Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Conditionals
Uploaded by
Marcella MagaldiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Conditionals
Uploaded by
Marcella MagaldiCopyright:
Available Formats
Conditionals
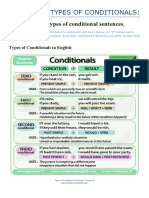
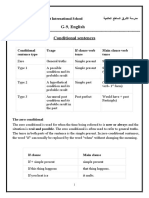
Zero conditional
The zero conditional uses the present tense in both
clauses and is used to talk about something that is
always or generally true.
- The present tense signifies that these actions are
both possible and typical.
- TYPE : If + simple present, simple present
If I wake up early, I always read in bed.
First conditional
The first conditional uses the present tense in the if
clause and the future tense in the result clause.
- This form is used to talk about something that is a
probable future result of a condition.
TYPE: If + simple present, will + base verb
Second conditional
The second conditional uses the past tense in the if clause
and a modal and base verb in the result clause.
- This form is used to talk about a hypothetical situation
that cannot happen or is unlikely to happen.
- TYPE: If + simple past, modal + base verb
Third conditional
The third conditional uses the past perfect in the if clause and a
modal and present perfect in the result clause.
- This form is used to talk about a hypothetical situation in the
past that did not happen – typically with an outcome that did
not happen and is perhaps the opposite of what did happen.
- Form: If + past perfect, modal + present perfect
Mixed Conditionals
Mixed conditionals combine the second and third conditionals to
present both an unreal condition either in the
past or the present and an unreal result either in the past or the
present.
- The first form presents an unreal condition in the past that changes
an unreal outcome in the present (the past changes the present).
- Form 1: If + past perfect, modal + base
- The second form presents an unreal condition in the present that changes
an unreal outcome in the past (the present changes the past).
- Form 2: If + simple past, would/could + present perfect
You might also like
- Types of Mixed ConditionalsDocument3 pagesTypes of Mixed ConditionalsДражен ЈовићNo ratings yet
- Form and Meaning: Zero ConditionalDocument2 pagesForm and Meaning: Zero ConditionalHampnie HambertNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument11 pagesConditionalsPetra StefanescuNo ratings yet
- English Grammar Practice: Explanations and Exercises with KeyFrom EverandEnglish Grammar Practice: Explanations and Exercises with KeyNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive Voice, Conditional Sentence & Reported SpeechDocument22 pagesActive and Passive Voice, Conditional Sentence & Reported SpeechTrịnh Quốc HiếuNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentenceDocument7 pagesConditional SentenceAbhieey Choi Soo Hyun100% (1)
- Conditional Sentence and WishesDocument11 pagesConditional Sentence and WishesMelati Dubidu Bidam67% (9)
- ConditionalDocument22 pagesConditionalMae CabanasNo ratings yet
- ConditionalDocument3 pagesConditionalSalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Conditionals IfDocument3 pagesConditionals IfSalsabila TritaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Conditional SentencesDocument2 pagesUnderstanding Conditional SentencesHafizullah ShirzadNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentences JDocument2 pagesConditional Sentences Jsaad saleemNo ratings yet
- Conditionals 1Document11 pagesConditionals 1Ciudadano KlandestinoNo ratings yet
- Understanding Conditional SentencesDocument2 pagesUnderstanding Conditional SentencesJamaica Bancairen ArtiagaNo ratings yet
- Kel. 11 Conditonal SentenceDocument15 pagesKel. 11 Conditonal SentenceNu FaNo ratings yet
- Learn the 5 Types of Conditional SentencesDocument2 pagesLearn the 5 Types of Conditional SentencesKahnMéndezNo ratings yet
- IF ClauseDocument5 pagesIF ClauseJuliette Viveros UlibarryNo ratings yet
- Mixed ConditionalsDocument4 pagesMixed Conditionalssee yaNo ratings yet
- Mixed ConditionalsDocument4 pagesMixed Conditionalssheyla fresnedaNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentenceDocument2 pagesConditional SentenceFitri HanidaNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH ConditionalsDocument8 pagesENGLISH ConditionalsaymarmarchettiNo ratings yet
- EnglishDocument4 pagesEnglishapi-278092100No ratings yet
- Cowan resumen: Types of conditional sentencesDocument18 pagesCowan resumen: Types of conditional sentencesvictoriaNo ratings yet
- Amanda. T Xii A 2: ConditionalDocument4 pagesAmanda. T Xii A 2: ConditionalGeraldine SitanggangNo ratings yet
- The Zero ConditionalDocument5 pagesThe Zero ConditionalEduard Hernan Cardona VillamilNo ratings yet
- Tên đề tài:: Trường Đại Học Hải Phòng Khoa Ngoại NgữDocument13 pagesTên đề tài:: Trường Đại Học Hải Phòng Khoa Ngoại Ngữmicheal longdikNo ratings yet
- Conditionals: Learn types and uses in argumentsDocument7 pagesConditionals: Learn types and uses in argumentsRoxan Pascua GanadoNo ratings yet
- 1st and Zero - ConditionalsDocument3 pages1st and Zero - ConditionalsDarkCreeper13No ratings yet
- G5+8 - Ms. Amara - Conditional SentencesDocument10 pagesG5+8 - Ms. Amara - Conditional SentencesHadjab LyesNo ratings yet
- Learn about the 3 types of conditional sentencesDocument3 pagesLearn about the 3 types of conditional sentencesDian daniNo ratings yet
- "The Unreal Past": ConditionalsDocument3 pages"The Unreal Past": ConditionalsLuisa Fernanda Orozco LópezNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentences & Passive VoiceDocument8 pagesConditional Sentences & Passive Voicesfhrdia19No ratings yet
- Conditional Sentence Type Usage If Clause Verb Tense Main Clause Verb TenseDocument4 pagesConditional Sentence Type Usage If Clause Verb Tense Main Clause Verb TenseStancu AlinNo ratings yet
- Conditional Theory N Exercise For Class PDFDocument15 pagesConditional Theory N Exercise For Class PDFUmu NeroNo ratings yet
- Junior Two GrammarDocument29 pagesJunior Two GrammarRashid KhanNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument1 pageConditionalsSovann MonynithNo ratings yet
- Conditianal - If ClausesDocument15 pagesConditianal - If ClausesJbour LaithNo ratings yet
- Name:Hosea Roinaldo Class:XII MIPA 2/19 Conditional SentencesDocument4 pagesName:Hosea Roinaldo Class:XII MIPA 2/19 Conditional SentenceshosearoinaldoNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument4 pagesConditionalsAndeeeaNo ratings yet
- MIXED CONDITIONALS (1)Document1 pageMIXED CONDITIONALS (1)ad7120118No ratings yet
- InggrisDocument4 pagesInggrisZhong XinaNo ratings yet
- Conditionals ExplainedDocument2 pagesConditionals ExplainedFlorencia Custo BlanchNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument2 pagesConditionalskonspyNo ratings yet
- S6 ConditionalsDocument20 pagesS6 ConditionalsPedro FERREIRANo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentences G 9 ENGDocument3 pagesConditional Sentences G 9 ENGEnas MujaliNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentence TypeDocument6 pagesConditional Sentence TypeHarsh SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Zero, First, Second, Third and Mixed ConditionalsDocument4 pagesZero, First, Second, Third and Mixed ConditionalschelseaNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentence TypesDocument8 pagesConditional Sentence TypesShim HanelNo ratings yet
- The Hypothetical ConstructionsDocument22 pagesThe Hypothetical ConstructionsComan AlexandraNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Conditional Sentences: ClauseDocument8 pages2.1 Conditional Sentences: ClauseArmeliaNo ratings yet
- Type 1 Conditional (Open Condition)Document4 pagesType 1 Conditional (Open Condition)Hung TranNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentencesDocument13 pagesConditional SentencesDiana DandiNo ratings yet
- If clause determines main clause outcomeDocument95 pagesIf clause determines main clause outcomemmmmmNo ratings yet
- Grammar: Conditional Sentences-Rules You Need To KnowDocument3 pagesGrammar: Conditional Sentences-Rules You Need To Knowgilca.monicaluizaNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentenceDocument3 pagesConditional SentenceLiwanto LeeNo ratings yet
- Annisa Awan RifqaDocument5 pagesAnnisa Awan RifqaAnnisa Awan RifqaNo ratings yet
- If Conditional ExplainedDocument9 pagesIf Conditional ExplainedSyifaa ZuchrufNo ratings yet
- Mixed ConditionalsDocument3 pagesMixed ConditionalsDASCALU ANANo ratings yet
- Conditional SentencesDocument14 pagesConditional SentencesShabira NadaNo ratings yet
- THE RISE OF EARLY GREEK PHILOSOPHYDocument2 pagesTHE RISE OF EARLY GREEK PHILOSOPHYMarcella MagaldiNo ratings yet
- Us. Government - Chapter 2Document3 pagesUs. Government - Chapter 2Marcella MagaldiNo ratings yet
- High 2's Yearbook Development ReportDocument4 pagesHigh 2's Yearbook Development ReportMarcella MagaldiNo ratings yet
- Essay 2 - Marcella Magaldi - CongressDocument10 pagesEssay 2 - Marcella Magaldi - CongressMarcella MagaldiNo ratings yet
- Marcella Magaldi - U.K. Literature EssayDocument7 pagesMarcella Magaldi - U.K. Literature EssayMarcella MagaldiNo ratings yet
- U.S. Government - Final ExamDocument4 pagesU.S. Government - Final ExamMarcella MagaldiNo ratings yet
- Script - Knowledge Fair - Marcella MagaldiDocument1 pageScript - Knowledge Fair - Marcella MagaldiMarcella MagaldiNo ratings yet
- Script - Knowledge Fair - Marcella MagaldiDocument1 pageScript - Knowledge Fair - Marcella MagaldiMarcella MagaldiNo ratings yet
- Class 13 May - Emotional IntelligenceDocument18 pagesClass 13 May - Emotional IntelligenceMarcella MagaldiNo ratings yet
- Script ComputersDocument2 pagesScript ComputersMarcella MagaldiNo ratings yet
- Script - Knowledge Fair - Marcella MagaldiDocument1 pageScript - Knowledge Fair - Marcella MagaldiMarcella MagaldiNo ratings yet
- Language - P1 3triDocument2 pagesLanguage - P1 3triMarcella MagaldiNo ratings yet