Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Epistasis Exam Questions
Uploaded by
y4heher0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views10 pagesOriginal Title
Epistasis_exam_questions.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views10 pagesEpistasis Exam Questions
Uploaded by
y4heherCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
Chapter 17 Epistasis exam question
Q1. In a breed of cattle the H allele for the hornless
condition is dominant to the h allele for the horned
condition. In the same breed of cattle the two alleles CR
(red) and CW (white) control coat colour. When red cattle
were crossed with white cattle all the offspring were
roan. Roan cattle have a mixture of red and white hairs.
(a) Explain what is meant by a dominant allele.
.....................................................................................
...............................................................................
.....................................................................................
...............................................................................
(1)
(b) Name the relationship between the two alleles that
control coat colour.
.....................................................................................
...............................................................................
(1)
(c) Horned, roan cattle were crossed with white cattle
heterozygous for the hornless condition. Complete
the genetic diagram to show the ratio of offspring
phenotypes you would expect.
Chapter 17 Epistasis exam question
Parental phenotypes Horned, roan
× hornless, white
Parental genotypes
Gametes
Offspring genotypes
Offspring phenotypes
Ratio of offspring
phenotypes
(4)
(d) The semen of prize dairy bulls may be collected for
in vitro fertilisation. The sperms in the semen can be
separated so that all the calves produced are of the
same sex. The two kinds of sperms differ by about
3% in DNA content.
(i) Explain what causes the sperms of one kind to
have 3% more DNA than sperms of the other
kind.
...............................................................................
.........................................................................
...............................................................................
.........................................................................
...............................................................................
Chapter 17 Epistasis exam question
.........................................................................
.........................................................................
.........................................................................
(2)
(ii) Suggest one reason why farmers would want
the calves to be all of the same sex.
...............................................................................
.........................................................................
...............................................................................
.........................................................................
(1)
(Total 9 marks)
Q2. Coat colour in Labrador dogs is controlled by two
different genes. Each gene has a dominant and a
recessive allele. The two genes are inherited
independently but the effects of the alleles interact to
produce three different coat colours. The table gives four
genotypes and the phenotypes they produce.
Genotype Phenotype
BbEe black
bbEe chocolate
Bbee yellow
bbee yellow
Chapter 17 Epistasis exam question
(a) What colour coat would you expect each of the
following genotypes to give?
(i) BBEe …………………………
(ii) bbEE …………………………
(2)
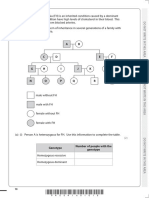
(b) A BbEe male was crossed with a bbee female.
Complete the genetic diagram to show the ratio of
offspring you would expect.
Parental phenotypes Black male
× Yellow female
Parental genotypes BbEe
bbee
Gametes
Offspring genotypes
Offspring phenotypes
Ratio of offspring
phenotypes
(3)
Chapter 17 Epistasis exam question
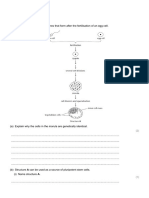
(c) The yellow coat colour of Labrador dogs is due to
the presence of the pigment phaeomelanin in the
hairs. The black and chocolate coat colours are due
to different amounts of another pigment, eumelanin,
deposited in these hairs. The more eumelanin there
is, the darker the hair. The diagram shows the action
of genes E and B in producing the different coat
colours.
Use this information to explain how
(i) the genotype bbee produces a yellow coat
colour;
...............................................................................
.........................................................................
...............................................................................
.........................................................................
...............................................................................
.........................................................................
...............................................................................
.........................................................................
(2)
Chapter 17 Epistasis exam question
(ii) the genotype BbEe produces a black coat
colour.
...............................................................................
.........................................................................
...............................................................................
.........................................................................
...............................................................................
.........................................................................
...............................................................................
..............................
(2)
(Total 9 marks)
Q3. The production of pigment in rabbit fur is controlled by
two genes.
One gene controls whether any pigment is made. This
gene has three alleles. Allele A codes for the production
of one form of the enzyme tyrosinase, which converts
tyrosine into a black pigment. Allele Ah codes for the
production of a second form of the enzyme, which
becomes inactive at temperatures close to a rabbit’s
core body temperature, so only the face, ears, legs and
tail are pigmented. A third allele, a, fails to code for a
functional tyrosinase.
The other gene controls the density of pigment in the fur.
This gene has two alleles. Allele B is dominant and
results in the production of large amounts of pigment,
making the fur black.
Allele b results in less pigment, so the fur appears
brown.
Chapter 17 Epistasis exam question
(a) How do multiple alleles of a gene arise?
.....................................................................................
...............................................................................
.....................................................................................
...............................................................................
.....................................................................................
...............................................................................
.....................................................................................
................................. (2)
(b) The table shows some genotypes and phenotypes.
Genoty
Phenotype
pe
A–B– all fur black
aaB– all fur white (albino)
white body fur with brown face, ears,
ahabb
legs and tail (Himalayan)
(i) What do the dashes represent in the genotype
of the black rabbit?
...............................................................................
.........................................................................
...............................................................................
.............................. (1)
Chapter 17 Epistasis exam question
(ii) Give all the possible genotypes for a Himalayan
rabbit with black face, ears, legs and tail.
...............................................................................
.........................................................................
...............................................................................
..............................
(2)
(iii) Suggest an explanation for the pigment being
present only in the tail, ears, face and legs of a
Himalayan rabbit.
...............................................................................
.........................................................................
...............................................................................
.........................................................................
...............................................................................
.........................................................................
...............................................................................
.........................................................................
(2)
(c) Using the information given, explain why the
phenotypes of rabbits with AABB and
AahBB genotypes are the same.
.....................................................................................
...............................................................................
.....................................................................................
...............................................................................
Chapter 17 Epistasis exam question
.....................................................................................
............................................................. (2)
(Total 9 marks)
Q4. Coat colour in mice is controlled by two genes,
each with two alleles. The genes are on different
chromosomes.
One gene controls the pigment colour. The presence of
allele A results in a yellow and black banding pattern on
individual hairs, producing an overall grey appearance
called agouti. Mice with the genotype aa do not make
the yellow pigment and are, therefore, black.
The other gene determines whether any pigment is
produced. The allele D is required for development of
coat colour. Mice with the genotype dd produce no
pigment and are called albino.
(a) What type of gene interaction is occurring between
the two genes? Explain your answer.
.....................................................................................
...............................................................................
.....................................................................................
...............................................................................
.....................................................................................
...............................................................................
.
.....................................................................................
.................................
(2)
(b) Give all the possible genotypes for a black mouse.
Chapter 17 Epistasis exam question
.....................................................................................
..............................................................................
(1)
(c) An agouti mouse of unknown genotype was
crossed with an albino mouse of unknown genotype.
Their offspring included albino, agouti and black
mice.
(i) What was the genotype of the agouti parent?
...............................................................................
.........................................................................
(1)
(ii) Give two possible genotypes for the albino
parent.
...............................................................................
.........................................................................
(1)
(iii) Suggest how the actual genotype of the albino
parent could be determined.
...............................................................................
.........................................................................
...............................................................................
.........................................................................
...............................................................................
.........................................................................
...............................................................................
..............................
(2)
(Total 7 marks)
You might also like
- Sex Linked Inheritance Practice QsDocument11 pagesSex Linked Inheritance Practice QsChloeNo ratings yet
- Inheritance worksheetDocument6 pagesInheritance worksheetRaahil MohamedNo ratings yet
- Darkness Subverted: Aboriginal Gothic in Black Australian Literature and FilmFrom EverandDarkness Subverted: Aboriginal Gothic in Black Australian Literature and FilmNo ratings yet
- Inheritance 1 QPDocument9 pagesInheritance 1 QPRushikesh HooliNo ratings yet
- Assessment For Learning YearDocument7 pagesAssessment For Learning YearJenNo ratings yet
- InheritanceDocument24 pagesInheritanceariesya suhaimiNo ratings yet
- Unittest 2grade 10Document6 pagesUnittest 2grade 10Shamshad ShaheerNo ratings yet
- Biology (Modular) Module Bi5: General Certificate of Education Tystysgrif Addysg Gyffredinol Uwch AdvancedDocument20 pagesBiology (Modular) Module Bi5: General Certificate of Education Tystysgrif Addysg Gyffredinol Uwch Advancedskarun1No ratings yet
- Linked Gene Question To Practice: JQ JQDocument7 pagesLinked Gene Question To Practice: JQ JQAyaan Asim Khan100% (1)
- 7: Genetics, Population Genetics and Evolutionary Processes - Topic QuestionsDocument12 pages7: Genetics, Population Genetics and Evolutionary Processes - Topic QuestionslenaNo ratings yet
- Genetics HigherDocument12 pagesGenetics HigherKanayNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Cell Division (Moderate) QPDocument9 pages1.2 Cell Division (Moderate) QPEnoch AdebiyiNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Cell Division (Hard) QPDocument18 pages1.2 Cell Division (Hard) QPehodariNo ratings yet
- Inheritance 1 QPDocument9 pagesInheritance 1 QPmaria keziaNo ratings yet
- Genetics 3: Bedford School 1Document4 pagesGenetics 3: Bedford School 1George AshcroftNo ratings yet
- Block WorksheetDocument8 pagesBlock WorksheetaditiNo ratings yet
- Exampro GCSE Biology: B2.5 InheritanceDocument35 pagesExampro GCSE Biology: B2.5 InheritanceMeera ParaNo ratings yet
- A Level Biology Topic 3 Practise QuestionsDocument27 pagesA Level Biology Topic 3 Practise QuestionsannabelkhewittNo ratings yet
- GeneticsDocument35 pagesGeneticsSmithNo ratings yet
- 17.2 Inheritance Igcse Cie Biology Ext Theory QPDocument11 pages17.2 Inheritance Igcse Cie Biology Ext Theory QPivannn510510No ratings yet
- 1.3 ProteinsDocument38 pages1.3 ProteinsericychenNo ratings yet
- Archaeopteryx: © Wlad74/Istock/ThinkstockDocument13 pagesArchaeopteryx: © Wlad74/Istock/Thinkstockgreg heffleyNo ratings yet
- Exercise Grade 8 PDFDocument17 pagesExercise Grade 8 PDFShanti Damayanti0% (1)
- Activity GeneticsDocument5 pagesActivity GeneticsZayan vlogsNo ratings yet
- Inheritance and Variation Worksheet Year 9 SCSSDocument1 pageInheritance and Variation Worksheet Year 9 SCSSBarminga KamurenNo ratings yet
- Stages of Mitosis Diagram ExplainedDocument6 pagesStages of Mitosis Diagram ExplainedBeaNo ratings yet
- X IG First Assesment 2023Document4 pagesX IG First Assesment 2023Dr. M. PrinceNo ratings yet
- Formative assessment on inheritance in goatsDocument4 pagesFormative assessment on inheritance in goatsTarshihiNo ratings yet
- Pedigree Analysis WS GeneticsDocument11 pagesPedigree Analysis WS Geneticsshishir.saripalli22No ratings yet
- 1.4 DNA and Protein SynthesisDocument44 pages1.4 DNA and Protein SynthesisericychenNo ratings yet
- 3a ReproductionDocument25 pages3a ReproductionThaarvena Retina100% (1)
- Reproduction 2 QP PDFDocument12 pagesReproduction 2 QP PDFAlexia Micallef GattNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology FoundationDocument11 pagesCell Biology Foundationrubannalini8No ratings yet
- Practice Qs End of Yr Test Y9Document32 pagesPractice Qs End of Yr Test Y9ashokNo ratings yet
- Mitosis QuestionsDocument10 pagesMitosis QuestionscapremaeNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument26 pagesCell DivisionimanomarbayoumiNo ratings yet
- HSB ReviewDocument3 pagesHSB ReviewKelvin RequenaNo ratings yet
- 9.2 Meiosis Questions PupilsDocument8 pages9.2 Meiosis Questions PupilsHarryNo ratings yet
- Inheritance 2 QPDocument10 pagesInheritance 2 QPIsini sehansa amarathungaNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction 2Document30 pagesHuman Reproduction 2Huma NazneyNo ratings yet
- 9C Practice PaperDocument42 pages9C Practice PapersabiasezenNo ratings yet
- Quiz_Sp_2Document5 pagesQuiz_Sp_2limshenrong2728No ratings yet
- 4.5 Species and Taxonomy QP 2Document13 pages4.5 Species and Taxonomy QP 2MuffarrahNo ratings yet
- IB Biology Chap 1.1 InheritanceDocument15 pagesIB Biology Chap 1.1 InheritanceLaura WNo ratings yet
- Hardy-Weinberg 1Document3 pagesHardy-Weinberg 1uponichidinma123No ratings yet
- AW3 TestDocument7 pagesAW3 TestHuseyn HuseynovNo ratings yet
- 2015 - June 1B QP PDFDocument32 pages2015 - June 1B QP PDFSimilar12345No ratings yet
- InheritanceDocument37 pagesInheritanceTariq JacksonNo ratings yet
- Benjamin Watson - AQA - Biology - Inheritance Variation Evolution - GraspIT - GCSE - Write On WorksheetDocument18 pagesBenjamin Watson - AQA - Biology - Inheritance Variation Evolution - GraspIT - GCSE - Write On WorksheetboobooNo ratings yet
- 3B Inheritance: Time: 1 Hour 17 Minutes Total Marks Available: 77 Total Marks AchievedDocument30 pages3B Inheritance: Time: 1 Hour 17 Minutes Total Marks Available: 77 Total Marks AchievedRabia RafiqueNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Heredity and VariationDocument14 pagesChapter 3 Heredity and Variationuncleya07100% (1)
- SLP 1Document4 pagesSLP 1Md. Hefjur Rahman ShamimNo ratings yet
- IASB T03C Practice PaperDocument13 pagesIASB T03C Practice PaperfatmanassersocialsNo ratings yet
- Exampro GCSE Biology: B1 Chapter 6 VariationDocument26 pagesExampro GCSE Biology: B1 Chapter 6 VariationMeera ParaNo ratings yet
- KS3 Bio 7B Reproduction 116marksDocument36 pagesKS3 Bio 7B Reproduction 116marksyasmen farouk100% (1)
- 2.3 Cell Cycle and DivisonDocument72 pages2.3 Cell Cycle and DivisonOvina RanasingheNo ratings yet
- ReproductionDocument14 pagesReproductionTariq JacksonNo ratings yet
- Science Revision 2 For Year 6Document5 pagesScience Revision 2 For Year 6Aliha MuzarinNo ratings yet
- 1.5 The Origin of CellsDocument1 page1.5 The Origin of CellsedeceNo ratings yet
- pET 30aDocument2 pagespET 30aKrunal PatelNo ratings yet
- Cichlid Science 2019: Abstract BookDocument70 pagesCichlid Science 2019: Abstract BookJd DiazNo ratings yet
- Melcs BiotechnologyDocument3 pagesMelcs BiotechnologyEarlyn Joy Villaruel Eniola67% (3)
- Tutorial - Ernst - ChromHMMDocument55 pagesTutorial - Ernst - ChromHMMKS VelArcNo ratings yet
- Amgen Lab Med Bio p.1 2017-18Document7 pagesAmgen Lab Med Bio p.1 2017-18Rana MehaiNo ratings yet
- Luciana Parisi Symbiotic Architecture Prehending DigitalityDocument29 pagesLuciana Parisi Symbiotic Architecture Prehending Digitalitycalum morganNo ratings yet
- Types of Nucleic Acids: Return To TOC 1Document95 pagesTypes of Nucleic Acids: Return To TOC 1Hey itsJamNo ratings yet
- Hiperfect Transfection Reagent Handbook: Fifth Edition October 2010Document72 pagesHiperfect Transfection Reagent Handbook: Fifth Edition October 2010Byron Castillo PipuulNo ratings yet
- BTN 315 Exam Prep ch5 10 1Document4 pagesBTN 315 Exam Prep ch5 10 1Corbyn JasonNo ratings yet
- Dihybrid Crosses Worksheet KEYDocument2 pagesDihybrid Crosses Worksheet KEYJennifer Shawki100% (1)
- 3 - Structure of DNA, RNA, GenesDocument206 pages3 - Structure of DNA, RNA, GenesJustina VillageNo ratings yet
- Intro To Genetics Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesIntro To Genetics Lesson Planapi-242297727No ratings yet
- Module 1.4Document19 pagesModule 1.4Valery Mae CaraigNo ratings yet
- 01sex LinkageDocument26 pages01sex LinkageAehronCatilocNo ratings yet
- SARS-CoronaVirus - DOI:10.1128/JVI.03079-15 - Journal of Virology 2016 Zeng 6573Document10 pagesSARS-CoronaVirus - DOI:10.1128/JVI.03079-15 - Journal of Virology 2016 Zeng 6573TN HomesteaderNo ratings yet
- Genetic Lab NotebookDocument11 pagesGenetic Lab NotebookKevin Chen100% (1)
- 13Document13 pages13AmaniNo ratings yet
- The Existence of GenesDocument2 pagesThe Existence of GenesMrMarkitosNo ratings yet
- Full Download Test Bank For Concepts of Genetics 12th by Klug PDF Full ChapterDocument6 pagesFull Download Test Bank For Concepts of Genetics 12th by Klug PDF Full Chapterhemato.unlaughlf4d100% (14)
- Literature Review Genetic EngineeringDocument11 pagesLiterature Review Genetic Engineeringapi-253913975100% (1)
- Revisión 2021 Genética Niemann Pick.Document22 pagesRevisión 2021 Genética Niemann Pick.patricia.rtorreshotmail.comNo ratings yet
- Gizmos - Evolution, Natural and Artificial SelectionDocument9 pagesGizmos - Evolution, Natural and Artificial SelectionAsh50% (2)
- Phylogeny and Classification, Student Learning: Name: - Period: - DateDocument3 pagesPhylogeny and Classification, Student Learning: Name: - Period: - DateL ChanNo ratings yet
- Build a Paper Model of DNA in 10 StepsDocument2 pagesBuild a Paper Model of DNA in 10 StepsMarcela Ino100% (1)
- History Genetics Immuno HO BB Ms TanDocument3 pagesHistory Genetics Immuno HO BB Ms TanJoey MagnoNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 Introduction To Cell DivisionDocument27 pagesUnit 8 Introduction To Cell DivisionTeo PhiriNo ratings yet
- Plant BreedingDocument5 pagesPlant BreedingbutterfilyNo ratings yet
- CBSE Biology Class XII Principles and Processes of BiotechnologyDocument7 pagesCBSE Biology Class XII Principles and Processes of BiotechnologyAkshat JainNo ratings yet
- Unpacking The Self: Physical and Sexual SelfDocument2 pagesUnpacking The Self: Physical and Sexual Selfmelissa86% (7)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (811)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessFrom Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (33)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesFrom EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (397)
- Human: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueFrom EverandHuman: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (38)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceFrom EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (18)
- Crypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondFrom EverandCrypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainFrom EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (65)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveFrom EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (66)
- The Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindFrom EverandThe Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (93)
- This Is Your Brain On Parasites: How Tiny Creatures Manipulate Our Behavior and Shape SocietyFrom EverandThis Is Your Brain On Parasites: How Tiny Creatures Manipulate Our Behavior and Shape SocietyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (31)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedFrom EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomFrom EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (215)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildFrom EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceFrom EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (515)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorFrom EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNo ratings yet
- Eels: An Exploration, from New Zealand to the Sargasso, of the World's Most Mysterious FishFrom EverandEels: An Exploration, from New Zealand to the Sargasso, of the World's Most Mysterious FishRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (30)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsFrom EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Superlative: The Biology of ExtremesFrom EverandSuperlative: The Biology of ExtremesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (51)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldFrom EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- The Second Brain: A Groundbreaking New Understanding of Nervous Disorders of the Stomach and IntestineFrom EverandThe Second Brain: A Groundbreaking New Understanding of Nervous Disorders of the Stomach and IntestineRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (17)
- Younger for Life: Feel Great and Look Your Best with the New Science of AutojuvenationFrom EverandYounger for Life: Feel Great and Look Your Best with the New Science of AutojuvenationRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Darwin's Dangerous Idea: Evolution and the Meaning of LifeFrom EverandDarwin's Dangerous Idea: Evolution and the Meaning of LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (523)
- Fearfully and Wonderfully: The Marvel of Bearing God's ImageFrom EverandFearfully and Wonderfully: The Marvel of Bearing God's ImageRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (40)
- The Dragons of Eden: Speculations on the Evolution of Human IntelligenceFrom EverandThe Dragons of Eden: Speculations on the Evolution of Human IntelligenceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (632)