Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Acc003 Summary CO 3 Cash and Cash Equivalent
Uploaded by
Hayes HareOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Acc003 Summary CO 3 Cash and Cash Equivalent
Uploaded by
Hayes HareCopyright:
Available Formats
Sales Type Lease- LESSOR
Objectives:
- To understand a sales type lease on the part of lessor.
- To define gross investment and net investment in a sales type lease.
- To recognize gross income on sale and interest income in a sales type lease.
Introduction
- The lessor in a sales type lease is actually a manufacturer or dealer that uses the lease as a means
of facilitating the sale of product.
- The accounting for a sales type lease exhibits many similarities to that for a direct financing lease.
- However, a sales type lease involves the recognition of a manufacturer or dealer profit on the
transfer of the asset to the lessee in addition to the recognition of interest income.
Sales Type Lease
1. Gross investment in the lease is equal to the gross rentals for the entire lease term plus the
absolute amount of the residual value, whether guaranteed or unguaranteed. (This is the same
gross investment in a direct financing lease.)
2. Net investment in the lease is equal to the present value of the gross rentals plus the present
value of the residual value, whether guaranteed or unguaranteed.
3. Unearned interest income is the difference between the gross investment and net investment in
the lease.
4. Sales revenue in equal to the net investment in the lease (present value of lease payments) or fair
value of the asset, whichever is lower.
5. Cost of goods sold is equal to the cost of the asset sold minus the present value of unguaranteed
residual value plus the initial direct cost paid by the lessor.
6. Gross income is the usual formula of sales revenue minus cost of goods sold.
7. Initial direct cost is experienced immediately in a sales type lease as component of cost of goods
sold.
Intermediate Accounting | Acc003 Cash and Cash Equivalent
Journal entries-Books of Lessor Company
1. To record the sale:
Lease receivable 2,000,000
Sales 1,440,000
Unearned interest income 560,000
The gross income of P440, 000 is not separately recorded because it is included already in the sales
revenue.
2. To record the cost of goods sold, assuming the perpetual system is used:
Cost of goods sold 1,000,000
Inventory 1,000,000
3. To record the collection of the annual rental:
Cash 400,000
Lease receivable 400,000
4. To record the interest income for 2021:
Unearned interest income 172,800
Interest income (12% x 1,440,000) 172,800
Sales type lease with residual value
Lessor Company is a dealer in machinery.
On January 1, 2021, a machinery, is leased to another entity with the following provisions:
Annual rental payable at the end of each year 800,000
Lease term 5 years
Useful life of machinery 5 years
Cost of machinery 2,000,000
Residual value 200,000
Initial direct cost paid by lessor 100,000
Implicit interest rate 10%
Present value of an ordinary annuity of 1 for 5 periods at 10% 3.7908
Present value of 1 for 5 periods at 10% 0.6209
At the end of the lease term on December 31, 2025, the machinery shall revert to Lessor Company.
The perpetual inventory system is used.
Note that the residual value may be guaranteed or unguaranteed.
Intermediate Accounting | Acc003 Cash and Cash Equivalent
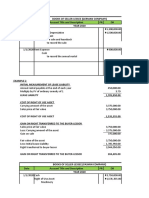
Journal entries on January 1, 2021
Lease receivable 4,200,000
Cost of goods sold 2,000,000
Sales 3,156,820
Unearned interest income 1,043,180
Inventory 2,000,000
Cost of goods sold 100,000
Cash 100,000
The initial direct cost is charged directly to cost of goods sold.
Sales 3,156,820
Cost of goods sold 2,100,000
Gross income 1,056,820
Cost of machinery sold 2,000,000
Initial direct cost 100,000
Cost of goods sold 2,100,000
Intermediate Accounting | Acc003 Cash and Cash Equivalent
Observe that the lease receivable and unearned interest income are the same whether the scenario is
guaranteed or unguaranteed residual value.
However, there is a difference in the computation of the sales and the cost of goods sold.
Under the residual value guarantee scenario, the present value of the residual value is included in the
sales revenue because the lessor knows that the entire asset has been sold.
However, under the unguaranteed residual value scenario, the present value of the unguaranteed residual
value is not included in the sales revenue.
Accordingly, the present value of the unguaranteed residual value is deducted from the cost of
unguaranteed residual value is deducted from the cost of the underlying asset in computing cost of goods
sold.
The reason is that this portion of the leased asset is in effect “not sold” in the sense that the lessor will be
receiving back at the end of the lease term the underlying asset with unguaranteed residual value of
P200,000 and present value of P124,180.
Moreover, the unguaranteed residual value is not considered lease payment as far as the lessee is
concerned.
Intermediate Accounting | Acc003 Cash and Cash Equivalent
Journal entries
To record the sale and the initial direct cost on January 1, 2021 under the concept of unguaranteed
residual value:
Lease receivable 4,200,000
Cost of goods sold 1,875,820
Sales 3,032,640
Unearned interest income 1,043,180
Inventory 2,000,000
Cost of goods sold 100,000
Cash 100,000
Journal entries-December 31, 2021
1. Cash 800,000
Lease receivable 800,000
2. Unearned interest income 315,682
Interest income 315,685
Journal entries-December 31, 2022
1. Cash 800,000
Lease receivable 800,000
2. Unearned interest income 267,250
Interest income 267,250
Intermediate Accounting | Acc003 Cash and Cash Equivalent
Return of asset to lessor
It is to be pointed out that in the illustration the sales type lease provides that the underlying asset shall
revert to the lessor upon termination of the contract.
However, if the underlying asset shall not revert to the lessor, the residual value is completely ignored by
the lessor in the computation of unearned interest income and gross income on the sale.
The underlying asset shall remain with the lessee if the lease provides for either a purchase option that is
reasonably certain to be exercised or transfer of title to the lessee upon the lease expiration.
Sales type lease with purchase option
An entity is a dealer in equipment. On January 1, 2021, an equipment is leased to another entity with the
following provisions:
Annual rental payable at the end of the year 500,000
Lease term 4 years
Useful life of equipment 5 years
Cost of equipment 1,500,000
Initial direct cost paid by lessor 100,000
Purchase option 200,000
Implicit interest rate 8%
PV of an ordinary annuity of 1 at 8% for 4 periods 3.312
PV of 1 at 8% for 4 periods 0.735
It is reasonably certain that the lease shall exercise the purchase option on December 31, 2024.
Intermediate Accounting | Acc003 Cash and Cash Equivalent
Journal entry- January 1, 2021
If the perpetual system is used, the journal entry to record the sale is:
Lease receivable 2,200,000
Cost of goods sold 1,100,000
Sales 1,803,000
Unearned interest income 397,000
Inventory 1, 000,000
Cash 100,000
Table of amortization
Table of amortization of the net lease receivable and interest income:
Payment represents the annual rental.
Interest is equal to the preceding present value times the interest rate.
Thus, for 2021, P1, 803,000 times 8% equals P144, 240, and so on.
Principal is the portion of the annual rental payment after deducting interest.
Intermediate Accounting | Acc003 Cash and Cash Equivalent
Thus, for 2021, P500, 000 minus P144, 240 equals P355, 760 and so on.
Present value is the balance of the present value after deducting the principal payment.
Thus, on December 31, 2021, P1, 803,000 minus P355, 760 equals P1, 447,240 and so on.
Journal entries
Exercise of purchase option
On December 31, 2024, if the entries are properly posted, the lease receivable had a balance of P200, 000
equal to the purchase option and the unearned interest income had a zero balance.
The purchase option is exercised by the lessee on December 31, 2024.
Cash 200,000
Lease receivable 200,000
Nonexercise of purchase option
The purchase option is not exercised by the lessee and the fair value of the underlying asset is P100, 000
only.
Inventory 100,000
Loss on finance lease 100,000
Lease receivable 200,000
Actual sale of underlying asset
When a lessor actually sells an asset that it has been leasing under a finance lease, the difference between
the sale price and the carrying amount of the lease receivable is recognized in profit or loss.
Intermediate Accounting | Acc003 Cash and Cash Equivalent
The carrying amount of the lease receivable is equal to the balance of the lease receivable minus the
unearned interest income.
Illustration
Disclosures-Lessor
A lessor shall disclose the following amounts for the reporting period:
1.For finance lease:
a. Selling profit or loss
b. Finance income on the net investment in the lease
c. Income relating to variable lease payments not included in the measurement of net investment in
the lease.
2. For operating lease, lease income, separately disclosing income relating to variable lease payments that
do not depend on an index or rate.
Additional disclosures
A lessor shall disclose additional qualitative and quantitative information about leasing activities
necessary to assess the
effect of leases on financial position, financial performance and cash flows.
Intermediate Accounting | Acc003 Cash and Cash Equivalent
This additional information includes, but is not limited to, information that helps users of financial
statements to assess:
1. The nature of the lessor’s leasing activities
2. How the lessor manages the risks associated with any rights it retains in the underlying asset.
In particular, a lessor shall disclose its risk management strategy for the rights it retains in
underlying asset, including any means by which the lessor reduces that risk.
Intermediate Accounting | Acc003 Cash and Cash Equivalent
You might also like
- Equity Valuation: Models from Leading Investment BanksFrom EverandEquity Valuation: Models from Leading Investment BanksJan ViebigNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Ia2Document18 pagesChapter 14 Ia2JM Valonda Villena, CPA, MBA67% (3)
- Module 10-SALES TYPE LEASE - LESSORDocument8 pagesModule 10-SALES TYPE LEASE - LESSORJeanivyle CarmonaNo ratings yet
- SALES TYPE LEASE KEY TERMSDocument19 pagesSALES TYPE LEASE KEY TERMSRogelynCodillaNo ratings yet
- Illustrative Problem - Sales Type Lease With Residual ValueDocument2 pagesIllustrative Problem - Sales Type Lease With Residual ValueQueen ValleNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Notes and Loans ReceivableDocument6 pagesAccounting For Notes and Loans ReceivableBvreanchtz Mantilla CalagingNo ratings yet
- Current Cost AccountingDocument23 pagesCurrent Cost AccountingToni Rose Hernandez Lualhati0% (1)
- 162 003Document5 pages162 003Alvin John San Juan33% (3)
- Chapter 3. Exercises Income StatementDocument6 pagesChapter 3. Exercises Income StatementHECTOR ORTEGANo ratings yet
- Ias 1 - Questions..Document8 pagesIas 1 - Questions..Timothy KawumaNo ratings yet
- Accounts Receivable CalculationDocument5 pagesAccounts Receivable CalculationCarmina SanchezNo ratings yet
- Assignment June 2022Document3 pagesAssignment June 2022AirForce ManNo ratings yet
- Item 1 of 5 lease contract tax calculationDocument4 pagesItem 1 of 5 lease contract tax calculationClaudette ClementeNo ratings yet
- Sale and Leaseback DiscussionDocument16 pagesSale and Leaseback DiscussionRyll BedasNo ratings yet
- Lease - LessorDocument8 pagesLease - LessorMonique ElineNo ratings yet
- CH 3 In-Class ExercisesDocument2 pagesCH 3 In-Class ExercisesAbdullah alhamaadNo ratings yet
- Fancy Furniture Company Financial StatementsDocument2 pagesFancy Furniture Company Financial StatementsShashank GuptaNo ratings yet
- Acctg For Special Transaction - Second Lesson PDFDocument6 pagesAcctg For Special Transaction - Second Lesson PDFDebbie Grace Latiban LinazaNo ratings yet
- ACC203 - AssignmentDocument2 pagesACC203 - AssignmentHailsey WinterNo ratings yet
- 162 003Document4 pages162 003Angelli LamiqueNo ratings yet
- Problem SolutionsDocument5 pagesProblem Solutionsmd nayonNo ratings yet
- Review Notes #2 - Comprehensive Problem PDFDocument3 pagesReview Notes #2 - Comprehensive Problem PDFtankofdoom 4No ratings yet
- Cost AccountingDocument3 pagesCost AccountingXen XeonNo ratings yet
- Ia CH 6 & 7 NR LR 2020Document112 pagesIa CH 6 & 7 NR LR 2020Jm Sevalla57% (14)
- Corporate Reporting Assignment 1 - GroupDocument18 pagesCorporate Reporting Assignment 1 - GroupangelaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Notes and Loans Receivable PDFDocument43 pagesModule 1 Notes and Loans Receivable PDFALEXA GENMARY GULFAN0% (1)
- Cash and Accrual BasisDocument4 pagesCash and Accrual BasisSeulgi KangNo ratings yet
- AFM-Module 2 IDocument10 pagesAFM-Module 2 IkanikaNo ratings yet
- Of Financial PositionDocument3 pagesOf Financial PositionIrah LouiseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 40 IFRIC InterpretationsDocument5 pagesChapter 40 IFRIC InterpretationsEllen MaskariñoNo ratings yet
- Notes Receivable Journal EntriesDocument10 pagesNotes Receivable Journal EntriesAnaluz Cristine B. CeaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 AFSDocument14 pagesAssignment 1 AFSSimra SalmanNo ratings yet
- PRACTICEDocument4 pagesPRACTICEGleeson Jay NiedoNo ratings yet
- Example 1: Classification of Leases: 1. Calculating Present Value of Minimum Lease PaymentsDocument9 pagesExample 1: Classification of Leases: 1. Calculating Present Value of Minimum Lease PaymentsJessa BasadreNo ratings yet
- Sources of OUTPUT VATDocument37 pagesSources of OUTPUT VATKiro ParafrostNo ratings yet
- Capital and Revenue TransactionsDocument7 pagesCapital and Revenue Transactionscarolm790No ratings yet
- Audit of Error Correction and Cash and AccrualsDocument4 pagesAudit of Error Correction and Cash and AccrualsRafael BarbinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 Ia2Document21 pagesChapter 15 Ia2JM Valonda Villena, CPA, MBANo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Current LiabilitiesDocument6 pagesChapter 1 - Current LiabilitiesXiena100% (1)
- Financial Statement Analysis for Entity Providing Trial BalanceDocument3 pagesFinancial Statement Analysis for Entity Providing Trial BalanceMansour HamjaNo ratings yet
- Asdos Pert 2Document2 pagesAsdos Pert 2mutiaoooNo ratings yet
- Accounting Review ExercisesDocument13 pagesAccounting Review Exercisesa.pashai5571No ratings yet
- Financial Accounting and Reporting Problems Freebie PDFDocument46 pagesFinancial Accounting and Reporting Problems Freebie PDFC/PVT DAET, SHAINA JOYNo ratings yet
- PRACTICE QUESTIONS 1 (IA3) (Midterms) : AnswerDocument21 pagesPRACTICE QUESTIONS 1 (IA3) (Midterms) : AnswerShiena ApasNo ratings yet
- ACC110 P3Quiz2 AnswersDocument12 pagesACC110 P3Quiz2 AnswersTricia Mae FernandezNo ratings yet
- Financial Problems Jan 19Document17 pagesFinancial Problems Jan 19ledmabaya23No ratings yet
- Group Activity 1 Aec 217Document5 pagesGroup Activity 1 Aec 217Enitsuj Eam EugarbalNo ratings yet
- Group Activity 1 Cash and Accrual AdjustmentsDocument5 pagesGroup Activity 1 Cash and Accrual AdjustmentsEnitsuj Eam EugarbalNo ratings yet
- Insurance ClaimsDocument17 pagesInsurance Claimshk7012004No ratings yet
- Act1111 Final ExamDocument7 pagesAct1111 Final ExamHaidee Flavier SabidoNo ratings yet
- Practice Exercise 1.1Document4 pagesPractice Exercise 1.1leshz zynNo ratings yet
- Cash vs Accrual Basis AccountingDocument4 pagesCash vs Accrual Basis AccountingSeulgi KangNo ratings yet
- 6727 Statement of Financial PositionDocument3 pages6727 Statement of Financial PositionJane ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Ia3 Midterm QuizDocument11 pagesIa3 Midterm QuizJalyn Jalando-onNo ratings yet
- Guideline Answers For Accounting Group - IDocument14 pagesGuideline Answers For Accounting Group - ITrisha IyerNo ratings yet
- CFAS Chapter40 IFRIC Interpretations (Gutierrez-Ingat)Document19 pagesCFAS Chapter40 IFRIC Interpretations (Gutierrez-Ingat)Fran GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Illustration: Preparation of Master Budget (Manufacturing Company)Document4 pagesIllustration: Preparation of Master Budget (Manufacturing Company)shimelisNo ratings yet
- For Students - Interpretation of FS - Ratio Analysis - Example, ExercisesDocument10 pagesFor Students - Interpretation of FS - Ratio Analysis - Example, ExercisesdimniousNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Strategic CostDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Strategic CostHayes HareNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Strategic CostDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Strategic CostHayes HareNo ratings yet
- KAP On COVID 19 - SampleDocument5 pagesKAP On COVID 19 - SampleHayes HareNo ratings yet
- Partnership Accounting NotesDocument5 pagesPartnership Accounting NotesHayes Hare100% (1)
- ITE002 - AIS Topic 3 Ethics - Fraud - Internal ControlsDocument24 pagesITE002 - AIS Topic 3 Ethics - Fraud - Internal ControlsHayes HareNo ratings yet
- Stock Acquisition Quiz 100% AnswerDocument2 pagesStock Acquisition Quiz 100% AnswerJohn BalanquitNo ratings yet
- Corporate Financing and Planning Course4Document15 pagesCorporate Financing and Planning Course4edoardozanetta99No ratings yet
- BBC Business Model and Strategic Initiatives Case AnalysisDocument16 pagesBBC Business Model and Strategic Initiatives Case Analysisadrishm0% (1)
- Keith Wicks Revised Grocery Study 03-17-14Document30 pagesKeith Wicks Revised Grocery Study 03-17-14cottswdrbNo ratings yet
- Gmail - Contact The BankDocument1 pageGmail - Contact The BankFira tubeNo ratings yet
- SP Capital IQDocument11 pagesSP Capital IQemirav2100% (1)
- Revista Economica Vol 4 2012Document677 pagesRevista Economica Vol 4 2012lucia_balanoiuNo ratings yet
- Final Output Chapter 25-26Document27 pagesFinal Output Chapter 25-26Syrell Nabor100% (4)
- Voluntary Petition: United States Bankruptcy Court Central District of CaliforniaDocument47 pagesVoluntary Petition: United States Bankruptcy Court Central District of CaliforniaChapter 11 DocketsNo ratings yet
- MF ISIN CodeDocument49 pagesMF ISIN CodeshriramNo ratings yet
- Activity: (50,000) 0 0 0 0 Net Income (50,000) 2,366Document4 pagesActivity: (50,000) 0 0 0 0 Net Income (50,000) 2,366PirvuNo ratings yet
- Executive Summary 1 Chapter 2 - MarketinDocument3 pagesExecutive Summary 1 Chapter 2 - MarketinAreseenNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting Chapter 2Document19 pagesFinancial Accounting Chapter 2abhinav2018No ratings yet
- VCM Module 7 - Tools Used in Asset-Based Valuation and Asset-Based Valuation MethodsDocument58 pagesVCM Module 7 - Tools Used in Asset-Based Valuation and Asset-Based Valuation MethodsLaurie Mae ToledoNo ratings yet
- IEB Report For Penn National 9.18.13Document307 pagesIEB Report For Penn National 9.18.13MassLiveNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Issues in Accounting: Solution ManualDocument20 pagesContemporary Issues in Accounting: Solution ManualKeiLiew0% (1)
- Module 1Document23 pagesModule 1prabhakarnandyNo ratings yet
- Competitiveness Strategy ProductivityDocument15 pagesCompetitiveness Strategy ProductivityMohit DhonifNo ratings yet
- HVS - Market-Update-Maldives-Sustaining-for-the-Future-Tourism-Environment-and-InvestmentDocument11 pagesHVS - Market-Update-Maldives-Sustaining-for-the-Future-Tourism-Environment-and-InvestmentYak MirelNo ratings yet
- A Case Study of Profitability Analysis of Standard Chartered Bank Nepal LTDDocument16 pagesA Case Study of Profitability Analysis of Standard Chartered Bank Nepal LTDDiwesh Tamrakar100% (1)
- Inflation Advantages and DisadvantagesDocument4 pagesInflation Advantages and DisadvantagesGhanshyam AhireNo ratings yet
- 808 Chapman FATCA Tax International Clients Assets 1017Document19 pages808 Chapman FATCA Tax International Clients Assets 1017FreeInformation4ALLNo ratings yet
- ForeclosureDefenseHandbook PDFDocument116 pagesForeclosureDefenseHandbook PDFjoe100% (3)
- Financial Management Theory and Practice 15th Edition Brigham Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesFinancial Management Theory and Practice 15th Edition Brigham Solutions Manualartisticvinosezk57No ratings yet
- IRS Publication 535Document56 pagesIRS Publication 535private completelyNo ratings yet
- CBM FinalDocument37 pagesCBM FinalSaili SarmalkarNo ratings yet
- Tesla Case PDFDocument108 pagesTesla Case PDFJeremiah Peter100% (1)
- BCG Building An Integrated Marketing and Sales Engine For B2B June 2018 NL Tcm9 196057Document8 pagesBCG Building An Integrated Marketing and Sales Engine For B2B June 2018 NL Tcm9 196057OIGRESNo ratings yet
- IFMDocument3 pagesIFMsoniya_justme2002No ratings yet
- Commodity Covariance ContractingDocument18 pagesCommodity Covariance Contractingpacman_dellNo ratings yet