Professional Documents
Culture Documents
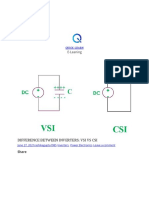
Syllabus Topic: Control of Current Source Inverter (CSI)
Uploaded by
Goud SannyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Syllabus Topic: Control of Current Source Inverter (CSI)
Uploaded by
Goud SannyCopyright:
Available Formats
Syllabus topic : Control of current source
inverter(CSI)
Definition: The current source inverter converts the input direct
current into an alternating current. In current source inverter, the
input current remains constant but this input current is adjustable.
The current source inverter is also called current fed inverter. The
output voltage of the inverter is independent of the load. The
magnitude and nature of the load current depends on the nature of
load impedance.
Current Source Inverter Control
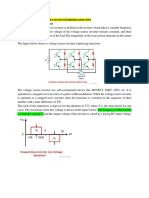
A thyristor current source inverter is shown in the figure below. The
diodes D1-D6 and capacitor C1-C6 provide commutation of thyristor T1-
T6, which are fired with a phase difference of 60º in the sequence of
their number. It also shows the nature of the output current
waveform. The inverter act as a current source due to large
inductance LD in DC link. The fundamental component of motor phase
current is shown in the figure below.
The torque is controlled by varying DC link current Id by changing the
value of Vd. When the supply is AC, a controlled rectifier is connected
between the supply and inverter. When the supply is, DC a chopper
is interposed between the supply and inverter.
The major
advantage of current source inverter is its reliability. In the case of
current source inverter a commutation failure in the same leg does
not occur due to the presence of a large inductance Ld.
In an induction motor, the rise and fall of current are very fast. This
rise and fall of current provide large motor spikes. Therefore a motor
of low leakage inductance is used. The commutation capacitance C1-
C6 reduce the voltage spikes by reducing the rate of rising and fall of
the current. A large value of capacitance is required to sufficiently
reduced the voltage spikes.
You might also like
- PSBD Unit 3 Page No 95Document8 pagesPSBD Unit 3 Page No 95Vishal BhatNo ratings yet
- Febrication of Remote Control Gantry CraneDocument46 pagesFebrication of Remote Control Gantry CraneDebashishParidaNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Simulation of Bidirectional Ac-Dc Power ConverterDocument4 pagesModeling and Simulation of Bidirectional Ac-Dc Power ConverterKalyan Reddy AnuguNo ratings yet
- First Quadrant Single Phase Ac To DC Converter Semiconverter Separately Excited DC MotorDocument9 pagesFirst Quadrant Single Phase Ac To DC Converter Semiconverter Separately Excited DC MotorzaidNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics L2 ConvertersDocument6 pagesPower Electronics L2 ConvertersBakri BugaNo ratings yet
- Project On InverterDocument22 pagesProject On InverterSaikat Mitra43% (7)
- Bridge Rectifier: Circuit Diagram & Its WorkingDocument12 pagesBridge Rectifier: Circuit Diagram & Its WorkingChandra Sekhar CNo ratings yet
- Z Source ConverterDocument12 pagesZ Source Converterravirnjn88No ratings yet
- PDF Sinewavechokes 1 3Document3 pagesPDF Sinewavechokes 1 3Vanesa JeronimoNo ratings yet
- Buck Converter: Assignment - 4 (OE)Document6 pagesBuck Converter: Assignment - 4 (OE)Muskan Kaur CheemaNo ratings yet
- Buck ConverterDocument52 pagesBuck Convertermayankrkl50% (2)
- Presentation 1Document26 pagesPresentation 1Siva ForeviewNo ratings yet
- AVR'sDocument3 pagesAVR'sMeghanath AdkonkarNo ratings yet
- Electronic Circuits Power Supply Electronic Basic Components AC Power Devices Like Home AppliancesDocument21 pagesElectronic Circuits Power Supply Electronic Basic Components AC Power Devices Like Home AppliancesTushar GoelNo ratings yet
- Boost Converter: The Basic Schematic of A Boost Converter. The Switch Is Typically A MOSFET, IGBT, or BJTDocument7 pagesBoost Converter: The Basic Schematic of A Boost Converter. The Switch Is Typically A MOSFET, IGBT, or BJTSpk SudhinNo ratings yet
- Study of AC and-WPS OfficeDocument6 pagesStudy of AC and-WPS OfficeBeena PalNo ratings yet
- T10A Converters and Inverters: Chapter - 4Document11 pagesT10A Converters and Inverters: Chapter - 4lvsaruNo ratings yet
- DC Power Supply CircuitDocument7 pagesDC Power Supply CircuitEhtasham Ul HassanNo ratings yet
- Single Ended Primary Inductor ConverterDocument4 pagesSingle Ended Primary Inductor ConverterAmarnath M DamodaranNo ratings yet
- Electrical SeminarDocument14 pagesElectrical Seminarrahulraj20No ratings yet
- Buck ConverterDocument5 pagesBuck ConverterM Zeeshan WazirNo ratings yet
- Single Phase InverterDocument7 pagesSingle Phase InverterBHALAJI BIRLANo ratings yet
- Boost Converter - WikipediaDocument13 pagesBoost Converter - WikipediaADITYA PANDEYNo ratings yet
- Ripple Current Reduction Technique For DC To DC Converter Using Tapped InductorDocument6 pagesRipple Current Reduction Technique For DC To DC Converter Using Tapped InductorInternational Journal of Latest Research in Engineering and TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Simple AC To DC Converter Using Bridge RectifierDocument2 pagesSimple AC To DC Converter Using Bridge RectifierMahum JamilNo ratings yet
- Direct Current and Alternating CurrentDocument4 pagesDirect Current and Alternating CurrentYuva RajNo ratings yet
- LLC Resonant Converter For Battery Charging Applications: A.Sakul Hameed, S.Prabhu, Dr.M.SathiskumarDocument8 pagesLLC Resonant Converter For Battery Charging Applications: A.Sakul Hameed, S.Prabhu, Dr.M.SathiskumartheijesNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of Luo Converter For Electric Vehicle ApplicationsDocument5 pagesDesign and Implementation of Luo Converter For Electric Vehicle ApplicationsseventhsensegroupNo ratings yet
- DC Power Supply DocumentationDocument4 pagesDC Power Supply DocumentationAashi BhawsarNo ratings yet
- Regulated DC Power SupplyDocument15 pagesRegulated DC Power SupplynalumilanimeNo ratings yet
- Q. What Do You Mean by Half Wave Rectification and Full Wave Rectification?Document5 pagesQ. What Do You Mean by Half Wave Rectification and Full Wave Rectification?Huidrom SharatNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- DC-DC Konverter Basic DesignDocument16 pagesDC-DC Konverter Basic DesignTaufik InsaniNo ratings yet
- Tugas 6 Kendali Mesin Listrik Industri - Aulia Silfani - 20130072Document8 pagesTugas 6 Kendali Mesin Listrik Industri - Aulia Silfani - 20130072Aulia SilfaniNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 14 (Ch. 5) DC-DC Converters: ECE 452 Power ElectronicsDocument24 pagesLECTURE 14 (Ch. 5) DC-DC Converters: ECE 452 Power ElectronicsHarsha AnantwarNo ratings yet
- 12V To 24V DC DC ConverterDocument4 pages12V To 24V DC DC ConverterDavid Arrata ParralesNo ratings yet
- Power Supply Description:: The Power Supply Circuit Comprises of Four Basic PartsDocument19 pagesPower Supply Description:: The Power Supply Circuit Comprises of Four Basic PartsEr. Piush Jindal100% (1)
- 3 Level InverterDocument63 pages3 Level InverterThirumal ValavanNo ratings yet
- Batch 2 PE CEP Report 2Document10 pagesBatch 2 PE CEP Report 2Mohsin IqbalNo ratings yet
- Active Power Factor Correction Technique For Single Phase Full Bridge RectifierDocument6 pagesActive Power Factor Correction Technique For Single Phase Full Bridge RectifierAnand KumarNo ratings yet
- Power Supply 1Document6 pagesPower Supply 1api-19786583No ratings yet
- DC - AC ConvertorsDocument3 pagesDC - AC Convertorskarthick LNo ratings yet
- Resonant DC Link InvertersDocument6 pagesResonant DC Link InvertersSanchit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Final ReviewDocument19 pagesFinal ReviewSanyam JainNo ratings yet
- Using A Synchronous Converter For Harmonic Mitigation With AC DrivesDocument10 pagesUsing A Synchronous Converter For Harmonic Mitigation With AC Drivesmit85No ratings yet
- Epp Project-Jon's PartDocument3 pagesEpp Project-Jon's PartJonathanCharanrajNo ratings yet
- ANE 620S Course Notes 2015Document177 pagesANE 620S Course Notes 2015TimothyShapamNo ratings yet
- 4 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page4 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- Safety-enhanced-high-step-up-DC-DC-converter-for-ac-photovoltaic-module-applications Chapter 2 DC-DC Converters 12 PageDocument16 pagesSafety-enhanced-high-step-up-DC-DC-converter-for-ac-photovoltaic-module-applications Chapter 2 DC-DC Converters 12 PageVenkatesh ChintalaNo ratings yet
- Lab Innovation Project DC DCDocument15 pagesLab Innovation Project DC DCAyush MittalNo ratings yet
- Welcome To All The Teacher's Of: SmitDocument30 pagesWelcome To All The Teacher's Of: Smitsrvdhar100% (2)
- Transformer Based Resonant DC Inverter For Brushless DC Motor Drive SystemDocument7 pagesTransformer Based Resonant DC Inverter For Brushless DC Motor Drive SystemStudents Xerox ChidambaramNo ratings yet
- Boost Converter - WikipediaDocument6 pagesBoost Converter - WikipediaSudip MondalNo ratings yet
- Centre Tapped Transformer SpecificationsDocument4 pagesCentre Tapped Transformer SpecificationsALNATRON GROUPSNo ratings yet
- Converter Vs InverterDocument8 pagesConverter Vs InverterPrasad ChandramohananNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- CSI and VSI (ch-1) DifferenceDocument9 pagesCSI and VSI (ch-1) DifferenceGoud SannyNo ratings yet
- Answer QB 2Document22 pagesAnswer QB 2Goud SannyNo ratings yet
- W19 Apy 2160913Document2 pagesW19 Apy 2160913Goud SannyNo ratings yet
- W20 Apy 2160913Document2 pagesW20 Apy 2160913Goud SannyNo ratings yet
- S21 Apy 2160913Document1 pageS21 Apy 2160913Goud SannyNo ratings yet