Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Obesity
Obesity
Uploaded by
JUAN CARLOS OJEDA-GARCESOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Obesity
Obesity
Uploaded by
JUAN CARLOS OJEDA-GARCESCopyright:
Available Formats
PRIMEVIEW
OBESITY
For the Primer, visit doi:10.1038/nrdp.2017.34
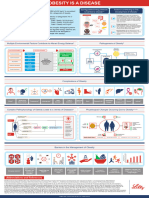
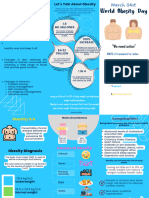
Approximately 40% of the world Metabolic imprinting DIAGNOSIS
EPIDEMIOLOGY Microbiota is the programming
population is overweight or
obese. Obesity is associated with the of metabolism at the
genetic and epigenetic Various methods are available to determine
development of type 2 diabetes mellitus,
level by prenatal and adiposity. Although the body mass index (BMI)
cardiovascular diseases and some types
Visceral obesity Metabolic neonatal factors, such is not a perfect index of adiposity, it is often
of cancer. Some of these comorbidities imprinting
is more common as excessive maternal used in clinical practice because of its simplicity
are considered features of the gestational weight gain,
in men than in and good correlation with cardiometabolic risk.
metabolic syndrome. women and poses rapid neonatal weight The BMI should be complemented by measuring
a higher risk gain or breastfeeding. the ratio of waist-to-hip circumferences to
of developing discriminate between subcutaneous obesity
MECHANISMS complications and visceral obesity.
than subcutaneous Genetics
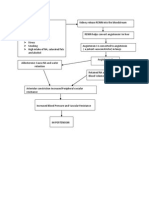
The pathogenesis of obesity is complex and obesity.
More than Underweight Extreme obese
determined by the interaction of genetic, 2.1 billion
environmental and psychosocial factors acting Reduced adults are Normal Obese
energy
through several physiological mediators (such as expenditure estimated to be
hormones, cytokines and the nervous system) to overweight or obese, Overweight
regulate food intake, energy expenditure and fat of which 1.5 billion
accumulation. Pathological changes in adipocytes are overweight and
might explain some of the complications Excess 640 million BMI (kg/m2)
associated with obesity. Subcutaneous fat tissue energy are obese.
accommodates the energy surplus through intake
adipocyte hyperplasia, acting as a metabolic 18.5 25 30 40
‘sink’. By contrast, visceral adipocytes often
undergo hypertrophy, resulting in hypoxia, The worldwide
excess secretion of pro-inflammatory adipokines number of
and an inability to store excess lipids, which children and MANAGEMENT
causes low-grade systemic inflammation, insulin adolescents with
resistance and deposition of triglycerides obesity has doubled Management of obesity is aimed at weight loss.
Obesity
in non-adipose tissues. since 1980, and is now Lifestyle interventions, dietary changes and
Social and prevention
estimated to be physical activity are the first-line approach,
cultural factors should focus on
FTO 110 million. followed by medical treatment and bariatric
controlling excessive
weight gain and maintaining surgery in selected patients. Drugs approved
MC4R weight loss. Interventions for use include lipase inhibitors and agonists
should start as early as of the glucagon‑like peptide receptor,
LEPR
QUALITY OF LIFE possible, even during serotonin receptor and adrenergic receptor.
pregnancy. Criteria for surgery are a BMI of >40 kg/m2 or
Obesity is associated with atherosclerosis and myocardial extent of a BMI of >35 kg/m2 with comorbidities such as
Subcutaneous Visceral several comorbidities, including infarction) and cancers weight loss hypertension or dyslipidaemia.
fat fat
endocrine disorders (such (endometrial, liver and kidney needed remains Personalized precision nutrition
as type 2 diabetes mellitus), cancer, among others). Obesity unclear. Global health based on phenotypical and
LEP respiratory problems (for also has a substantial impact costs associated with obesity and genotypical characteristics holds
POMC
example, sleep apnoea), on quality of life. Weight loss its complications are estimated promise for the prevention and
cardiovascular diseases (such as improves quality of life, but the to be ~US$2 trillion. management of obesity.
Written by Liesbet Lieben; designed by Laura Marshall Article number: 17035; doi:10.1038/nrdp.2017.35; published online 15 Jun 2017
©
2
0
1
7
M
a
c
m
i
l
l
a
n
P
u
b
l
i
s
h
e
r
s
L
i
m
i
t
e
d
,
p
a
r
t
o
f
S
p
r
i
n
g
e
r
N
a
t
u
r
e
.
A
l
l
r
i
g
h
t
s
r
e
s
e
r
v
e
d
.
You might also like
- Strength Training & Weight Training 101Document28 pagesStrength Training & Weight Training 101Maru PabloNo ratings yet
- 30 Minute Hiit WorkoutDocument5 pages30 Minute Hiit WorkoutAmaz GadNo ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument48 pagesDiabetes Mellitusladylisette67% (3)
- Effects of Obesity On Infections With Emphasis On Skin Infections and Wound HealingDocument6 pagesEffects of Obesity On Infections With Emphasis On Skin Infections and Wound HealingFirdani Mutiara100% (1)
- Revised PPT Obesitas Anak FitriaDocument22 pagesRevised PPT Obesitas Anak FitriaFitri RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Hypertension PathophysiologyDocument1 pageHypertension PathophysiologyTiffany Blanca Evangelista RaiNo ratings yet
- SF 8 Automatic Input DataDocument28 pagesSF 8 Automatic Input DataJenneth Miranda75% (4)
- The 16 Best Weight Loss Programs For 2021Document23 pagesThe 16 Best Weight Loss Programs For 2021مواطن تونسيNo ratings yet
- Obesity and Metabolic SyndromeDocument53 pagesObesity and Metabolic SyndromeindahNo ratings yet
- Dietary Treatment ObesityDocument52 pagesDietary Treatment Obesitymark pavlovicNo ratings yet
- HbA1C AS AN INDEX OF GLYCEMIC STATUS IN OBESE TYPE 2 DIABETICSDocument6 pagesHbA1C AS AN INDEX OF GLYCEMIC STATUS IN OBESE TYPE 2 DIABETICSInternational Journal of Clinical and Biomedical Research (IJCBR)No ratings yet
- Principles of Nutritional AssesmentDocument6 pagesPrinciples of Nutritional AssesmentHendro Dan MithochanNo ratings yet
- School Form 8 Sf8 Learner Basic Health and Nutrition Report AutomaticDocument12 pagesSchool Form 8 Sf8 Learner Basic Health and Nutrition Report AutomaticYojmhie Joy Ko100% (2)
- BMI and Weight Management Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesBMI and Weight Management Lesson PlanVee Nemoco100% (1)
- Betacell Protection and The Metabolic SyndromeDocument2 pagesBetacell Protection and The Metabolic Syndromesivasct4No ratings yet
- Pathogenesis of Obesity: Josanne VassalloDocument4 pagesPathogenesis of Obesity: Josanne VassalloAdkhiatul MuslihatinNo ratings yet
- Obesity and NeurologyDocument13 pagesObesity and NeurologyDangelo AugustoNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Care in ObesityDocument21 pagesPharmaceutical Care in ObesityRawan AmerNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia and Morbidly ObesedDocument6 pagesAnesthesia and Morbidly Obesedppica8111No ratings yet
- Pcos in AdolescentsDocument4 pagesPcos in AdolescentsSemo NonaNo ratings yet
- DM - Circresaha.120.316101Document24 pagesDM - Circresaha.120.316101reski utamiNo ratings yet
- Big Can Be Beautiful, TIVA in The ObeseDocument7 pagesBig Can Be Beautiful, TIVA in The ObeseHernán GiménezNo ratings yet
- Morbid ObesityDocument6 pagesMorbid ObesityerzaraptorNo ratings yet
- Circresaha 120 316101Document24 pagesCircresaha 120 316101mohamed khalilNo ratings yet
- OBEsity Print Version 1Document34 pagesOBEsity Print Version 1Tarin IslamNo ratings yet
- Computational Drug Repurposing Approach To Identify Potential Fatty Acid-Binding Protein-4 Inhibitors To Develop Novel Antiobesity TherapyDocument11 pagesComputational Drug Repurposing Approach To Identify Potential Fatty Acid-Binding Protein-4 Inhibitors To Develop Novel Antiobesity Therapywadelkrid1270No ratings yet
- Dietary Sugars LiverDocument15 pagesDietary Sugars Liverlakshminivas PingaliNo ratings yet
- Obesity Is A Disease InfographicDocument1 pageObesity Is A Disease InfographicFranco PacelloNo ratings yet
- CPH Lab NutritionDocument3 pagesCPH Lab NutritionLuningning UmarNo ratings yet
- Review of Childhood Obesity: From Epidemiology, Etiology, and Comorbidities To Clinical Assessment and TreatmentDocument15 pagesReview of Childhood Obesity: From Epidemiology, Etiology, and Comorbidities To Clinical Assessment and TreatmentDouglas castroNo ratings yet
- Precision Obesity Care On The Horizon: CirculationDocument3 pagesPrecision Obesity Care On The Horizon: CirculationCarlosMoscosoNo ratings yet
- Dietary Management of ObesityDocument30 pagesDietary Management of ObesityMalon MwambaziNo ratings yet
- Energy Balance in ObesityDocument5 pagesEnergy Balance in ObesityNurmasturaNo ratings yet
- ArticleDocument8 pagesArticleOlivia TettehNo ratings yet
- Adipose Tissue Pietrobelli 06Document5 pagesAdipose Tissue Pietrobelli 06SauloAntonioCarmonaBarlettiNo ratings yet
- Obesity Epidemiology Pathophysiology and TherapeuticsDocument9 pagesObesity Epidemiology Pathophysiology and Therapeuticsnadya wijayaNo ratings yet
- Obesity in Adults, A Clinical Practice GuidelineDocument17 pagesObesity in Adults, A Clinical Practice GuidelineMari PaoNo ratings yet
- Obesity PDFDocument7 pagesObesity PDFRoderick RichardNo ratings yet
- Micrornas ObesidadDocument13 pagesMicrornas ObesidadJorge González CasanovaNo ratings yet
- Obesity and Responsibility: Is It Time To Rethink Agency?Document8 pagesObesity and Responsibility: Is It Time To Rethink Agency?Ibrahima Séga Jr SangaréNo ratings yet
- Penyebab Obesitas 1Document6 pagesPenyebab Obesitas 1IngsukiniNo ratings yet
- Addressing Obesity in DiabetesDocument11 pagesAddressing Obesity in DiabetesFahmi Fauzi SugandiNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Diabetes Mellitus: Otential That The Children of Diabetic Mothers Will AlsoDocument6 pagesPathophysiology Diabetes Mellitus: Otential That The Children of Diabetic Mothers Will AlsoKevin Van Eric O. SaballoNo ratings yet
- Treatment and Prevention of Childhood Obesity: Sponsored byDocument4 pagesTreatment and Prevention of Childhood Obesity: Sponsored byThusith WijayawardenaNo ratings yet
- Addressing Overweight, Obesity, NCD CVCBDocument33 pagesAddressing Overweight, Obesity, NCD CVCBSiti Ika FitrasyahNo ratings yet
- El Sayedmoustafa2013 ConclusionDocument13 pagesEl Sayedmoustafa2013 ConclusionvisiniNo ratings yet
- Obesity A Review of Pathophysiology and Classific - 2023 - Mayo Clinic ProceediDocument16 pagesObesity A Review of Pathophysiology and Classific - 2023 - Mayo Clinic Proceedialerta.bfcmNo ratings yet
- Blue Professional Dental Care Trifold BrochureDocument2 pagesBlue Professional Dental Care Trifold BrochureAleta WrayNo ratings yet
- EBK Ve Obezojenik KimyasallarDocument19 pagesEBK Ve Obezojenik KimyasallarMakbule ERÇAKIRNo ratings yet
- Bosy Westphal2018Document7 pagesBosy Westphal2018leticia.altunaNo ratings yet
- Cellulitis in Obesity: Adverse Outcomes Affected by Increases in Body Mass IndexDocument7 pagesCellulitis in Obesity: Adverse Outcomes Affected by Increases in Body Mass IndexirenesmbNo ratings yet
- RRL Matrix 4Document2 pagesRRL Matrix 4Cath RamilNo ratings yet
- Bariatric BailyDocument10 pagesBariatric Bailybv2328002No ratings yet
- Ambiente e ObesidadeDocument4 pagesAmbiente e ObesidadeCristiano KalataNo ratings yet
- Ijcem 3 126Document5 pagesIjcem 3 126sajantkNo ratings yet
- Food Fads: The Keto Diet and The Gut: Cause For Concern?Document2 pagesFood Fads: The Keto Diet and The Gut: Cause For Concern?Bogdan LeonardNo ratings yet
- Peso e Percepção CorporalDocument6 pagesPeso e Percepção CorporalDas Dores de HolandaNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms of Weight Regain After Weight Loss - The Role of Adipose TissueDocument14 pagesMechanisms of Weight Regain After Weight Loss - The Role of Adipose TissueThiago SartiNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Overweight and ObesityDocument12 pages3.3 Overweight and Obesityemilya marlissaNo ratings yet
- Mental Consequences of ObesityDocument7 pagesMental Consequences of Obesitykeshav singhNo ratings yet
- 2 A Canela Atenua A Adiposidade e Afeta A ExpressãoDocument11 pages2 A Canela Atenua A Adiposidade e Afeta A Expressãoguto hdNo ratings yet
- Obesity Bray AJCN 55 488 1992Document7 pagesObesity Bray AJCN 55 488 1992Harsh ChordiyaNo ratings yet
- Roles of The Gut Microbiome in Weight Management (Carmody y Bisanz, 2023)Document16 pagesRoles of The Gut Microbiome in Weight Management (Carmody y Bisanz, 2023)csrpirataNo ratings yet
- Pediatricobesity: Etiologyandtreatment: Melissa K. Crocker,, Jack A. YanovskiDocument24 pagesPediatricobesity: Etiologyandtreatment: Melissa K. Crocker,, Jack A. YanovskiAyline Araceli AlavaNo ratings yet
- Normal Weight Obesity SyndromeDocument13 pagesNormal Weight Obesity SyndromeMarcelo SabbatiniNo ratings yet
- Poster ResearchDocument1 pagePoster Researchapi-660775071No ratings yet
- Dia Mundial Obesidad-2Document2 pagesDia Mundial Obesidad-2lnjacquelinemartinezNo ratings yet
- Obesity Final Draft-3Document5 pagesObesity Final Draft-3api-643535648No ratings yet
- Kuliah - Obesity - Metabolic Syndrome 2016Document45 pagesKuliah - Obesity - Metabolic Syndrome 2016Vivi DeviyanaNo ratings yet
- Childhood Obesity: Causes, Consequences and Prevention ApproachesFrom EverandChildhood Obesity: Causes, Consequences and Prevention ApproachesNo ratings yet
- BIOS LIFE - Clinical Studies SummaryDocument4 pagesBIOS LIFE - Clinical Studies SummaryHisWellnessNo ratings yet
- Kel LabDocument92 pagesKel LabAzmi Alvaro PENo ratings yet
- AstaReal CardioDocument2 pagesAstaReal CardioAmy HtunNo ratings yet
- Identification ClauseDocument10 pagesIdentification ClauseLAURANo ratings yet
- Lipids and Dyslipoproteinemia - 2020Document116 pagesLipids and Dyslipoproteinemia - 2020Aria Jean MostajoNo ratings yet
- Risk Factors For DiabetesDocument2 pagesRisk Factors For Diabetesmainehoona100% (1)
- PhenQ SwitzerlandDocument2 pagesPhenQ SwitzerlandHimanshu SharmaNo ratings yet
- AnalizeDocument2 pagesAnalizeClaudiaElenaNo ratings yet
- How To Solve ABGsDocument1 pageHow To Solve ABGsCiara GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Efficacy of A Novel Herbal Formulation For Weight Loss Demonstrated in A 16-WeekDocument31 pagesEfficacy of A Novel Herbal Formulation For Weight Loss Demonstrated in A 16-WeekAstri YuliandiniNo ratings yet
- Kepmenkes - 832 - 2006 Rs Rujukan HivDocument7 pagesKepmenkes - 832 - 2006 Rs Rujukan HivAnonymous ZqWMMC3No ratings yet
- Chloe Ting - 2021 Summer Shred Challenge - Free Workout ProgramDocument1 pageChloe Ting - 2021 Summer Shred Challenge - Free Workout ProgramAnniie GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Reducing Sedentary Behaviors Sit Less and Move More PDFDocument2 pagesReducing Sedentary Behaviors Sit Less and Move More PDFArthur0% (1)
- Metabolic Syndrome DiagnosisDocument4 pagesMetabolic Syndrome Diagnosisdrpiratheepan4274No ratings yet
- Consequences of Overweight and ObesityDocument2 pagesConsequences of Overweight and Obesitykezia lohoNo ratings yet
- Zbornik Radova 2013Document471 pagesZbornik Radova 2013Donat GrajqevciNo ratings yet
- Bmifa Boys Z 5 19 LabelsDocument1 pageBmifa Boys Z 5 19 LabelsRhea JavierNo ratings yet
- Lipid Profile: HDL & LDL CholesterolDocument6 pagesLipid Profile: HDL & LDL CholesterolQasmNo ratings yet
- Body Mass Index WorksheetDocument3 pagesBody Mass Index WorksheetJohn OsborneNo ratings yet