Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Đ C Chem Lab Report 4
Đ C Chem Lab Report 4
Uploaded by
Đức PhanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Đ C Chem Lab Report 4
Đ C Chem Lab Report 4
Uploaded by
Đức PhanCopyright:
Available Formats
I/ Introduction:
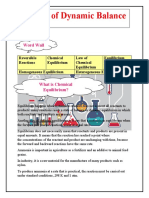
Reversible chemical reactions are those in which the reactants generate products, which then
combine to return the reactants. The concentrations of the reactants and products will stabilize
at an equilibrium point during reversible reactions. In a chemical equation, a reversible reaction
is indicated by a double arrow pointing in both directions.
Reversible reaction:
A+B C+D
When under stress, a reversible reaction at equilibrium may become perturbed. Changes in
concentration, temperature, or pressure are examples of stresses. Until equilibrium is restored,
the reaction mixture's composition will change (Le Chatelier’s principle). We will observe the
impact of introducing stressors to several chemical systems that are in equilibrium in this
experiment, and we'll also check to see if the outcomes follow Le Chatelier’s principle.
You might also like
- Q4W2 616936307126976Document21 pagesQ4W2 616936307126976Jameel CailanNo ratings yet
- State of EquilibriumDocument25 pagesState of EquilibriumBrent Nillas ZuñigaNo ratings yet
- Homework - 8chemical Equilibrium FINALDocument20 pagesHomework - 8chemical Equilibrium FINALNwachukwu ObiNo ratings yet
- ANAchem Module9Document6 pagesANAchem Module9Marie Antonette BaligodNo ratings yet
- Topic 7 - Chemistry - IBDocument22 pagesTopic 7 - Chemistry - IBAN NGUYENNo ratings yet
- 04 EquilibriumDocument19 pages04 EquilibriumAntony Joseph PoullisNo ratings yet
- 11 Chemistry Notes Ch07 Equilibrium KvsDocument5 pages11 Chemistry Notes Ch07 Equilibrium Kvsthakursingh143No ratings yet
- Notes Reversible Reactions and EquilibriumDocument8 pagesNotes Reversible Reactions and EquilibriumThomas PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Note PDFDocument28 pagesNote PDFMekonnen AdonayNo ratings yet
- Gen ChemDocument6 pagesGen ChemGwyne CuecacoNo ratings yet
- L13 PDFDocument26 pagesL13 PDFJoshua RomeaNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium 1Document31 pagesEquilibrium 1Viren W.No ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 Q4 Module 2 1Document15 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 Q4 Module 2 1Darwin Grande AlvaredaNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium and Le Chatelier's PrincipleDocument11 pagesEquilibrium and Le Chatelier's Principleyour mamaNo ratings yet
- A. Title of ExperimentDocument6 pagesA. Title of ExperimentAmeliaNo ratings yet
- Reversible ReactionsDocument2 pagesReversible Reactionsusulasia777No ratings yet
- Principles of Chemical EquilibriumDocument17 pagesPrinciples of Chemical EquilibriumkaditasookdeoNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2: 4 Summative Test ReviewerDocument1 pageGeneral Chemistry 2: 4 Summative Test ReviewerNogeeka Precious DemisanaNo ratings yet
- Handout No. 9 in General Chemistry 2: Co Qah + Melc LWDocument10 pagesHandout No. 9 in General Chemistry 2: Co Qah + Melc LWPortgas D. AceNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Equilibrium - 1Document3 pagesUnit 7 Equilibrium - 1aleenashaji.abraham1No ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibrium Chemistry Grade 12: Everything Science WWW - Everythingscience.co - ZaDocument10 pagesChemical Equilibrium Chemistry Grade 12: Everything Science WWW - Everythingscience.co - ZaWaqas LuckyNo ratings yet
- Chemical EquilibriumDocument46 pagesChemical EquilibriumMary Rose AguilaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction EquilibriaDocument14 pagesChemical Reaction EquilibriaOmkar DolareNo ratings yet
- GC2 Week11 Lesson ProperDocument6 pagesGC2 Week11 Lesson ProperReyNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium NotesDocument3 pagesEquilibrium NotesSaumiaDevadasNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibrium .PresentationDocument17 pagesChemical Equilibrium .PresentationtalhawasimNo ratings yet
- EquilibriumDocument4 pagesEquilibriumBikave JohnsonNo ratings yet
- 5, Part 1 CHM 101Document9 pages5, Part 1 CHM 101josephmartinsogbu30No ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibria NotesDocument7 pagesChemical Equilibria NotesImranMalikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Lecture Notes: Acids, Bases, and PH: Educational GoalsDocument28 pagesChapter 8 Lecture Notes: Acids, Bases, and PH: Educational GoalstiaraNo ratings yet
- TSFX Chem Tips PDFDocument19 pagesTSFX Chem Tips PDFIra HenryNo ratings yet
- EquilibriaDocument7 pagesEquilibriashivakafle039No ratings yet
- Topic 7-17 NotesDocument76 pagesTopic 7-17 NotesHamzaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibrium - ClassnotesDocument36 pagesChemical Equilibrium - ClassnotesArindol SarkarNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibrium2Document4 pagesChemical Equilibrium2Raiyan RahmanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibrium (CURRENT) - CN - STDT3ADocument1 pageChemical Equilibrium (CURRENT) - CN - STDT3ANkemzi Elias NzetengenleNo ratings yet
- 1 Lab Handout PDFDocument5 pages1 Lab Handout PDFKhud SarNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium NotesDocument14 pagesEquilibrium NotessusrudhansNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction IIIDocument2 pagesChemical Reaction IIIPrinceblesed EdemNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium NotesDocument12 pagesEquilibrium Notesarjunrkumar2024No ratings yet
- Equilibrium Class 11 Notes Chemistry Chapter 7Document11 pagesEquilibrium Class 11 Notes Chemistry Chapter 7Kanishk RanjitNo ratings yet
- Chemical EquilibriumDocument4 pagesChemical EquilibriumDraver ZemaNo ratings yet
- Chemical EquilibriumDocument34 pagesChemical EquilibriumLala Rifa0% (1)
- Prac-10 EquilibriumDocument22 pagesPrac-10 EquilibriumCristiano PassarelliNo ratings yet
- EQUILIBRIUMDocument13 pagesEQUILIBRIUMFarhan Al ZayedNo ratings yet
- Informe Nº5Document4 pagesInforme Nº5Alejandro Duvan Lopez RojasNo ratings yet
- Army Public School Gopalpur: EquilibriumDocument11 pagesArmy Public School Gopalpur: EquilibriumAshok KumarNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Chemistry-EquilibriumDocument71 pagesCBSE Class 11 Chemistry-EquilibriumkrkdjcjjddjNo ratings yet
- Chemical EquilibriumDocument9 pagesChemical EquilibriumGodspower OgbonnayaNo ratings yet
- Reversible ReactionDocument2 pagesReversible ReactionShakilNo ratings yet
- 11 Chemistry Notes EquilibriumDocument10 pages11 Chemistry Notes Equilibriumgansan105No ratings yet
- Le Châtelier's PrincipleDocument7 pagesLe Châtelier's PrincipleBob AbramsNo ratings yet
- Simple Physical Phenomena at EquilibriumDocument9 pagesSimple Physical Phenomena at Equilibriumtifanny gamboaNo ratings yet
- A State of Dynamic Balance - FactsDocument15 pagesA State of Dynamic Balance - FactsAlshaimaa SolimanNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Chemistry Revision Notes EquilibriumDocument14 pagesClass 11 Chemistry Revision Notes EquilibriumSwastika DasNo ratings yet
- GenChem2 - Lesson 13Document10 pagesGenChem2 - Lesson 13assassin1252005No ratings yet
- M2 L7 Le Chateliers PrincipleDocument12 pagesM2 L7 Le Chateliers PrincipleKevinNo ratings yet
- Chemical EquilibriumDocument3 pagesChemical EquilibriumNhie AiyuNo ratings yet
- Lab 5Document3 pagesLab 5Đức PhanNo ratings yet
- Lab 4Document3 pagesLab 4Đức PhanNo ratings yet
- Lab 1Document4 pagesLab 1Đức PhanNo ratings yet
- Lab 2Document3 pagesLab 2Đức PhanNo ratings yet