Professional Documents
Culture Documents
HSB Multiple Choice Blood, Heart, Kidney, Skin
Uploaded by
Ariel Lakatoo MingCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
HSB Multiple Choice Blood, Heart, Kidney, Skin
Uploaded by
Ariel Lakatoo MingCopyright:
Available Formats
HUMAN & SOCIAL BIOLOGY
MULTIPLE CHOICE
INSTRUCTIONS: Shade the correct answer on your answer sheet.
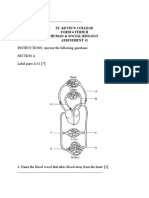
1. Which of the following statements explains 4. The chamber labelled G is the
why we need a transport system? a) left atrium
a) Simple diffusion is efficient enough to b) left ventricle
transport substances around the body. c) right atrium
b) The human body has a small surface to d) right ventricle
volume ratio.
c) The human body has a large surface area 5. Where is the pulmonary vein?
to volume ratio. a) 1
d) Transport distances around the human b) 2
body are short. c) 3
d) 4
2. Materials transported around the human
body include: 6. The roles of the valves in the heart is to
I urea a) regulate heartbeat
II heat b) reduce blood pressure
III hormones c) prevent backflow of blood
IV carbon dioxide d) cause contractions of the chambers
a) I, II & III
7. During one complete circuit around the
b) II, III & IV
body, the blood flows through the heart
c) I, III & IV
a) once
d) all of the above
b) twice
c) three times
Items 3 -5 refer to the following diagram of a d) four times
section of the human heart
Items 8-10 refer to the following diagram which
shows cells found in the human body.
3. Which blood vessels carry deoxygenated
blood? 8. Which cell transports oxygen around the
a) 1 & 2 body?
b) 2 & 3
c) 1 & 3 9. Which cell engulfs bacteria?
d) 3 & 4
10. Which cell produces antibodies and d) ball and socket
antitoxins?
Items 13-14 refer to the diagram below which shows
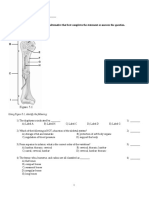
Items 11 & 12 refer to the following diagram of a section of a human bone.
the human skeleton.
13. Which part contributes MOST to the strength of
the bone?
a) 1
b) 2
c) 3
d) 4
14. The part labelled 2 is
a) spongy bone
b) hollow bone
c) contains red bone marrow
d) a hinge joint
15. Cartilage is important as it
a) connects one bone to another
b) connects muscles to bones
c) lubricates the joints
d) is a shock absorber
16. Which type of joint is found at the knee?
a) fixed
b) hinge
c) ball and socket
11. Which bone is labelled T d) partially moveable
a) femur
b) sacrum
c) humerus 17. Muscles that work in opposition to cause
d) clavicle movement at a joint are called?
a) opposite
b) automatic
12. Which type of joint holds the bones of c) pentadactyl
the structure labelled P together? d) antagonistic
a) hinge
b) fixed
c) none 18. Excretion is defined as
a) the loss of salts and water through sweat
b) the production of metabolic waste in the body Items 22-24 are based on the diagram of the human
c) the removal of metabolic waste from the body skin.
d) the removal of undigested food from the body
19. Metabolic waste does NOT include:
a) urea
b) faeces
c) salts
d) carbon dioxide
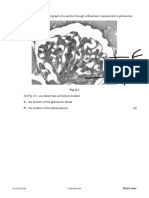
Item 20 refers to the following diagram of a nephron
22. Which structure is labelled O?
a) fat cell
b) hair follicle
c) blood vessel
d) sweat gland
23. Which structure is labelled L?
a) fat cell
b) hair follicle
c) blood vessel
d) sweat gland
24. Which structure is labelled P?
a) fat cell
20. In which region of the nephron does ultrafiltration b) hair follicle
take place? c) blood vessel
a) V d) sweat gland
b) W
c) Y 25. Which structure is labelled M?
d) Z a) fat cell
b) hair follicle
21. Which labelled region is the Loop of Henle? c) blood vessel
a) V d) sweat gland
b) W
c) Y
d) Z
You might also like
- CSEC GeographyFieldStudy SBAForm Strategy SheetDocument1 pageCSEC GeographyFieldStudy SBAForm Strategy SheetLeighton Thompson67% (3)
- 14 Test Bank Cardiovascular Physiology MCQ Test Bank With AnswersDocument45 pages14 Test Bank Cardiovascular Physiology MCQ Test Bank With Answersmugtaba100% (4)
- Urinary SystemDocument5 pagesUrinary SystemJushelle Anne Tigoy Pilare100% (1)
- Science Quest 8 AC 3E c04 PDFDocument94 pagesScience Quest 8 AC 3E c04 PDFmaxx100% (1)
- Body Book ProjectDocument3 pagesBody Book ProjectPsic. Ó. Bernardo Duarte B.No ratings yet
- CBT Sample Q&A 1 - NMC CBT Sample Questions (Ac)Document7 pagesCBT Sample Q&A 1 - NMC CBT Sample Questions (Ac)James Norman Ong100% (8)
- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration AssessmentDocument8 pagesPhotosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Assessmentapi-489727615100% (1)
- Sbe Gen Ed March 2023 QuestionnaireDocument14 pagesSbe Gen Ed March 2023 QuestionnaireMary Mel GarciaNo ratings yet
- The Role of Occupational Therapy in Cardiac RehabilitationDocument35 pagesThe Role of Occupational Therapy in Cardiac Rehabilitationsdsd100% (1)
- 7structural Organization in Animals PDFDocument8 pages7structural Organization in Animals PDFDharmendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Finalized Second Term ExaminationsDocument7 pagesFinalized Second Term ExaminationsRafiu GiwaNo ratings yet
- Tissues Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument8 pagesTissues Multiple Choice QuestionsUday HaldarNo ratings yet
- DPP - Daily Practice Problems: Chapter-Wise SheetsDocument6 pagesDPP - Daily Practice Problems: Chapter-Wise Sheetsshambhumg13No ratings yet
- BIOLOGY SSC II 1st Term ExamDocument1 pageBIOLOGY SSC II 1st Term ExamAdnan MoeenNo ratings yet
- 9 Science Exemplar Chapter 6Document8 pages9 Science Exemplar Chapter 6AKHILA.SURESHNo ratings yet
- NHPC MODEL QuestionsDocument9 pagesNHPC MODEL QuestionsSuperhealth CareNo ratings yet
- Animal Physiology Test PaperDocument3 pagesAnimal Physiology Test PaperRenjith Moorikkaran MNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy PaperDocument3 pagesHuman Anatomy PaperFaisal AwanNo ratings yet
- Locomotion and MovementDocument9 pagesLocomotion and MovementRamanna ChowdaryNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument8 pagesTissuesJanak Priya pandNo ratings yet
- MECEE BL Model Entrance Exam 2079 Morning ShiftDocument16 pagesMECEE BL Model Entrance Exam 2079 Morning Shiftmedical ChyNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes Part 2Document14 pagesBiology Notes Part 2ranajawad579No ratings yet
- HSB Mock Paper 01 - CorrectedDocument8 pagesHSB Mock Paper 01 - CorrectedNicketa AndersonNo ratings yet
- Structural OrgnisationDocument14 pagesStructural OrgnisationNalla Raghuram ChowdaryNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Ss3Document14 pagesScience 9 Ss3harrshanrmt20No ratings yet
- Animal AnatomyDocument10 pagesAnimal Anatomypcstrange20031637No ratings yet
- Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocument19 pagesStructural Organisation in Animalssrinu.lichflNo ratings yet
- Met-3 Droppers ZoologyDocument4 pagesMet-3 Droppers Zoologybikki970684No ratings yet
- 9 Cbse - Term-1 - ScienceDocument13 pages9 Cbse - Term-1 - ScienceSHUAIN PARAMBIL (EMP324)No ratings yet
- BSN 2 Semester Subject: A & P Topic Wise McqsDocument23 pagesBSN 2 Semester Subject: A & P Topic Wise McqsAbdul Hameed KhanNo ratings yet
- Johnson Foundation School Class 9A Biology Annual Consolidated Revision 04 /03 /2022 I. MCQ'SDocument3 pagesJohnson Foundation School Class 9A Biology Annual Consolidated Revision 04 /03 /2022 I. MCQ'Ssrimayi2502No ratings yet
- Neet Structural Organisation in Animals TestDocument3 pagesNeet Structural Organisation in Animals TestShrishNo ratings yet
- Guided QuestionsDocument4 pagesGuided QuestionssolanasnowieNo ratings yet
- Life Science: Chapter 17: Structure and MovementDocument113 pagesLife Science: Chapter 17: Structure and MovementCosmina MariaNo ratings yet
- SGBAU B.Pharm 1 SEM Human-Anatomy-n-Physiology-I 2018Document2 pagesSGBAU B.Pharm 1 SEM Human-Anatomy-n-Physiology-I 2018Abhay DeulkarNo ratings yet
- Xii Neet Locomotion LDocument9 pagesXii Neet Locomotion LShagufta100% (1)
- Anatomy Paper For KmuDocument7 pagesAnatomy Paper For KmuMuhammadsiddique khanNo ratings yet
- Bio finalDocument10 pagesBio finalAbhijit SahooNo ratings yet
- NAME 10-13 QuestionDocument29 pagesNAME 10-13 QuestionAASHISHNo ratings yet
- Zoology QP 04-08-2023Document17 pagesZoology QP 04-08-2023sujathadevarakonda81No ratings yet
- Locomotion and Movement-1Document41 pagesLocomotion and Movement-1Satender Yadav100% (1)
- UnittestDocument5 pagesUnittestapi-298312370No ratings yet
- Worksheet No. 1-Transport System in Living OrganismsDocument5 pagesWorksheet No. 1-Transport System in Living OrganismsKais AdhamNo ratings yet
- Revision 1Document5 pagesRevision 1nevankurainneeliyaraNo ratings yet
- Inte Multiple Choice 4th FormDocument2 pagesInte Multiple Choice 4th FormDaniella WardNo ratings yet
- Practice ExamDocument3 pagesPractice ExamKeanaNo ratings yet
- NDA Biology Minor Mock Test 02Document4 pagesNDA Biology Minor Mock Test 02Ankit Singh RajputNo ratings yet
- NCS - Revision - SCIENCE ONLINE MCQ TEST (28082020) - Que-30-08-2020Document3 pagesNCS - Revision - SCIENCE ONLINE MCQ TEST (28082020) - Que-30-08-2020Diksha GuptaNo ratings yet
- Highlighted Question Bank Locomotor 2023Document9 pagesHighlighted Question Bank Locomotor 2023mohamedelkomy4400No ratings yet
- KSMS Quarterly Exam BiologyDocument4 pagesKSMS Quarterly Exam BiologySumitaNo ratings yet
- Final Ingles Medico I 05-11Document4 pagesFinal Ingles Medico I 05-11alinelucioalvesNo ratings yet
- Glencoe Life Science4Document130 pagesGlencoe Life Science4Cosmina MariaNo ratings yet
- Model Test Paper Science CBSE Class IXDocument5 pagesModel Test Paper Science CBSE Class IXAnanthakrishnan Tinneveli VNo ratings yet
- Psg-Qp-Body MovementsDocument2 pagesPsg-Qp-Body Movementsphysicsbooks.storeNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument10 pagesUntitledIreyana BarrientosNo ratings yet
- A) MarasmusDocument21 pagesA) Marasmusrathai0% (1)
- C.S.E - Medical Science - 2005 (Preliminary) : Time Allowed: 2 Hours Maximum MarksDocument17 pagesC.S.E - Medical Science - 2005 (Preliminary) : Time Allowed: 2 Hours Maximum MarksAV LucentNo ratings yet
- FST (Girls) Bio 2022Document2 pagesFST (Girls) Bio 2022Abdul qadoosNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument5 pagesRespiratory Systemshahirah77No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology 2nd Edition Martini Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument67 pagesAnatomy and Physiology 2nd Edition Martini Test Bank Full Chapter PDFserenafinnodx100% (10)
- Biology Prelims 2023Document6 pagesBiology Prelims 2023SwethanaNo ratings yet
- InteGRATED SCIENCE - ExcretionDocument2 pagesInteGRATED SCIENCE - Excretionnehru09No ratings yet
- NEET BIOLOGY Structural Organization of AnimalsDocument93 pagesNEET BIOLOGY Structural Organization of AnimalsMonish KumarNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System Exam Multiple-Choice: Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDocument3 pagesSkeletal System Exam Multiple-Choice: Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionIqra AsifNo ratings yet
- SMT - Sridevi Awasiyavidyapeeth: Second Term Examination 2021-22 Sub: Science All Questions Are CompulsoryDocument2 pagesSMT - Sridevi Awasiyavidyapeeth: Second Term Examination 2021-22 Sub: Science All Questions Are CompulsoryAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- QP B Pharm 30012020Document135 pagesQP B Pharm 30012020Spy HanNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper For Grade 6Document4 pagesSample Paper For Grade 6Navvye AnandNo ratings yet
- Geo SbaDocument20 pagesGeo SbaAriel Lakatoo Ming100% (1)
- Sports 2015Document16 pagesSports 2015Ariel Lakatoo MingNo ratings yet
- Sports Day Events ScoreDocument3 pagesSports Day Events ScoreAriel Lakatoo MingNo ratings yet
- Request LetterDocument1 pageRequest LetterAriel Lakatoo MingNo ratings yet
- March Past Rules and RegulationsDocument3 pagesMarch Past Rules and RegulationsAriel Lakatoo MingNo ratings yet
- St. Kevin's College Form 4 Biology Assessment 1Document2 pagesSt. Kevin's College Form 4 Biology Assessment 1Ariel Lakatoo MingNo ratings yet
- Major Coastal Features and Wave Patterns Reveal Ongoing ErosionDocument18 pagesMajor Coastal Features and Wave Patterns Reveal Ongoing ErosionAriel Lakatoo MingNo ratings yet
- Sports Day Events ParticipantsDocument8 pagesSports Day Events ParticipantsAriel Lakatoo MingNo ratings yet
- Geography Form 2 AssessmentDocument2 pagesGeography Form 2 AssessmentAriel Lakatoo MingNo ratings yet
- Geography Form 3 Assessment Water CycleDocument2 pagesGeography Form 3 Assessment Water CycleAriel Lakatoo MingNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS Assessment Gravitational Potential EnergyDocument2 pagesPHYSICS Assessment Gravitational Potential EnergyAriel Lakatoo MingNo ratings yet
- Geography 2Document3 pagesGeography 2Ariel Lakatoo MingNo ratings yet
- Geography Form 1 AssessmentDocument2 pagesGeography Form 1 AssessmentAriel Lakatoo MingNo ratings yet
- Form 3 Geography AssessmentDocument3 pagesForm 3 Geography AssessmentAriel Lakatoo MingNo ratings yet
- ST Kevin'S College End of Term I Examinations Social Studies Form 3Document2 pagesST Kevin'S College End of Term I Examinations Social Studies Form 3Ariel Lakatoo MingNo ratings yet
- Geography Rivers and Limestone Multiple ChoiceDocument4 pagesGeography Rivers and Limestone Multiple ChoiceAriel Lakatoo Ming100% (1)
- Human & Social Biology Form 5 Past PapersDocument2 pagesHuman & Social Biology Form 5 Past PapersAriel Lakatoo MingNo ratings yet
- Geography 2Document3 pagesGeography 2Ariel Lakatoo MingNo ratings yet
- Suffixes and PrefixesDocument5 pagesSuffixes and Prefixesilinca vasileNo ratings yet
- Oral Surgery Oral Medicine Oral PathologyDocument7 pagesOral Surgery Oral Medicine Oral PathologyDiego LemurNo ratings yet
- Initial Assessment: - Rambam Medical Center - DR Nordkin DmitriDocument60 pagesInitial Assessment: - Rambam Medical Center - DR Nordkin Dmitridheviant12No ratings yet
- Physiology Lecture 10 Q-Bank (Cardiac Muscle - Action Potentials)Document15 pagesPhysiology Lecture 10 Q-Bank (Cardiac Muscle - Action Potentials)ChrisOrtNo ratings yet
- Control and Coordination: Chapter - 7Document9 pagesControl and Coordination: Chapter - 7milind dhamaniya100% (1)
- HomeostasisDocument30 pagesHomeostasisSana MostofaNo ratings yet
- Internal Medicine - Phase 3: Important Legal InformationDocument19 pagesInternal Medicine - Phase 3: Important Legal InformationClaire YabaNo ratings yet
- SDL R VS OldDocument6 pagesSDL R VS Oldsejal3vijNo ratings yet
- Sensory receptors classification and propertiesDocument13 pagesSensory receptors classification and propertiesbnmjgcNo ratings yet
- Template CVDocument4 pagesTemplate CVNurul FaikaNo ratings yet
- Seminar on Myocardial InfarctionDocument17 pagesSeminar on Myocardial InfarctionSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- Potassium Chloride Drug OverviewDocument2 pagesPotassium Chloride Drug OverviewmichelleNo ratings yet
- Gangguan Asam BasaDocument51 pagesGangguan Asam BasaYudhistira YuliandraNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Atrial Septal DefectDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Atrial Septal Defectbobtaguba50% (2)
- Approach to Hypertension ManagementDocument11 pagesApproach to Hypertension ManagementNoreenNo ratings yet
- 3.2. KARBOHIDRAT II GlikolisisDocument27 pages3.2. KARBOHIDRAT II GlikolisisRikka TakaradaNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary Syndrome Update: Charles Shoalmire, MSN, RN, ACNP-BCDocument31 pagesAcute Coronary Syndrome Update: Charles Shoalmire, MSN, RN, ACNP-BCDwi Akbarina YahyaNo ratings yet
- Question Bank: Gaseous ExchangeDocument3 pagesQuestion Bank: Gaseous Exchangewallace120No ratings yet
- Maxillofacial Trauma: Airway ManagementDocument39 pagesMaxillofacial Trauma: Airway Managementريام الموسويNo ratings yet
- COURSE TASK 1 Increased ICP POLICIOS, SHARMAINE ANNE M. BSN 3Y2 - 3ADocument2 pagesCOURSE TASK 1 Increased ICP POLICIOS, SHARMAINE ANNE M. BSN 3Y2 - 3ASHARMAINE ANNE POLICIOS100% (1)
- Ecg - Partea I - Mircea CintezaDocument16 pagesEcg - Partea I - Mircea CintezaAndrei CiobotaruNo ratings yet
- Above Normal: (After A Meal)Document2 pagesAbove Normal: (After A Meal)Uzma AdnanNo ratings yet
- UFS Mid-Year Exam Paper 1Document8 pagesUFS Mid-Year Exam Paper 1TsholofeloNo ratings yet