Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Independent Research Assignment - Gallstones
Uploaded by
jena Dorrington0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views3 pagesRudimentary knowledge regarding gallstones and pathophysiology as well as risks and treatments
Original Title
Independent Research Assignment- Gallstones
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentRudimentary knowledge regarding gallstones and pathophysiology as well as risks and treatments
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views3 pagesIndependent Research Assignment - Gallstones
Uploaded by
jena DorringtonRudimentary knowledge regarding gallstones and pathophysiology as well as risks and treatments
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
PHGY 216 Independent Research Assignment
Name: Jena Dorrington
Student Number: 20167926
Gallstones
How Do I Know If I Have Gallstones?
What Are Gallstones?
It is possible to experience little to no symptoms if
Gallstones are characterized as hardened deposits
you have gallstones. However, if these gallstones
derived from bile which is a digestive fluid that is
cause a blockage by getting stuck in one of the ducts,
produced in the liver and it is stored in the
then some common symptoms and signs include1;
gallbladder. There are two main types of gallstones;
➢ Nausea or vomiting
cholesterol and pigment stones. Roughly 80% of
➢ Pain in the right shoulder or back
gallstones turn out to be cholesterol stones which are
➢ Pain in the upper or central abdominal
predominantly made of cholesterol, a waxy-like
regions, often experienced more on the right
substance required by the body to build and maintain
side
healthy cells. Meanwhile, pigment stones are
➢ Other digestion issues (indigestion,
composed of bile salts and bilirubin, a compound that
heartburn, etc)
is produced during the normal breakdown of the red
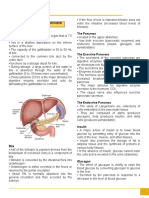
Figure 2: Overview of Biliary Tract
blood cells. Currently the cause behind gallstone
formation is not fully understood, however
researchers suggest that it could occur when there is1;
➢ A higher than normal concentration of
cholesterol or bilirubin in the bile
➢ More concentrated bile due to the
gallbladder not fully emptying
Some risk factors that may increase an individual’s
risk of developing gallstones include1;
➢ Genetics
➢ Obesity
➢ Pregnancy
➢ Specific medications
➢ Experiencing other medical conditions Credit: https://radiologykey.com/the-biliary-tree/
➢ Prolonged fasting What Do Gallstones Affect?
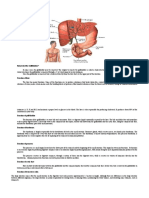
Figure 1: Overview of Gallstone Location Gallstones are one of the most prevalent medical
conditions that affects the body’s biliary system. The
biliary tract consists of the liver, bile ducts and
gallbladder and each part of the system plays a role in
the production, secretion and storage of bile. Bile is a
very important digestive fluid that is made of
electrolytes, bile salts, bile pigments, cholesterol, and
other lipids. The two main functions of bile include
helping the digestion of fats and the elimination of
waste products, such as excess cholesterol and
hemoglobin, from the body1. When bile is released
from the liver, it flows through the right and left
hepatic ducts which merges to form the common bile
duct. The bile moves through this common hepatic
Credit:https://www.webmd.com/digestive-disorders/g duct, past the Oddi sphincter, and into the duodenum
allstones segment of the small intestine. In between meals,
roughly half of the bile produced in the liver moves
to the small intestine and the other half is redirected
to the cystic duct and into the gallbladder where it is
stored. Once food enters the small intestine, a mix of
nerve and hormonal signals causes the gallbladder to patients can expect to experience some soreness and
contract, forcing the bile into the duct system and into the average recovery time is 7 to 10 days3.The
the small intestine2. absence of a gallbladder does not impact the body’s
What Do Gallstones Do To The Body? digestive capabilities, although consuming large
Gallstones can vary in size, shape, and quantity and amounts of high fat foods may be more difficult to
typically occur when the bile becomes too digest. Instead of bile being stored in the gallbladder,
concentrated and with time, small crystal like bile will simply flow directly from the liver to the
structures may form. These small structures get small intestine. Other forms of treatment include oral
lodged in the gallbladder’s mucus, and eventually medications which act to dissolve the gallstones over
grow and solidify into gallstones. Most patients that time. However, this tends to be a lengthy process and
have gallstones are asymptomatic, although studies it does not stop the reformation of gallstones after
show that roughly 10% of these patients will treatment has ended3.
experience some symptoms within 5 years1. In certain Where Can I Go To Learn More About
cases, the gallstone(s) may move into the cystic duct Gallstones?
opening, blocking the flow of bile from the (1) Healthline-
gallbladder into the biliary ducts. If this duct remains https://www.healthline.com/health/gallstone
blocked for several hours, it can cause inflammation s
in the gallbladder wall. The gallstone may also move (2) Medical News Today-
into the bile duct, causing obstruction of the bile’s https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/
movement. These bile obstructions lead to the 153981
buildup of bile in the liver and gallbladder and so the Action Plan
patient may develop jaundice, which is the yellowing
➢ Only gallstones that are blocking the biliary
of the skin due to the increased levels of bilirubin in
ducts cause patients to express symptoms
the blood1. Compared to the healthy physiological
➢ Be aware of the possible symptoms related
state of the biliary system, the presence of gallstones
to gallstones, especially if you possess some
and the possible obstruction of the biliary ducts puts a
of the associated risk factors
lot of stress on this system which can lead to the
➢ If diagnosed with gallstones, avoid high fat
patient experiencing progressive and worsening
foods until fully treated
symptoms if not treated quickly. The imbalance of
➢ Consult a medical professional as to what
the components that make up the bile indicates
the best course of treatment would be
homeostasis impairment and as a result, multiple
systems could be affected. For instance, gallstones References
can affect the body’s digestive system because, as 1.Jones, M. (2021, February 08). Gallstones
mentioned earlier, one of bile’s main functions is to (Cholelithiasis). Retrieved April 16, 2021, from
break down fat in the small intestine. If there is a https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459370/
blockage due to the presence of gallstones, the bile
can no longer access the small intestine, and so fats 2. Lindenmeyer, C. (n.d.). Gallbladder and biliary tract -
cannot be emulsified and broken down, thereby liver and gallbladder disorders. Retrieved April 16, 2021,
affecting fat absorption1. from
What Can I Do About Gallstones? https://www.merckmanuals.com/en-ca/home/liver-and-gal
Treatment for gallstones vary depending on the lbladder-disorders/biology-of-the-liver-and-gallbladder/ga
patient’s symptoms and situation. Due to frequent llbladder-and-biliary-tract
gallstone recurrence, the typical course of treatment
for gallstones is a cholecystectomy, a surgical 3.Laparoscopic gallbladder surgery for gallstones. (n.d.).
procedure involving the removal of the gallbladder. Retrieved April 16, 2021, from
This form of treatment is minimally invasive with https://www.uofmhealth.org/health-library/hw106860#:~:t
low complication risk and it is the most effective way ext=Most%20people%20can%20return%20to,precautions
to prevent future gallstone formation. After surgery, %20are%20needed%20after%20surgery
You might also like
- TMC Dosing ChartDocument6 pagesTMC Dosing ChartScott100% (1)
- Case Study CholecystitisDocument27 pagesCase Study Cholecystitisyhanne98% (225)
- Cholecystitis With CholelithiasisDocument20 pagesCholecystitis With CholelithiasisrhyanneNo ratings yet
- Case Scenario CholeDocument4 pagesCase Scenario CholeAlden MendozaNo ratings yet
- Cholelithiasis RLDocument29 pagesCholelithiasis RLPrincess Joanna Marie B DelfinoNo ratings yet
- Case Study CholecystitisDocument27 pagesCase Study CholecystitisBandana RajpootNo ratings yet
- VI. Patho-Physiology: Removal of The Gallbladder?Document3 pagesVI. Patho-Physiology: Removal of The Gallbladder?Maui ReyesNo ratings yet
- Biliary AtresiaDocument25 pagesBiliary AtresiaMohamed Na3eemNo ratings yet
- Physiology 8 WeekDocument16 pagesPhysiology 8 WeekAnshulNo ratings yet
- Kolelitiasis in EnglishDocument18 pagesKolelitiasis in EnglishReza AkbarNo ratings yet
- Cholelithiasis: Introduction: General Illness InformationDocument9 pagesCholelithiasis: Introduction: General Illness InformationJhangot Abad GabucoNo ratings yet
- Jay W. Marks, M.D. Dennis Lee, M.D. Bile Liver: GallstonesDocument11 pagesJay W. Marks, M.D. Dennis Lee, M.D. Bile Liver: GallstonesAvilla Ane LukitoNo ratings yet
- Biliary DisorderDocument10 pagesBiliary DisorderChristine Joy FloresNo ratings yet
- BelleDocument7 pagesBelleNemo Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- B. Synthesis of The DiseaseDocument5 pagesB. Synthesis of The DiseaseQaz ZaqNo ratings yet
- Case Stydy On CholithiasisDocument29 pagesCase Stydy On CholithiasisDaniel TalleyNo ratings yet
- Liver Disease: Overview of The LiverDocument6 pagesLiver Disease: Overview of The LiverMustafa AlmasoudiNo ratings yet
- What Is Biliary Atresia?Document6 pagesWhat Is Biliary Atresia?echi_maniezz8719No ratings yet
- Chole ReportingDocument5 pagesChole ReportingMarcieNo ratings yet
- Dave Jay S. Manriquez RN. Acute CholecystitisDocument11 pagesDave Jay S. Manriquez RN. Acute CholecystitisChilleMaeNo ratings yet
- It All Begins in The Digestive System: Good HealthDocument24 pagesIt All Begins in The Digestive System: Good HealthLit'l TardNo ratings yet
- Cholelithiasis Brief DiscussionDocument8 pagesCholelithiasis Brief Discussionriel100% (6)
- Cholecystitis IntroductionDocument4 pagesCholecystitis IntroductionJechelle Ann Pabustan Martin-BoniquitNo ratings yet
- CholedocholithiasisDocument44 pagesCholedocholithiasisGerli Bismonte100% (6)
- Ntroduction: (1) (2) (3) Go ToDocument6 pagesNtroduction: (1) (2) (3) Go ToretnaNo ratings yet
- Cholelithiasis: Group MembersDocument12 pagesCholelithiasis: Group MembersShiela GutierrezNo ratings yet
- DigestiveDocument4 pagesDigestiveZenab AlmussallamNo ratings yet
- GallstoneDocument6 pagesGallstoneMushfique HussainNo ratings yet
- Cholesterol Stone. People Are at Most Risk For Cholecystitis or Cholelithiasis Is Obese Women Who HaveDocument4 pagesCholesterol Stone. People Are at Most Risk For Cholecystitis or Cholelithiasis Is Obese Women Who HavePatriot DolorNo ratings yet
- Case Study CholecystitisDocument28 pagesCase Study CholecystitisK EV INNo ratings yet
- Liver Transplantation: What Is Liver Transplantation? Who Needs A Liver Transplant?Document12 pagesLiver Transplantation: What Is Liver Transplantation? Who Needs A Liver Transplant?RatihSeptianiNo ratings yet
- Reporting CholeDocument4 pagesReporting CholeMarcieNo ratings yet
- CHOLECYSTITISDocument4 pagesCHOLECYSTITISMarcieNo ratings yet
- Fecal EliminationDocument4 pagesFecal EliminationEzra MaeNo ratings yet
- What Are GallstonesDocument15 pagesWhat Are GallstonesStepyn SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Ecture Iver Oxicology L G: Susceptibility of The LiverDocument10 pagesEcture Iver Oxicology L G: Susceptibility of The LiverDaisy LuNo ratings yet
- Extrahepatic Biliary AtresiaDocument3 pagesExtrahepatic Biliary AtresiaTiti Afrianto100% (1)
- CholedocholithiasisDocument3 pagesCholedocholithiasisPao AcelajadoNo ratings yet
- Pathology of The Liver: Systems Pathology II-PA5402 Dr. Khan T-W-RDocument78 pagesPathology of The Liver: Systems Pathology II-PA5402 Dr. Khan T-W-RCrystal Lynn Keener SciariniNo ratings yet
- LP Eliminasi Riska TiariniDocument17 pagesLP Eliminasi Riska TiariniRiska TiariniNo ratings yet
- EBL Case 7Document5 pagesEBL Case 7T LolaNo ratings yet
- Cholelithiasis: - Other Names: - Gallbladder Attack - Biliary Colic - Gallstone Attack - Bile Calculus - Biliary CalculusDocument101 pagesCholelithiasis: - Other Names: - Gallbladder Attack - Biliary Colic - Gallstone Attack - Bile Calculus - Biliary CalculusYvonne100% (1)
- Tujuan Pembelajaran Minggu PertamaDocument36 pagesTujuan Pembelajaran Minggu PertamaMaha PutraNo ratings yet
- Cholecystectomy With Intraoperative CholangiogramDocument8 pagesCholecystectomy With Intraoperative CholangiogramLourd Andrew VillegasNo ratings yet
- Polycystic Kidneys, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesFrom EverandPolycystic Kidneys, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesNo ratings yet
- Diverticulosis, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesFrom EverandDiverticulosis, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Liver Cirrhosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesFrom EverandLiver Cirrhosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Acalculous Cholecystopathy, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Acalculous Cholecystopathy, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- The Liver and Gallbladder Miracle Cleanse: An All-Natural, At-Home Flush to Purify & Rejuvenate Your BodyFrom EverandThe Liver and Gallbladder Miracle Cleanse: An All-Natural, At-Home Flush to Purify & Rejuvenate Your BodyNo ratings yet
- The Essential Kidney Disease Cookbook: Over 150 Delicious Kidney-Friendly Meals to Ensure You Manage Your Kidney DiseaseFrom EverandThe Essential Kidney Disease Cookbook: Over 150 Delicious Kidney-Friendly Meals to Ensure You Manage Your Kidney DiseaseNo ratings yet
- Gastric Outlet Obstruction, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandGastric Outlet Obstruction, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Constipation: How To Treat Constipation: How To Prevent Constipation: Along With Nutrition, Diet, And Exercise For ConstipationFrom EverandConstipation: How To Treat Constipation: How To Prevent Constipation: Along With Nutrition, Diet, And Exercise For ConstipationNo ratings yet
- Ascites, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandAscites, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Inflammation of Digestive Tract, a Simple Guide to the Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandInflammation of Digestive Tract, a Simple Guide to the Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Colon Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Colon Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Leaky Gut Syndrome for Beginners - The Self-Help Book - How to Correctly Interpret the Symptoms of a Leaky Gut, Identify the Causes and Heal Your Gut Step by StepFrom EverandLeaky Gut Syndrome for Beginners - The Self-Help Book - How to Correctly Interpret the Symptoms of a Leaky Gut, Identify the Causes and Heal Your Gut Step by StepNo ratings yet
- Z+blood TransfusionDocument16 pagesZ+blood TransfusionilhamaminsyaputraNo ratings yet
- CancerDocument20 pagesCancerJulio BenitesNo ratings yet
- Postdoctoral Fellow in NeurochemistryDocument4 pagesPostdoctoral Fellow in Neurochemistrysaudagar_minang72No ratings yet
- 07 Staining Part 2 and MountingDocument12 pages07 Staining Part 2 and MountingMae BillynNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi MusculoskeletalDocument25 pagesFisiologi MusculoskeletalSuardimanAchoNo ratings yet
- Weathering of RocksDocument2 pagesWeathering of Rocksvee propagandaNo ratings yet
- 2020B1A70383H BioPhy Ass1Document6 pages2020B1A70383H BioPhy Ass1polsaagyapolsNo ratings yet
- Cellular REspiration Virtual Lab Snails and ElodeaDocument4 pagesCellular REspiration Virtual Lab Snails and Elodeasheisbonjing PHNo ratings yet
- 13500-0004 BiladylTriladyl Es 120814Document2 pages13500-0004 BiladylTriladyl Es 120814Fabio FerreiraNo ratings yet
- 5.2 Factors Affecting Membrane StructureDocument21 pages5.2 Factors Affecting Membrane StructureLisa MillardNo ratings yet
- PUB - NEWater - Quality 1Document1 pagePUB - NEWater - Quality 1Weijin LeowNo ratings yet
- Name:-Zain Abbas Rollno: - 9837 Program: - DPT (6Th) Submitted To Ma'M Iqra NawazDocument19 pagesName:-Zain Abbas Rollno: - 9837 Program: - DPT (6Th) Submitted To Ma'M Iqra NawazAbdul MuqeetNo ratings yet
- Biology 9th Specs 1 PDFDocument1 pageBiology 9th Specs 1 PDFAamir HabibNo ratings yet
- Sage Genetics Lecture 2017 ExpoDocument55 pagesSage Genetics Lecture 2017 ExpoJosé Nigadera de la SotaNo ratings yet
- JOURNAL5Document28 pagesJOURNAL5Decy Manzano100% (1)
- 1 Intro To Ichthyology 2017Document21 pages1 Intro To Ichthyology 2017Enin SofiyaNo ratings yet
- ABO-Rh Blood Typing With Synthetic Blood: Teacher'S Manual and Student GuideDocument32 pagesABO-Rh Blood Typing With Synthetic Blood: Teacher'S Manual and Student GuideMylan Gaston100% (1)
- Amano P6 - Rice BranDocument6 pagesAmano P6 - Rice BranlaviniakartikaNo ratings yet
- Clone 123C3: Monoclonal Mouse Anti-Human CD56 Code M7304Document3 pagesClone 123C3: Monoclonal Mouse Anti-Human CD56 Code M7304Jaimier CajandabNo ratings yet
- Fuicodan y CancerDocument9 pagesFuicodan y CancerJefry Jose González LopezNo ratings yet
- UrochordatevolutionDocument15 pagesUrochordatevolutionRodrigo CarralNo ratings yet
- Markeri MereDocument6 pagesMarkeri MereGigiPetreaNo ratings yet
- ASPMN Position Statement Pain Assesement NonVerbalDocument9 pagesASPMN Position Statement Pain Assesement NonVerbalKitesaMedeksaNo ratings yet
- మన ఊరి ఆకుకూరలుDocument115 pagesమన ఊరి ఆకుకూరలుPraveen Vonti100% (1)
- Ecg Made EasyDocument45 pagesEcg Made EasyfisiopopNo ratings yet
- Sindroma MetabolikDocument24 pagesSindroma MetabolikAnissa Aulia AdjaniNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument7 pagesLab ReportJade PategaNo ratings yet
- Chlorophyll Fluorescence and Growth Evaluation of Ornamental Foliage Plants in Response To Light Intensity Levels Under Continuous Lighting ConditionsDocument13 pagesChlorophyll Fluorescence and Growth Evaluation of Ornamental Foliage Plants in Response To Light Intensity Levels Under Continuous Lighting ConditionsSai RaisaNo ratings yet
- Immunology Course Question Set 1 + AnswersDocument6 pagesImmunology Course Question Set 1 + AnswersAnnTranNo ratings yet