Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sets Therory
Uploaded by
Lexico0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesThis document defines key concepts about sets including:
(1) A set is a collection of distinct objects that can be represented in roster or set-builder form.
(2) There are different types of sets such as empty, finite, infinite, and singleton sets.
(3) A subset is a set where all elements are contained within another set. Two sets are equal if they contain the same elements.
Original Description:
Original Title
sets therory
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document defines key concepts about sets including:
(1) A set is a collection of distinct objects that can be represented in roster or set-builder form.
(2) There are different types of sets such as empty, finite, infinite, and singleton sets.
(3) A subset is a set where all elements are contained within another set. Two sets are equal if they contain the same elements.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesSets Therory
Uploaded by
LexicoThis document defines key concepts about sets including:
(1) A set is a collection of distinct objects that can be represented in roster or set-builder form.
(2) There are different types of sets such as empty, finite, infinite, and singleton sets.
(3) A subset is a set where all elements are contained within another set. Two sets are equal if they contain the same elements.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
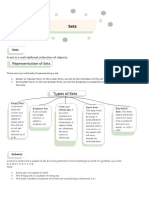
KEY POINTS
A set is a well-defined collection of objects.
There are two methods of representing a set:
(a) Roster or Tabular form e.g. natural numbers
less than 5 = {1, 2, 3, 4}
(b) Set-builder form or Rule method e.g.: Vowels in English
alphabet= {x : x is a vowel in the
English alphabet }
Types of sets:
(i) Empty set or Null set or void set
(ii) Finite set
(iii) Infinite set
(iv) Singleton set
Subset: A set A is said to be a subset of set
B if , . We write it as A B.
Equal sets: Two sets A and B are equal if they have exactly the
same elements i.e A = B if A B and B A.
Power set: The collection of all subsets of a set A is called
power set of A, denoted by P(A) i.e. P(A) = { B : B A }
If A is a set with n(A) = m then n [P(A)] = 2m
.
Equivalent sets: Two finite sets A and B are equivalent, if their
STUDYGUIDE360
cardinal numbers are same i.e., n(A) = n(B).
2 [XI – Mathematics]
Proper subset and super set: If A B then A is called the
proper subset of B and B is called the superset of A.
Types of Intervals
Open Interval (a, b) = { x R : a < x < b }
Closed Interval [a, b] = { x R : a x b }
Semi open or Semi closed Interval,
(a,b] = { x R : a < x ≤ b}
[a,b) = { x R : a ≤ x < b}
Union of two sets A and B is,
A B = { x : x A or x B }
Intersection of two sets A and B is,
A B = { x : x A and x B}
A
B
AUB
STUDYGUIDE360
3 [XI – Mathematics]
Disjoint sets: Two sets A and B are said to be disjoint if A B =
Difference of sets A and B is,
A – B = { x : x A and x B}
Difference of sets B and A is,
B – A = { x : x B and x A }
Complement of a set A, denoted by A' or Ac
is
A' = Ac
= U – A = { x : x U and x A}
A
A
B
A – B
U A B
STUDYGUIDE360
You might also like
- Set Theory PDFDocument54 pagesSet Theory PDFArlyn Calderon100% (2)
- Set TheroyDocument22 pagesSet TheroyManojNo ratings yet
- Set TheoryDocument36 pagesSet Theorysuperwicked sourabh64% (11)
- Chapter 2 of Discrete MathematicsDocument137 pagesChapter 2 of Discrete MathematicsSergey Kojoian67% (3)
- Chapter 1 SetsDocument11 pagesChapter 1 Setsendeavour909897No ratings yet
- Set Notations & Venn DiagramsDocument65 pagesSet Notations & Venn DiagramsRitu KaurNo ratings yet
- Set and SubsetDocument32 pagesSet and SubsetLance AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Sets and SubsetsDocument11 pagesSets and Subsetsyaoi yuriNo ratings yet
- Sets, Relation and FunctionDocument16 pagesSets, Relation and FunctionAshwani Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02 Algebra of SetsDocument14 pagesChapter 02 Algebra of SetsJo Y ANo ratings yet
- Sets and RelationsDocument9 pagesSets and RelationsAditya NandaNo ratings yet
- MathsDocument19 pagesMathsDivyanshi BansalNo ratings yet
- تحليل التوافقي شابتر 1Document48 pagesتحليل التوافقي شابتر 1إيهاب توفيق القادريNo ratings yet
- With Question/Answer AnimationsDocument34 pagesWith Question/Answer AnimationsGamesome GoshawkNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 Landasan Matematika: Arranged by Group 3 Name/NimDocument6 pagesAssignment 3 Landasan Matematika: Arranged by Group 3 Name/NimRendy B. SuharsonoNo ratings yet
- MMW Module 2.2 (Part 1)Document5 pagesMMW Module 2.2 (Part 1)ROJE DANNELL GALVANNo ratings yet
- Part 2Document5 pagesPart 2Catherine CarpioNo ratings yet
- LECTURE#1Document68 pagesLECTURE#1cosc19111058 KFUEITNo ratings yet
- Set Theory PPT 211014031034Document41 pagesSet Theory PPT 211014031034jungjeyoo300No ratings yet
- SETSDocument3 pagesSETSAniket DasNo ratings yet
- Set Theory and Relations - MaterialDocument46 pagesSet Theory and Relations - MaterialRavi teja NalamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Set 1Document49 pagesChapter 2 Set 1Nehsan TamilNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability - Power Point Slides Lecture 01Document75 pagesStatistics and Probability - Power Point Slides Lecture 01Saqib AltafNo ratings yet
- Sets Lecture NotesDocument5 pagesSets Lecture NotesRhenan WafooNo ratings yet
- NOTESDocument4 pagesNOTESjescy pauloNo ratings yet
- SetsDocument32 pagesSetsssNo ratings yet
- Start Download: CBSE Class 11 and 12 Maths Notes: Sets, Relations and Binary OperationsDocument12 pagesStart Download: CBSE Class 11 and 12 Maths Notes: Sets, Relations and Binary OperationspreetiNo ratings yet
- Module 1 NotesDocument8 pagesModule 1 Notesprojectbba350No ratings yet
- Lesson 2.2Document113 pagesLesson 2.2Maricris GatdulaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document25 pagesLecture 3Варис ВарисовNo ratings yet
- Basic Structures: Sets, Functions, Sequences, Sums, and MatricesDocument45 pagesBasic Structures: Sets, Functions, Sequences, Sums, and MatricesSameer A.ANo ratings yet
- Chapter2 - Part1 - SetDocument59 pagesChapter2 - Part1 - SetliasakinahNo ratings yet
- Set and RelationsDocument18 pagesSet and Relationsabos3odNo ratings yet
- Set Theory-1Document24 pagesSet Theory-1nathanmunene254No ratings yet
- Definition of Set: ExampleDocument8 pagesDefinition of Set: ExampleHammad AliNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 DMSDocument14 pagesUnit 3 DMSshubhamNo ratings yet
- Definition. A Set Is A Collection of Unordered, Well-Defined and DistinctDocument33 pagesDefinition. A Set Is A Collection of Unordered, Well-Defined and DistinctChristopher AdvinculaNo ratings yet
- Ch-1 Sets NotesDocument3 pagesCh-1 Sets NotesPreetiNo ratings yet
- MODULE - Week1Document27 pagesMODULE - Week1Danny Kim PigarNo ratings yet
- 2-Basic ProbabilityDocument17 pages2-Basic ProbabilityMaryam AhmedNo ratings yet
- ADA Assignment 2 PDFDocument10 pagesADA Assignment 2 PDFRahmatullah MuhammadiNo ratings yet
- Relationship Between The SetDocument2 pagesRelationship Between The Setwawan saputraNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Maths Notes Chapter 1 Studyguide360Document12 pagesClass 11 Maths Notes Chapter 1 Studyguide360Shyam AdhikaryNo ratings yet
- Set: in Our Daily Life We Use Phrases Like A Bunch of Keys, A Set of Books, A Tea Set, ADocument20 pagesSet: in Our Daily Life We Use Phrases Like A Bunch of Keys, A Set of Books, A Tea Set, ADeepak SharmaNo ratings yet
- SetsDocument23 pagesSetsAlfie Kier JovenNo ratings yet
- Sets & Relation TheoryDocument8 pagesSets & Relation TheorySushila TanwarNo ratings yet
- Discreate MathematicsDocument137 pagesDiscreate Mathematicsareeba tariqNo ratings yet
- 5 6249032366044479593 PDFDocument22 pages5 6249032366044479593 PDFs91No ratings yet
- The Notation For Sets: We Sometimes Denote A Set by Listing Its Elements, SeparatedDocument7 pagesThe Notation For Sets: We Sometimes Denote A Set by Listing Its Elements, SeparatedsajedulNo ratings yet
- Module 2.2 Sets and Set OperationsDocument8 pagesModule 2.2 Sets and Set Operations22-02923No ratings yet
- Sets SummaryDocument10 pagesSets SummaryAmeya ThakurNo ratings yet
- AdvancedMath Sets F5 Loibanguti (2022)Document37 pagesAdvancedMath Sets F5 Loibanguti (2022)samson stanley mgayaNo ratings yet
- 1 Sets: 1.1 Sets and Their RepresentationsDocument21 pages1 Sets: 1.1 Sets and Their RepresentationsAswithNo ratings yet
- 935176656X MathDocument16 pages935176656X MathMayank Kumar ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2 Language of Mathematics - Copy1Document11 pagesMODULE 2 Language of Mathematics - Copy1Har VyNo ratings yet
- Xi Formulae Complete BookDocument36 pagesXi Formulae Complete BookRahul SinghNo ratings yet
- Sets 1Document32 pagesSets 1Romel SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Set TheoryDocument27 pagesSet Theorynakuchima 221No ratings yet
- UNIT-3: - Relations and Ordering - Lattices - Boolean AlzebraDocument61 pagesUNIT-3: - Relations and Ordering - Lattices - Boolean Alzebranaman jaiswalNo ratings yet
- Straight LinesDocument1 pageStraight LinesLexicoNo ratings yet
- Binomial TheoryDocument4 pagesBinomial TheoryLexicoNo ratings yet
- Linear EnequlitiesDocument2 pagesLinear EnequlitiesLexicoNo ratings yet
- ADocument1 pageALexicoNo ratings yet