotton - G. herbaceum
American/compodia cotton - G. Hirsutum
Egyptian/Sea Island cotton - G. barbadense
Stem fibre: Jute (Chanal) - Corchorus capsularis, C. olitorius
Mesta(Pulichai keerai / Decan hemp) - Hibiscus carnabinus
Sunhemp - Crotalaria juncea
Leaf fibre: Sisal hemp - Agave sisalana
g. Fodder / Forage: It refers to vegetative matter, fresh or preserved, utilized as feed for
animals. It includes hay, silage, pasturage and fodder.
Example
Grasses : bajra napier grass, guinea grass, fodder sorghum, fodder maize
Legumes : lucerne, desmanthus
h. Spices and Condiments: Crop plants or their products used to season, flavour, taste and
add colour to the fresh or preserved food.
Example: ginger, garlic, fenugreek, cumin, turmeric chillies, onion, coriander, anise and
asafetida.
i. Medicinal plants: Plants / products used for stimulating, numbing, drowsing or relishing
effects and used for preparation of medicines.
Example: Tobacco, opium, poppy, mint.
j. Beverages: Products of crops used for preparation of mild, agreeable and simulating
drinking. Example – tea, coffee, cocoa (Plantation crops)
k. Green manure: They are grown mainly to enrich the nutritional status of the soil.
Example
Agathi - Sesbania grandiflora
Daincha - Sesbania aculeata
Manila agathi - Sesbania rostrata
Sesbania - Sesbania speciosa
Sunhemp - Crotalaria juncea
Kozhunji - Tephrosia purpurea
Pillipesara - Phaseolus trilobus
All leguminous are considered as green manure crops
3. Based on Botany (Scientific Classification)
Crop plants are dealt with under the natural orders or the families under which they
come, in a systematic arrangement. It has advantages in the understanding of the
morphological character of any particular family of crop plants with different agro botanical
peculiarities.
Example:
Poaceae - Rice, wheat, oat, maize, sugarcane, barley
Papilionaceae - Peas, cowpea, redgram, black gram, green gram, bengal gram, groundnut,
soybean
Malvaceae - Cotton
Tiliaceae - Jute
Asteraceae - Sunflower, safflower, niger
Pedaliaceae - Sesame
Euphorbiaceae - Castor, tapioca
4. Based on Seasons
Crops are grouped under the seasons in which their major field duration falls.
a) Kharif: Crops grown during June-July to September-October which requires a warm wet
weather during their major period of growth and shorter day length for flowering.
Example: rice, maize, castor, groundnut,
b) Rabi Crops: Crops grown during October-November to January-February which require
cold dry weather for their major growth period and longer day length for flowering.
Example: wheat, mustard, barley, oats, potato, Bengal gram, berseem, cabbage and
cauliflower.
c) Summer crops: Crops grown during February-March to May-June which require warm
dry weather for growth and longer day length for flowering. This classification is not a
universal one. It only indicates the period when a particular crop is raised.
Example: kharif rice, kharif maize, rabi maize, summer pulse etc.
5. Based on climatic condition
1) Tropical crop : Coconut, sugarcane
2) Sub-tropical crop : Rice, cotton
3) Temperate crop : Wheat, barley
4) Polar crop : All pines, pasture grasses
You might also like
- CELTA. Assignment 3Document7 pagesCELTA. Assignment 3Mehdi RoostapourNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Major Crop FieldsDocument32 pagesIntroduction To Major Crop FieldsCHANDANINo ratings yet
- Classification of Crop PlantsDocument46 pagesClassification of Crop PlantsMani MekalaiNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 1c - Agrl Classification of Crop PlantsDocument28 pagesLECTURE 1c - Agrl Classification of Crop PlantsMugilan SenthilnathanNo ratings yet
- 3.classification of Crop PlantsDocument48 pages3.classification of Crop PlantsAmìt Ķ MäzùmdérNo ratings yet
- Rice, Cereals & Pulses: HmhubDocument5 pagesRice, Cereals & Pulses: HmhubchefsachinNo ratings yet
- Crop Groups and TerminologiesDocument1 pageCrop Groups and TerminologiesIJ SeducoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Field Crops - Agricultural Classification of Field CropsDocument88 pagesIntroduction To Field Crops - Agricultural Classification of Field CropsNanthiniNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Major Field CropsDocument217 pagesIntroduction To Major Field CropsRahul SunilNo ratings yet
- Economic Botany ZoologyDocument26 pagesEconomic Botany ZoologyMD Taufique HussainNo ratings yet
- Practical Lec Classification of PlantDocument3 pagesPractical Lec Classification of Plantkn kkNo ratings yet
- Classification of CropsDocument116 pagesClassification of CropsDanica DayaganonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3bDocument5 pagesChapter 3bKavieswarNo ratings yet
- Kitubo SHS. TVL. ACP2. Agricultural Crops Production Handouts PDFDocument21 pagesKitubo SHS. TVL. ACP2. Agricultural Crops Production Handouts PDFCarl SeanNo ratings yet
- Agronomy 1 22Document75 pagesAgronomy 1 22Krishna SewaNo ratings yet
- Iv) Economic Importance & Value Added Products of PulsesDocument2 pagesIv) Economic Importance & Value Added Products of PulsesAncy A RNo ratings yet
- Classification of CropsDocument8 pagesClassification of Cropspriaj46No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document7 pagesChapter 2KavieswarNo ratings yet
- Botanical NameDocument20 pagesBotanical NameAnonymous rDMCLoNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument6 pagesUntitledAlipsa Samal B (221210096)No ratings yet
- Classification and Naming CropsDocument52 pagesClassification and Naming CropsSanaullah IqbalNo ratings yet
- Corn ProductionDocument12 pagesCorn ProductionAmeerah Cabangal83% (6)
- Crop Identification and NamesDocument4 pagesCrop Identification and NamesehsanranaNo ratings yet
- Classification of Major Crops of The PhilsDocument44 pagesClassification of Major Crops of The Philsbayongancarlo1026No ratings yet
- Legume - WikipediaDocument48 pagesLegume - WikipediaBashiir NuurNo ratings yet
- Classification of Crops.2020Document43 pagesClassification of Crops.2020Jhunell JuanNo ratings yet
- CROP SCI 2 PPT - Sept 18 222023 1Document6 pagesCROP SCI 2 PPT - Sept 18 222023 1Arjie TVNo ratings yet
- أ.د. نبيل على خليلDocument133 pagesأ.د. نبيل على خليلAhmed OrabyNo ratings yet
- Pseudocereals - Overview: Topic HighlightsDocument6 pagesPseudocereals - Overview: Topic HighlightsLuis Jaime Perez CordobaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 TLEDocument2 pagesLesson 4 TLELunaNo ratings yet
- Botany Tuber Crops Final - CompressedDocument18 pagesBotany Tuber Crops Final - CompressedAyisha PSNo ratings yet
- Saldivar 2016Document6 pagesSaldivar 2016maymaycute1510No ratings yet
- Sorghum Bicolor (2n 20)Document8 pagesSorghum Bicolor (2n 20)KavieswarNo ratings yet
- Legumes 1st ClassDocument19 pagesLegumes 1st Classraisameh23No ratings yet
- Cereals and Legume TechnologyDocument23 pagesCereals and Legume TechnologyLê Tất TiếnNo ratings yet
- Agro 246 MCQsDocument16 pagesAgro 246 MCQscricket letestNo ratings yet
- Power Point 01Document12 pagesPower Point 01salmanahmed47516No ratings yet
- Botanical ClassificationDocument34 pagesBotanical Classificationjeanbonono1818No ratings yet
- Introduction To BotanyDocument25 pagesIntroduction To BotanyJenniferNo ratings yet
- Overview On Millets (Nutri Cereals) : January 2015Document6 pagesOverview On Millets (Nutri Cereals) : January 2015kartik100% (1)
- The SeedDocument32 pagesThe SeedMuhammad TauseefNo ratings yet
- Задание №7. Практическое занятие -Style of drawing up proposals for the foreign language of the main types of forages.Document3 pagesЗадание №7. Практическое занятие -Style of drawing up proposals for the foreign language of the main types of forages.elhanamir2000No ratings yet
- Classification Feed and FodderDocument4 pagesClassification Feed and FoddermathiNo ratings yet
- Nutritious Underutilized Species - Amaranth 1682 01Document4 pagesNutritious Underutilized Species - Amaranth 1682 01Mariana LuaboNo ratings yet
- Corn Agronomy: Castor BeanDocument3 pagesCorn Agronomy: Castor BeanMekon-Engineering MkeNo ratings yet
- Classification and Naming CropsDocument52 pagesClassification and Naming CropsAbdur RafeyNo ratings yet
- Grain: Grains and Cereals ClassificationDocument4 pagesGrain: Grains and Cereals Classificationx456456456xNo ratings yet
- UNIT-1 FullDocument87 pagesUNIT-1 Fullsyedali24779No ratings yet
- Crops ClassificationDocument14 pagesCrops ClassificationMoiz Khan YousufzaiNo ratings yet
- Wheat, Any of Several Species of Cereal Grasses of The Genus Triticum (FamilyDocument5 pagesWheat, Any of Several Species of Cereal Grasses of The Genus Triticum (FamilyJayzi VicenteNo ratings yet
- Oryza Sativa Manihot Esculenta Ipomoea Batatas Colocasia Esculenta Zingiber Officinaale Musa Pennisetum Purpureum Zea Mays Saccharum Vigna RadiataDocument2 pagesOryza Sativa Manihot Esculenta Ipomoea Batatas Colocasia Esculenta Zingiber Officinaale Musa Pennisetum Purpureum Zea Mays Saccharum Vigna RadiataJoseph DenoyoNo ratings yet
- Classification of Crop PlantsDocument4 pagesClassification of Crop PlantsHrudaya BiharaNo ratings yet
- Serna-Saldivar2004 - Foods From MaizeDocument12 pagesSerna-Saldivar2004 - Foods From MaizeKatacska18No ratings yet
- Evolution of Oryza SativaDocument11 pagesEvolution of Oryza Sativaangelotagupa12345100% (1)
- Farinaceous DishesDocument23 pagesFarinaceous DishesNhoemz Agpalo DollenteNo ratings yet
- Serealia Dan Kacang-KacanganDocument130 pagesSerealia Dan Kacang-KacanganAnissa YulianaNo ratings yet
- Seed Oil Production: BY Leenus PVT LTDDocument11 pagesSeed Oil Production: BY Leenus PVT LTDGondu SudheerNo ratings yet
- Food and Cash Crops Social ScienceDocument19 pagesFood and Cash Crops Social ScienceSUKIRTHI K 19RBAR064No ratings yet
- Cope ProgramDocument5 pagesCope ProgramLucas MayoNo ratings yet
- Reteta Alexandrei Pentru Sapun de RufeDocument4 pagesReteta Alexandrei Pentru Sapun de Rufeluna_nicoleNo ratings yet
- Second Monthly Exam in Tle 8Document4 pagesSecond Monthly Exam in Tle 8Israel MarquezNo ratings yet
- Fodder Development Proposal - May 2009Document12 pagesFodder Development Proposal - May 2009Philip OlesitauNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Pizza HutDocument27 pagesProject Report On Pizza HutMRUNALI ISHWARKARNo ratings yet
- SK Convent: This Question Paper Consists of 20 Questions. Answer All QuestionsDocument6 pagesSK Convent: This Question Paper Consists of 20 Questions. Answer All QuestionsBara ThiNo ratings yet
- Citric Acid Production by Koji Fermentat PDFDocument5 pagesCitric Acid Production by Koji Fermentat PDFtuti lestariantiNo ratings yet
- Riso SuppliesDocument2 pagesRiso SuppliesGreta GrigelionytėNo ratings yet
- Mandi DataDocument61 pagesMandi DataKaran VadheraNo ratings yet
- CombinepdfDocument7 pagesCombinepdfZahra JamilNo ratings yet
- Nutrition-Module 230817 083933Document536 pagesNutrition-Module 230817 083933Romm JacobNo ratings yet
- Circular 42-Grade 6 To AL To Magic Artisan S VillageDocument2 pagesCircular 42-Grade 6 To AL To Magic Artisan S VillageRakhi JadavNo ratings yet
- Bihar Food PolicyDocument15 pagesBihar Food PolicyLakshmi Bayanna Pantulu NidasanametlaNo ratings yet
- Đề Thi Sinh Giỏi Lớp 9: Your answersDocument5 pagesĐề Thi Sinh Giỏi Lớp 9: Your answersnguyễn Đình TuấnNo ratings yet
- Kitchen By: Price ListDocument38 pagesKitchen By: Price ListasbachdinNo ratings yet
- 1 Colonization of AmericaDocument52 pages1 Colonization of Americamarinusm100% (1)
- Coconut Milk Powder SpecsheetDocument1 pageCoconut Milk Powder SpecsheetMarison J. Pintu Batu0% (1)
- Mama DeLucas Pizza Daily ChecklistDocument1 pageMama DeLucas Pizza Daily ChecklistDavid HusayranNo ratings yet
- Chapter 24: An Introduction To Chinese CuisineDocument31 pagesChapter 24: An Introduction To Chinese CuisineRettNo ratings yet
- #1 Homestay ApplicationDocument2 pages#1 Homestay ApplicationRobinson JudeNo ratings yet
- English 2Document91 pagesEnglish 2Josselin BorgesNo ratings yet
- The Legend of Lake TobaDocument5 pagesThe Legend of Lake TobasukirnoNo ratings yet
- MFD RebasadofinalDocument120 pagesMFD RebasadofinalRODOLFO CRESPONo ratings yet
- Management of Strategy: Mcdonald MalaysiaDocument20 pagesManagement of Strategy: Mcdonald MalaysiaChiaki Hidayah100% (2)
- (English (Auto-Generated) ) 10000 Most Common English Words With Examples and Meanings - 1 500 Words (DownSub - Com)Document62 pages(English (Auto-Generated) ) 10000 Most Common English Words With Examples and Meanings - 1 500 Words (DownSub - Com)Maulana Yazid Al AnnuriNo ratings yet
- Food Culture of KozhikodeDocument9 pagesFood Culture of KozhikodePranav Chandran100% (1)
- More Botanicals, More Superfruits,: More Solutions by NexiraDocument19 pagesMore Botanicals, More Superfruits,: More Solutions by NexiraVic Veeraj GoyaramNo ratings yet
- Together 3 Worksheets Unit2Document11 pagesTogether 3 Worksheets Unit2jubrignoleNo ratings yet
- Understanding Nutrition Whitney 13th Edition Solutions ManualDocument24 pagesUnderstanding Nutrition Whitney 13th Edition Solutions ManualXavierKimydfj100% (29)