Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Yyyymd Y: Cyyyyy Yyy Yy Yy Yyy
Uploaded by
cambreayaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Yyyymd Y: Cyyyyy Yyy Yy Yy Yyy
Uploaded by
cambreayaCopyright:
Available Formats
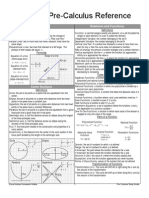
Standard form is where A, B, and C are real numbers, and A and B are not both 0: Ax+By=C
Finding Intercepts: when graphing the equation of a line, find the intercepts as follows: Let y=0 to find the x-intercept. Let x=0 to find the y-intercept.
Midpoint Formula: If the endpoints of a line segment PQ are:
x1+x2 , y1+y2
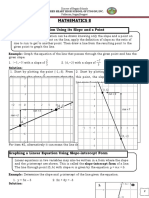
Slope Formula: The slope of the line through the distinct points (x1,y1) and (x2,y2) is: m=
Slopes of Horizontal & Vertical Lines: The slope of a horizontal line is 0. The slope of a vertical line is undefined.
Orientation of a Line in the Plane: A positive slope indicates that the line goes up (rises) from left to right. A negative slope indicates that the line goes down (falls) from left to right.
Slopes of Parallel Lines: Two nonvertical lines with the same slope are parallel. Two nonvertical parallel lines have the same slope.
Slopes of Perpendicular Lines: If neither is vertical, perpendicular lines have slopes that are negative reciprocals; that is, their product is -1. Also, lines with slopes that are negative reciprocals are perpendicular. A line with 0 slope is perpendicular to a line with undefined slope.
Slope-Intercept Form of the equation of a line with slope m and yintercept (0,b) is: y=mx+b
Point-Slope Form of the equation of a line with slope m passing through the point (x1,y1) is: y-y1=m(x-x1)
Equations of Horizontal & Vertical Lines: The horizontal line through the point (a,b) has equation y=b The vertical line through the point (a,b) has equation x=a
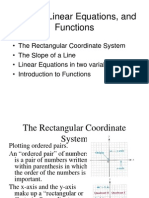
A Relation is any set of ordered pairs. A Function is a relation in which, for each value of the first component of the ordered pairs, there is exactly one value of the second component. OR a function is a set of ordered pairs in which no first component is repeated. OR a function is a rule or correspondence that assigns exactly one range value to each distinct domain value. Domain and Range: In a relation, the set of all values of the independent variable (x) is the domain. The set of all values of the dependent variable (y) is the range.
Agreement on Domain: The domain of a relation is assumed to be all real numbers that produce real numbers when substituted for the independent variable. Vertical Line Test: If every vertical line intersects the graph of a relation in no more than one point, then the relation represents a function.
Writing an Equation Using Function Notation: Step 1) Solve the equation for y. Step 2) Replace y with f(x) Linear Function: A function that can be defined by f(x)= ax+b For real numbers a and b, is a linear function. The value of a is the slope m of the graph of the function.
Graphs of Linear Systems in Two Variables contains 3 cases located on page 270 (Section 5.1) Solving a Linear System by Substitution contains 5 steps located on page 271 (Section 5.1) If an equation in a system contains decimal coefficients, its best to clear the decimals by multiplying on page 273 purple box. Solving a Linear System by Elimination contains 5 steps on page 274 (Section 5.1) Special Cases of Linear Systems found on page 276 (Section 5.1) Solving an Applied Problem by Writing a System of Equations contains 6 steps located on page 293 (Section 5.3)
You might also like
- Linear EquationsDocument4 pagesLinear Equations4ma3x100% (1)
- Linear Equations: Section 1.1 p1Document42 pagesLinear Equations: Section 1.1 p1陳育禾100% (1)
- Math ReviewerDocument2 pagesMath ReviewerAilah Janine SalamatNo ratings yet
- Linear EquationDocument3 pagesLinear Equationapi-150539480No ratings yet
- Graphs, Linear Equations, and FunctionsDocument46 pagesGraphs, Linear Equations, and FunctionsAmit BhararaNo ratings yet
- Y MX + BDocument6 pagesY MX + BAbhinav aroraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Linear EquationsDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Linear EquationsJami MendozaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Graphing Linear Equations and FunctionsDocument9 pagesChapter 3 Graphing Linear Equations and FunctionsNina HNo ratings yet
- Mathematics For Management Chapter OneDocument15 pagesMathematics For Management Chapter OneKubaNo ratings yet
- M102 Lines HandoutDocument1 pageM102 Lines HandoutLorenzo TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Gradeup Short Notes On Point and Straight Line - pdf-21Document5 pagesGradeup Short Notes On Point and Straight Line - pdf-21Tafazzul HazqueelNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Properties of Linear FunctionsDocument8 pages2.1 Properties of Linear FunctionsVon A. DamirezNo ratings yet
- Functions and Line in Coordinate: University of Kirkuk Civil Engineering Department 1 Stage, 1 SemsterDocument12 pagesFunctions and Line in Coordinate: University of Kirkuk Civil Engineering Department 1 Stage, 1 SemsterMohammed O IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Linear FunctionsDocument19 pagesLinear FunctionsTheresa Grace Balansag-Calimpusan AlsongNo ratings yet
- Linear Equation - WikipediaDocument24 pagesLinear Equation - WikipediaChristine Mae BetangcorNo ratings yet
- Chapter One - Linear Equations and Its Interpretive ApplicationDocument12 pagesChapter One - Linear Equations and Its Interpretive ApplicationTewodrose Teklehawariat BelayhunNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Linear Equations, Functions and Their ApplicationsDocument18 pagesChapter 1 Linear Equations, Functions and Their Applicationsyonas100% (1)
- KeenDocument22 pagesKeenVince OjedaNo ratings yet
- MGMT221 IDocument12 pagesMGMT221 IChristy Hernandez0% (1)
- Graphing WorkbookDocument21 pagesGraphing WorkbookElaine zhuNo ratings yet
- Business MathesDocument152 pagesBusiness MathesBelay MezgeboNo ratings yet
- GED Maths Graphs Cheat SheetsDocument11 pagesGED Maths Graphs Cheat SheetsKelsoNo ratings yet
- Algebra Chapter 3 Group 3 Compiled CompressedDocument68 pagesAlgebra Chapter 3 Group 3 Compiled CompressedRey Roluna100% (1)
- MGMT 221 Ch. 1Document13 pagesMGMT 221 Ch. 1kebron100% (1)
- 11 Maths Notes 10 Straight Lines PDFDocument7 pages11 Maths Notes 10 Straight Lines PDFArpit MalikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Functions and Graphs 1.1 Functions: Example 2 GivenDocument8 pagesChapter 1 Functions and Graphs 1.1 Functions: Example 2 GivenKae Yi SiewNo ratings yet
- Maths For Exams of CbseDocument3 pagesMaths For Exams of CbseSandeep RathiNo ratings yet
- Pre-Algebra Ch.11 Quiz 2Document3 pagesPre-Algebra Ch.11 Quiz 2KaitlynNo ratings yet
- 1 Chapter 1 Linear Equeation EditedDocument9 pages1 Chapter 1 Linear Equeation EditeduuuNo ratings yet
- Try To Graph and Name The Following EquationsDocument46 pagesTry To Graph and Name The Following EquationsStephanie DecidaNo ratings yet
- Calculus Book IDocument19 pagesCalculus Book ITeresa Villena GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Straight LinesDocument1 pageStraight LinesLexicoNo ratings yet
- Pre - Calculus: A Simplified ApproachDocument15 pagesPre - Calculus: A Simplified ApproachlpuelearningNo ratings yet
- Linear Equations and Their Interpretive ApplicationDocument51 pagesLinear Equations and Their Interpretive ApplicationDèřæ Ô MáNo ratings yet
- Segment Lines InequalitiesDocument25 pagesSegment Lines InequalitiesAzeNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesLinear Algebra Cheat SheetMiriam Quan100% (1)
- Mathematics 8: Graphing A Linear Equation Using Its Slope and A PointDocument5 pagesMathematics 8: Graphing A Linear Equation Using Its Slope and A PointRoella Mae Tudias AlodNo ratings yet
- Linear Equations in Two Variables Class 9Document2 pagesLinear Equations in Two Variables Class 9Ashwani PathakNo ratings yet
- Pre CalcDocument2 pagesPre Calcapi-213604106No ratings yet
- System of Linear Equations: Slide For MA1203 Business Mathematics II Week 1 & 2Document28 pagesSystem of Linear Equations: Slide For MA1203 Business Mathematics II Week 1 & 2Tamene KibrNo ratings yet
- Linear Equations and GraphsDocument25 pagesLinear Equations and GraphsSonu JhaNo ratings yet
- CUBOIDDocument32 pagesCUBOIDlamloum1No ratings yet
- Maths For FinanceDocument22 pagesMaths For FinanceWonde BiruNo ratings yet
- Cu 3Document39 pagesCu 3omgitsjediNo ratings yet
- Straight Line: AIEEE SyllabusDocument27 pagesStraight Line: AIEEE SyllabusDeepali KotaryNo ratings yet
- Rectangular Coordinate System - LectureDocument4 pagesRectangular Coordinate System - LectureRose Ann Sta. AnaNo ratings yet
- Maths CH 1 EditedDocument27 pagesMaths CH 1 EditedTäð Œvê MîðNo ratings yet
- Math Grade 9 Study GuideDocument11 pagesMath Grade 9 Study GuideDan PetrenkoNo ratings yet
- Linear Equations and GraphsDocument25 pagesLinear Equations and GraphsDexter CarpioNo ratings yet
- Mathsunit 1 MathsForMgtDocument16 pagesMathsunit 1 MathsForMgtDawit MekonnenNo ratings yet
- Bab 1Document8 pagesBab 1jak92No ratings yet
- Grade 9 Math Exam Study NotesDocument6 pagesGrade 9 Math Exam Study Notescynthia_88No ratings yet
- Linear Equations in Two Variables Class 9Document2 pagesLinear Equations in Two Variables Class 9streakof happinesssNo ratings yet
- GRADE 8 3rd Quarter ReviewerDocument9 pagesGRADE 8 3rd Quarter ReviewerGracella BurladoNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra NotesDocument6 pagesLinear Algebra NotesAngela ZhouNo ratings yet
- Straight Line Demonstration Dharmendra MeenaDocument28 pagesStraight Line Demonstration Dharmendra MeenaRahul JatNo ratings yet
- 1.1: Functions and Their Graphs: Learning ObjectivesDocument22 pages1.1: Functions and Their Graphs: Learning ObjectiveskofinyameNo ratings yet
- Topic 9 Linear Equation and FunctionDocument47 pagesTopic 9 Linear Equation and Function1221305124No ratings yet