Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gen Patho MDTRM
Uploaded by
rienz nicnic peraltaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gen Patho MDTRM
Uploaded by
rienz nicnic peraltaCopyright:
Available Formats
General Patholog
A. Case Study: A 40 year old patient got a car accident and he was found to have
femoral shaft fracture and then he suddenly developed dyspnea, cyanosis, and
shock and passed away immediately after surgery. There was no massive blood
loss at the time of trauma or during surgery. What is the probable cause of
death? Explain.
The probable cause of death is shock and fat embolism. The reason behind this
is that hypovolemic or traumatic shock may occur due to crucial damaged on
extremities resulting to hemmorhage. Based on the case the patient suffers
from femoral shaft fracture which then resulted to developing dyspnea,
cyanosis. We all know that bone is a very vascular body structure, a fracture
can lead to lost of large quantity of blood. However according to the case,
there was no massive blood loss at the time of trauma which could be because
there is no external lesion which then resulted to blood accumulation to the
site of fracture. Due to the femoral fracture of the patient, it allows marrow
contents (fats) out into the circulation. Possibly this resulted to obstruction of
the arteries from the brain or the lungs.
Dyspnea, or the shortness of breath of the patient resulted to cyanosis
because there is a poor supply of oxygen throughout the body.
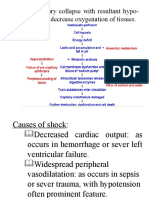
B. Discuss the causes of hypovolemic and cardiogenic shock.
HYPOVOLEMIC SHOCK CARDIOGENIC SHOCK
- This is shocked caused by reduced This is shock that results from severe
blood volume. This type of shock causes: depression of cardiac performance. It
haemorrhage, diarrhea and vomiting, primarily results from pump failure. This
burns, trauma, and the like. type of shock causes: myopathic and
mechanical.
Haemorrhage- Due to oxygen Myophatic causes of cardiogenic shock
deprivation, endothelial cell apoptosis is includes the following: acute myocardial
induced following hypovolemic shock. infraction, mycocarditis, dilated
Most often, hypovolemic shock is cardiomyopathy/hypertrophic
secondary to rapid blood loss. cardiomyopathy, and myocardial
depression in septic shock.
Diarrhea and vomiting- It is also possible
to get hypovolemic shock from losing a Mechanical is divided into two:
large amount of fluids after a lot of Intracardiac and Extracardiac.
diarrhea, throwing up or sweating. Intracardiac involves the following: left
ventricle outflow obstruction, reduction
Burns- it results form the interplay of in forward cardiac output, and
direct tissue injury, hypovolemia, and the arrhythmia. Under extracardiac, it
release of multiple mediators of involves the following: pericardial
inflammation, with effects on both the temponade, tension pneumothorax,
microcirculation and the function of the
heart and lungs. acute massive pulumunary
hypertension,a and sever pulumunary
hypertension.
You might also like
- Medicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtFrom EverandMedicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Covid-19 Test Report: Patient Name: Akash GargDocument1 pageCovid-19 Test Report: Patient Name: Akash GargGenestrings Diagnostic CenterNo ratings yet
- Lessons Learned From The Dog GenomeDocument11 pagesLessons Learned From The Dog GenomebellonicoNo ratings yet
- ShockDocument63 pagesShockAhmedNo ratings yet
- Principles of Managent of Hypovolemic Shock in ADocument43 pagesPrinciples of Managent of Hypovolemic Shock in Aasi basseyNo ratings yet
- Cardiogenic Shock: by Fritzanella LafondDocument42 pagesCardiogenic Shock: by Fritzanella LafondhaphahapNo ratings yet
- Shock and Its Nursing InterventionsDocument3 pagesShock and Its Nursing InterventionsWendy EscalanteNo ratings yet
- Cardiogenic ShockDocument21 pagesCardiogenic ShockIslamOteshNo ratings yet
- Cardiogenic ShockDocument26 pagesCardiogenic ShockAnggun V. M SitumorangNo ratings yet
- Cardiogenic Shock: Historical AspectsDocument24 pagesCardiogenic Shock: Historical AspectsnugessurNo ratings yet
- SHOCK DiscussionDocument22 pagesSHOCK DiscussionNavpreet Kaur100% (1)
- JericaDocument5 pagesJericaapi-26570979No ratings yet
- 7 - Hemodynamic Disorders ShockDocument21 pages7 - Hemodynamic Disorders ShockShna SaadiNo ratings yet
- HemodynamicDocument20 pagesHemodynamicمحمد آل راشدNo ratings yet
- Shock AssignmentDocument6 pagesShock Assignmentareebafarooq820No ratings yet
- Shock Seminar-IDocument26 pagesShock Seminar-ISimran JosanNo ratings yet
- Syahirah's Essay - ShockDocument3 pagesSyahirah's Essay - ShockNursyahirah IshakNo ratings yet
- Cardiogenic ShockDocument11 pagesCardiogenic ShockSunil YadavNo ratings yet
- Shock: Ii PharmdDocument25 pagesShock: Ii PharmdBharath GowdaNo ratings yet
- DR Dhiman BanikCariogenic Shock Final 2022 DDDocument59 pagesDR Dhiman BanikCariogenic Shock Final 2022 DDCloudySkyNo ratings yet
- Lec. 10 Hemodynamics DisordersDocument22 pagesLec. 10 Hemodynamics DisordersSamiroNo ratings yet
- ShockDocument2 pagesShockSherin ThomasNo ratings yet
- Cva Power PointDocument167 pagesCva Power PointJen Passilan100% (14)
- Loss of ConciousnessDocument57 pagesLoss of ConciousnessMuhamad AdiwibowoNo ratings yet
- Shock Mbbs 5Document56 pagesShock Mbbs 5Nadun MethwadaneNo ratings yet
- نسخة HeartDocument29 pagesنسخة HeartKyunaNo ratings yet
- 3 ShockDocument12 pages3 ShockAiden JosephatNo ratings yet
- ShockDocument64 pagesShockAnusha VergheseNo ratings yet
- Myocardial InfarctionDocument20 pagesMyocardial Infarction* mokhtar !!50% (2)
- Type Description Principal Mechanism Clinical Examples Cardiogenic ShockDocument1 pageType Description Principal Mechanism Clinical Examples Cardiogenic ShockRLI23ny100% (1)
- 4th Auguest 2016 Fluid and Hemodynamic Disorders 2011Document81 pages4th Auguest 2016 Fluid and Hemodynamic Disorders 2011Majkel Benche Custodio MllNo ratings yet
- ShockDocument36 pagesShockJohnryan NdiranguNo ratings yet
- In The Name of Allah, The Most Beneficent, The Most MercifulDocument40 pagesIn The Name of Allah, The Most Beneficent, The Most MercifulISMAILNo ratings yet
- Presenter: DR Edalia Facilitator: Prof AdamDocument35 pagesPresenter: DR Edalia Facilitator: Prof AdamUzma KhanNo ratings yet
- Complications of FracturesDocument19 pagesComplications of Fracturesمحمد رأفتNo ratings yet
- Although Shock Has Been Recognised For Over 100 YearsDocument4 pagesAlthough Shock Has Been Recognised For Over 100 YearsRusty HoganNo ratings yet
- MR Elamin ShockDocument70 pagesMR Elamin ShockMohammed Abd AlgadirNo ratings yet
- Cardiac FailureDocument13 pagesCardiac FailureButool FatimaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8Document7 pagesLecture 8Grafu Andreea AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Shock - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDocument5 pagesShock - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfSYAFIRA LAILA NURULITANo ratings yet
- Shock: Karolina Doskocz gr2BDocument4 pagesShock: Karolina Doskocz gr2BKarolina DoskoczNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10Document13 pagesLecture 10Grafu Andreea AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Shock and AkiDocument22 pagesShock and AkikiflomNo ratings yet
- Hypovolemic ShockDocument10 pagesHypovolemic ShockAbdillah Fat-hiNo ratings yet
- 04 08 ShockDocument6 pages04 08 Shockthev0206No ratings yet
- Shock HypovolemicDocument16 pagesShock HypovolemicTitinNo ratings yet
- 3 - Heart Failure (Modified)Document17 pages3 - Heart Failure (Modified)Ali Al-QudsiNo ratings yet
- HypovolemiaDocument11 pagesHypovolemiaMaheenUsmaniNo ratings yet
- Diffrent Types of ShockDocument6 pagesDiffrent Types of ShockBasit AliNo ratings yet
- Complications of Acute Myocardial InfarctionDocument5 pagesComplications of Acute Myocardial Infarctionlourdesfercab_at_msn100% (1)
- Ischemic Heart Disease (IHD)Document35 pagesIschemic Heart Disease (IHD)Ali Akand AsifNo ratings yet
- StrokeDocument3 pagesStrokeLyn LynNo ratings yet
- Aula de ChoqueDocument16 pagesAula de Choqueapi-3726545100% (1)
- IntroductionDocument13 pagesIntroductionSiyara AntonyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document5 pagesLecture 5Isak ShatikaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory Failure (Shock) : Dr. Bernardo Dámaso MataDocument84 pagesCirculatory Failure (Shock) : Dr. Bernardo Dámaso MataDeivis Dan ErickNo ratings yet
- Cardiogenic ShockDocument31 pagesCardiogenic ShockLovelights ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Aaa Ayush Patel (Shock)Document53 pagesAaa Ayush Patel (Shock)Ayush PatelNo ratings yet
- Shock NotesDocument7 pagesShock NotesAnitha NoronhaNo ratings yet
- Cardiomyopathy: Restrictive Heart DiseaseDocument18 pagesCardiomyopathy: Restrictive Heart DiseaseMitch GabuyaNo ratings yet
- Kardiogenik SyokDocument43 pagesKardiogenik SyokGalih Arief Harimurti WawolumajaNo ratings yet
- STROKE: Handbook with activities, exercises and mental challengesFrom EverandSTROKE: Handbook with activities, exercises and mental challengesNo ratings yet
- Pracs PoeDocument2 pagesPracs Poerienz nicnic peraltaNo ratings yet
- Pain ToneDocument20 pagesPain Tonerienz nicnic peraltaNo ratings yet
- Key AnswersDocument1 pageKey Answersrienz nicnic peraltaNo ratings yet
- NSTP2 Activity On AccidentsDocument1 pageNSTP2 Activity On Accidentsrienz nicnic peraltaNo ratings yet
- TABLE of GENETIC DISORDERSDocument9 pagesTABLE of GENETIC DISORDERSrienz nicnic peraltaNo ratings yet
- Note in PE (Self Defence)Document2 pagesNote in PE (Self Defence)rienz nicnic peraltaNo ratings yet
- Brodmann Areas 1Document1 pageBrodmann Areas 1rienz nicnic peraltaNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Breathing How Ventilation Is RegulatedDocument2 pagesAutonomic Breathing How Ventilation Is Regulatedrienz nicnic peraltaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Indications For Ultraviolet RadiationDocument3 pagesClinical Indications For Ultraviolet Radiationrienz nicnic peraltaNo ratings yet
- Definition of Antidiuretic HormoneDocument2 pagesDefinition of Antidiuretic Hormonerienz nicnic peraltaNo ratings yet
- KINESIOLOGYDocument1 pageKINESIOLOGYrienz nicnic peraltaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument7 pagesRespiratory Systemrienz nicnic peraltaNo ratings yet
- The Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone System - RAASDocument3 pagesThe Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone System - RAASrienz nicnic peraltaNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Psycho-Social and Health Problems Faced by Homeless Population in Visakhapatnam CityDocument8 pagesUnderstanding The Psycho-Social and Health Problems Faced by Homeless Population in Visakhapatnam CityMutluri AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggris UTS Kelas 5 SMT 2Document5 pagesBahasa Inggris UTS Kelas 5 SMT 2Aulia Laily MaulindaNo ratings yet
- Externalities & Public GoodsDocument13 pagesExternalities & Public GoodsAkshay ModakNo ratings yet
- Assignment 15th BatchDocument2 pagesAssignment 15th Batchgagon-2021816127No ratings yet
- EntDocument11 pagesEntkhuzaima9No ratings yet
- What Has Psychotherapy Inherited From Carl RogersDocument4 pagesWhat Has Psychotherapy Inherited From Carl Rogerscris kalitoNo ratings yet
- Contribution - 2019 - She Ji The Journal of Design Economics and InnovationDocument1 pageContribution - 2019 - She Ji The Journal of Design Economics and InnovationnitakuriNo ratings yet
- ICTAPP 23 36 FinalVersionDocument7 pagesICTAPP 23 36 FinalVersionzobiNo ratings yet
- Format For Recording Medical Examinatios of SeafarersDocument4 pagesFormat For Recording Medical Examinatios of SeafarersАлексNo ratings yet
- Ijcpd-15-S103 MetanalysisDocument11 pagesIjcpd-15-S103 MetanalysisGabriela ZuritaNo ratings yet
- Total Health Chapter 1,2 Review GameDocument123 pagesTotal Health Chapter 1,2 Review GameAlicia HigdonNo ratings yet
- Carestream Quantum Medical Imaging QS 550 Tubestand DC30 034 RH 201506Document50 pagesCarestream Quantum Medical Imaging QS 550 Tubestand DC30 034 RH 201506D “DAKHobby” KNo ratings yet
- Anti-Inflammatory Diet: What Is Inflammation?Document13 pagesAnti-Inflammatory Diet: What Is Inflammation?Perrela PerrelaNo ratings yet
- Vha Class III ListingDocument2,575 pagesVha Class III ListingpvenkyNo ratings yet
- Blended Learning 1 (Week 5)Document6 pagesBlended Learning 1 (Week 5)nurul syazwaniNo ratings yet
- Natu Es Dsmepa 1ST - 2ND QuarterDocument38 pagesNatu Es Dsmepa 1ST - 2ND QuarterSenen AtienzaNo ratings yet
- CID Cheese Mozzarella LiteDocument8 pagesCID Cheese Mozzarella LiteBayu SyurahmadNo ratings yet
- Occupational Therapy Assessment: 1. SensesDocument17 pagesOccupational Therapy Assessment: 1. SensesVIJAYA DHARSHINI M Bachelor in Occupational Therapy (BOT)No ratings yet
- P RM 01 Incident Reporting PolicyDocument44 pagesP RM 01 Incident Reporting PolicypatientsafetyNo ratings yet
- Dengue Fever 2Document5 pagesDengue Fever 2Gayitiri MenonNo ratings yet
- Angelina Hull Student - Heritagehs - Argumentative Essay - Student Name - Class Period - Spring 19 - H English 1Document5 pagesAngelina Hull Student - Heritagehs - Argumentative Essay - Student Name - Class Period - Spring 19 - H English 1api-461590822No ratings yet
- Basic Guide To Proposal Writing: Step 1: Developing Your Proposal IdeaDocument11 pagesBasic Guide To Proposal Writing: Step 1: Developing Your Proposal Ideanisaralamjan8616100% (2)
- Ineffective Health MaintenanceDocument2 pagesIneffective Health MaintenanceMonchee Yuson67% (6)
- Clinical Surgical 1Document2 pagesClinical Surgical 1Ohana NanaNo ratings yet
- Eating Disorders: Anorexia Nervosa/Bulimia NervosaDocument15 pagesEating Disorders: Anorexia Nervosa/Bulimia NervosaCay Sevilla100% (8)
- Formal Special Areas: Border Management Red Corridor PncpcaDocument29 pagesFormal Special Areas: Border Management Red Corridor PncpcaAnirban MandalNo ratings yet
- 4217 - First Aid and Safety EducationDocument6 pages4217 - First Aid and Safety EducationSalahuddeen AbubakarNo ratings yet
- Hannahs CVDocument2 pagesHannahs CVabbief1No ratings yet