Professional Documents
Culture Documents
8-2 Notes Geometry
Uploaded by
Noah BlautCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
8-2 Notes Geometry
Uploaded by
Noah BlautCopyright:
Available Formats
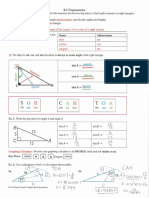
8-2 The Pythagorean Theorem and Its Converse
Learning ®: Use the Pythagorean Theorem and the Converse of the Pythagorean Theorem.
THE PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM
The Pythagorean Theorem relates the lengths of the hyp otenuse (side opposite the right angle) tiypotenuce
and lets (sides adjacent to the right angle) of a right triangle. L
leg
Pythagorean Theorem
In a right triangle, the sum of the squares of the lengths
:1 of the legs is equal to the square of the length of the c
hypotenuse.
-
C A
A Pythagorean triple is a set of three whole numbers a, b, and c, such that a2 + b 2 = c2.
Common Pythagorean Triples
3,4,5 5, 12, 13 8, 15, 17 7, 24, 25
6, 8, 10 10,24,26 16,30,34 14, 48, 50
9, 12, 15 15,36,39 24,45, 51 21,72,75
3x, 4x, 5x 5x, 12x, 13x 8x, 15x, 17x 7x, 24x, 25x
The most common Pythagorean triples are in bold.
The other triples are found by multiplying each number in the triple by the same factor.
CONVERSE OF THE PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM
Converse of the Pythagorean Theorem
If the sum of the squares of the lengths of the shortest sides of a
triangle is equal to the square of the length of the longest side,
then the triangle is a right triangle.
Ifc2 = a2 + 2, then AABC isajihttriangle. J ' A
CLASSIFYING TRIANGLES
The Converse of the Pythagorean Theorem and the Pythagorean Inequality Theorems can be used
to classify triangles as right, acute, or obtuse.
• If c2 = a2 + b2, then the triangle is
• If c2 > a2 + Li 2 , then the triangle is obtuse Pythagorean Inequality
Theorems
• If c2 <a2 + Li2, then the triangle is acute.
J
EUS 08 Special Right Triangles and Trigonometry Pre-AP Geometry
8-2 EXAMPLES
1. Find x by using the Pythagorean Theorem or a Pythagorean triple.
a. b.
'TuiJ
2. Determine whether each set of numbers can be the measures of the sides of a triangle. If so, classify the
triangle as acute, obtuse, or right. Justify your answer.
a. 4,12,13 b. 10, 12,23
I 23
2 37 V
L > ft
3. Determine whether L\XYZ is an acute, right, or obtuse triangle for the given vertices.
X(-3,-2),Y(-1,0),Z(0,-1) ( ? a
XY=
CA LOO_
XZ =
Fr
4. Find the area of the triangle.
26 in
20rn
lbl'1
26 1 0-1
EUS 08 Special Right Triangles and Trigonometry Pre-AP Geometry
You might also like
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- 6 1 Angles of PolygonsDocument2 pages6 1 Angles of PolygonsNoah BlautNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- 8-4 Notes GeometryDocument2 pages8-4 Notes GeometryNoah Blaut100% (1)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- 8-1 Altitude To Hypotenuse TheoremDocument1 page8-1 Altitude To Hypotenuse TheoremNoah BlautNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- 8-1 Altitude To Hypotenuse TheoremDocument1 page8-1 Altitude To Hypotenuse TheoremNoah BlautNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Guns Germs and Steel Video Worksheet - AP HUGDocument2 pagesGuns Germs and Steel Video Worksheet - AP HUGNoah BlautNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Hs Geometry PDFDocument26 pagesHs Geometry PDFapi-255155256No ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- MATH 8 Q3 MODULE 5 22pDocument22 pagesMATH 8 Q3 MODULE 5 22pMarian IntalNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument24 pagesLesson PlanMagbag Elise100% (1)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- 7.1 Geometric MeanDocument21 pages7.1 Geometric MeanLastCardHolder0% (1)
- Lines and Angles 5.2Document29 pagesLines and Angles 5.2Raheel Abbas BhalamNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- CSEC Mathematics June 2008 P2 (Trinidad) 16pgsDocument16 pagesCSEC Mathematics June 2008 P2 (Trinidad) 16pgszarzsultan12No ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Calculus I With Analytic Geometry Test RevDocument5 pagesCalculus I With Analytic Geometry Test Revarbee.iiooNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Unit 3.3. Stereographic ProjectionDocument36 pagesUnit 3.3. Stereographic Projectioncoxebe7133No ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Projection of SolidsDocument23 pagesProjection of SolidsUsama AnsariNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- 2011 Trig Star Sample TestDocument6 pages2011 Trig Star Sample TestlsudhakarNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Geometry SheetDocument10 pagesGeometry SheetRakibul Hasan ArjuNo ratings yet
- WHLP Math 8 q3 Week8Document34 pagesWHLP Math 8 q3 Week8Abib LapineteNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Objectives To Find Compositions of Isometries, Including Glide ReflectionsDocument7 pagesObjectives To Find Compositions of Isometries, Including Glide ReflectionsAbood SafadiNo ratings yet
- MensurationDocument3 pagesMensurationemit.deshunNo ratings yet
- LAS 8-Quarter 3-Module 3Document11 pagesLAS 8-Quarter 3-Module 3Ara Herrera50% (4)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Vector Revision Worksheet G12Document5 pagesVector Revision Worksheet G12ayat essaNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Objectives: Laboratory 1. The Structure of Mechanisms, Fundamentals and ExamplesDocument11 pagesObjectives: Laboratory 1. The Structure of Mechanisms, Fundamentals and ExamplesGabriel IulianNo ratings yet
- Triangle 3Document12 pagesTriangle 3Vilas ShindeNo ratings yet
- Regents Exam Questions G.CO.B.7: Triangle Congruency NameDocument7 pagesRegents Exam Questions G.CO.B.7: Triangle Congruency NameAzat TurapbekovNo ratings yet
- NAT Reviewer Math Grade 6Document2 pagesNAT Reviewer Math Grade 6Kaymart BarridaNo ratings yet
- TesselationsDocument12 pagesTesselationskrittinkalraNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Class 9Document91 pagesWorksheet Class 9bulletinsocketNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- 8907class - XDocument8 pages8907class - XeagleyeNo ratings yet
- Short Notes and Formulas For Mensuration (2D Figures)Document11 pagesShort Notes and Formulas For Mensuration (2D Figures)jigneshNo ratings yet
- Maths 1B Practice PapersDocument22 pagesMaths 1B Practice Papersyashwanth2006.schoolNo ratings yet
- (August 15, 2018) Diagnostic TestDocument5 pages(August 15, 2018) Diagnostic TestReyniel Layson VergaraNo ratings yet
- Y7 Math RevisionDocument6 pagesY7 Math RevisionAskiitians Education CentreNo ratings yet
- Translation of The Kimberling's Glossary Into Barycentrics (V48-Dvipdfm)Document231 pagesTranslation of The Kimberling's Glossary Into Barycentrics (V48-Dvipdfm)AltananyNo ratings yet
- IGO 2019 Booklet enDocument43 pagesIGO 2019 Booklet enNicolas RubioNo ratings yet
- MHT Cet Question Bank MathsDocument31 pagesMHT Cet Question Bank Maths86bqmhkypwNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)