Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ISO 27001 Controls 2022
Uploaded by
Andres50%(2)50% found this document useful (2 votes)
2K views1 pageThis document outlines controls for information security based on ISO 27001 and ISO 27002 standards. It is organized into sections covering organizational controls, people controls, physical controls, and technological controls. Each section lists specific controls that organizations can implement to help ensure the confidentiality, integrity and availability of their information systems and assets. Some examples of controls mentioned include policies for information security, information security roles, physical security perimeters, access control measures, and secure authentication methods.
Original Description:
ISO 27001 and ISO 27002. Information security controls
Original Title
ISO 27001 controls 2022_
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document outlines controls for information security based on ISO 27001 and ISO 27002 standards. It is organized into sections covering organizational controls, people controls, physical controls, and technological controls. Each section lists specific controls that organizations can implement to help ensure the confidentiality, integrity and availability of their information systems and assets. Some examples of controls mentioned include policies for information security, information security roles, physical security perimeters, access control measures, and secure authentication methods.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
50%(2)50% found this document useful (2 votes)
2K views1 pageISO 27001 Controls 2022
Uploaded by
AndresThis document outlines controls for information security based on ISO 27001 and ISO 27002 standards. It is organized into sections covering organizational controls, people controls, physical controls, and technological controls. Each section lists specific controls that organizations can implement to help ensure the confidentiality, integrity and availability of their information systems and assets. Some examples of controls mentioned include policies for information security, information security roles, physical security perimeters, access control measures, and secure authentication methods.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
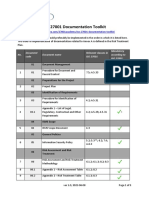
ISO 27001 and ISO 27002.
Information security controls, 2022
5. Organizational controls 6. People controls 8. Technological controls
5.1. Policies for information security 6.1. Screening 8.1. User endpoint devices
5.2. Information security roles and responsibilities 6.2. Terms and conditions of employment 8.2. Privileged access rights
5.3. Segregation of duties 6.3. Information security awareness, education and 8.3. Information access restriction
5.4. Management responsibilities training 8.4. Access to source code
5.5. Contact with authorities 6.4. Disciplinary process 8.5. Secure authentication
5.6. Contact with special interest groups 6.5. Responsibilities after termination or change of 8.6. Capacity management
5.7. Threat intelligence employment 8.7. Protection against malware
5.8. Information security in project management 6.6. Confidentiality or non-disclosure agreements 8.8. Management of technical vulnerabilities
5.9. Inventory of information and other associated assets 6.7. Remote working 8.9. Configuration management
5.10. Acceptable use of information and other associated assets 6.8. Information security event reporting 8.10. Information deletion
5.11. Return of assets 8.11. Data masking
5.12. Classification of information 7. Physical controls 8.12. Data leakage prevention
5.13. Labelling of information 8.13. Information backup
5.14. Information transfer 7.1. Physical security perimeter 8.14. Redundancy of information processing facilities
5.15. Access control 7.2. Physical entry 8.15. Logging
5.16. Identity management 7.3. Securing offices, rooms and facilities 8.16. Monitoring activities
5.17. Authentication information 7.4. Physical security monitoring 8.17. Clock synchronization
5.18. Access rights 7.5. Protecting against physical and environmental 8.18. Use of privileged utility programs
5.19. Information security in supplier relationships threats 8.19. Installation of software on operational systems
5.20. Addressing information security within supplier agreements 7.6. Working in secure areas 8.20. Network security
5.21. Managing information security in the ICT supply chain 7.7. Clear desk and clear screen 8.21. Security of network services
5.22. Monitoring, review and change management of supplier services 7.8. Equipment siting and protection 8.22. Segregation of networks
5.23. Information security for use of cloud services 7.9. Security of assets off-premises 8.23. Web filtering
5.24. Information security incident management planning and 7.10. Storage media 8.24. Use of cryptography
preparation 7.11. Supporting utilities 8.25. Secure development life cycle
5.25. Assessment and decision on information security events 7.12. Cabling security 8.26. Application security requirements
5.26. Response to information security incidents 7.13. Equipment maintenance 8.27. Secure system architecture and engineering
5.27. Learning from information security incidents 7.14. Secure disposal or re-use of equipment principles
5.28. Collection of evidence 8.28. Secure coding
5.29. Information security during disruption 8.29. Security testing in development and acceptance
5.30. ICT readiness for business continuity 8.30. Outsourced development
5.31. Legal, statutory, regulatory and contractual requirements 8.31. Separation of development, test and production
5.32. Intellectual property rights environments
5.33. Protection of records 8.32. Change management
5.34. Privacy and protection of PII 8.33. Test information
5.35. Independent review of information security 8.34. Protection of information systems during audit
5.36. Compliance with policies, rules and standards for information testing
security
5.37. Documented operating procedures
*New control, 2022
by Andrey Prozorov, CISM, CIPP/E, CDPSE, LA 27001 - www.patreon.com/AndreyProzorov Control: measure that maintains and/or modifies risk
You might also like
- ISO 27001 MappingDocument17 pagesISO 27001 MappingNikolas Kyriakidis100% (1)
- Information security - Edition 2022: Risk management. Management systems. The ISO/IEC 27001:2022 standard. The ISO/IEC 27002:2022 controls.From EverandInformation security - Edition 2022: Risk management. Management systems. The ISO/IEC 27001:2022 standard. The ISO/IEC 27002:2022 controls.No ratings yet
- Control Mapping: ISO 27002:2013 TO ISO 27002:2022Document6 pagesControl Mapping: ISO 27002:2013 TO ISO 27002:2022Chi Jui Han100% (4)
- Free Template Statement of Applicability ISO27001 2022Document39 pagesFree Template Statement of Applicability ISO27001 2022Ruta Diferente100% (1)
- MSECB ISO IEC 27002 MappingDocument10 pagesMSECB ISO IEC 27002 MappingAhi PolaNo ratings yet
- CT05 1 ISO 27001 Documentation KitDocument25 pagesCT05 1 ISO 27001 Documentation Kitfahrizal fatah100% (6)
- ISO IEC 27001 Lead Implementer A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionFrom EverandISO IEC 27001 Lead Implementer A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNo ratings yet
- ISO 27001 Annex A Controls in Plain English: A Step-by-Step Handbook for Information Security Practitioners in Small BusinessesFrom EverandISO 27001 Annex A Controls in Plain English: A Step-by-Step Handbook for Information Security Practitioners in Small BusinessesNo ratings yet
- ISO 27001 2022 Documentation Simplified Checklist and GuideDocument8 pagesISO 27001 2022 Documentation Simplified Checklist and GuideTechnical - GR50% (2)
- ISO 27001 - 2022. How To Prepare For A Certification AuditDocument33 pagesISO 27001 - 2022. How To Prepare For A Certification AuditAmmar Hassan100% (3)
- ISO IEC 27001 Lead Auditor A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionFrom EverandISO IEC 27001 Lead Auditor A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNo ratings yet
- ISO 27001 Controls – A guide to implementing and auditingFrom EverandISO 27001 Controls – A guide to implementing and auditingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- ISO 27001 2022 Gap Analysis ToolDocument16 pagesISO 27001 2022 Gap Analysis ToolMuhammed Ali Ahmad100% (5)
- List of Documents ISO 27001Document5 pagesList of Documents ISO 27001Taraj O K100% (2)
- Main Changes in ISO 27001-2022Document3 pagesMain Changes in ISO 27001-2022Umesh Rane80% (5)
- ISO 27001 ChecklistDocument32 pagesISO 27001 ChecklistVishal Vasu100% (4)
- ISO-27001-Checklist & Gap AnalysisDocument32 pagesISO-27001-Checklist & Gap AnalysisAlpesh Patel25% (4)
- Nine Steps to Success: North American edition: An ISO 27001 Implementation OverviewFrom EverandNine Steps to Success: North American edition: An ISO 27001 Implementation OverviewNo ratings yet
- Anonymized ISO 27001 Assessment ReportDocument50 pagesAnonymized ISO 27001 Assessment ReportaNo ratings yet
- ISO/IEC 27001:2022: An introduction to information security and the ISMS standardFrom EverandISO/IEC 27001:2022: An introduction to information security and the ISMS standardRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- How To Comply With Iso 27001 2022 Security Controls Using Siem PDFDocument23 pagesHow To Comply With Iso 27001 2022 Security Controls Using Siem PDFThang Manh100% (1)
- ISO 27001 - 2022 Audit ChecklistDocument10 pagesISO 27001 - 2022 Audit Checklistahmet erkolNo ratings yet
- ISO 27001 Documentation Simplified Checklist and GuideDocument7 pagesISO 27001 Documentation Simplified Checklist and GuideS100% (1)
- List of Documents ISO 27001 2022 Documentation Toolkit ENDocument5 pagesList of Documents ISO 27001 2022 Documentation Toolkit ENLETSOGILENo ratings yet
- ISO IEC 27005-2022 Information Security, Cybersecurity and Privacy Protection - Guidance On Managing Information SecuDocument70 pagesISO IEC 27005-2022 Information Security, Cybersecurity and Privacy Protection - Guidance On Managing Information Secu李哲祥81% (16)
- Business Case For Iso 27001Document7 pagesBusiness Case For Iso 27001Sandy Bouvier-IngramNo ratings yet
- PDF Iso Iec 27001 2022Document26 pagesPDF Iso Iec 27001 2022Kî Fëh85% (72)
- IS0 - IEC 27001 Implementation GuideDocument79 pagesIS0 - IEC 27001 Implementation GuideJABERO861108100% (4)
- ISO IEC 27001 Lead Implementer A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionFrom EverandISO IEC 27001 Lead Implementer A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionNo ratings yet
- ISO 27701 Audit Checklist - © Lumiform 2023Document3 pagesISO 27701 Audit Checklist - © Lumiform 2023Bruce ROBERTSON100% (1)
- The IS0 / IEC 27001 StandardDocument4 pagesThe IS0 / IEC 27001 StandardUmesh Rane100% (1)
- Everything You Need To Know About The ISO 27001 2022 Standard Update 1Document4 pagesEverything You Need To Know About The ISO 27001 2022 Standard Update 1Sudhanshu Kumar SinhaNo ratings yet
- ISO 27001 2022 How To Conduct An ISMS Gap Analysis 1684315308Document23 pagesISO 27001 2022 How To Conduct An ISMS Gap Analysis 1684315308Harshit mathur100% (4)
- ISO 27001-2022 Gap Analysis ChecklistDocument34 pagesISO 27001-2022 Gap Analysis Checklistttestxyz100% (1)
- ISO 2700 - 2022 Audit ChecklistDocument7 pagesISO 2700 - 2022 Audit ChecklistM Tabish100% (4)
- ISO27k Standards ListingDocument6 pagesISO27k Standards ListingTikCGNo ratings yet
- ISO27001 in a Windows Environment: The best practice implementation handbook for a Microsoft Windows environmentFrom EverandISO27001 in a Windows Environment: The best practice implementation handbook for a Microsoft Windows environmentNo ratings yet
- ISMS Control Checklist 2022Document31 pagesISMS Control Checklist 2022Anele Patriarca100% (1)
- ISO 27001 Implementation ChecklistDocument8 pagesISO 27001 Implementation ChecklistHost Jakarta100% (1)
- Iso 27701.2019Document76 pagesIso 27701.2019Febree Alandiestya100% (2)
- ISMS Statement of ApplicabilityDocument20 pagesISMS Statement of ApplicabilityNatália Gomes Knob100% (1)
- Understanding THE UPDATED ISO 27001Document15 pagesUnderstanding THE UPDATED ISO 27001Rishabh Batra100% (4)
- 27001-Gap-Analysis ToolDocument15 pages27001-Gap-Analysis ToolPeter Rendek0% (2)
- ISO27001 2022 Self-Assessment Checklist - (9p)Document9 pagesISO27001 2022 Self-Assessment Checklist - (9p)Rodrigo Benavente100% (1)
- ISO 27001 Gap Analysis Sample Excerpt PDFDocument8 pagesISO 27001 Gap Analysis Sample Excerpt PDFsathish kumarNo ratings yet
- Secure & Simple – A Small-Business Guide to Implementing ISO 27001 On Your Own: The Plain English, Step-by-Step Handbook for Information Security PractitionersFrom EverandSecure & Simple – A Small-Business Guide to Implementing ISO 27001 On Your Own: The Plain English, Step-by-Step Handbook for Information Security PractitionersNo ratings yet
- Easiest OperatingInstructions BODocument24 pagesEasiest OperatingInstructions BOidkwhiiNo ratings yet
- Oracle Database Backup and Recovery Advanced User GuideDocument586 pagesOracle Database Backup and Recovery Advanced User Guideapi-25919427100% (1)
- DSPC News WritingDocument2 pagesDSPC News WritingEA Crisostomo100% (2)
- PowerVisa UsersGuide RevBDocument274 pagesPowerVisa UsersGuide RevBChema JuarezNo ratings yet
- ProtocolDocument19 pagesProtocolAlin StelianNo ratings yet
- Smart City Berlin: Case StudyDocument2 pagesSmart City Berlin: Case StudyThái DươngNo ratings yet
- CyberSecurity Book PDFDocument96 pagesCyberSecurity Book PDFGabby67% (3)
- Network Security BasicsDocument5 pagesNetwork Security BasicsDavid Aguirre BurneoNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument22 pagesProjectSandeep SharmaNo ratings yet
- Army Ranger HandbookDocument327 pagesArmy Ranger HandbookGasMaskBob100% (2)
- Cyber Security Assessments of Industrial Control SystemsDocument68 pagesCyber Security Assessments of Industrial Control Systemsjosethompson100% (1)
- Cryptographic Hash FunctionsDocument16 pagesCryptographic Hash FunctionsUrvil SitapareNo ratings yet
- Rajib Saha NEW BIODATA (1) .Doc, New-2-1Document2 pagesRajib Saha NEW BIODATA (1) .Doc, New-2-1Rajib SahaNo ratings yet
- Application Schema ParameterDocument75 pagesApplication Schema ParameterMallikNo ratings yet
- Adfs O365Document10 pagesAdfs O365smisatNo ratings yet
- FAQs Cisco Cert Exam Discount Vouchers For NetAcadDocument9 pagesFAQs Cisco Cert Exam Discount Vouchers For NetAcadAathi HariNo ratings yet
- Takahe Installation: Global Partner For SuccessDocument60 pagesTakahe Installation: Global Partner For SuccessAnonymous S6SqIOIp8No ratings yet
- Denial of ServiceDocument48 pagesDenial of ServiceViv EkNo ratings yet
- Information Security A Case Study3Document8 pagesInformation Security A Case Study3ragunathrevNo ratings yet
- BrowseControl UserGuideDocument58 pagesBrowseControl UserGuidest_cruzerioNo ratings yet
- Siex-Hc S-Flow EngDocument12 pagesSiex-Hc S-Flow EngAhmed SalamaNo ratings yet
- The Evolution On Nato Cyber PolicyDocument13 pagesThe Evolution On Nato Cyber PolicyEvelina50No ratings yet
- DUMRDUMRESS016Document24 pagesDUMRDUMRESS016Praveen Kumar BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Asst Professors - Clinical Departments - in Dme-Result Notification For InterviewDocument5 pagesAsst Professors - Clinical Departments - in Dme-Result Notification For InterviewChetan AnandNo ratings yet
- FDocument13 pagesFsurajitpal4uNo ratings yet
- License - EASEUS Data Recovery Wizard Professional 5.5.1Document2 pagesLicense - EASEUS Data Recovery Wizard Professional 5.5.1willie_5745757No ratings yet
- C4 General PDFDocument62 pagesC4 General PDFNadim JilaniNo ratings yet
- Far Cry 6 IiDocument9 pagesFar Cry 6 IiBukuPilihanNo ratings yet
- Web DesignDocument4 pagesWeb DesignJosiahNo ratings yet
- N Wireless Modem Router: User ManualDocument100 pagesN Wireless Modem Router: User ManualJolanda d'AvoineNo ratings yet