Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction
Introduction
Uploaded by
Christelle BassilOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction
Introduction
Uploaded by
Christelle BassilCopyright:
Available Formats
Economics:
23 September 2021;
Scarcity=rare, we always want more, and can’t have all we want. We face scarcity which is why we
have to make choices.
An incentive is a reward that encourages an action or a penalty that discourages an action.
Economics are a social science that studies the choices that everyone makes facing scarcity.
Economics are divided in 2 main parts: microeconomics and macroeconomics.
- Microeconomics: the study of choices that individuals and businesses make, how their choices
interact in markets, and the influence of governments (ex: why are people downloading more
movies?)
- Macroeconomics: the study of performance of the national and global economies (ex: why does
the unemployment rate fluctuate?)
7 October 2021;
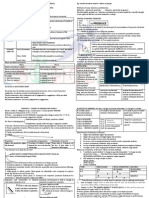
Graph:
- Positive relationship: when x and y increase/decrease at the same time, if they move in the
same directions for example: x1=4 & y1=6 and x2=6 & y2=8
27 October 2021
Being efficient= getting what you want at a low cost
Tradeoff= take something for something else opportunity cost = (loss)/gain.
Chose at margin= minimum cost with a max benefit (I studied the minimum required for the minimum
grade and went to the party the max of time).
Example: loss 10 oranges and gain 5 apples
−10
Opportunity cost = =−2 (the opportunity cost is always negative because the loss is negative)
5
When the price of factors of production increase, the supplies decrease.
Equilibrium: point intersection de supply and demand.
Quantity equilibrium= quantity supply (Qs) = quantity demanded (Qd)
Qd<Qs surplus (Qs-Qd>0)
Qd > Qs shortage =black market (Qs-Qd<0)
Black market price> price expected
When the demand increases, the demand curve shifts rightward.
- Surplus: price over the equilibrium price.
- Shortage: price under the equilibrium price.
The equilibrium changes when either the demand or the supply changes/shifts.
Demanded shifted, equilibrium changed but the supply didn’t change; the point of equilibrium did.
You might also like
- Ib MicroEconomics NotesDocument15 pagesIb MicroEconomics Noteswhisper69100% (2)
- Summary Of "Brief Introduction To The Thought Of Keynes" By Dudley Dillard: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESFrom EverandSummary Of "Brief Introduction To The Thought Of Keynes" By Dudley Dillard: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESNo ratings yet
- ECON 251 Financial Theory - Notes H1Document28 pagesECON 251 Financial Theory - Notes H1mingymag83% (6)
- Economics NotesDocument5 pagesEconomics NotesNaghul MxNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics I Lecture Notes 1 11Document94 pagesMicroeconomics I Lecture Notes 1 11g6766wfr54No ratings yet
- Microeconomics: Department of Economics Faculty of Economics and Management Doc. Ing. Iveta Zentková, Phd. 07 / 2006Document78 pagesMicroeconomics: Department of Economics Faculty of Economics and Management Doc. Ing. Iveta Zentková, Phd. 07 / 2006Tomasz KapłonNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics NotesDocument40 pagesMacroeconomics Noteshjay1058No ratings yet
- Intro To EconDocument6 pagesIntro To Econ4gjhfv2yvfNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument26 pagesNotesEwa PateckaNo ratings yet
- Econ Post-Midterm Study GuideDocument3 pagesEcon Post-Midterm Study Guiderwyrick1No ratings yet
- Microeconomics: Dr. Ahmed Said AhmedDocument18 pagesMicroeconomics: Dr. Ahmed Said Ahmedmariam raafatNo ratings yet
- Micro (4 Tuan Dau)Document3 pagesMicro (4 Tuan Dau)Nguyen Trung Kien ( Swinburne HN)No ratings yet
- Econ 100.2 - LE 1 CoverageDocument11 pagesEcon 100.2 - LE 1 CoverageRed TigerNo ratings yet
- Notebook - MicroeconomicsDocument12 pagesNotebook - MicroeconomicsElectron I'mNo ratings yet
- REVISIONDocument18 pagesREVISIONVương Hoàng Yến TrangNo ratings yet
- Eco NotesDocument11 pagesEco NotesANIKET ROUTNo ratings yet
- Chapter Summary Note of Chapter #1Document10 pagesChapter Summary Note of Chapter #1Jung ParkNo ratings yet
- Introduction TO Economics Introduction TO EconomicsDocument21 pagesIntroduction TO Economics Introduction TO EconomicsMd Mubashshir HossainNo ratings yet
- ECODocument15 pagesECOtrantuancuong0509No ratings yet
- Chapters 1&3 (Supply and Demand)Document3 pagesChapters 1&3 (Supply and Demand)Jim ThiveosNo ratings yet
- MicroeconomicsDocument51 pagesMicroeconomicshjay1058No ratings yet
- Class Notes For ECON1002Document14 pagesClass Notes For ECON1002James & Jessica ScullyNo ratings yet
- ECO401 Economics: Short NotesDocument25 pagesECO401 Economics: Short NotesusmanNo ratings yet
- AP Macroeconomics Ultimate Guide Notes - KnowtDocument73 pagesAP Macroeconomics Ultimate Guide Notes - Knowtstorageb23No ratings yet
- Economics Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesEconomics Cheat Sheetalysoccer449100% (2)
- Principles of EconomicsDocument2 pagesPrinciples of Economicsvqutrang.thestratic3No ratings yet
- NOTESDocument8 pagesNOTESTrisha Mae KhoNo ratings yet
- Eco IonsDocument8 pagesEco IonstarasakhujaNo ratings yet
- SampleDocument11 pagesSamplegacharagodwinNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics Notes by DR Idrees QAU IslamabadDocument142 pagesMicroeconomics Notes by DR Idrees QAU IslamabadAtiq100% (2)
- Microeconomics PrincipleDocument12 pagesMicroeconomics PrincipleFay YanikaNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics Lesson 1Document18 pagesMicroeconomics Lesson 1Lan PhạmNo ratings yet
- 1.central Problem of EconDocument11 pages1.central Problem of EconCharlesNo ratings yet
- Basic Micro EconDocument12 pagesBasic Micro EconRenz RayarkNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document7 pagesAssignment 1Ab NeophyteNo ratings yet
- Definitions For IB Economics 2012Document26 pagesDefinitions For IB Economics 2012RegeWaysNo ratings yet
- Summary Note - FinalDocument28 pagesSummary Note - Finalnguyenngocquynhgiang6674No ratings yet
- Senior School Certificate Examination MARCH - 2008Document12 pagesSenior School Certificate Examination MARCH - 2008Gaurav PratikNo ratings yet
- L1 Notes Micro 2022 23 FinalDocument62 pagesL1 Notes Micro 2022 23 FinalSudeep SubrahmanyaNo ratings yet
- Managerial EconomicsDocument9 pagesManagerial EconomicsGaurav AnandNo ratings yet
- Tema 1 y Tema 2..es - enDocument10 pagesTema 1 y Tema 2..es - enLaura FerrerNo ratings yet
- All NotesDocument24 pagesAll NotesluenaprendelinguasNo ratings yet
- لقطة شاشة ٢٠٢٣-٠٩-١٤ في ١٠.٢٥.٣٦ مDocument33 pagesلقطة شاشة ٢٠٢٣-٠٩-١٤ في ١٠.٢٥.٣٦ مnesmatarek454No ratings yet
- S4 CH1 A. What Is Economics?: D. ChoiceDocument5 pagesS4 CH1 A. What Is Economics?: D. ChoiceMia PoonNo ratings yet
- Slutsky Equation As An ElasticityDocument5 pagesSlutsky Equation As An ElasticityGerald HartmanNo ratings yet
- Definitions For IB Economics Section 1.1 Competitive Markets: Demand and SupplyDocument26 pagesDefinitions For IB Economics Section 1.1 Competitive Markets: Demand and SupplyDavid posterNo ratings yet
- Economics For Ca-Cpt - Quick Revision VersionDocument14 pagesEconomics For Ca-Cpt - Quick Revision VersionCA Suman Gadamsetti75% (4)
- ECO401 Short NotesDocument22 pagesECO401 Short NotesSoul Relaxing VibesNo ratings yet
- Economics Practice Questions and Answers - Year 11 Preliminary (Likely Not 100% Accurate)Document6 pagesEconomics Practice Questions and Answers - Year 11 Preliminary (Likely Not 100% Accurate)Jack CarterNo ratings yet
- ECO111Document2 pagesECO111lisany1012No ratings yet
- APMacro Unit 1Document36 pagesAPMacro Unit 1Joshua CheungNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics Chapters 1 17Document312 pagesMacroeconomics Chapters 1 17KezNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of Demand and Supply - SynthesisDocument6 pagesElasticity of Demand and Supply - SynthesisPrincess GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Micro Economic 1Document34 pagesMicro Economic 1Steven RivaldoNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - NotesDocument14 pagesUnit 1 - NotesChristal NicelyNo ratings yet
- Marc Delingat Economics Course Summary (Part 1)Document23 pagesMarc Delingat Economics Course Summary (Part 1)monkaratNo ratings yet
- Objective of ECO401 (1 22) Short NotesDocument14 pagesObjective of ECO401 (1 22) Short NotesRao Tanveer AsadNo ratings yet
- Session 5Document1 pageSession 5Christelle BassilNo ratings yet
- Chap 3Document1 pageChap 3Christelle BassilNo ratings yet
- Chap 2Document3 pagesChap 2Christelle BassilNo ratings yet
- Chap 1Document4 pagesChap 1Christelle BassilNo ratings yet
- Interview QSTDocument3 pagesInterview QSTChristelle BassilNo ratings yet
- Chap 4Document3 pagesChap 4Christelle BassilNo ratings yet
- Chap 9Document2 pagesChap 9Christelle BassilNo ratings yet
- R'SDDocument1 pageR'SDChristelle BassilNo ratings yet