Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Untitled
Uploaded by
lala roqueOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Untitled
Uploaded by
lala roqueCopyright:
Available Formats
Course Code ENG 412
Course Title TRANSLATION AND EDITING OF TEXT
Course Credit 3 UNITS
Pre-requisites None
Course Description This course provides the pre-service English teachers with the principles, methods, and approaches of translation and adaptation of various
literary and non-literary texts. It provides them exercises that require them to translate and adapt texts from one language to another (i.e.
English to Filipino to Mother Tongue). Consequently, they will be able to demonstrate content knowledge and application of translation skills
in providing contextualized materials that develop their learners’ critical, creative, and other higher order thinking skills.
A. University Vision
A leading Higher Education Institution that prepares visionary and ethical leaders who shall create a positive impact to society.
B. University Mission
Universidad de Manila promotes is committed to provide equal opportunities by developing the learners’ knowledge, skills, and values, through quality education and
dynamic technology-driven systems, in a diverse yet inclusive environment for learning, research and community engagement.
C. Core Values
E – Ethics and Integrity
Q – Quality and Excellence
U – Unity and Collaboration
A – Achievement and Passion
L – Leadership and Innovation
D. College of Education Vision
Center of Excellence in Teacher-Education, research, extension and linkages as well as a leader in fostering competent, conscientious, versatile and holistic
teachers able to adapt to fast evolving new realities in the local and global learning environment.
E. College of Education Mission
The College of Education is committed to strive to pursue the highest level of excellence, advance the frontiers of knowledge using creative and innovative hybrid
approaches and engender lifelong learning.
F. College of Education Core Values
TRANSLATION AND EDITING OF TEXT Page 1 of 8
E Empowered
D Dynamic and Globally Competitive
U Upright Ethically and Morally
C Committed to Excellence
A Adaptable and Resilient
R Research and Extension Oriented
E Education with a Heart
“In EDUcation, we CARE”
G. Institutional Learning Outcomes
1. Professional Competence. Demonstrate understanding and mastery of the fundamental knowledge and skills required for effective practice in the field of
specialization.
2. Critical Thinking Problem Solving Skills. Exercise critical and creative thinking in providing solutions to discipline-related problems.
3. Productivity. Contribute to city and nation-building and development through application of new technology.
4. Communication Skills. Apply effective communication skills, both orally and in writing.
5. Interpersonal Skills. Work effectively in multi-disciplinary and multicultural teams.
6. Collaboration. Allows team members to solve problems together, thus expediting the process of finishing a task.
7. Research-minded. Display skills to assess and apply its insights effectively and the ability to identify appropriate sources of evidence and interpret potentially complex
and conflicting findings in appropriate specific practice settings.
8. Lifelong learning. Utilize lifelong learning skills in pursuit of personal development and in professional practice excellence.
9. Social and Ethical Responsibility. Holds personal values and beliefs as ethical professional consistent with Filipino family values, industry-desired values and global
citizen values.
10. Nationalism. Serves others willingly as a way towards contributing a nation-building and participates in influencing public policy towards the promotion of just
society.
H. Program Intended Learning Outcomes (PILO)
1. Exhibit competence in language concepts and procedures.
2. Exhibit proficiency in relating communication to other curricular areas.
TRANSLATION AND EDITING OF TEXT Page 2 of 8
3. Use English as a global language in a multilingual context as it applies to the teaching of language and literature.
4. Demonstrate proficiency in oral and written communication.
I. Course Intended Learning Outcomes (CILO)
Students in order to evidence success in this course, the students will be able to:
1. demonstrate current, research-based knowledge and understanding of the basic concepts and principles of assessment and how they are applied in teaching
and learning;
2. identify learning outcomes that are aligned with learning competencies;
3. demonstrate knowledge in designing, developing, selecting, and using appropriate diagnostic, formative and summative assessment strategies in line with K
to 12 standards, guidelines and requirements.
4. demonstrate content knowledge and application of translation theories and approaches to literary and non-literary texts through translation (conventional text
translation and technology-based translation) using English, Filipino, and Mother Tongue; and B.
5. compile adapted/translated/contextualized materials that develop English students’ critical and creative thinking skills in English and other languages.
Teaching Strategies
Student Learning Outcomes Content Synchronous Assessment
Asynchronous
Face-to-Face Virtual
At the end of these weeks, the preservice • Timeline task on • Timeline task, oral
TRANSLATION AND EDITING OF TEXT Page 3 of 8
teacher (PST) should be able to: 1. Overview of Translation Viewing funny videos on the history participation, group
erroneous meanings or purposes, translation task, and TPS
a. identify the history, purposes, 1. History of Translation ordeals in translation as connections, and as formative assessment
connections, and theoretical bases of 2. Purposes of Translation springboard to discuss the theoretical bases on overview of
translation as an applied language context; 3. Translation as part of Applied hows and whys of of translation translation
and Linguistics translation
4. Theoretical Bases of Translation • Giving • Short objective quiz on
b. discuss the relevance of context (Jakobson, Holmes, Kelly) • Lecture discussion on examples of history, purposes,
retention as a relevant process in translation 5. Context Retention translation as an applied translated texts to connections, and
from one language to the other. 6. Principle of Equivalence 7. linguistic study and task, show equivalence theoretical bases of
Fidelity theories on translation, and fidelity from translation
and context retention source language
to target language • Summarizing
• Group activity to Translation Theories
translate given short through Mind Maps
Cebuano text to English (focusing on Structure
and vice versa of Mind Map, Creativity
and Artistry, and
• Think-Pair-Share (TPS) Synthesis of Lesson on
activities on the relevance Translation)
of context retention as a
relevant process in
translation from one
language to the other
At the end of these weeks, the preservice 2. Types of Translation and Techniques • Making a concept map of • Showing sample • Interpretation of
teacher (PST) should be able to: in Translating the different types of translated literary Translated
translations in different works and Poem/Song/Stories
a. describe and differentiate the types of 1. Interpretation as an Act of contexts analyzing them as Performance
translations in different contexts; and Translation a class Presentation (focusing
• Group activities to try the on Choice of Text,
TRANSLATION AND EDITING OF TEXT Page 4 of 8
b. apply types and techniques in 2. Sense-to-Sense and Faithful types of translation (sense- • Teacher’s Actual Translation
translating songs, poems, stories, and non- Translations to-sense vs. faithful, literal presentation of an Faithfulness,
fiction texts to English, Filipino, and vs. legal vs. technical, prose interpretation of a Submission of Written
Mother Tongue. 3. Literal, Legal, and Technical vs. poetic, interlingual, translated song as Output, Continued
Translations intralingual, and model for Presence of Literary
intersemiotic) and applying students’ output Style, and Language
4. Literary Translation translation Mechanics)
theories/processes during the • Consultation
5. Prose Translation tasks and feedbacking
of instructor on
6. Poetic Translation • Roundtable discussion on one’s
the role of editing in the interpretation and
7. Interlingual, Intralingual, and translation writing process translation of a
Inters miotic Translation Codes literary text
• Literary translation
8. Editing as Part of the Translation applying the types and
Writing Process techniques in translating
songs, poems, stories, and
non-fiction texts to English,
Filipino, and Mother Tongue
– group/pair planning, actual
translation writing, practice,
and presentation
• Class discussion of choice
of literary translation text in
terms of appropriateness to
grade level/ student language
tasks, and competencies
MIDTERM EXAMINATION
Formative Assessment
TRANSLATION AND EDITING OF TEXT Page 5 of 8
3. Technology-Based Translation • Roundtable discussion on Short responses
At the end of these weeks, the preservice the technology-based • Grouping and Seatwork
teacher (PST) should be able to: 1. Translation Applications – translation types practice for Class
Benefits and Limitations original dubbing Participation
a. describe and differentiate the 2. Computer-Assisted/ Machine • Video presentation on and subtitling Quiz
technology-based translation types; and Translation artists’ dubbing and tasks
3. DubbingTest item formulation subtitling of Filipino movies • Differentiation table on
b. apply technology-based translations in - Item analysis to English and vice versa Original technology-based
dubbing and subtitling Filipino movies to - Reliability Subtitling and translation types as
English and vice versa. - Measures of relationship • Visiting Amara.org to Dubbing of a formative assessment
- Index of determination translate YouTube and Filipino/
- Subtitling similar videos through Cebuano Movie • Process assessment on
subtitling or Episode to group Subtitling and
English and/or Dubbing task
vice versa
(focusing on
Effective Use of
Technology,
Actual
Translation
Faithfulness,
Effort and Group
Collaboration,
and Impact of
Final Output)
At the end of these weeks, the preservice
teacher (PST) should be able to: 4. Editing • Mind mapping on • Analyzing Objective quiz on
copyreading, role of editors, sample style Copyreading and
a. discuss copyreading, role of editors, 1. Review on Copyreading and the style sheet, and use of sheets of famous Proofreading symbols
TRANSLATION AND EDITING OF TEXT Page 6 of 8
the style sheet, and grammar in order to Proofreading accurate grammar in texts publications and Advanced Grammar
recognize editing as an important part of the and Composition
translation process; and 2. Role of Editors in a Publication • Compiling concerns • Answering
3. Process of Editing and Publishing translated texts worksheets on grammar
b. compile translated contextualized • Answering worksheets appropriate as review as formative
learning materials in order to develop 4. The Style Sheet to review grammar rules, learning materials assessment on editing
critical and creative skills of English avoiding sentence errors, and to be used to
learners 5. Standard English and Review on writing effective sentences English language • Compilation of
Grammar Rules and paragraphs learners Translated Texts
(focusing on
6. Editing in the Translation Process • Actual editing tasks – • Process Appropriateness of
visiting a JHS/SHS English assessment or Translated Texts as
class and ask students on Reflection Learning Materials,
their difficulties in writing writing on one’s Organization of
and help them through editing endeavor Compilation, and Group
editing their compositions with students Effort and
having Collaboration)
• Roundtable discussion difficulties in
on the role of editors, the writing and
need for grammar expertise, composition and
and openness in editing and trying to help
the writing process as future them out
teachers and linguists
J. Learning Environment: Physical classroom/Virtual
K. Classroom Policy: Attendance/Drop-out Policy
L. Course Requirement: Written works, Quizzes, Major Exams, Class participation, Project
M. Grading System:
Class Standing (60%)
Recitation/Participation
Quizzes
Module Performance
TRANSLATION AND EDITING OF TEXT Page 7 of 8
Major Exams (40%)
Final Grade = Midterm (50%) + Finals (50%)
N. Resources: Textbooks, web links
O. References: 4EnglishPrototypeSyllabiCompendium.pdf
Haque, Z. (2009). Translating literary prose: Problems and solution. Retrieved on April 26, 2014 from TranslationDirectory.com
Hodges P. (2013). Literary approach to translation theory. Retrieved on November 5, 2010 from
http://www.translationdirectory.com/articles/article2085.php
P. Instructor: Maribel J. Roque
Q. Consultation Hour:
Prepared by: Reviewed by: Approved by:
MARIBEL J. ROQUE DR. AMALFI B. TABIN, JR. DR. RONALD A. HERRERA
INSTRUCTOR DEAN VPAA
TRANSLATION AND EDITING OF TEXT Page 8 of 8
You might also like
- Language Assessment Principles (HaTay2008)Document14 pagesLanguage Assessment Principles (HaTay2008)loantnuNo ratings yet
- OIPD in LinguisticsDocument7 pagesOIPD in LinguisticsBela AtthynaNo ratings yet
- Eng211CO2021 22 DALUMAYDocument5 pagesEng211CO2021 22 DALUMAYCiarrah PosterNo ratings yet
- Grammar: - Presented byDocument39 pagesGrammar: - Presented bySazlina SamahNo ratings yet
- University of The CordillerasDocument7 pagesUniversity of The CordillerasNorma AbdulNo ratings yet
- Group 2 The Curriculum For LanguageDocument11 pagesGroup 2 The Curriculum For LanguageAngelica Lyca GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Sec Edu Ys 3 & 4 Official ProgDocument44 pagesSec Edu Ys 3 & 4 Official ProgMed DjbaliNo ratings yet
- English Programmes: FOR Basic EducationDocument19 pagesEnglish Programmes: FOR Basic EducationFaouzi HarrathiNo ratings yet
- English LET ReviewerDocument15 pagesEnglish LET ReviewerAdelisa NiñalNo ratings yet
- Esl Efl Foundation SyllabusDocument7 pagesEsl Efl Foundation Syllabusapi-4572716320% (1)
- COURSE OUTLINE - Applied Linguistics-OKDocument9 pagesCOURSE OUTLINE - Applied Linguistics-OKNi Nengah HardiyantiNo ratings yet
- Reviewer KemeDocument3 pagesReviewer KemeMarc Lorenz AlbaridoNo ratings yet
- English DLLDocument5 pagesEnglish DLLGellie Mae SiocoNo ratings yet
- Recommendations and Curricular Foundations of PRONI and The Use of Project Based LearningDocument2 pagesRecommendations and Curricular Foundations of PRONI and The Use of Project Based LearningAngelus AnimarumNo ratings yet
- Eng221CO2021 22Document6 pagesEng221CO2021 22Dimple BolotaoloNo ratings yet
- Presentation Section5 FarajnezhadDocument39 pagesPresentation Section5 FarajnezhadHadeer Abd El AzizNo ratings yet
- RPKPS Translation English-Indonesia (2021)Document26 pagesRPKPS Translation English-Indonesia (2021)Nerds Vags IrfanNo ratings yet
- I.Objectives: School Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Teaching Dates and Time QuarterDocument4 pagesI.Objectives: School Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Teaching Dates and Time Quarteramelyn.manosoNo ratings yet
- Arteaga - TED 407 Syllabus - Spring 2021 - TuesdayDocument16 pagesArteaga - TED 407 Syllabus - Spring 2021 - TuesdayHenry PapadinNo ratings yet
- CTL Assignment-1-18035432 1Document60 pagesCTL Assignment-1-18035432 1api-518571213No ratings yet
- BSC CSE ENG 1101-English Reading Skills and Public SpeakingDocument5 pagesBSC CSE ENG 1101-English Reading Skills and Public Speakingrtasneem2432No ratings yet
- EL100Document5 pagesEL100Lourene May Apolinares GalgoNo ratings yet
- Skills For Study 1 TBDocument118 pagesSkills For Study 1 TBFrancesca Sweeney-AndroulakiNo ratings yet
- Edelt 105 CompilationDocument9 pagesEdelt 105 CompilationRhea BermejoNo ratings yet
- Communicative Language TeachingDocument18 pagesCommunicative Language Teachingapi-480582631100% (1)
- Aven 123Document16 pagesAven 123Beberly Kim AmaroNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication Q2 W7Document4 pagesOral Communication Q2 W7Fhats DuncabNo ratings yet
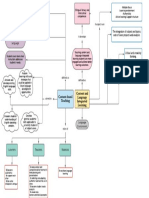
- Mind MapDocument1 pageMind MapRosa HidalgoNo ratings yet
- Approaches and Methods in LanguageDocument32 pagesApproaches and Methods in LanguageJessemar Solante Jaron WaoNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - Introduction To LinguisticsDocument9 pagesSyllabus - Introduction To LinguisticsEdel Mae OpenaNo ratings yet
- Approaches For Language Arts Teaching: ContinuationDocument35 pagesApproaches For Language Arts Teaching: ContinuationIrish Kay RiezaNo ratings yet
- Curriculum KLMPK 4 On Process 1Document29 pagesCurriculum KLMPK 4 On Process 1reini kurniawati effendiNo ratings yet
- Didactics of EnglishDocument18 pagesDidactics of EnglishlicethNo ratings yet
- Reading and WritingDocument15 pagesReading and WritingShalom Boker TovNo ratings yet
- s3 Reading VocabularyDocument39 pagess3 Reading Vocabularytlswodms90No ratings yet
- Week 7 CLTDocument29 pagesWeek 7 CLTCarolina HoyosNo ratings yet
- Competence-9033 (Compatibility Mode)Document68 pagesCompetence-9033 (Compatibility Mode)Umar SianturiNo ratings yet
- College of Education: The Premier University in Zamboanga Del NorteDocument3 pagesCollege of Education: The Premier University in Zamboanga Del NorteHerford Rei GuibangguibangNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - Introduction To LinguisticsDocument6 pagesSyllabus - Introduction To LinguisticsEdel Mae OpenaNo ratings yet
- Biliteracy Strategies Description Beeman and UrowDocument8 pagesBiliteracy Strategies Description Beeman and UrowDavidNo ratings yet
- Immersion Teaching Strategies Observation Checklist: The Bridge: From Research To PracticeDocument4 pagesImmersion Teaching Strategies Observation Checklist: The Bridge: From Research To PracticepmakmakNo ratings yet
- Syllabus ESPDocument4 pagesSyllabus ESPJeane DagatanNo ratings yet
- The Teaching of The Language SubjectsDocument50 pagesThe Teaching of The Language SubjectsMelynNo ratings yet
- Translation and Editing of Text SyllabusDocument6 pagesTranslation and Editing of Text SyllabusCarmie Lactaotao Dasalla100% (2)
- UntitledDocument9 pagesUntitledlala roqueNo ratings yet
- Curriculum and Assessment Guide (CAG) Elementary 2011-2012 Houghton Mifflin Sixth GradeDocument19 pagesCurriculum and Assessment Guide (CAG) Elementary 2011-2012 Houghton Mifflin Sixth GradePerihan SayedNo ratings yet
- Academic Conversations S JCC Day 3Document34 pagesAcademic Conversations S JCC Day 3Maryjane Bailo Lamela100% (1)
- RB Grad II PerfectionareDocument41 pagesRB Grad II PerfectionareGabriela AvramNo ratings yet
- SYL EL118 Language Learning Materials DevelopmentDocument9 pagesSYL EL118 Language Learning Materials DevelopmentREAS FAITHNo ratings yet
- Developing Specific Types of MaterialsDocument52 pagesDeveloping Specific Types of MaterialsFatima Abayon100% (1)
- English MethodologiesDocument27 pagesEnglish Methodologiesmargaret duffieldNo ratings yet
- I.Objectives: School Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Teaching Dates and Time QuarterDocument4 pagesI.Objectives: School Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Teaching Dates and Time Quarteramelyn.manosoNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication Q2 W6Document3 pagesOral Communication Q2 W6Fhats DuncabNo ratings yet
- College Department Bachelor of Secondary Education Major in EnglishDocument9 pagesCollege Department Bachelor of Secondary Education Major in EnglishLhoriebeth MangobaNo ratings yet
- The+Language+Triptych+ Coyle,+2010Document4 pagesThe+Language+Triptych+ Coyle,+2010sara MvNo ratings yet
- Activity 6 Topic 1 Module 3 PassDocument4 pagesActivity 6 Topic 1 Module 3 PassJe Rel100% (5)
- Gennuso 4 Shifts Protocol Lesson Analysis and ReflectionDocument9 pagesGennuso 4 Shifts Protocol Lesson Analysis and Reflectionapi-550159336No ratings yet
- Should Have, Could Have, Would Have : MYP Unit PlannerDocument11 pagesShould Have, Could Have, Would Have : MYP Unit PlannerBarbara MUINo ratings yet
- Research and Teaching On L2 Reading Week 3Document18 pagesResearch and Teaching On L2 Reading Week 3Yohanes Nugroho WidiyantoNo ratings yet
- Multilingualism and Translanguaging in Chinese Language ClassroomsFrom EverandMultilingualism and Translanguaging in Chinese Language ClassroomsNo ratings yet
- Course Description: Course Code Course Title Course Credit Pre-RequisitesDocument9 pagesCourse Description: Course Code Course Title Course Credit Pre-Requisiteslala roqueNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument9 pagesUntitledlala roqueNo ratings yet
- Matrix For Project Proposal Team BuildingDocument4 pagesMatrix For Project Proposal Team Buildinglala roqueNo ratings yet
- PARENTSDocument16 pagesPARENTSlala roqueNo ratings yet
- Project Proposal Marcos O.KDocument5 pagesProject Proposal Marcos O.Klala roqueNo ratings yet
- Matrix For Marcos OkDocument3 pagesMatrix For Marcos Oklala roqueNo ratings yet
- Weber's "Ideal Types" - Definition, Meaning, Purpose and UseDocument10 pagesWeber's "Ideal Types" - Definition, Meaning, Purpose and UseVishal AnandNo ratings yet
- Literature ReviewDocument5 pagesLiterature Reviewapi-519794167No ratings yet
- Definition and Scope of StatisticsDocument39 pagesDefinition and Scope of StatisticsRimple Abhishek Delisha ViraajvirNo ratings yet
- Medicine 1 - Paper 2Document14 pagesMedicine 1 - Paper 2Mohammad taha RanjiNo ratings yet
- G11 ABM Org and MGT Lesson 1 (Part 2)Document14 pagesG11 ABM Org and MGT Lesson 1 (Part 2)Leo SuingNo ratings yet
- Diass Final ExamDocument2 pagesDiass Final ExamNorberto J. Manjares Jr.No ratings yet
- Matematika 1 - Q2 - W3Document5 pagesMatematika 1 - Q2 - W3Darel TaroyNo ratings yet
- Bcu g88 Magc 206 Midterm Lesson 1Document4 pagesBcu g88 Magc 206 Midterm Lesson 1Joan BayanganNo ratings yet
- SUMMARIZINGDocument18 pagesSUMMARIZINGjohn mark moralesNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering Tools and PracticesDocument14 pagesSoftware Engineering Tools and Practicesabebe besobelaNo ratings yet
- ErasmusPlus KA2 2021-2027 PartnershipsForCooperationAndExchangesOfPractices Projects Overview 2023-10-03Document1,217 pagesErasmusPlus KA2 2021-2027 PartnershipsForCooperationAndExchangesOfPractices Projects Overview 2023-10-03AyaNo ratings yet
- Functional Safety Concepts in Motor ControlDocument9 pagesFunctional Safety Concepts in Motor ControlYan LiuNo ratings yet
- RW Module 6Document4 pagesRW Module 6Jaren Pauline D. HidalgoNo ratings yet
- Navigating Assessment in The Digital Realm: Experiences of Educators in A Distance Learning EnvironmentDocument7 pagesNavigating Assessment in The Digital Realm: Experiences of Educators in A Distance Learning Environmentindex PubNo ratings yet
- Interview Assignment Anam 42210Document8 pagesInterview Assignment Anam 42210Seerat FatimaNo ratings yet
- Meghna Raj Saxena, Akarsh Pathak, Aditya Pratap Singh, Ishika ShuklaDocument4 pagesMeghna Raj Saxena, Akarsh Pathak, Aditya Pratap Singh, Ishika ShuklaGAIKWAD MAYURNo ratings yet
- BSC Mechatronik PDF - enDocument2 pagesBSC Mechatronik PDF - enMereNo ratings yet
- Longman Linguistics: AppliedDocument6 pagesLongman Linguistics: AppliedAleNo ratings yet
- Postgraduate Student Handbook SGS 20.1.21Document49 pagesPostgraduate Student Handbook SGS 20.1.21zen AlkaffNo ratings yet
- My Final NagidDocument36 pagesMy Final NagidRenalene BelardoNo ratings yet
- Psychology 10th Edition Wade Test BankDocument88 pagesPsychology 10th Edition Wade Test BankMichaelJohnsonijybp100% (19)
- The Impacts of Alcohol Consumption To The Academic Performance of SHS Students: A Case StudyDocument9 pagesThe Impacts of Alcohol Consumption To The Academic Performance of SHS Students: A Case StudyKlowie DuiganNo ratings yet
- The Role of Pragmatics in Translation and The Pragmatic Difficulties That Encounter TranslatorsDocument22 pagesThe Role of Pragmatics in Translation and The Pragmatic Difficulties That Encounter Translatorsabdullah al-eryaniNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Importance of A Mother's Role in A Child's LifeDocument1 pageUnderstanding The Importance of A Mother's Role in A Child's Lifeyuuki konnoNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Technology and The Rise of CivilizationsDocument10 pagesModule 1 - Technology and The Rise of CivilizationsTOBI JASPER WANGNo ratings yet
- That Provide Support and Facilitate Understanding of TextsDocument3 pagesThat Provide Support and Facilitate Understanding of TextsJanelle Lusung VenzonNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of The Quality of Occupational Health and Safety Management Systems Based OnDocument17 pagesEvaluation of The Quality of Occupational Health and Safety Management Systems Based OnWilisMilayantiNo ratings yet
- The Perceived Impact of Historical Heritage Preservation On The Cultural Identity of Architecture Students in The City of MalolosDocument16 pagesThe Perceived Impact of Historical Heritage Preservation On The Cultural Identity of Architecture Students in The City of MalolosDarlene ivyNo ratings yet
- MGP HKT Lor - 110942Document1 pageMGP HKT Lor - 110942Sparsh ShukalNo ratings yet
- Statics 1 - Copy-1-2Document193 pagesStatics 1 - Copy-1-2Mohammed Ali100% (3)