Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Eco - Demand Summary Chart
Eco - Demand Summary Chart
Uploaded by
Kiran hanoteOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Eco - Demand Summary Chart
Eco - Demand Summary Chart
Uploaded by
Kiran hanoteCopyright:
Available Formats
Faculty – CA Rachna Parakh Dubey
1. Meaning: Demand means quantity (vi) Fashion on Good
of goods & service that a person is Demand (vii) Habit forming Good
willing to buy/ able to purchase at (iii) Price is independent variable. (viii) Demonstration effect / band wagon
given price during given period of (iv) One sided law. effect.
time. (v) Qualitative statement. 11. Change in Demand:
2. Types of Demand: (vi) 1st law of purchase → Alfred A. Change in Quantity Demand:
Marshal. → Rise in Quantity demand, due to fall
Individual Demand Market Demand 6. Assumption of Law of demand: in price, keeping other factor
(i) Ceteris Peribus constant.
Demand of single Total demand of (ii) Man is Rational → Fall in quantity demand, due to rise
consumer. all consumer (iii) Normal goods. in price keeping other factor
Household residing in area. 7. Demand schedule: constant.
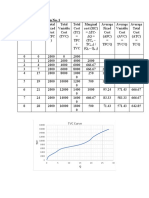
demand. Industry demand. P Q P A B C C P Q P Q
1 100 1 100 50 40 190 2 10 1 20
3. Factor Affecting Individual 2 80 2 80 40 30 150
Demand 1 20 2 10
3 60 3 60 30 20 110
(i) Price of a commodity: Price of a 4 40 4 40 20 10 70 y - axis
commodity is inversely related. 5 20 5 20 10 0 30 Contraction
When P↑ demand ↓, when P↓ d↑. Individual Market C
Price
(ii) Income of consumer: Income Demand demand A
Expansion
affect demand in following way: schedule schedule B
A. Normal Goods: In case of normal Tabular Horizontal
Goods, when demand↑, Income↑. representation summation of O Quantity x - axis
B. Inferior Goods: In case of Inferior showing individual B. Change in Demand:
good, when demand↓, Income↑. different demand → Increase in demand due to
(iii) Taste of Preference: If taste has quantity, which schedule. favourable changes in other factor
orange, the demand ↑. Eg. consume can keeping price constant.
Typewriter vs keyboard. buy at various → Decrease in demand, due to
(iv) Related Commodity: price. unfavourable changes in other
A. Complementary Goods: Those 8. Demand Curve: factor keeping price constant.
goods which are used together to P↑ D↓ * Downward P I Q P I Q
satisfy given demand. Eg. Car, slope 10 1000 10 10 2000 20
P↓ D↑
Petrol. * Negative slope 10 2000 20 10 1000 10
y - axis D2
Inverse Relation: Price of Petrol ↑,
9. Demand function: Demand D1
demand of car ↓.
function shows the functional
B. Substitute Goods: Those goods D3
Price
relationship b/w demand & factor
which are used in place of each
affecting.
other to satisfy given demand.
Direct Relation: Tea of price ↑, 𝐷𝑥 = 𝑓(𝑃𝑥 , 𝑃𝑦 , 𝐼, 𝑇, … … … . . )
10. Exceptions of Law of Demand: O Quantity x - axis
Demand of coffee ↓
(i) Emergencies like war &
(v) Future price Expectation 12. Reason for Law of Demand:
curfew: (P↑D↑) • Income effect.
4. Factor affecting Market Demand:
(ii) Giffen goods: Sir Robert Giffen, • Substitution effect.
(i) Size & types of population:
London school of economics, 19th
(Direct relation) Pop. ↑, Demand↑ • New customer creating more
century.
(ii) Season & Weather: eg. Rainy demand.
→ Giffen goods are special variety
season – Raincoat ↑, summer • Many uses of a commodity.
of inferior goods on which
season – Raincoat ↓.
consumer spend large amount of • Law of diminishing marginal utility.
(iii) Credit Policy: If credit policy 13. Types of Demand:
his income. This goods purchase
liberal, demand ↑, if credit policy is • Joint demand.
strict demand↓. even their price↑ (P↑ D↑). eg.,
Bread, meat. • Composite demand.
(iv) Taxation Policy: If people have to • Derived demand.
pay high tax, demand ↑, If credit
• Autonomous demand.
policy is strict demand ↓.
• Firm v/s industry demand.
(v) Income Distribution: If income
evenly distributed b/w to people, (iii) Veblon Goods: Sir TB Veblon,
• Cross demand.
demand ↑, if income is unevenly Doctrine of conspicous 14. Demand Forecasting:
distributed b/w people, demand ↓. Consumption. The art of predicting probable demand
(iv) Speculative Goods: Share for product/service at some future date
5. Law of Demand: Law of demand market goods. P↑D↑ eg. Share, based on past behaviour pattern of
variables.
states that inverse relation b/w Debentures .
price & demand. Eg. P↑ D↓ ; P↓ D↑ (v) Ignorance of consumer: If
consumer don’t know about the
Features of law of demand: price, he is ready to purchase
(i) Inverse relation b/w price, even at high price.
demand. Eg. Onion (Reliance fresh Rs
(ii) Not proportionate change. 70kg) & (Street vendor Rs 10kg).
APT – Best Classes for CA/CS/ACCA/CUET/X-XII Call - 9755557307
You might also like
- Assignment: Prepare Price Moves For Your Company Pro-Packs (I/III)Document3 pagesAssignment: Prepare Price Moves For Your Company Pro-Packs (I/III)Shishir GuptaNo ratings yet
- CIPS Level 4 - Diploma in Procurement and Supply Module 3 - Commercial ContractingDocument5 pagesCIPS Level 4 - Diploma in Procurement and Supply Module 3 - Commercial ContractingJalal Quteineh100% (2)
- p3 Demand and Low DemandDocument12 pagesp3 Demand and Low DemandRapmonsterNo ratings yet
- C2 Micro EcoDocument11 pagesC2 Micro EcoShashwat JhaNo ratings yet
- Demand and Supply Lesson 3Document7 pagesDemand and Supply Lesson 3Alex HongoNo ratings yet
- Section 2 Demand Supply 230308Document40 pagesSection 2 Demand Supply 230308tmyng04No ratings yet
- Chapter II - MicroeconomicsDocument46 pagesChapter II - MicroeconomicsDuresa GemechuNo ratings yet
- Introductory LectureDocument22 pagesIntroductory LectureVenkata Rami ReddyNo ratings yet
- Introductory LectureDocument16 pagesIntroductory LectureayushiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Supply, Demand, and Market EquilibriumDocument26 pagesChapter 2: Supply, Demand, and Market EquilibriumDiễn VânNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics Tutorial 2Document8 pagesMicroeconomics Tutorial 2Yeah cxyNo ratings yet
- 2nd CEC ReviewerDocument3 pages2nd CEC ReviewerFeiNo ratings yet
- Theory of DemandDocument23 pagesTheory of DemandCHARMAINE ALONZONo ratings yet
- LU02 - Demand and SupplyDocument70 pagesLU02 - Demand and Supplysiengching1234No ratings yet
- Chapter-2 (Business Economics)Document55 pagesChapter-2 (Business Economics)Jaber MohammadNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics: Demand and SupplyDocument55 pagesMicroeconomics: Demand and SupplyNhi NhiNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics: Demand and SupplyDocument56 pagesMicroeconomics: Demand and SupplyThế KiênNo ratings yet
- EN - Slide C2-KTVM-21 - 22 (SV)Document56 pagesEN - Slide C2-KTVM-21 - 22 (SV)Nguyễn Mỹ ChâuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Demand (ECO415)Document28 pagesChapter 2 Demand (ECO415)hurin inaniNo ratings yet
- Theory of Demand Lecture NotesDocument23 pagesTheory of Demand Lecture NotesCHARMAINE ALONZONo ratings yet
- Demand - Supply Market EquilibriumDocument58 pagesDemand - Supply Market Equilibriumnagarajan adityaNo ratings yet
- Market Forces: Demand and SupplyDocument59 pagesMarket Forces: Demand and SupplyDimasSigitKrispriajiNo ratings yet
- 1.2.2 DemandDocument21 pages1.2.2 Demandgyb5pb4v8bNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3 - Demand and Supply AnalysisDocument24 pagesChapter - 3 - Demand and Supply AnalysisAvi JhaNo ratings yet
- DemandDocument28 pagesDemandshubhip17No ratings yet
- Law of Demand by Dr. Punam HoodaDocument17 pagesLaw of Demand by Dr. Punam HoodaAVIRAL PRATAP SINGH CHAWDANo ratings yet
- Demand Analysis Super Crash Course by Malik TutorialDocument12 pagesDemand Analysis Super Crash Course by Malik Tutorialasimrashid05950No ratings yet
- M E Final 4 Con DDocument20 pagesM E Final 4 Con DNikhil LathiyaNo ratings yet
- ECU 402 - Notes Lec 2 - DEMANDDocument13 pagesECU 402 - Notes Lec 2 - DEMANDIncognito44No ratings yet
- Lecture 1 2022Document51 pagesLecture 1 2022Binguni RantharuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Demand, Supply, EquilibriumDocument43 pagesChapter 2 Demand, Supply, EquilibriumTahmima HoqueNo ratings yet
- En Slide c2-Ktvm-23 24 (SV)Document71 pagesEn Slide c2-Ktvm-23 24 (SV)Xuân lam LêNo ratings yet
- Week 1b - MTDocument27 pagesWeek 1b - MTThaveesha NethminiNo ratings yet
- Law of Demand CurveDocument24 pagesLaw of Demand Curvepgdtaxsept2022weekendclassNo ratings yet
- Economics NotesDocument80 pagesEconomics Notesgavin_d265No ratings yet
- Introduction To Economics (Econ. 101)Document64 pagesIntroduction To Economics (Econ. 101)Ali HassenNo ratings yet
- Demand and Supply AnalysisDocument47 pagesDemand and Supply AnalysisAcua RioNo ratings yet
- Chap 3Document63 pagesChap 3Abhijith ViratNo ratings yet
- Ot22 Ades Semes Econ8Document3 pagesOt22 Ades Semes Econ8ana luciaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Market Forces-Demand and SupplyDocument28 pagesChapter 2 Market Forces-Demand and Supplydimitri foxNo ratings yet
- Demand Anaylysis MEDocument87 pagesDemand Anaylysis MEShyam PrajaptiNo ratings yet
- Econ 281 Chapter02Document86 pagesEcon 281 Chapter02Elon MuskNo ratings yet
- An Increase in Price of The GoodDocument4 pagesAn Increase in Price of The Goodada lumNo ratings yet
- 110 CH 2 - Unit 1 - Law of Demand and Elasticity of Demand 1703091149Document19 pages110 CH 2 - Unit 1 - Law of Demand and Elasticity of Demand 1703091149IJAZ AHAMED S 2212053No ratings yet
- Krugman Mods 3e Irm Micro Econ Mod05Document6 pagesKrugman Mods 3e Irm Micro Econ Mod05Saleha IftikharNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - DDDocument5 pagesLesson 1 - DDAniket HeliwalNo ratings yet
- 28d637db-1543-49e2-a6c6-33f33233f2aeDocument26 pages28d637db-1543-49e2-a6c6-33f33233f2aeindian meme templatesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Demand and SupplyDocument64 pagesChapter 2 - Demand and SupplyidolhevevNo ratings yet
- ElasticityDocument3 pagesElasticityritoja770No ratings yet
- Demand and Supply AnalysisDocument22 pagesDemand and Supply Analysisdipu jaiswalNo ratings yet
- Elements of Economics - Demand and Supply Elements of Economics - Demand and SupplyDocument11 pagesElements of Economics - Demand and Supply Elements of Economics - Demand and SupplyRajKumarNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER-4.1-Curve, Schedule, and ShiftersDocument25 pagesCHAPTER-4.1-Curve, Schedule, and ShiftersIra Jesus Yapching Jr.No ratings yet
- Demand and Elasticity of DemandDocument7 pagesDemand and Elasticity of DemandaakaNo ratings yet
- DemandDocument26 pagesDemandeniNo ratings yet
- Theroy of Demand and Supply For BIMDocument79 pagesTheroy of Demand and Supply For BIMinfinity warzNo ratings yet
- Chapter II - Quan NguyenDocument37 pagesChapter II - Quan Nguyenyorelec910No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Demand SupplyDocument79 pagesChapter 2 Demand SupplyLinh Khánh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Oswaal ICSE Class 10 Economics Application Revision Notes For 2023 ExamDocument28 pagesOswaal ICSE Class 10 Economics Application Revision Notes For 2023 ExamAdithi MadhyastaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Market Forces-Demand and SupplyDocument29 pagesChapter 2 Market Forces-Demand and SupplyYayandi HasnulNo ratings yet
- II D&S Eko Manjerial GJL 2021Document57 pagesII D&S Eko Manjerial GJL 2021EVI ADRIANINo ratings yet
- Part 3 Demand PDFDocument17 pagesPart 3 Demand PDFYash KalaNo ratings yet
- Cfa Level 1 Test QuestionsDocument9 pagesCfa Level 1 Test QuestionsVikram SuranaNo ratings yet
- Lectures 3 4 and 5Document47 pagesLectures 3 4 and 5Pratyush BaruaNo ratings yet
- Porters 5 Forces Framework Applied To FlouaDocument2 pagesPorters 5 Forces Framework Applied To FlouasivaniNo ratings yet
- Marketing ChannelDocument5 pagesMarketing Channelagricultural and biosystems engineering100% (1)
- Engineering Economics: DepreciationDocument50 pagesEngineering Economics: DepreciationLeahlainne MinisterioNo ratings yet
- WWW Wallstreetmojo Com Liquidation Value #SalvageDocument30 pagesWWW Wallstreetmojo Com Liquidation Value #SalvagehieutlbkreportNo ratings yet
- SB2170 Howard AndersonDocument4 pagesSB2170 Howard AndersonRob PortNo ratings yet
- PG-20-183 Finlatics Market Performance ReportDocument1 pagePG-20-183 Finlatics Market Performance ReportShreyas KotkarNo ratings yet
- Tax Invoice: KALPANA GAS AGENCY (0000125491)Document1 pageTax Invoice: KALPANA GAS AGENCY (0000125491)SureshNo ratings yet
- Q Ap M: 1 Out of 1 PointsDocument3 pagesQ Ap M: 1 Out of 1 PointsUmair MalikNo ratings yet
- Predicting The Markets Chapter 1 Charts: Predicting The PastDocument14 pagesPredicting The Markets Chapter 1 Charts: Predicting The PastscribbugNo ratings yet
- Commentary #1: Microeconomics: Adelene LaiDocument4 pagesCommentary #1: Microeconomics: Adelene LaiMohd UvaisNo ratings yet
- Current Economic Situation of Sri LankaDocument2 pagesCurrent Economic Situation of Sri LankaPasinda PiyumalNo ratings yet
- Method of Banks Valuation: Horvátová Eva UDC: 336.717 JEL: G21Document11 pagesMethod of Banks Valuation: Horvátová Eva UDC: 336.717 JEL: G21VARUN SINGLANo ratings yet
- Edexcel Economics Unit 1 Topic 7.2 Goverment Faliure Complete AS-level Series NotesDocument4 pagesEdexcel Economics Unit 1 Topic 7.2 Goverment Faliure Complete AS-level Series NotesShahab HasanNo ratings yet
- Corporate Finance - Chapter 18Document3 pagesCorporate Finance - Chapter 18Bella LsiaNo ratings yet
- BSA 2C InventoriesDocument36 pagesBSA 2C InventoriesAudrey BienNo ratings yet
- Answer To The Question No. 1: TVC CurveDocument19 pagesAnswer To The Question No. 1: TVC CurveTahfizul Hasan ZihanNo ratings yet
- Hut300 Industrial Economics & Foreign Trade, December 2022Document3 pagesHut300 Industrial Economics & Foreign Trade, December 2022lordofthunder888No ratings yet
- Bec Module 2Document8 pagesBec Module 2cheskaNo ratings yet
- Coed Scents A National Producer of Young Adult Perfumes andDocument2 pagesCoed Scents A National Producer of Young Adult Perfumes andDoreenNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Corporate Financial Management 5th Edition Glen Arnold Test Bank PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Corporate Financial Management 5th Edition Glen Arnold Test Bank PDFhofstadgypsyus100% (12)
- Master Weaver QuestDocument5 pagesMaster Weaver Questguest5624No ratings yet
- FTSE Actuaries UK Index-Linked Gilts All Stocks IndexDocument2 pagesFTSE Actuaries UK Index-Linked Gilts All Stocks IndexAlokNo ratings yet
- What Is Marketing ManagementDocument28 pagesWhat Is Marketing ManagementBidyut Bhusan PandaNo ratings yet
- Gr11 - Worksheet - Demand & SupplyDocument2 pagesGr11 - Worksheet - Demand & Supplysnsmiddleschool2020No ratings yet
- PPE - FinalDocument71 pagesPPE - FinalKristen KooNo ratings yet
- Certs - Managerial EconomicsDocument42 pagesCerts - Managerial EconomicsCJ ManaloNo ratings yet