Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Spdi
Spdi
Uploaded by
Adrian san0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesThe document summarizes the hydrological cycle, or water cycle, outlining the main processes by which water is distributed across Earth. These include evaporation, transpiration, sublimation, condensation, transportation of water vapor through the atmosphere, runoff into streams and rivers, evapotranspiration, and infiltration into soil. Water exists in solid, liquid, and gas forms as it moves continuously between the atmosphere and Earth via this cyclical process.
Original Description:
Original Title
spdi
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes the hydrological cycle, or water cycle, outlining the main processes by which water is distributed across Earth. These include evaporation, transpiration, sublimation, condensation, transportation of water vapor through the atmosphere, runoff into streams and rivers, evapotranspiration, and infiltration into soil. Water exists in solid, liquid, and gas forms as it moves continuously between the atmosphere and Earth via this cyclical process.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesSpdi
Spdi
Uploaded by
Adrian sanThe document summarizes the hydrological cycle, or water cycle, outlining the main processes by which water is distributed across Earth. These include evaporation, transpiration, sublimation, condensation, transportation of water vapor through the atmosphere, runoff into streams and rivers, evapotranspiration, and infiltration into soil. Water exists in solid, liquid, and gas forms as it moves continuously between the atmosphere and Earth via this cyclical process.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
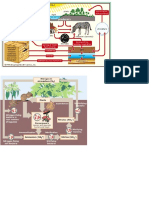
Hydrological cycle of water
Water Cycle (Hydrologic Cycle)- continuousmovement of water
between the earth andatmosphere
1. Evaporationchange of state of water (a liquid) to water vapour
2. Transpirationevaporation of liquid water from plants and
treesinto the atmosphere (90% of all water that enters theroots
transpires into the atmosphere)
3. Sublimationprocess where ice and snow (a solid) changesinto
water vapor (a gas) without movingthrough the liquid phase
4. Condensationfrom the gas phase to the liquid phase; watervapor
(a gas) changes back into a waterdroplets(a liquid)e.g. clouds, fog,
dew, or frost form
5. Transportationthe movement of solid, liquid and gaseous
waterthroughthe atmosphere. Without this movement, the
waterevaporated over the ocean would not precipitateover land
6. Runofremains on the surface and flows into streams,rivers,
andeventually large bodies (lakes or the ocean)
7. Evapotranspiration- the process oftransferring moisture from the
earth to theatmosphere by evaporation of water andtranspiration
from plants
8. Infiltration- process by which water in theground surface enters
the soil
Water is many time heavier that air by 803
Water is 800 times denser that air
Measurement of rainfall intensity is inches/hr
You might also like
- Water Cycle: DescriptionDocument3 pagesWater Cycle: Descriptionrotsacrreijav123No ratings yet
- Description: O Cycle, Describes TheDocument5 pagesDescription: O Cycle, Describes TheJan Mikel RiparipNo ratings yet
- Spdi ADocument2 pagesSpdi ARam CaniculaNo ratings yet
- Phosphorus CycleDocument6 pagesPhosphorus CycleMarlyn P LavadorNo ratings yet
- Hydrological Cycle NotesDocument16 pagesHydrological Cycle NotesMalia Damit100% (1)
- Atmospheric Moisture AND PrecipitationsDocument40 pagesAtmospheric Moisture AND PrecipitationsUsama UsamaArqemNo ratings yet
- Water CycleDocument6 pagesWater CycleEmmanuel de LeonNo ratings yet
- Definitions of Hydrology and Hydraulics: (Source: Wikipedia)Document5 pagesDefinitions of Hydrology and Hydraulics: (Source: Wikipedia)Steve ChecaNo ratings yet
- Montaril Water CycleDocument3 pagesMontaril Water CycleAdrian MontarilNo ratings yet
- Lecture 06 Hydrologic CycleDocument4 pagesLecture 06 Hydrologic CycleClow NNo ratings yet
- The Water Cycle On EarthDocument4 pagesThe Water Cycle On Earthjarina jeydNo ratings yet
- Science Project Don by Ansh YadavDocument21 pagesScience Project Don by Ansh YadavIsha YadavNo ratings yet
- The Water CycleDocument11 pagesThe Water CycleGemlyn de CastroNo ratings yet
- Water ResourcesDocument27 pagesWater Resourcessharon ranjitha paulNo ratings yet
- The Water Cycle On EarthDocument3 pagesThe Water Cycle On EarthNaveen PrabhuNo ratings yet
- PDC Topic - Understanding and Designing For A Bioregions Climate and Landscape - Terra PermaDocument18 pagesPDC Topic - Understanding and Designing For A Bioregions Climate and Landscape - Terra Permagns_vcNo ratings yet
- Water Cycle - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument10 pagesWater Cycle - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediasofianina05No ratings yet
- Water Cycle, Also Called Hydrologic Cycle, Cycle That Involves TheDocument2 pagesWater Cycle, Also Called Hydrologic Cycle, Cycle That Involves Themiguel itsonNo ratings yet
- Hydrology #2Document17 pagesHydrology #2Kent Jonas C. GensisNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY 2 - The Water CycleDocument1 pageACTIVITY 2 - The Water CycleLucy RoseNo ratings yet
- Description: O Cycle, Describes TheDocument14 pagesDescription: O Cycle, Describes TheMonika KshetriNo ratings yet
- HydroDocument5 pagesHydrojoanne_mendoza_1No ratings yet
- Water Cycle ProcessDocument7 pagesWater Cycle ProcessGading GaharunniNo ratings yet
- Topic HydrologyDocument6 pagesTopic HydrologyvictorNo ratings yet
- Hidrogeoph 1 CorrectDocument17 pagesHidrogeoph 1 CorrectToddy SamuelNo ratings yet
- The Water CycleDocument10 pagesThe Water Cycledenivo2904No ratings yet
- Explanation WatercycleDocument1 pageExplanation WatercycleGita NoviantiNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 EsciDocument2 pagesActivity 2 EsciGago SayoNo ratings yet
- Hydrologic CycleDocument7 pagesHydrologic CycleMeshal HolmesNo ratings yet
- Water CycleDocument7 pagesWater CycleMinahil ManiNo ratings yet
- Water CycleDocument4 pagesWater Cyclehanouf.ghulamNo ratings yet
- Water Cycle: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchDocument13 pagesWater Cycle: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchJan Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- DAYAH - Assignment 1 Water CycleDocument2 pagesDAYAH - Assignment 1 Water CycleHidayah AhmadNo ratings yet
- Water CycleDocument2 pagesWater CycleAnellah Ali100% (1)
- Water CycleDocument16 pagesWater CycleClarize Gemala GayaniloNo ratings yet
- Science - EvaporationDocument3 pagesScience - EvaporationxavierNo ratings yet
- Cour 1 ADocument6 pagesCour 1 ANadia Sama MamaneNo ratings yet
- Group 1 ReportDocument19 pagesGroup 1 ReportKimmy Jane FloresNo ratings yet
- Water CycleDocument1 pageWater CycleElene BakuridzeNo ratings yet
- Unit-4: Introduction To Water PowerDocument11 pagesUnit-4: Introduction To Water PowerPavankumar PavankumarpvNo ratings yet
- HydrologyDocument2 pagesHydrologyKurt Francis AcostaNo ratings yet
- Spheres of Earth: HydrosphereDocument17 pagesSpheres of Earth: HydrosphereTanveer Al FaisalNo ratings yet
- The Stages of The Cycle AreDocument2 pagesThe Stages of The Cycle AreJosefina Policarpio IINo ratings yet
- Assignment - IDocument15 pagesAssignment - IAniket PrakashNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Hydrology: Lecture By, Dr. (MRS.) Rina B Fernandez Geography Department Nowrosjee Wadia College, PuneDocument12 pagesChapter 4 Hydrology: Lecture By, Dr. (MRS.) Rina B Fernandez Geography Department Nowrosjee Wadia College, PuneKunal SawantNo ratings yet
- The Various Inputs in Hydrological CycleDocument2 pagesThe Various Inputs in Hydrological CycleAstha soniNo ratings yet
- Water CycleDocument2 pagesWater CycleraymundoNo ratings yet
- The Hydrological CycleDocument6 pagesThe Hydrological CycleF A L L E NNo ratings yet
- Hydrologic CycleDocument5 pagesHydrologic CyclesupermaneditNo ratings yet
- Sanitation, Plumbing Design, and InstallationDocument12 pagesSanitation, Plumbing Design, and InstallationHaRriet De Guzman VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- The Earth's Atmosphere 02Document16 pagesThe Earth's Atmosphere 02Reihnard RosariioNo ratings yet
- Hydrologic CycleDocument3 pagesHydrologic CycleDjoanna Joyce LeanoNo ratings yet
- The Water Cycle The Water Cycle: 9. Snowmelt 9. Snowmelt Runoff RunoffDocument1 pageThe Water Cycle The Water Cycle: 9. Snowmelt 9. Snowmelt Runoff RunoffSteven CandraNo ratings yet
- The Basic Hydrologic (Water) CycleDocument9 pagesThe Basic Hydrologic (Water) CycleMiguel ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Water Cycle: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument17 pagesWater Cycle: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaGaurav YadavNo ratings yet
- Lecture Contents:: Hydrologic Cycle Annual World Water Budget Evaporation, Transpiration and CondensationDocument23 pagesLecture Contents:: Hydrologic Cycle Annual World Water Budget Evaporation, Transpiration and Condensationabdulrehman khushikNo ratings yet
- Water CycleDocument11 pagesWater Cycleanika tahsinNo ratings yet
- Evaporation, Transpiration and Precipitation | Water Cycle for Kids | Children's Water BooksFrom EverandEvaporation, Transpiration and Precipitation | Water Cycle for Kids | Children's Water BooksNo ratings yet
- There Goes the Water: A Song About the Water CycleFrom EverandThere Goes the Water: A Song About the Water CycleRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)