Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Shoulder Joint Exam
Uploaded by
Nicky Wei Wei0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesThe document provides instructions for performing an examination of the shoulder joint. Key steps include visually inspecting for asymmetry, swelling or muscle wasting; palpating important bony landmarks and soft tissues to check for temperature changes; and assessing the patient's active and passive range of motion in motions like forward flexion, extension, abduction, and internal/external rotation. Special tests are also described to check for issues like nerve impingement, rotator cuff tears, instability, and tendinitis. The exam involves a thorough look, feel, and assessment of motion.
Original Description:
Original Title
Shoulder joint exam
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides instructions for performing an examination of the shoulder joint. Key steps include visually inspecting for asymmetry, swelling or muscle wasting; palpating important bony landmarks and soft tissues to check for temperature changes; and assessing the patient's active and passive range of motion in motions like forward flexion, extension, abduction, and internal/external rotation. Special tests are also described to check for issues like nerve impingement, rotator cuff tears, instability, and tendinitis. The exam involves a thorough look, feel, and assessment of motion.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesShoulder Joint Exam
Uploaded by
Nicky Wei WeiThe document provides instructions for performing an examination of the shoulder joint. Key steps include visually inspecting for asymmetry, swelling or muscle wasting; palpating important bony landmarks and soft tissues to check for temperature changes; and assessing the patient's active and passive range of motion in motions like forward flexion, extension, abduction, and internal/external rotation. Special tests are also described to check for issues like nerve impingement, rotator cuff tears, instability, and tendinitis. The exam involves a thorough look, feel, and assessment of motion.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
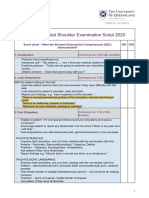
Shoulder joint exam:
Look
-front to side to back
-look for asymmetry, erythema, swelling, muscle wasting
-front: any scoliosis, side: any kyphosis
Feel
-go from anterior medial to lateral to posterior medial
-important locations: sternoclavicular joint, clavicle, acromioclavicular, coracoid process, anterior
groove, posterior groove of shoulder, trapezius muscle, C-spine and scapula
-feel for temp change in both shoulder joint
Move:
-forward flexion: 0 to 180
-extension: 0 to 45-60
-abduction: 0 to 80-90
-adduction: 0 to 45
-external rotation: 0 to 80-90
-internal rotation: put hand towards the back and see thumb should reach T4-T8
-if pt able to achieve active full ROM, no need to do passive
-passive only do for the movements which you think has limited ROM, feel for any crepitus when
helping pt move and assess maximum ROM achievable
Special tests (just pick and learn 1 for each):
-nerve impingement test: Neer's test
-acromioclavicular joint stability: cross-over test
-rotator cuff: supra, infraspinatus and subscapluaris
-supraspinatus: empty-can test
-infraspinatus: resisted external rotation
-subscapularis: lift-off test
-shoulder instability: apprehension test
-bicep tendinitis: yergason's test (resisted supination)
You might also like
- The American Physical Therapy Association Book of Body Repair and Maintenance: Hundreds of Stretches and Exercises for Every Part of the Human BodyFrom EverandThe American Physical Therapy Association Book of Body Repair and Maintenance: Hundreds of Stretches and Exercises for Every Part of the Human BodyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (9)
- Skeletal Muscle System OSCE ExaminationDocument14 pagesSkeletal Muscle System OSCE ExaminationMaryam A Albalooshi100% (2)
- Orthopedic Exam Notes Apu PDFDocument6 pagesOrthopedic Exam Notes Apu PDFabiramirajalaksmiNo ratings yet
- Knee ExaminationDocument40 pagesKnee ExaminationWasim R. Issa0% (1)
- Examination of The Joints and ExtremitiesDocument66 pagesExamination of The Joints and Extremitiesapi-25914483No ratings yet
- Hip and Buttock PainDocument26 pagesHip and Buttock PainEdy SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Examination of The ShoulderDocument33 pagesExamination of The ShoulderAnonymous 9QxPDpNo ratings yet
- Examination of Cervical SpineDocument39 pagesExamination of Cervical SpinedrkanthikirangNo ratings yet
- History & Physical Examination of The ShoulderDocument53 pagesHistory & Physical Examination of The ShoulderzaimmuhtarNo ratings yet
- GALS AssessmentDocument46 pagesGALS AssessmentdrindrasNo ratings yet
- 2-Physical Examination and SkillsDocument48 pages2-Physical Examination and SkillsHari ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Examination of SpineDocument54 pagesExamination of Spinenams ortho100% (1)
- Physical Examination of Spine (TN)Document55 pagesPhysical Examination of Spine (TN)Francesc OktofabregasNo ratings yet
- Done By: Team Leader:: Maha Alghofaili Khulood AlraddadiDocument5 pagesDone By: Team Leader:: Maha Alghofaili Khulood AlraddadiFelixNo ratings yet
- Done By: Team Leader:: Rawan Altaleb Khulood AlraddadiDocument6 pagesDone By: Team Leader:: Rawan Altaleb Khulood Alraddadishagufta lailaNo ratings yet
- Shoulder ExaminationDocument4 pagesShoulder ExaminationYS NateNo ratings yet
- Examination of The ShoulderDocument20 pagesExamination of The ShoulderMalvino Giovanni100% (1)
- PDII Checklist Musculoskeletal StudentDocument3 pagesPDII Checklist Musculoskeletal Studentmre07No ratings yet
- Shoulder ExamDocument12 pagesShoulder Examckyew64No ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal SystemDocument5 pagesMusculoskeletal SystemDale Ros CollamatNo ratings yet
- PE Essential Checklist For OSCE Part 1Document3 pagesPE Essential Checklist For OSCE Part 1Palwasha MalikNo ratings yet
- Spine and Shoulder ExaminationDocument3 pagesSpine and Shoulder ExaminationNabighah ZukriNo ratings yet
- SLAP LesionDocument16 pagesSLAP Lesionselvaraj sNo ratings yet
- NASM Guide PT 2 12Document55 pagesNASM Guide PT 2 12Laylah-BlueNo ratings yet
- Mus Culo Skel TalDocument4 pagesMus Culo Skel TalAnonymous uYrfPbNo ratings yet
- ShoulderDocument35 pagesShoulderHala AhmadNo ratings yet
- MSK Spine ScriptDocument4 pagesMSK Spine ScriptRay ChangNo ratings yet
- Knee Exam ChecklistDocument2 pagesKnee Exam ChecklistGrInDoVe9097No ratings yet
- Fam Med OsceDocument5 pagesFam Med OsceNathan KimNo ratings yet
- Edited - Adhesive CapsulitisDocument5 pagesEdited - Adhesive Capsulitiseternal_lynnNo ratings yet
- Lower Limb Examination: Kyaw Htet AgDocument65 pagesLower Limb Examination: Kyaw Htet AgKyaw Htet AungNo ratings yet
- Obaid Knee ExaminationsDocument3 pagesObaid Knee ExaminationsAlaa ElbulukNo ratings yet
- MSK Shoulder ScriptDocument4 pagesMSK Shoulder ScriptRay ChangNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination of Musculoskeletal SystemDocument3 pagesPhysical Examination of Musculoskeletal Systemni RoraNo ratings yet
- Physical Ex of ElbowDocument23 pagesPhysical Ex of ElbowNgurah AndhikaNo ratings yet
- Cervical Spondylosis With RadiculopathyDocument26 pagesCervical Spondylosis With RadiculopathyKashish SahotaNo ratings yet
- Rodilla Workbook PDF - CompressedDocument15 pagesRodilla Workbook PDF - CompressedMarcos Perez AlbertNo ratings yet
- Lower Limb TendinopathyDocument8 pagesLower Limb TendinopathyMfxMazprofxNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The Muscle System: Stream A Week 2 PracticalDocument3 pagesAssessment of The Muscle System: Stream A Week 2 PracticalBonnie DauzetNo ratings yet
- PE and Diagnosis of ElbowDocument58 pagesPE and Diagnosis of Elbowmupt77No ratings yet
- Assess ScoliosisDocument11 pagesAssess ScoliosismalakNo ratings yet
- PT Measurement Practical-2Document28 pagesPT Measurement Practical-2Anthony PatrickNo ratings yet
- Shoulder ExaminationDocument25 pagesShoulder ExaminationFahad MNo ratings yet
- Approach To ArthralgiaDocument5 pagesApproach To ArthralgiaBlaire FultoneNo ratings yet
- Shoulder Examination Don't Miss The EXPOSURE Look:: From FrontDocument3 pagesShoulder Examination Don't Miss The EXPOSURE Look:: From FrontAlaa ElbulukNo ratings yet
- PA Shoulder Case PresentationDocument13 pagesPA Shoulder Case Presentationselvaraj sNo ratings yet
- 1B Hip ExaminationDocument13 pages1B Hip Examinationnickmirad2No ratings yet
- MSK Knee ScriptDocument5 pagesMSK Knee ScriptRay ChangNo ratings yet
- Knee PP Revision:: 1. Flexion (0 - 135)Document13 pagesKnee PP Revision:: 1. Flexion (0 - 135)senoNo ratings yet
- Ortho PE NotesDocument35 pagesOrtho PE NotesSudesna Roy ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Thoracic Outlet SyndromeDocument26 pagesThoracic Outlet SyndromeJobinpreet KohliNo ratings yet
- Knee ExaminationDocument16 pagesKnee Examinationckyew64No ratings yet
- Cervical SpineDocument36 pagesCervical Spinesena erayNo ratings yet
- Kines Final GoniDocument21 pagesKines Final GoniDhirenPatelNo ratings yet
- Done By: Team Leader:: Heba Allsharif Khulood AlraddadiDocument4 pagesDone By: Team Leader:: Heba Allsharif Khulood AlraddadiMuhammad BilalNo ratings yet
- Clinical ExaminationDocument17 pagesClinical Examinationli man shekNo ratings yet
- Gait, Arms, Legs, Spine TestDocument2 pagesGait, Arms, Legs, Spine TestJessica Febrina WuisanNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics of The Spine and HipDocument32 pagesBiomechanics of The Spine and HipbastianusjuatmadjaNo ratings yet
- Tos 1Document15 pagesTos 1selvaraj sNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination Lower LimbsDocument26 pagesPhysical Examination Lower LimbsFahad MNo ratings yet
- AbstractDocument1 pageAbstractNicky Wei WeiNo ratings yet
- Questionnaires Instruments and FeedbackDocument2 pagesQuestionnaires Instruments and FeedbackNicky Wei WeiNo ratings yet
- IVC DOPS NotesDocument1 pageIVC DOPS NotesNicky Wei WeiNo ratings yet
- Important FPP OSCE TopicsDocument1 pageImportant FPP OSCE TopicsNicky Wei WeiNo ratings yet
- Osce AnalysisDocument3 pagesOsce AnalysisNicky Wei WeiNo ratings yet
- Syphilis STI (25 May)Document3 pagesSyphilis STI (25 May)Nicky Wei WeiNo ratings yet
- Osteosarcoma (15 June)Document4 pagesOsteosarcoma (15 June)Nicky Wei WeiNo ratings yet
- Heavy Periods (2 June)Document4 pagesHeavy Periods (2 June)Nicky Wei WeiNo ratings yet
- Altered Bowel Habits (9 June)Document4 pagesAltered Bowel Habits (9 June)Nicky Wei WeiNo ratings yet