Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gestational-Condition 2
Uploaded by
Trisha Oloresisimo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views9 pagesOriginal Title
GESTATIONAL-CONDITION 2.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views9 pagesGestational-Condition 2
Uploaded by
Trisha OloresisimoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 9
GESTATIONAL CONDITION: 1ST excruciating pain (cervical
TRIMESTER BLEEDING motion tenderness)
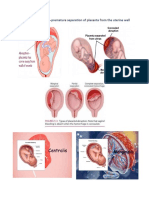
ECTOPIC PREGNANCY o Shoulder pain
Accumulation of
Implantation (of blastocyst)
blood in the
occurs outside the uterine cavity
peritoneal
either in the surface of the ovary
area/diaphragm that
or the cervix
irritates the phrenic
Common in the fallopian tube
nerve
o 80% in the ampulla Risk factors:
o 12% in the isthmus o Obstruction
o 8% in interstitial/fimbria Adhesion in FT from
o Fallopian tube cannot previous infection
accommodate the needs of Prevents the
baby, cannot enlarge in size movement of egg cell
Assessment: o Congenital malformations
o Amenorrhea Abnormalities of FT
o Sharp knife stabbing pain in o Scars from tubal surgery
the lower abdominal Prevents the egg cell
quadrants o Uterine tumor
If pregnant, there is Prevents the
no pain implantation
o Scant vaginal spotting Tends to occupy FT
Increase blood loss
o Shock (rapid thready pulse, MANAGEMENT
rapid RR, decrease BP) 1. Unruptured pregnancy
o Leukocytosis – elevated FT is still intact but only the
WBC client feels pain at LQ and
o No gestational sac during scant bleeding
UTZ Oral administration of
o Rigid abdomen methotrexate
o Umbilicus develop a bluish o Has sclerotic effect
tinge (Cullen’s sign) o Could easily shrink and
Most important sign absorb products of
o Extensive or dull vaginal and conception
abdominal pain Hysterosalpingogram or UTZ
o Movement of the cervix and o Using dye
pelvis exam causes
o Cover or color the o If blood is present in
uterus and FT the cul-de-sac –
o If it flows smoothly, ruptured ectopic
there is no obstruction o If non-clotting/leaked
o Some will be allergic to blood – ectopic
the dye pregnancy)
o Difficulty of breathing – o If blood clots – maternal
side effect blood
o Can be done midway E – extrauterine pregnancy
before menstruation, 6- C – Cullen’s sign
12 days before T – tender, rigid, abdominal
menstruation pain (LQ), amenorrhea
Mifepristone – abortifacient O - observe for shock
o Destroys the products P - prepare for surgery
of conception (laparoscopy)
2. Ruptured ectopic pregnancy I – inject Rhogam
Cullen’s sign, rigid abdominal o To prevent Rh blood
Blood sample is drawn incompatibility
immediately C – care for the client
o Hgb, typing, hcg level ABORTION
IVF
o Decrease blood volume Medical term for any interruption
BT of pregnancy before a fetus is
Therapy: laparoscopy viable
o Remove damaged FT Viable fetus – fetus of more than
Rh (D) immune globulin 20-24 weeks gestation
Culdocentesis – aspirate blood Early miscarriage – occurs before
from cul-de-sac (posterior 16th week (4 months)
portion of ovaries) Late miscarriage – occurs between
o Consent 16th and 24th weeks (4-6 months)
o Lithotomy position 1st 6th week – developing placenta is
o Prepare perineum tentatively attached to the
o Speculum is introduced deciduas
o Spinal needle directed 6-12 weeks – a moderate degree of
to posterior portion of attachment to the myometrium
the cervix After 12 weeks – attachment is
Result: penetrating and deep
o Vaginal spotting – more o Avoid strenuous activity
bleeding for 24-48 hours
Bleeding before 6 weeks – severe o Once bleeding stops, can
o Risk of baby lost resume activity
Bleeding after week 12 – profuse o Coitus is restricted for
Causes: 2 weeks
o A – abnormal fetal Could lead to
development infection
o B – bleeding due to o For dilation and
implantation abnormalities curettage
o O – ovary fails to produce Raspa
progesterone 2. Imminent/inevitable
o R – recurrent systemic s/s
infection o cervical dilatation and
o T – teratogenic drug uterine contraction
Pregnant clients o moderate vaginal
should not be taking bleeding
drugs w/o o severe/painful cramping
prescription o cervix is open
Assessment: txt
o Vaginal spotting o ask to come to the clinic
o Lower abdominal cramps and bring tissue
o Fever and body malaise fragments to be
o Signs of infection examined
o vacuum extraction
TYPES
removal of baby
1. Threatened o after discharged – ask
s/s the woman to assess
o scant vaginal bleeding vaginal bleeding by
o slight cramping recording the number of
o cervix is closed pads she uses
txt 6-8 pads/day –
o ask to come to the clinic normal
to have FHT to be
checked or UTZ to 3. Complete
evaluate the viability of s/s
fetus o The entire products of
o HCG test = double conception are expelled
spontaneously without o Prostaglandin
resistance suppository or
o D&C is done to be sure misoprostol (Cytotec) if
4. Incomplete pregnancy is over 14
s/s weeks, to dilate the
o part of the fetus cervix
(usually the fetus) is o Oxytocin stimulation of
expelled but the administration of
membrane or placenta is mifepristone
retained in the uterus o DIC – disseminate
txt intravascular coagulation
o D&C or suction Increase
curettage to evacuate bleeding
the remainder of 6. Recurrent pregnancy/habitual
pregnancy Always experiencing abortion
Placenta and s/s
membranes are o defective spermatozoa
still in the uterus or ova
– prevents uterus abnormal fetal
to contract and development
cause profuse o deviation of the uterus
bleeding such as bicornuate
5. Missed/early pregnancy failure uterus
s/s divided into 2 at
o fetus die in the uterus the center
but is not expelled shape like horn
o determine when the prevents
fetus does not increase development of
in size baby
o no FHT o chorioamnionitis or
o fetus dies at 4-6 weeks uterine infection
before the onset of
miscarriage
o blood is dark and COMPLICATIONS
different odor
Hemorrhage
txt
Infection
o UTZ
Septic abortion
o D&E
o Self-abortion
o Insert something to kill the HYPEREMESIS GRAVIDARUM
baby
Pernicious or persistent vomiting
If left untreated = toxic shock
N/V that is prolonged, beyond 12
syndrome, septicemia, kidney
weeks
failure, death
Severe dehydration, weight loss
NURSING MANAGEMENT Associated with helicobacter pylori
(causes peptic ulcer)
Perform the appropriate
Elevated hcg – first hormone
management and prevent
produced by placenta
complications
Could lead to fluid and electrolyte
Monitor vital signs, bleeding and
imbalance and nutritional imbalance
pain
o No food will be retained and
Document IVF, lab test and
absorb in the body
prepare for emergency surgical
Assessment:
intervention
o Severe N/V
Prepare administration of RhoGAM
Causes weakness and
to Rh (-) mother
confusion
Advise iron supplement
o Elevated hct due to
Refraining from sexual intercourse
dehydration
until next menses and advise use of
o Low Na, K, and chloride
barrier contraception
o Hypokalemic
A – age before viability o Polyneuritis – numbness and
tingling sensation
B – bleeding is scant, low abdominal
o Weight loss – decrease
cramps, fever
intake
O – observe for infection, hemorrhage o Urine test (+) for ketones
Client is unable to
R – record v/s, bleeding, pain and IVF
eat
T – toxic shock syndrome, septicemia, Body will be making
kidney failure, death use of fat as a
source of energy
I – inject RhoGAM, give iron
o Poor skin turgor and mucous
supplement
membrane
O – ovary fails to produce o If left untreated,
progesterone associated with intrauterine
restriction, preterm birth,
N – no sexual intercourse, notify HCP
fetal death
Malnourished and o Administer IVF
small baby because o Record I and O
of growth and o Advise SFF once vomiting
development has subsided
restriction o Administer antiemetics as
Therapeutic management: prescribed
o Hospitalization to receive o Attends to client’s
fluid replacement emotional and psychological
Lactated ringer needs
solution (3L) with E – exaggerated N/V beyond 1st
vitamin B – to trimester
improve numbness M – metabolic alkalosis,
o Withheld oral food and hypoproteinemia
fluid o Vomiting hypoproteinemia
o Antiemetic – – use of protein
metoclopramide or reglan E – electrolyte, fluid, vitamins and
o Measure I and O and minerals replacement and nutrition
amount of vomitus S – skin turgor and mucus
o If no vomiting within 24 hrs membrane assessment for
– may start small amount of dehydration
clear liquids I – ingest bland solid foods
Small frequent o Avoid foods that are spicy,
feeding oily, and greasy
o Dry crackers, dry toast or S – strict hygiene and bedrest
cereal be added every 2 o More on oral hygiene
hours the soft diet o Bedrest as the client is
o If vomiting return – TPN is weak
used
Risk of fluid and
electrolyte and
nutritional imbalance
Nursing care management
o Ensure that the client has
no oral intake until vomiting
stops
GESTATIONAL TROPHOBLASTIC o Layer responsible in
DISEASE / HYDATIDIFORM MOLE producing maternal
(H-MOLE) – molar pregnancy hormones
An abnormal proliferation and A macerated embryo of approx.
degeneration of the trophoblastic 9 weeks gestation may be
villi present and fetal blood may be
As the cells degenerate, they present in the villi
become filled and appear as clear Has 69 chromosomes
fluid filled, grape-sized vesicles Rarely lead to choriocarcinoma
Trophoblast was formed from o But client is high risk to
placenta have choriocarcinoma –
There was no placenta formed cancer that affects the
during pregnancy fetal membrane
Risk factors: ASSESSMENT
o Low protein intake
o Women older than 35 y/o Uterus tends to expand faster
o Blood group A who marries than normally
group O men + urine test of HCG (1-2M)
o NV: 400,000 IU
TYPES o Could lead to enlargement
1. Complete mole of uterus - unusual
All trophoblastic villi swell and Marked N/V
become cystic UTZ show dense growth (snowflake
If embryo form, it dies at 1-2 pattern)
mm in size with no fetal blood o It will confirm the presence
present in the villi of mole
Empty ovum – the sperm enters (-) FHR – no baby inside the uterus
empty egg and its chromosome Vaginal bleeding (approx. 16 weeks)
replicates – dark brown
Snowstorm – can be seen in Early s/s of preeclampsia
UTZ o Proteinuria, edema, HPN
2. Partial mole before 20th week
Some of the villi form normally MANAGEMENT
syncytiotrophoblastic (outer)
layer of villi is swollen and Suction curettage
misshapen Pelvic exam
Chest xray
Serum test for HCG
o Every 2 weeks until normal 2nd TRIMESTER BLEEDING:
o Every month for 6 months INCOMPETENT CERVIX –
o Every 2 months for a total premature cervical dilatation
of 1 year
Premature cervical dilatation
o There should be negative
Inability of the cervix to support
HCG within a year
growing weight of pregnancy
o Positive HCG – client still
associate with repeated
has h-mole
spontaneous 2nd trimester abortion
o Clients are discouraged to
Painless dilatation of the cervix in
be pregnant withing 1 year
the absence of uterine
due to hcg monitoring
contractions
Use oral contraceptive (progestin)
o Dilates too early as early as
o Not COC
20 weeks or 5 months
o Should only contain
o Could lead to the delivery
progesterone due to risk of
of the viable fetus –
choriocarcinoma
weakened tissue of the
o Estrogen could facilitate
cervix
the regrowth of cancer
Assessment:
cells
o Bloody show
Methotrexate – drug of choice for
Pink-stained vaginal
choriocarcinoma
bleeding
Dactinomycin – added regimen if
1st symptom
metastasis occur
o Increased pelvic
H – HCG is elevated, uterus is large
pressure/low abdominal
for gestational age, persistent
pressure
bleeding, N/V
o Followed by rupture of
M – mole is detected by UTZ and
membranes
removed by vacuum aspiration and
BOW ruptures,
curettage
uterine contraction
O – observe for s/s of shock,
is present affecting
prepare for BT and IV
cervical dilatations
L – lower the risk by avoiding
o Uterine contractions begins
pregnancy for at least 1 year
and a short labor, the fetus
E - educated on the need to
is born if present
monitor HCG for 1 year
o Occurs approx. week 20 of
pregnancy
o Progressive dilatation of
the cervix
o Urinary frequency o Bedrest
Affecting the o Coitus is temporarily
bladder during restricted – could lead to
dilatation or delivery infection
Risk factors: o Tocolytic drug (ritodrine,
o Maternal age terbutaline)
o Congenital structural Stop uterine
defects contraction
o Trauma to the cervix I – inability of the cervix to
Repeated abortion support the growing baby
D&C N – no douching
Frequent insertion C – cervical cerclage
of instrument O – occur at week 20, blood show –
Treatment: pink
o Cervical cerclage – M – maternal age, congenital
performed between 14-16 structure defects, trauma of
weeks pregnancy because no cervix
thinning and shortening of P – premature cervical dilation
cervix without uterine contraction
o Mc Donald – temporary E – elevated pelvic pressure
(NSD) T – Trendelenburg (modified)
Sewing the cervix to E – encourage bed rest
prevent the early N – no coitus temporarily
delivery T – tocolytic drug
Removing the suture only during 2nd pregnancy will be
at 38th weeks able to know if the client is
wherein the baby will experiencing incompetent cervix
be delivered
o Shirodkar – permanent (CS)
Suture will not be
removed
Removing after birth
Nursing management:
o Modified Trendelenburg
position
To decrease
pressure in the
pelvic area
You might also like
- ABORTIONDocument3 pagesABORTIONAngel MoncadaNo ratings yet
- Module 4F Operative Obstetrics PDFDocument11 pagesModule 4F Operative Obstetrics PDFYori Nicole Martine CuyosNo ratings yet
- Diagnosing Ectopic Pregnancy with Beta-hCG and UltrasoundDocument7 pagesDiagnosing Ectopic Pregnancy with Beta-hCG and UltrasoundSe CretNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 Midterms M1 M4 1 2Document47 pagesNCM 109 Midterms M1 M4 1 2bsn1kgangNo ratings yet
- Ob RVG Panda ManilaDocument45 pagesOb RVG Panda ManilaMikaelle GasparNo ratings yet
- HIGH RISK PREGNANCY COMPLICATIONSDocument12 pagesHIGH RISK PREGNANCY COMPLICATIONSggrrk7100% (2)
- Obstetric Highlights, Elmar P. SakalaDocument47 pagesObstetric Highlights, Elmar P. Sakaladukelist5660% (1)
- Obstetrics nursing: Bleeding disorders in pregnancyDocument9 pagesObstetrics nursing: Bleeding disorders in pregnancyHANNAH BANGKILINGNo ratings yet
- By: Huzaifa HamidDocument31 pagesBy: Huzaifa Hamidرفاعي آكرمNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 ReviewerDocument8 pagesNCM 109 ReviewerAlma Janella TOSINO100% (2)
- #4 - NCM 109 - TransesDocument22 pages#4 - NCM 109 - TransesJaimie BanaagNo ratings yet
- Perdarahan Antepartum - EmiliaDocument26 pagesPerdarahan Antepartum - EmiliaEmilia NazmaNo ratings yet
- Notes Base 2Document14 pagesNotes Base 2Mark FuerteNo ratings yet
- Post-partum hge - @Medicine_Way2Document6 pagesPost-partum hge - @Medicine_Way2saeed hasan saeedNo ratings yet
- Nclex Pregnancy ComplicationsDocument6 pagesNclex Pregnancy Complicationsvienny kayeNo ratings yet
- 2 Nursing Care of the Pregnant Client Gestational ConditionDocument120 pages2 Nursing Care of the Pregnant Client Gestational ConditionjustinjareddNo ratings yet
- MCN 2Document7 pagesMCN 2GabNo ratings yet
- Previa Vs AbruptioDocument1 pagePrevia Vs AbruptioJamaica QuetuaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 APH, PP, VP, AbruptioDocument55 pagesTutorial 3 APH, PP, VP, AbruptioBahirahNo ratings yet
- Antepartum Hemorrhage CausesDocument9 pagesAntepartum Hemorrhage CausesadiNo ratings yet
- First Trimester BleedingDocument12 pagesFirst Trimester BleedingKevin de SilvaNo ratings yet
- OSCE Revision OBG DocumentDocument60 pagesOSCE Revision OBG DocumentshreyaNo ratings yet
- Emed - OB Part 1Document6 pagesEmed - OB Part 1Princess Cate MercadoNo ratings yet
- Abruptio Placentae: Moses Quinanola Oral Revalida 2 SemesterDocument6 pagesAbruptio Placentae: Moses Quinanola Oral Revalida 2 SemesterBrian OrejudosNo ratings yet
- High Risk Pregnancy FinaleDocument149 pagesHigh Risk Pregnancy FinaleQuolette Constante100% (1)
- Placental Abnormalities Normal Placenta: © Mary Andrea G. Agorilla, Ust-Con 2021 - 1Document3 pagesPlacental Abnormalities Normal Placenta: © Mary Andrea G. Agorilla, Ust-Con 2021 - 1Mary AgorillaNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child NursingDocument43 pagesMaternal and Child NursingSophia WongNo ratings yet
- Ob Final ReviewDocument13 pagesOb Final Reviewraquel maniegoNo ratings yet
- Care for At-Risk Mothers and ChildrenDocument11 pagesCare for At-Risk Mothers and ChildrenAyanami PascuaNo ratings yet
- POSTPARTAL HEMORRAGE Editable NotesDocument4 pagesPOSTPARTAL HEMORRAGE Editable NotesJkimNo ratings yet
- Placenta Previa and Abruptio Placenta: Causes, Symptoms and ManagementDocument3 pagesPlacenta Previa and Abruptio Placenta: Causes, Symptoms and ManagementVicente TurasNo ratings yet
- Module For Abnormal OB 1 - 120227Document129 pagesModule For Abnormal OB 1 - 120227Elizabeth MadejaNo ratings yet
- OB Reviewerv2Document9 pagesOB Reviewerv2Andrassy Twinkle AlineaNo ratings yet
- Vaginal Bleeding in PregnancyDocument4 pagesVaginal Bleeding in PregnancyAra BaltarNo ratings yet
- 2 Topics at RiskDocument5 pages2 Topics at RiskGeraldine PatayanNo ratings yet
- Diagnosing and Treating Ectopic PregnancyDocument14 pagesDiagnosing and Treating Ectopic PregnancyAngel MoncadaNo ratings yet
- OB Review Sheet FinalDocument22 pagesOB Review Sheet FinalEmma KnoxNo ratings yet
- Early Pregnancy Complications: by Harvir Singh Supervised by DR Ranjit and DR SyafiqahDocument33 pagesEarly Pregnancy Complications: by Harvir Singh Supervised by DR Ranjit and DR SyafiqahShre RanjithamNo ratings yet
- SCRT NTSDocument11 pagesSCRT NTSBella CamposNo ratings yet
- Definition: Genital Tract Bleeding From 28th Incidence: 2 - 3 % of All PregnanciesDocument31 pagesDefinition: Genital Tract Bleeding From 28th Incidence: 2 - 3 % of All PregnanciesMRT RadiologyNo ratings yet
- Miscarriage & Early Pregnancy LossDocument38 pagesMiscarriage & Early Pregnancy LossLuqman OsmanNo ratings yet
- Abruptio Placenta and AbortionDocument10 pagesAbruptio Placenta and Abortiondanica grace gubaNo ratings yet
- Interstitial PXDocument56 pagesInterstitial PXmenkir tegegneNo ratings yet
- Bleeding During PregnancyDocument5 pagesBleeding During PregnancyMaryela Maceda GalozoNo ratings yet
- Gestational ConditionsDocument14 pagesGestational ConditionsMaricar EustaquioNo ratings yet
- Obstructed Labour DiagnosisDocument2 pagesObstructed Labour DiagnosisAvinash BarhateNo ratings yet
- Labor and Delivery HormonesDocument7 pagesLabor and Delivery HormonesMikaella CondeNo ratings yet
- MCN NotesDocument20 pagesMCN NotesLiamLexus JavierNo ratings yet
- Nle - High-Risk PregnancyDocument113 pagesNle - High-Risk Pregnancytachycardia01No ratings yet
- Postpartum Hemorrhage CausesDocument9 pagesPostpartum Hemorrhage CausesJonathanNo ratings yet
- Postpartal ComplicationDocument4 pagesPostpartal ComplicationHanna AligatoNo ratings yet
- 1.antepartum HeamorrhageDocument26 pages1.antepartum Heamorrhagems khanNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Previa AbruptioDocument28 pagesWeek 3 Previa Abruptiomico zarsadiazNo ratings yet
- Oral Revalida 2019Document28 pagesOral Revalida 2019April Cabarlo100% (6)
- Abnormal OB - Uphi LectureDocument16 pagesAbnormal OB - Uphi LectureQuerubin DandoyNo ratings yet
- Jose, Leana Louisse D. Cornell Notes On Ncm109 Module 1 & 2 (Complications of Pregnancy) 02/18/21 Assessment For Risk FactorsDocument19 pagesJose, Leana Louisse D. Cornell Notes On Ncm109 Module 1 & 2 (Complications of Pregnancy) 02/18/21 Assessment For Risk FactorsLiana Louisse JoseNo ratings yet
- SafariViewService - 16 Feb 2019 12.09Document1 pageSafariViewService - 16 Feb 2019 12.09Ngakan Ketut DarmawanNo ratings yet
- Abortion Guide: Causes, Types, Symptoms & TreatmentDocument36 pagesAbortion Guide: Causes, Types, Symptoms & TreatmentdimlyNo ratings yet
- Case Study of Cesarean SectionDocument9 pagesCase Study of Cesarean Sectionzarian wu72% (18)
- It's Not Just a Heavy Period; The Miscarriage HandbookFrom EverandIt's Not Just a Heavy Period; The Miscarriage HandbookRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Quality Form Oplan Kalusugan Sa Deped Accomplishment Report FormDocument36 pagesQuality Form Oplan Kalusugan Sa Deped Accomplishment Report FormBulaay ZarenNo ratings yet
- Journal Template For Review article-REVDocument3 pagesJournal Template For Review article-REVDoctorRonZ7No ratings yet
- EPISIOTOMYDocument1 pageEPISIOTOMYmealiellaNo ratings yet
- Polytechnic University of The Philippines Sto Tomas Branch Sto. Tomas, BatangasDocument4 pagesPolytechnic University of The Philippines Sto Tomas Branch Sto. Tomas, BatangasJonalyn PlazaNo ratings yet
- Pid PROJECTDocument47 pagesPid PROJECTCapitallink cafe100% (1)
- Vaginal CytologyDocument4 pagesVaginal Cytologyابراهيم عبدالله100% (1)
- Spontaneous Vaginal Delivery Case StudyDocument2 pagesSpontaneous Vaginal Delivery Case StudychloeNo ratings yet
- Herbs That Stop Leakage: Lung Leakage Kidney LeakageDocument8 pagesHerbs That Stop Leakage: Lung Leakage Kidney LeakageEdison HlmNo ratings yet
- WEEK 1 SLM 1 Hormones in Reproductive Systems SLM 1Document12 pagesWEEK 1 SLM 1 Hormones in Reproductive Systems SLM 1yuri sabileNo ratings yet
- GRAND ROUND FETOMATERNAL 1-13 Juni 2021Document42 pagesGRAND ROUND FETOMATERNAL 1-13 Juni 2021Ahmad FitriawanNo ratings yet
- Als-Shs Perdev Activity Module3Document2 pagesAls-Shs Perdev Activity Module3Joa PingalNo ratings yet
- Incompetent NCPDocument1 pageIncompetent NCPMina RacadioNo ratings yet
- Biology G12 Vol1 2023Document160 pagesBiology G12 Vol1 2023thyadiadarsh8113No ratings yet
- Sexuality and Sexual HealthDocument60 pagesSexuality and Sexual HealthMonika shankarNo ratings yet
- Uterine Myoma Case Study Group A FinalDocument88 pagesUterine Myoma Case Study Group A Finallowell cerezoNo ratings yet
- Ovarian Cycle & Menestrual CycleDocument16 pagesOvarian Cycle & Menestrual CycleRolando Ian Maranan RNNo ratings yet
- Chapter Quiz 1. MCNDocument4 pagesChapter Quiz 1. MCNAngie SaquingNo ratings yet
- Central Luzon Doctors' Hospital Nursing Ethics Course SyllabusDocument4 pagesCentral Luzon Doctors' Hospital Nursing Ethics Course SyllabusJane Bautista50% (2)
- Hormone Study Finds Dogon Menstrual Rituals Elicit Honest SignalsDocument12 pagesHormone Study Finds Dogon Menstrual Rituals Elicit Honest Signalscj.email4all5645No ratings yet
- Breech Presentation: (English Case)Document56 pagesBreech Presentation: (English Case)Heri FarnasNo ratings yet
- 8th Grade Biology Notes on ContraceptionDocument3 pages8th Grade Biology Notes on ContraceptionahmedNo ratings yet
- University of Iowa Press Spring 2022 Catalog of BooksDocument28 pagesUniversity of Iowa Press Spring 2022 Catalog of BooksUniversity of Iowa PressNo ratings yet
- ARH DepEd Policy v3Document13 pagesARH DepEd Policy v3Annielou Olivera100% (2)
- Candela CO2Re BRDocument8 pagesCandela CO2Re BRAlex ZPNo ratings yet
- A Collection of Post-Objectivst Essays.Document221 pagesA Collection of Post-Objectivst Essays.Leo_The_Magnificent50% (2)
- Publication-UNFPA WHO Study - MONGOLIADocument53 pagesPublication-UNFPA WHO Study - MONGOLIAKabir AhmedNo ratings yet
- Human Rights Law DELFORGEDocument15 pagesHuman Rights Law DELFORGEVictoire Delforge100% (1)
- Q1 Animal Production (Swine) NC II 9-12 - Module 4Document18 pagesQ1 Animal Production (Swine) NC II 9-12 - Module 4dominador man-onNo ratings yet
- Batac - Gloria.impactofscdecisiononrhprograms.20171109 WordDocument53 pagesBatac - Gloria.impactofscdecisiononrhprograms.20171109 Wordjei joaquinNo ratings yet
- Internal and external female reproductive organsDocument2 pagesInternal and external female reproductive organs青No ratings yet