Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Straight Lines
Uploaded by
Lexico0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageThe document defines key concepts related to lines and slopes in a coordinate plane. It explains that the locus of an equation is the set of all points that satisfy the given equation, and the equation of a locus specifies the equation in x and y satisfied by points on the locus. A line can be defined as the locus of points satisfying the equation ax + by + c = 0. The slope of a line is defined as its tangent, and is denoted by m. Slope can be used to determine whether lines are parallel, perpendicular, or neither. The point-slope form provides the equation of a line passing through a given point with a given slope.
Original Description:
Original Title
straight lines
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document defines key concepts related to lines and slopes in a coordinate plane. It explains that the locus of an equation is the set of all points that satisfy the given equation, and the equation of a locus specifies the equation in x and y satisfied by points on the locus. A line can be defined as the locus of points satisfying the equation ax + by + c = 0. The slope of a line is defined as its tangent, and is denoted by m. Slope can be used to determine whether lines are parallel, perpendicular, or neither. The point-slope form provides the equation of a line passing through a given point with a given slope.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageStraight Lines
Uploaded by
LexicoThe document defines key concepts related to lines and slopes in a coordinate plane. It explains that the locus of an equation is the set of all points that satisfy the given equation, and the equation of a locus specifies the equation in x and y satisfied by points on the locus. A line can be defined as the locus of points satisfying the equation ax + by + c = 0. The slope of a line is defined as its tangent, and is denoted by m. Slope can be used to determine whether lines are parallel, perpendicular, or neither. The point-slope form provides the equation of a line passing through a given point with a given slope.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
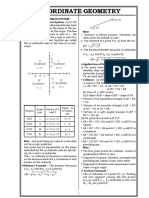
Locus of an equation: In the coordinate plane, locus of an
equation is the pictorial representation of the set of all those
points which satisfy the given equation.
Equation of a locus: is the equation in x and y that is satisfied by
the coordinates of every point on the locus.
A line is also defined as the locus of a point satisfying the
condition ax + by + c = 0 where a, b, c are constants.
Slope of a straight line:
If is the inclination of a line then tan is defined as slope of the
straight line L and denoted by m
m = tan, ≠ 90°
If 0° < < 90° then m > 0 and
90° < < 1800° then m < 0
Note-1: The slope of a line whose inclination is 90° is not
defined. Slope of x-axis is zero and slope of y-axis is not defined
Note-2: Slope of any horizontal line i.e. || to x-axis is zero. Slope
of a vertical line i.e. || to y-axis is not zero.
Three points A, B and C lying in a plane are collinear, if slope of
AB = Slope of BC.
Slope of a line through given points (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) is given
STUDYGUIDE360
by
119 [XI – Mathematics]
Two lines are parallel to each other if and only if their slopes are
equal.
l l ||
Note: If slopes of lines 1
l and 2
l are not defined then they must
be to x-axis, so they are ||. Thus 1 2 l l || they have same
slope or both of them have not define slopes.
Two non- vertical lines are perpendicular to each other if and
only if their slopes are negative reciprocal of each other.
1 2 l l
Note: The above condition holds when the lines have non-zero
slopes i.e none of them to any axis.
Acute angle between two lines, whose slopes are m1 and m2
is given by , 1 + m1m2 ≠ 0 and obtuse angle is
= 180 – .
Point slope form:
Equation of a line passing through given point (x1, y1) and
having slope m is given by y – y1 = m(x – x1)
STUDYGUIDE360
You might also like
- Classnote 4fd099323fc42Document12 pagesClassnote 4fd099323fc42Faraz ZeyaNo ratings yet
- Key Concept (Straight Line, Circle, Parabola, Ellipse, Hyperbola)Document21 pagesKey Concept (Straight Line, Circle, Parabola, Ellipse, Hyperbola)Ayah100% (1)
- Chapter 1 Linear Equations, Functions and Their ApplicationsDocument18 pagesChapter 1 Linear Equations, Functions and Their Applicationsyonas100% (1)
- Linear Equations: Section 1.1 p1Document42 pagesLinear Equations: Section 1.1 p1陳育禾100% (1)
- Equation of A LineDocument2 pagesEquation of A LineBinu Kumar SNo ratings yet
- Straight Line Demonstration Dharmendra MeenaDocument28 pagesStraight Line Demonstration Dharmendra MeenaRahul JatNo ratings yet
- 11 TH Two Dimensional GeometryDocument20 pages11 TH Two Dimensional GeometryUmakant AvateNo ratings yet
- Angle Between Two LineDocument4 pagesAngle Between Two Linecircleteam123No ratings yet
- Straight LinesDocument6 pagesStraight LinesSteveMathewKuruvillaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Points To RememberDocument9 pagesChapter 10 Points To RememberMokshita JainNo ratings yet
- Linear FunctionsDocument19 pagesLinear FunctionsTheresa Grace Balansag-Calimpusan AlsongNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Maths Notes Chapter 11 Three Dimensional GeometryDocument5 pagesCBSE Class 12 Maths Notes Chapter 11 Three Dimensional GeometryCharles Murgasan Charles MurgasanNo ratings yet
- Straight LinesDocument12 pagesStraight LinesKshitij BansalNo ratings yet
- Yyyymd Y: Cyyyyy Yyy Yy Yy YyyDocument4 pagesYyyymd Y: Cyyyyy Yyy Yy Yy YyycambreayaNo ratings yet
- 11 Maths Notes 10 Straight Lines PDFDocument7 pages11 Maths Notes 10 Straight Lines PDFArpit MalikNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document11 pagesLecture 4Haider AliNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1 ArDocument25 pagesChapter - 1 Arrandompupil2008No ratings yet
- Straight LineDocument27 pagesStraight Lineapi-27807453850% (2)
- Gradeup Short Notes On Point and Straight Line - pdf-21Document5 pagesGradeup Short Notes On Point and Straight Line - pdf-21Tafazzul HazqueelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document12 pagesChapter 1ghlafhlyNo ratings yet
- Straight LinesDocument5 pagesStraight LinesNutan MishraNo ratings yet
- Straight Lines Conceptsdssd-241Document12 pagesStraight Lines Conceptsdssd-241asdasd100% (1)
- 01 02 Linear Functions Straight LinesDocument47 pages01 02 Linear Functions Straight Linespop.korn7No ratings yet
- (Template) Chy-Straight LinesDocument20 pages(Template) Chy-Straight LinesVoot Kids75No ratings yet
- Graphing WorkbookDocument21 pagesGraphing WorkbookElaine zhuNo ratings yet
- M102 Lines HandoutDocument1 pageM102 Lines HandoutLorenzo TrinidadNo ratings yet
- MGMT 221 Ch. 1Document13 pagesMGMT 221 Ch. 1kebron100% (1)
- Straight Line Lecture - 1Document149 pagesStraight Line Lecture - 1Aditya TirthakarNo ratings yet
- Chapter One - Linear Equations and Its Interpretive ApplicationDocument12 pagesChapter One - Linear Equations and Its Interpretive ApplicationTewodrose Teklehawariat BelayhunNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Maths Notes Chapter 10 Studyguide360Document20 pagesClass 11 Maths Notes Chapter 10 Studyguide360zal adorNo ratings yet
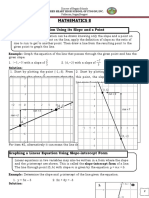
- Mathematics 8: Graphing A Linear Equation Using Its Slope and A PointDocument5 pagesMathematics 8: Graphing A Linear Equation Using Its Slope and A PointRoella Mae Tudias AlodNo ratings yet
- Business MathesDocument152 pagesBusiness MathesBelay MezgeboNo ratings yet
- A Research Paper On MathDocument151 pagesA Research Paper On MathFafa AgbakpeNo ratings yet
- Mathematics For Management Chapter OneDocument15 pagesMathematics For Management Chapter OneKubaNo ratings yet
- If You Know The Coordinates of A Group of Points You CanDocument16 pagesIf You Know The Coordinates of A Group of Points You CanSanaka LogesNo ratings yet
- 3d SynopsisDocument10 pages3d SynopsisUppu EshwarNo ratings yet
- Co-Ordinate Geometry: Y I II Quadrant Quadrant (-.,+) (+,+) 1 2 3Document11 pagesCo-Ordinate Geometry: Y I II Quadrant Quadrant (-.,+) (+,+) 1 2 3Aarti Sharma100% (1)
- 11 Three Dimensional Geometry 1Document21 pages11 Three Dimensional Geometry 1tiwarikistoNo ratings yet
- Business Math and Stats-Week 03Document17 pagesBusiness Math and Stats-Week 03Muhammad ZahidNo ratings yet
- Coordiante Geometry PDFDocument78 pagesCoordiante Geometry PDFRaj PatelNo ratings yet
- 3.2.1. Basics of GeometryDocument10 pages3.2.1. Basics of GeometryIsagaki RikuNo ratings yet
- XI - Maths - Chapter 10 - STRAIGHTLINESDocument47 pagesXI - Maths - Chapter 10 - STRAIGHTLINESStephen SatwikNo ratings yet
- Functions and Line in Coordinate: University of Kirkuk Civil Engineering Department 1 Stage, 1 SemsterDocument12 pagesFunctions and Line in Coordinate: University of Kirkuk Civil Engineering Department 1 Stage, 1 SemsterMohammed O IbrahimNo ratings yet
- StraightLine Sheet3Document79 pagesStraightLine Sheet3Harsh100% (1)
- Straight Line Session PDFDocument201 pagesStraight Line Session PDF8rg48v4zgfNo ratings yet
- Maths MicroprojectDocument1 pageMaths MicroprojectNarendra PalseNo ratings yet
- Define Perpendicular LinesDocument7 pagesDefine Perpendicular Linesapi-126876773No ratings yet
- HSSC-II Short Notes CH 4Document7 pagesHSSC-II Short Notes CH 4Mian EjazNo ratings yet
- The Rate of Change of A Function: Chapter - OneDocument6 pagesThe Rate of Change of A Function: Chapter - OneabasNo ratings yet
- Algebra Chapter 3 Group 3 Compiled CompressedDocument68 pagesAlgebra Chapter 3 Group 3 Compiled CompressedRey Roluna100% (1)
- Sheet - 01 - Straight LinesDocument15 pagesSheet - 01 - Straight LinesNoob Game PlayNo ratings yet
- m=tan θ= y y x x y y x xDocument8 pagesm=tan θ= y y x x y y x xauzaOne 4youNo ratings yet
- Straight Lines SynopsisDocument3 pagesStraight Lines SynopsisSameer Kumar Singh0% (1)
- Definition of Perpendicular LinesDocument7 pagesDefinition of Perpendicular Linesapi-126876773No ratings yet
- Xi-Quarterly Time TableDocument31 pagesXi-Quarterly Time TableInbloodNo ratings yet
- Coordinate Systems and Coordinates: 1. Co-Ordinate AxesDocument35 pagesCoordinate Systems and Coordinates: 1. Co-Ordinate AxessonalisabirNo ratings yet
- GED Maths Graphs Cheat SheetsDocument11 pagesGED Maths Graphs Cheat SheetsKelsoNo ratings yet
- MathsDocument138 pagesMathssolomonNo ratings yet
- CUBOIDDocument32 pagesCUBOIDlamloum1No ratings yet
- Binomial TheoryDocument4 pagesBinomial TheoryLexicoNo ratings yet
- Linear EnequlitiesDocument2 pagesLinear EnequlitiesLexicoNo ratings yet
- Sets TheroryDocument2 pagesSets TheroryLexicoNo ratings yet
- ADocument1 pageALexicoNo ratings yet