0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes) 579 views20 pagesDisaster Risk Reduction Management (DRRM)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content,
claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online on Scribd
Disaster Risk
Reduction
Management
(DRRM)
Geographic and Risk Profile of the Philippines
Historical Review of Risks, Hazards and Disasters in
the Philippines
Salient Features of PDRRM Act of 2010
Four Thematic Areas of the Philippine Disaster
Management System
The Role of the Youth in Disaster Preparedness and
Management�Disaster Risk Reduction Management (DRRM) Awareness/Readiness
Objectives:
At the end of the module, the students are expected to:
1. Discuss the most common types of disasters based on the
Philippine tisk profile
2. Reflect on the legal basis of the preventive program of the
government in addressing the impact of disaster
Content.
Disaster Awareness
a Philippine Risk Profile C. Impact of Disasters
B. Categories (Most Common): 1. Health care system
° Fires 2. Socio-economic
* Flood 3, Educational
* Earthquakes and 4, Psychological
Landslides 5. Spiritual
* Volcanic Eruption
* Pandemic
I. RA 10121: "Philippine Disaster Risk Reduction and Management
Act of 2010"
a
DISASTER
RISK
REDUCTION
MANAGEMENT
THE SDGs should aim to: — Reduce the underlying risk factors and
enhance resilience as part of Goal 11 Sustainable cities and
communities. (UNDP, 2015)
hitps://www youtube,com/watch¢v=4bN9yimMXro�SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT GOALS.
@ ievetoement GOALS
2 ie
ais
The Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction (2015-2030) is an
international document which was adopted by UN member states
between 14th and 18th of March 2015 at the World Conference on
Disaster Risk Reduction held in Sendai, Japan and endorsed by the
UN General Assembly in June 2015. It is the successor agreement to
the Hyogo Framework for Action (2005-2015), which had been the
most encompassing intemational accord to date on disaster risk
reduction. (UNDRR, 2015)
https://www.youtube.com/watch ?v=izoDdnaSxNO&t=25s
SENDAI FRAMEWORK
https://www youtube.com/watch@v=NésoXnTsaZq
SENDAI FRAMEWORK AND SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT GOALS
Community-Based Disaster Risk Reduction and Management
(CBDRRM) - a process of disaster risk reduction and management in
which at-risk communities are actively engaged in the identification,
analysis, treatment, monitoring, and evaluation of disaster risks in order
to reduce their vulnerabilities and enhance their capacities, and
where the people are at the heart of decision-making and
implementation of disaster tisk reduction and management activities.�Philippine Disaster Risk Profile
A disaster is a serious disruption, aoe
occurring over a relatively short
time, of the functioning of a
community or a society involving
widespread human, material,
economic or environmental loss
and impacts, which exceeds the
ability of the affected community
or society to cope using its own
resources.
The Philippine Disaster profile: Situated along two major tectonic
plates of the world — the
EURASIAN and PACIFIC Plates
* 300 volcanoes, 25 as active
* average of 20 quakes per day
* average of 20 typhoons a year, five (5) of these are destructive
* 36,289 kms. of coastline vulnerable to tsunami
Anatomy of a Disaster
Preimpact phase
(disaster prevention and education)
Impact phase
(information collection and disaster mitigation)
Post-impact phase
(long term rehabilitation following a disaster)
Categories of Disasters & their Common Types
* Natural disaster
+ Human-instigated disasters�Common Types of Natural / Human-Made Disaster
FIRE
Top Tips for Fire Safety
Install smoke alarmson every level of your home, inside
bedrooms, and outside sleeping areas
* Test smoke alarms every month. If they're not working, change
the batteries.
¢ Talk with all family members about a fire escape plan and
practice the plan twice a year.
© If a fire occurs in your home, GET OUT, STAY OUT and CALL FOR
HELP. Never go back inside for anything or anyone.
TYPHOONS/FLOODINGS
NORRMC OUTLINES GUIDANCE ON RAINY
SEASON PREPAREDNESS, COVERS COVID-19
UMM B OLS�Earthquake
Landslides
LANDSLIDE
Volcanic Eruption
YouTube [Video .). YouTube. https://youtu.be/9XDXTw_GiJs
A�Pandemic
YouTube [Video]. (n.d.). YouTube. https://youtu.be/i0ZabxxmH4Y
CORONA VIRUS
CORONAVIRUS ==>
Impact of Disasters
1, Health Care System
The five short-term impacts were noted as (Viewpoint Magazine, 2017)
More Emergency Department patient visits (due to the inability
of patients to see their own physicians and/or patient
displacement [e.g., temporary relocation]).
More necessary inpatient services (due to injuries or illnesses
consequent to the natural disaster).
Extended inpatient stays (due to the inabilty of patients to safely
retum to home environments folowing the natural disaster).
Prescription medication effects (due to lost medications,
prescriptions, and/or duplicated prescriptions).
Healthcare delivery system disruption (e.g., temporarily
damaged healthcare facilities, and need to relocate patients).�_
Socio-economic
+ Here are some of the biggest effects a nation might
experience. ( The World Reporter, 2017)
* a. Reduction in Tourism
* b. Cost for Repair and Treatment
+c. Likely to Happen Again
+ d. Financial Burden
3. Educational Impact
Each year disasters have a major impact on children, youth, and
education systems. In the disaster-prone region of the Asia Pacific,
around 200 million children per year will have their lives severely
disrupted by disasters in the coming decades. Every child has a right
to quality education, yet across the region, many children are unable
to realize this right due to the impact of these disasters. Educational
inequities are made worse because of schools being damaged or
destroyed (due to poor site selection, design, or construction), schools
being used as evacuation centers, and because disaster risk
reduction (DRR) policies are not being adequately resourced or
prioritized through different levels of governments and to the
community level. Being unable to realize these right puts children at
tisk of exploitation and violence and contributes to a lack of
economic participation. (Disaster impacts on education in the Asia
Pacific region in 2015)
4, Psychological Effects of Disaster
Disasters and mental health are related to a large extent; the effects
of disasters might have a negative impact on the affected
population. Along with the social and economic losses, the individuals
and communities experience mental instability which might
precipitate Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD), Anxiety, and
Depression in the population. Generally, disasters are measured by
the cost of social and economic damage, but there is no comparison
to the emotional suffering a person undergoes post-disaster.�5. Spiritual Effect
Spiritual health can often be a casualty of war in times of
unprecedented upheaval and change. There are a number of shifts
that occur in times of disaster in regard to an individual's faith, beliefs,
and spiritual practices. | think sometimes this can get neglected or
overlooked, especially by mainstream media coverage, and yet it is
every bit as important as our emotional and physical well-being. (Kelly
Isola)
Things to say:
* Lam so very sorry
* My heart is with you
* You have my deepest sympathy
* lam here for you
* You (your family) are in my prayers
* How can | support you?
RA 10121 also known as the "Philippine Disaster Risk Reduction and
Management Act of 2010" focuses on National Disaster Risk
Reduction and Management Plan 2011-2028.
AN ACT STRENGTHENING THE PHILIPPINE DISASTER RISK REDUCTION
AND MANAGEMENT SYSTEM, PROVIDING FOR THE NATIONAL
DISASTER RISK REDUCTION AND MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK, AND.
INSTITUTIONALIZING THE NATIONAL DISASTER RISK REDUCTION AND
MANAGEMENT PLAN, APPROPRIATING FUNDS THEREFOR AND FOR,
OTHER PURPOSE:
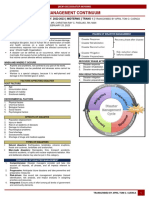
Four DRRM Thematic
Areas�Section 13. Accreditation, Mobilization, and Protection of Disaster
Volunteers and National Service Reserve Corps, CSOs, and the
Private Sector.
Section 14. Integration of Disaster Risk Reduction Education into the
School Curricula and Sangguniang Kabataan (Sk) Program and
Mandatory Training for the Public Sector Employees.
5 Steps to Emergency Preparedness
For Any Disaster
Let's TRY this interactive activity for beh
your class participation
i
Sample Risk Matrix
rr
Dore ere)
information rn)
procedure
Likelihood
If you had to leave your house in a hurry because of an emergency,
what are some important items you should take with you?
The __(item)__is important because...
Let's TRY this interactive activity for your class participation
1.Go to this link https://hazardhunter.aeorisk.gov.oh/mat
2. Enter your current location.
3. Screenshot the screen.
4. Send to our teams assignment bin this served as your Class
Participation for Module 5.�Disaster Risk Reduction Management (DRRM) Awareness/READINESS
NDRRM PLAN 2011-2028
At the end of the module, the students are expected to:
1. Classify the risk and hazards in their home setting.
2. Formulate strategies that will reduce and eliminate the identified hazards.
|. National Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Plan 2011-2028:
A. Disaster Prevention and Mitigation
B. Disaster Preparedness
C. Disaster Response
D. Disaster Rehabilitation and Recovery
Tools in risk/assessment
A. Significance or indications
B. Procedure
C. Data Interpretation
D. Inferences and recommendations
1. National Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Plan 2011-2028:
The National Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Plan (NDRRMP) fulfills the
requirement of RA No. 10121 of 2010, which provides the legal bass for policies,
plans, and programs to deal with disasters. The NDRRMP covers four thematic
‘areas, namely, (1) Disaster Prevention and Mifigation; (2) Disaster Preparedness;
(3) Disaster Response; and (4) Disaster Rehabilitation and Recovery, which
comespond to the structure of the National Disaster Risk Reduction and
Management Counci (NDRRMC). By law, the Office of Civil Defense formulates
and implements the NDRRMP and ensures that the physical framework, social,
economic, and environmental plans of communities, cities, municipalities, and
provinces cre consistent with such apian.�A. Disaster Preparedness and Mitigation
‘Overall responsible agency: Department of
Science and Technology (DOST)
Prevention & Mitigation coresponds to ony measure
taken in advance which cims to reduce the impact
of the disaster through various mitigation methods
which may be stuctural (embankments, cyclone
shelters, components of earthquake-esistant
construction, etc.) ornon-structual (soft components
such as Disaster Management Planning, insurance,
training on emergency management, etc)
tice of Civ Defense
(oco)
Department of Environment
‘ond Natural Resources
(Deny
Department of Public Works
(one Higveays(PW
oc
Department of Finance:
(00F]
Department of Science
fone Technology (COST
B. Disaster Preparedness.
Overall responsible agency: Department of Interior and Local Government (DILG)
Preparedness is about the knowlecige and capacties developed by governments, response
andrecovery organizations, communities, and incividuas to effectively anticipate, respond to
cand recover from the Impacts of Ikely, Imminent, or current disasters. ts based on a sound
andiysé of disaster rkks Gnd good Inkages with early waming systems and includes such
activites as contingency planning, the stockpling of equipment and suppies, the
development of arrangements for coordination, evacuation, and pubic information, and
associated training and field exerces. These must be supported by formal institutional, legal,
and budgetary capacities. The related tem “readiness” descibes the abilly to quickly and
appropriately respond when recured.
(TeAD AGENeY(tES)
Philippine Information Agency
(ia)
Depariment of Interior and Local
Govemmen! (lo coordinate) and
0C0 (te implement)
DitG end oco
uc�C. Disaster Response
‘Overall responsible agency: Department of Social Welfare and Development (DSWD)
A response corresponds to actions taken directly before, during, or immeciately
after a disaster in order to save lives, reduce health Impacts, ensure public safety
and meet the basic subsistence needs of the people affected.
Evacuation, rescue, and relief deal with the immediate actions taken up following
@ disastrous event aimed at saving people's lives and environmental damage.
Typicaly, It deals with isolating people impacted by disaster from the impacted
area after the disaster strikes (Evacuation) or rescuing them during or immeciately
after a disaster (rescue) and providing them with immediate assistance, food,
shelter, and other basic needs.
Unless you live In a mandatory evacuation zone, it Is recommended that you
make a plan to sheiterin place in your home Itt is safe to do so.
It you live In a mandatory evacuation zone, make a pian with friends or family to
shelter with them where you will be safer and more comfortable.
Only evacuate to shelters if you are unable fo shelter at home or with family or
flends. Note that your regular shelter may not be open this year. Check with local
authorities for the latest information about public shelters.
If you need to go to a disaster shelter, follow CDC recommendations for staying
safe and healthy in a public disaster shelter during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Department of Social Welfare
‘and Development (DSWD)
Disaster Risk Reduction and
‘Management Councils
(DRRMCs), OCD and DSWD
Department of National
Defense (DND), DiLG,
Department of Health (DOH)
Local government units (LGUs)
pswo
DOH
DOH
pswo�D. Disaster Rehabilitation and Recovery
Overall responsible agency: National Economic and Development
Authority (NEDA)
The main player during the rehabilitation and recovery is the
government with the reason that they have the full capacity for this
situation with the great help of the Local Government Unit (LGU).
Rehabilitation is about the restoration of basic services and facilities
for the functioning of a community, or a society affected by a disaster.
Reconstruction is the medium- and long-term rebuilding and
sustainable restoration of resilient critical infrastructures, services,
housing, facilities, and livelihoods required for the full functioning of a
community, or a society affected by a disaster, aligning with the
principles of sustainable development and “build back better”, to
avoid or reduce future disaster risk.
outcomes LEAD AGENCIES)
20. Damages, losses, andneeds assessed = OC
‘Agency to be determined
based on the affected Sectors
National Housing Authority
(NHA)
DPWH
kcesigememetaemiguaieeiae a
Components of Disaster Management�10 things you should know about DRRM:
https://www youtube, com/watch?v=y16aMLeh? |@&feaiure=voulu be&IbcId=IWwARSFsw aalMp
HMGo7ByaKBZieCONelif@mUPBokLGndo 5xx1fhONCuylo.
Disaster Management Policies
A. Disaster Response
The provision of emergency services and
public assistance during or immediately
after a disaster in order to save lives,
reduce health impacts, ensure public
safety and meet the basic subsistence needs of the people affected.
Disaster response is predominantly focused on immediate and short-
term needs and is sometimes called “disaster relief".
B. Disaster Management
It is defined as the process of identifying, analyzing, and quantifying
the probability of losses to undertake preventive or corrective actions
This involves two types of activities.
* Planning actions to reduce vulnerability in areas where risk can
be controlled, and
+ Establishing protective mechanisms against the potential
economic losses from uncontrollable factors of natural hazards
C. Disaster Risk Reduction
As part of the total picture of NDRRM Plan as a student, we need to
do this particular task in our own capacity and understanding to be
more resilient before, during,
and after the Disaster.
"YouTube n.d). YouTube. llos,/vovly be/zpbanoSehd
cvenaeena wwmewewns | The video vil decus SENDAI FRAMEWORK on DSASTER RIK
REDUCTION were RA 10121 through NORRM Plan is being linked to.
Disaster Management
Coordinating Agencies�11 Home Safety Challenge
Can you spot the 19 differences?
What's NOT safe? Mareen
Il. Tools in risk assessment
Risk assessments are critical for communities to recognize the risks they
face. Risk assessments serve as the first step in reducing the
vulnerabilities of communities. It identifies hazards and exposed
vulnerable sectors in the community. It guides communities to prioritize
actions and develop effective strategies for disaster prevention,
mitigation, preparedness, and response. Assessment tools on the
existing and potential hazards and risks shall be developed under the
new law. The identification, assessment, and prioritization of hazards
and risks are the responsibilities of the OCD at the national level (Sec.
9. c) and the LDRRMOs at the local level (Sec. 12.0.9).
Hazards and Vulnerabilities and therefore disaster risks to:
Avoid (prevent) or Limit
(mitigate and prepare for)
the adverse impacts of
hazards within the broad
context of — sustainable
development
Adaptive capacity�TYPES OF HAZARDS
ELECTRICAL HAZARDS
An electrical hazard is a dangerous
condition where a worker can or does
make electrical contact with energized
equipment or a conductor. From that
contact, the person's conditions may
sustain an injury from shock, and there is a
potential for the worker to receive an arc
flash (electrical explosion) bum, thermal
burn, or blast injury. purest reece tants
Electricity can either be ‘static’ or
"dynamic". Dynamic electricity is the uniform motion of electrons
through (electric current). Static electricity is the accumulation of
charge on surfaces as a result of contact and friction with another
surface. (Electrical Hazards, 2020)
CHEMICAL HAZARDS
Chemical hazards and toxic substances
pose a wide range of health hazards
(such as iitation, sensitization, and
carcinogenicity) and physical hazards
(such as flammability, corrosion, and
explosibility).. (UNITED STATES
DEPARTMENT OF LABOR)
PHYSICAL HAZARDS
contact. (heat, noise, air quality, slippery
floors, poor lighting, poorly designed work
station, etc.) (Wikipedia)
ze a A physical hazard is an agent, factor, or
circumstance that can cause harm with
eee eee�Flammable/Explosive Hazards
Flammable and combustible liquids are liquids that can burn. They are
classifie
or grouped, as either flammable or combustible by their
flashpoints. Generally speaking, flammable liquids will ignite (catch on
fire) and burn easily at normal working temperatures. Combustible
liquids have the abiity fo burn at temperatures that are usually above
working temperatures.
Flammable and combustible
liquids are present in almost
every workplace. Fuels and
many common products like
solvents, thinners, cleaners,
adhesives, paints, waxes and
polishes may be flammable or
combustible liquids. Everyone
who works with these liquids
must be aware of their hazards
and how to work safely with
them. (Government of
Canada, C. (2020)
a
(na.
hupa/www thinglink con/acene/716210807176060250
(a)
https://wrew moving com/tips/how-to-dispose-of
hazardous waste-before-you- move!
Other Hazards (Specify)
Ergonomic Hazard
Occur when the type of work,
body position, and working
conditions put a strain on your
body. Example: sore muscles
(GISLASON, 2018)�SAFETY AT HOME: COMMON SAFETY HAZARDS AROUND THE HOUSE
(StaySafe.org, 201 S
=
2. Poisoning ~~ «
‘Minimize The Risk
5. Choking
eer]
Min
re
a
7. Stoves 0 Sa
Cie ek
B. Procedure
Observation is a very useful way to assess. But, as with all assessment
fools, it needs to be well planned and designed. Because it is
observation, some people can tend to be a bit slack about planning
and record keeping. This is not good enough. (24)
The following is an example of an observation assessment instrument,
Note the following features
+ it gives clear instructions to both the assessor and candidate
about how to “do” the assessment
+ it gives a clear indication of the observable things to look for
and how to record those observations
+ it guides the assessor on how to make the final assessment
decision. (24)�C. Data Interpretation
Data interpretation refers to the implementation of processes
through which data is reviewed for the purpose of arriving at an
informed conclusion. The interpretation of data assigns a meaning
to the information analyzed and determines its signification and
implications.
D. Inferences and recommendations
Observations occur when we can see something happening. In
contrast, inferences are what we figure out based on experience
Helping students understand when information is implied, or not
directly stated, will improve their skills in drawing conclusions and
making inferences. These skills will be needed for all sorts of school
assignments, including reading, science, and social studies
Inferential thinking is a complex skill that will develop over time and
with experience. (22)
ACTIVITY 6 HAZARD ASSESSMENT
MAKE YOUR OWN SIMPLE HAZARD ASSESSMENT
+ DRAW YOUR HOME
+ LEVEL EACH PORTION OF YOUR HOME FOLLOWING THE HAZARD
CODE KEY.
+ TAKE A PICTURE OF YOUR DRAWING OF HAZARD ASSESSMENT.
+ DEADLINE NEXT MEETING.
zane
fe | eet
eee | uit
ska eat i, aru Spey
fers or po ptr
seine)
ove | nme
@ @ @|\e@ @
z
teat | terranes