Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Topic
Uploaded by
anandOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Topic
Uploaded by
anandCopyright:
Available Formats
TOPIC: TQM IMPLEMENTATION
TQM Implementation This subsection presents the weak areas of the firm’s TQM implementation
and the reasons leading to these weak areas. The assessment tool (see Appendix 5) was used to
evaluate the firm’s TQM implementation. The weak areas identified could be used by the firm to
further improve its TQM implementation; they were regarded as potential improvement
possibilities. Note that the identification of these weak areas was on the basis of unbiased, honest,
and fact-based judgements. Leadership There was strong evidence that top management
empowerment had not yet been implemented. The firm was centralized and hierarchical, and there
was a strong tendency for employees to do things according to what they were told. They tended to
wait for guidance from top managers or supervisors at all times. Thus, employees did not take any
risk or responsibility if things went wrong; otherwise, they would be punished or fined. If things went
wrong, employees tried to seek excuses to protect themselves in order to avoid being fined or
criticized.
Employees did not want to take any risk by doing things without permission. Top management did
not pursue long-term business success but focused instead on annual business success, which was
their most important goal. Top management still viewed product quality as less important than cost.
In addition, top managers often organized discussion meetings after quality problems had happened;
how to prevent problems from happening was not given sufficient attention. Top managers were
reluctant to accept or implement employee suggestions if money was needed for their
implementation. The firm’s many problems occurred due to its focus on immediate profits or short-
term benefits. Supplier Quality Management Long-term partnership between the firm and its
suppliers had not yet been established. The firm had a special policy of rewarding purchasing
personnel who could purchase products without immediate payment or less immediate payment.
This was due to the shortage of capital. Otherwise, the firm could not have sufficient materials to
maintain normal production. Such practices caused the problem that the firm would have to pay
more in the future.
The firm always received complaints from its suppliers. Due to the lack of partnership with suppliers
and as well as mutual trust, the firm had to implement strict non-value-added incoming inspection.
Purchasing price was the most important factor in selecting suppliers, with product quality falling
behind the price. Such a practice indicated that the firm selected such a supplier that could provide
the lowest price for technically accepted products. In a few cases, purchased products could not be
accepted technically. For example, qualified suppliers could provide carburization for gears at a price
of RMB 16 per kilogram, provided that the buyer pay immediately.
Submitted by :
You might also like
- LIFEAsia Base System Guide V10.1 LatestDocument291 pagesLIFEAsia Base System Guide V10.1 LatestCM100% (5)
- Questions For Make or BuyDocument42 pagesQuestions For Make or BuyTaha Madni67% (3)
- Ten Strategies For The Top ManagementDocument19 pagesTen Strategies For The Top ManagementAQuh C Jhane67% (3)
- Aug 6th Solved PaperDocument19 pagesAug 6th Solved Papernaanigaaduscribd100% (2)
- Serv100 Case StudyDocument4 pagesServ100 Case StudyAyessa YsabelleNo ratings yet
- Barriers To Total Quality Management ImplementationDocument4 pagesBarriers To Total Quality Management ImplementationYaseen Saleem83% (6)
- Operation Mangament CH15Document22 pagesOperation Mangament CH15Moe Alnaim100% (2)
- My PartDocument5 pagesMy PartZeeshan TahirNo ratings yet
- Cost of QualityDocument13 pagesCost of Qualityashish RautNo ratings yet
- Palatan, RJ - Bue311 Case Study 1Document2 pagesPalatan, RJ - Bue311 Case Study 1Raven ShadowsNo ratings yet
- Decision Making in BusinessDocument10 pagesDecision Making in BusinessbagumaNo ratings yet
- Total Quality ManagementDocument23 pagesTotal Quality ManagementMariaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5: Quality Sysyems Organizing and ImplementationDocument23 pagesUnit 5: Quality Sysyems Organizing and ImplementationVinitgaNo ratings yet
- Tool For Assessing Industry TQM Practice Versus The Deming PhilosophyDocument2 pagesTool For Assessing Industry TQM Practice Versus The Deming PhilosophyAbbasMureedNo ratings yet
- Management Commitment - Making A Commitment To Drive Improvement Within An OrganizationDocument4 pagesManagement Commitment - Making A Commitment To Drive Improvement Within An OrganizationKushagra RastogiNo ratings yet
- MGT407Document9 pagesMGT407JEMILA CLOTTEYNo ratings yet
- Deming's 14 PointsDocument3 pagesDeming's 14 PointsYinlinNo ratings yet
- GROUP 2 - Short Answers - Lecture 6Document6 pagesGROUP 2 - Short Answers - Lecture 6Nguyễn Thị Chuyên 2M-20ACNNo ratings yet
- Module 6 Performance AppraisalDocument8 pagesModule 6 Performance AppraisalAngel Calipdan ValdezNo ratings yet
- Concepts of TQMDocument12 pagesConcepts of TQMSavantNo ratings yet
- TQM GurusDocument18 pagesTQM GurusmbuyaivoneNo ratings yet
- Procurement Challenges and Solutions - Fleet and Transport ManagementDocument22 pagesProcurement Challenges and Solutions - Fleet and Transport Managementtonderai mangozheNo ratings yet
- HRSS em Involvement and RelasDocument6 pagesHRSS em Involvement and RelasRadhzz RajiNo ratings yet
- William Edwards Deming: - Statistical Process Control (SPC) Is A Method of QualityDocument11 pagesWilliam Edwards Deming: - Statistical Process Control (SPC) Is A Method of QualitymaxNo ratings yet
- Ethical Issue M5 1Document2 pagesEthical Issue M5 1Mbugua Wa IrunguNo ratings yet
- Demming's 14 PrinciplesDocument17 pagesDemming's 14 PrinciplesAaron Karthik100% (1)
- Answer:: Activity 7Document2 pagesAnswer:: Activity 7Jerica LumboyNo ratings yet
- Advantages and Disadvantages of AuditingDocument4 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of AuditingJaseng NokrekNo ratings yet
- SC MR Supplier de Volo PmentDocument3 pagesSC MR Supplier de Volo PmentJelena JovićNo ratings yet
- Case 1: Ethics Vs ProfitDocument1 pageCase 1: Ethics Vs ProfitAnnalyn ArnaldoNo ratings yet
- Good Performance Appraisal ExamplesDocument6 pagesGood Performance Appraisal ExamplesAndrey MilerNo ratings yet
- During My Training PeriodDocument5 pagesDuring My Training PeriodVijay BhattaraiNo ratings yet
- Deming's System of Profound Knowledge: 14 Points For ManagementDocument3 pagesDeming's System of Profound Knowledge: 14 Points For Managementgupta_rk06No ratings yet
- Lecture Guide Unit 2 - AE18 - Quality Guru & Kaizen Concept 2022-2023Document34 pagesLecture Guide Unit 2 - AE18 - Quality Guru & Kaizen Concept 2022-2023Yeye GatdulaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4: Quality Philosophy and Management Strategies: 1.0.1 William Edwards DemingDocument3 pagesLecture 4: Quality Philosophy and Management Strategies: 1.0.1 William Edwards DemingDiego PulidoNo ratings yet
- Blue Mark College: Level Iv AssignmentDocument14 pagesBlue Mark College: Level Iv AssignmentAmareNo ratings yet
- HRM Case StudyDocument8 pagesHRM Case StudyJohn Eric SancioNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Performance AppraisalDocument7 pagesIntroduction of Performance AppraisalMichael BobNo ratings yet
- Week 5Document5 pagesWeek 5ninnyragayNo ratings yet
- Sample Performance AppraisalDocument6 pagesSample Performance AppraisalReeces EwartNo ratings yet
- Pb12mat+Pengantar Manajemen Pert 13Document32 pagesPb12mat+Pengantar Manajemen Pert 13Eryell Zivana AntoniNo ratings yet
- DraftDocument4 pagesDraftRahat fahimNo ratings yet
- Name: Christine Ndanu ADMISSION NO: BBM/2041 /18 Unit: Total Quality in Supply Chain Management Unit Code: BBM 445 Assignment: CatDocument4 pagesName: Christine Ndanu ADMISSION NO: BBM/2041 /18 Unit: Total Quality in Supply Chain Management Unit Code: BBM 445 Assignment: CatHashi MohamedNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument8 pagesUntitled DocumentHeart Valerie VictaNo ratings yet
- Module 3-TQMDocument17 pagesModule 3-TQMRevenlie GalapinNo ratings yet
- Performance Appraisal GoalsDocument6 pagesPerformance Appraisal GoalsAlla nemmaNo ratings yet
- Deming'S 14 Points: Cristobal, Krizia Martin, Candice Paguiligan, Abbey Pita, Alyssa Rivera, SalveDocument15 pagesDeming'S 14 Points: Cristobal, Krizia Martin, Candice Paguiligan, Abbey Pita, Alyssa Rivera, SalveAditya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - Hom 211Document3 pagesChapter 12 - Hom 211KhioneNo ratings yet
- Hank Kolb Case SolutionDocument7 pagesHank Kolb Case SolutionAbhishek PalNo ratings yet
- Deming's 14 PointsDocument15 pagesDeming's 14 PointsJoshua Deo AcostaNo ratings yet
- Chap - 2 Quality Management Philosophy PDFDocument11 pagesChap - 2 Quality Management Philosophy PDFSnehlata SarafNo ratings yet
- Barriers To Total Quality Management ImplementationDocument6 pagesBarriers To Total Quality Management ImplementationVenkatNo ratings yet
- Empowerment+PPT SDPDocument23 pagesEmpowerment+PPT SDPEarl Clarence InesNo ratings yet
- Industrial Sociology Chap 4Document16 pagesIndustrial Sociology Chap 4Asha RaniNo ratings yet
- TQM - Barriers To TQM ImplementationDocument6 pagesTQM - Barriers To TQM ImplementationDhilip Prabakaran100% (1)
- Ethics in Performance AppraisalDocument4 pagesEthics in Performance AppraisalDeepak Nagwanshi75% (4)
- Measure Supplier PerformanceDocument6 pagesMeasure Supplier PerformanceDharmesh MistryNo ratings yet
- Paca112 Topic 1Document5 pagesPaca112 Topic 1Katrina PaquizNo ratings yet
- 1 Answer Introduction: Companies Having Advanced Functions of Procurement Often KnowDocument7 pages1 Answer Introduction: Companies Having Advanced Functions of Procurement Often KnowAkshatNo ratings yet
- Ae8006 - UavDocument2 pagesAe8006 - UavanandNo ratings yet
- Excel Engineering College (Autonomous) : Part-A Answer ALL Questions (10 X 2 20 Marks)Document4 pagesExcel Engineering College (Autonomous) : Part-A Answer ALL Questions (10 X 2 20 Marks)anandNo ratings yet
- EVS Pollution TETDocument12 pagesEVS Pollution TETRajani JPNo ratings yet
- GE2021-Environmental Science and EngineeringDocument2 pagesGE2021-Environmental Science and EngineeringanandNo ratings yet
- Unit - IV C 6: 4.2 Water ConservationDocument14 pagesUnit - IV C 6: 4.2 Water ConservationVISMAYA V NAIRNo ratings yet
- Ae8006 - UavDocument2 pagesAe8006 - UavanandNo ratings yet
- 2021 Review NF 1-6Document6 pages2021 Review NF 1-6anandNo ratings yet
- Department of Aeronautical Engineering Subject Code and Name: Ae8605-Experimental Stress AnalysisDocument1 pageDepartment of Aeronautical Engineering Subject Code and Name: Ae8605-Experimental Stress AnalysisanandNo ratings yet
- Sem and Tem Optical MicrosDocument50 pagesSem and Tem Optical MicrosanandNo ratings yet
- Differential Thermal Analysis & Differential Scanning CalorigraphyDocument19 pagesDifferential Thermal Analysis & Differential Scanning CalorigraphyanandNo ratings yet
- Tom - Int-3Document1 pageTom - Int-3anandNo ratings yet
- Ezgi Bengü Durak - Miraç Daşkin - Semiramis Oğuz - Elif ŞenyuvaDocument21 pagesEzgi Bengü Durak - Miraç Daşkin - Semiramis Oğuz - Elif ŞenyuvaSơnNo ratings yet
- Lug DesignDocument8 pagesLug DesignanandNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Stability AND Control Control: BY Y.K.SinhaDocument24 pagesAircraft Stability AND Control Control: BY Y.K.SinhaArunraj KasiNo ratings yet
- Aircraft StructuresDocument9 pagesAircraft Structuresvenu991100% (1)
- Factors Lift Drag. Foilsim Program: Top ViewDocument2 pagesFactors Lift Drag. Foilsim Program: Top ViewanandNo ratings yet
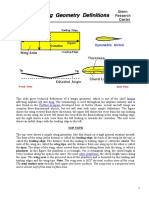
- Wing Area 1Document1 pageWing Area 1anandNo ratings yet
- Design of Aircraft Structures Under Special Consideration NDTDocument68 pagesDesign of Aircraft Structures Under Special Consideration NDTlandingxNo ratings yet
- Piston EngineDocument6 pagesPiston EngineanandNo ratings yet
- Aircraft SA & SD Formula Overview: Trusses PlatesDocument1 pageAircraft SA & SD Formula Overview: Trusses Platesnanduslns07No ratings yet
- Aircraft Structures DefinitionsDocument8 pagesAircraft Structures DefinitionsJerin CyriacNo ratings yet
- AE2028 2 Marks PDFDocument50 pagesAE2028 2 Marks PDFabhilashNo ratings yet
- Conception Aero FighterDocument34 pagesConception Aero Fighterdhruv pramanik100% (2)
- GED 107 EthicsDocument123 pagesGED 107 EthicsKevin Ramiro100% (2)
- Accreditation Form 0Document2 pagesAccreditation Form 0MalikNo ratings yet
- Rosales vs. Burgos, G.R. No. 143573, Jan. 30, 2009Document3 pagesRosales vs. Burgos, G.R. No. 143573, Jan. 30, 2009Jona CalibusoNo ratings yet
- 23 Calo vs. RoldanDocument2 pages23 Calo vs. RoldanGilbert YapNo ratings yet
- Cbse Class 10 Indtroduction To Financial Markets Annual Question Paper 2018 PDF Question Papers vqp1357.htmlDocument8 pagesCbse Class 10 Indtroduction To Financial Markets Annual Question Paper 2018 PDF Question Papers vqp1357.htmlhweta173No ratings yet
- Labour Code - I, LW 4012,8th SemDocument9 pagesLabour Code - I, LW 4012,8th SemfxujyrxfNo ratings yet
- Damodaram Sanjivayya National Law University Visakhapatnam, A.P., IndiaDocument25 pagesDamodaram Sanjivayya National Law University Visakhapatnam, A.P., Indiashaik hidayathulla100% (1)
- Remedies Lecture 2 - Limiting FactorsDocument4 pagesRemedies Lecture 2 - Limiting FactorsAdam 'Fez' FerrisNo ratings yet
- Industrial JurisprudenceDocument38 pagesIndustrial JurisprudenceNandha Kumaran100% (2)
- Tax Receipt Transport Department, Government of West Bengal Registration Authority UTTAR DINAJPUR RTO, West BengalDocument1 pageTax Receipt Transport Department, Government of West Bengal Registration Authority UTTAR DINAJPUR RTO, West BengalSiwam ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Catalan Vs Catalan-LeeDocument4 pagesCatalan Vs Catalan-LeeirvincubsNo ratings yet
- PEPDocument19 pagesPEPMusah Hidir100% (1)
- Presentation On Kiran Bedi.Document13 pagesPresentation On Kiran Bedi.Paridhi ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Ubstantive Ultra Vires Where....Document10 pagesUbstantive Ultra Vires Where....Brajesh SinghNo ratings yet
- SSC V FavilaDocument2 pagesSSC V FavilaAweGooseTreeNo ratings yet
- Drug Addiction in The Philippines ThesisDocument8 pagesDrug Addiction in The Philippines Thesisgbv8rcfq100% (2)
- Nomination and Declaration FormDocument2 pagesNomination and Declaration FormThe Silent MonkNo ratings yet
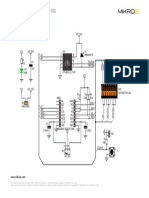
- Secure Soic Click Schematic v100Document1 pageSecure Soic Click Schematic v100Gogo GogevNo ratings yet
- Rentassist - Appform - Filled Up 2Document7 pagesRentassist - Appform - Filled Up 2Malvin ChuaNo ratings yet
- Hassan KAsi-1-1Document1 pageHassan KAsi-1-1afzalkasisimliNo ratings yet
- Ryotwari System and Mahalwari System For Upsc 00bb5430Document5 pagesRyotwari System and Mahalwari System For Upsc 00bb5430k.ganesh024No ratings yet
- NAS Intel (PPP) - PI, AW0400F 161K SQMT, FCL-40FTDocument2 pagesNAS Intel (PPP) - PI, AW0400F 161K SQMT, FCL-40FTthivahgaranNo ratings yet
- Arroyo Vs YuDocument3 pagesArroyo Vs YuWEDDANEVER CORNELNo ratings yet
- Tender Document Scrap MaterialDocument8 pagesTender Document Scrap MaterialDeepakNo ratings yet
- National Law University Odisha, Cuttack: Book ReviewDocument39 pagesNational Law University Odisha, Cuttack: Book ReviewBikash JhaNo ratings yet
- gv001 Multiple Choice PDFDocument2 pagesgv001 Multiple Choice PDFdurgaNo ratings yet
- Railways Tourism, Retiring Rooms, Holidays Customized Tours, LTC Tours, Maharajas, MahaparinirvanDocument2 pagesRailways Tourism, Retiring Rooms, Holidays Customized Tours, LTC Tours, Maharajas, MahaparinirvanNitesh SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Neta Itemfilea882Document7 pagesNeta Itemfilea882Boris AguilarNo ratings yet
- FZT651Document7 pagesFZT651Denis OliveiraNo ratings yet