Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Untitled
Untitled
Uploaded by
Amrutha Borigi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pagesThe d-block occupies the central region of the periodic table between the s- and p-blocks. Transition metals have incompletely filled d orbitals, except for Zn, Cd, Hg and Cn which are completely filled in the ground state. Transition metals generally display metallic properties like high strength, ductility, and conductivity due to their unpaired electrons, resulting in stronger interatomic bonding and higher enthalpies of atomization.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe d-block occupies the central region of the periodic table between the s- and p-blocks. Transition metals have incompletely filled d orbitals, except for Zn, Cd, Hg and Cn which are completely filled in the ground state. Transition metals generally display metallic properties like high strength, ductility, and conductivity due to their unpaired electrons, resulting in stronger interatomic bonding and higher enthalpies of atomization.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pagesUntitled
Untitled
Uploaded by
Amrutha BorigiThe d-block occupies the central region of the periodic table between the s- and p-blocks. Transition metals have incompletely filled d orbitals, except for Zn, Cd, Hg and Cn which are completely filled in the ground state. Transition metals generally display metallic properties like high strength, ductility, and conductivity due to their unpaired electrons, resulting in stronger interatomic bonding and higher enthalpies of atomization.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
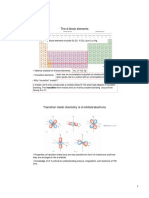
The d–block occupies the large middle section of the periodic tableflanked between
s– and p– blocks in the periodic table.
(n-1)d1– 10ns1–2.
Zn, Cd, Hg and Cn they are not regarded as transition elements because they are
completely filled at ground state.
eg:On the basis of incompletely filled 3d orbitals in case of scandium atom
in its ground state (3d1), it is regarded as a transition element. On the
other hand, zinc atom has completely filled d orbitals (3d10) in itsground state as
well as in its oxidised state, hence it is not regardedas a transition element.
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES:
Nearly all the transition elements display typical metallic properties such as
high tensile strength, ductility, malleability, high thermal and
electrical conductivity and metallic lustre. With the exceptions of Zn,Cd, Hg and
Mn, they have one or more typical metallic structures at
normal temperatures.
The transition metals (with the exceptionof Zn, Cd and Hg) are very hard and have
lowvolatility. Their melting and boiling points are
high.
The filling of 4f before 5d orbital results in a regular decrease in atomic radii
called LANTHANOID CONTRACTION.
Q)Why do the transition elements exhibit higher enthalpies of atomisation?
Because of large number of unpaired electrons in their atoms they have stronger
interatomic interaction and hence stronger bonding between atoms resulting in
higher enthalpies of atomisation.
TRANSITION METALS:(with higher oxidation state combinations)
(TiIVO2, VVO2+,CrV1O42–, MnVIIO4).
pg no :11,12,15 in NCERT Book are impotant.. <<<<<TABLES>>>>>./,.
Intertitial Compounds:
Interstitial compounds are those which are formed when small atoms like H, C or N
are trapped inside the crystal lattices of metals. They are usually non
stoichiometric and are neither typically ionic nor covalent,
for example, TiC, Mn4N, Fe3H, VH0.56 and TiH1.7, etc.
(i) They have high melting points, higher than those of pure metals.
(ii) They are very hard, some borides approach diamond in hardness.
(iii) They retain metallic conductivity.
(iv) They are chemically inert.
Oxidation state:
In the lanthanoids, La(II) and Ln(III) compounds are predominant species. However,
occasionally +2 and +4 ions in solution or in solid compounds are also obtained
Lantanum reactions:
Ln with H2O ---- Ln(OH)3 + H2
Ln with Acids ---- H2
Ln with Halogens ---- LnX3
Ln with Heated N ---- LnN
Ln with Heated S ---- LnS......., etc..,
Lanthanoid Property:
A well known alloy is mischmetall which consists of a lanthanoid metal(95%) and
iron (5%) and traces of S, C, Ca and Al. A good deal of mischmetall.
Some Applictions of D and F block elememnts :
Iron and steels are the most important construction materials. Their production is
based on the reduction of iron oxides, the removal of impurities and the addition
of carbon and alloying metals such as Cr, Mn
and Ni. Some compounds are manufactured for special purposes such as TiO for the
pigment industry and MnO2 for use in dry battery cells. The battery industry also
requires Zn and Ni/Cd. The elements of Group 11
are still worthy of being called the coinage metals, although Ag and
Au ...........////..>>>>>>>
<<<THE END>>>
You might also like
- Chemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandChemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- 10 - D - and F - Block Elements PDFDocument18 pages10 - D - and F - Block Elements PDFthinkiit100% (19)
- D and F Block ElementsDocument51 pagesD and F Block ElementsSatlip50% (2)
- D&F Block ElementsDocument16 pagesD&F Block ElementsManish kumarNo ratings yet
- Exam Pattern: - Quiz I (4 Sep, 8 Am) - Quiz II (16 Oct, 8 Am) - End-Sem (19 Nov) AttendanceDocument18 pagesExam Pattern: - Quiz I (4 Sep, 8 Am) - Quiz II (16 Oct, 8 Am) - End-Sem (19 Nov) AttendanceutkarshNo ratings yet
- Exactive & Q Exactive MS: Operational Qualification 1.1 Procedure & WorksheetsDocument28 pagesExactive & Q Exactive MS: Operational Qualification 1.1 Procedure & WorksheetsAlexander Nieto Vela100% (1)
- Chemistry of Transition and Inner Transition Elements+.Document60 pagesChemistry of Transition and Inner Transition Elements+.Nidhi Singh75% (4)
- General Properties of The Transition Elements: F BlockDocument2 pagesGeneral Properties of The Transition Elements: F BlockSanju PatelNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry: 6. Transition MetalsDocument34 pagesInorganic Chemistry: 6. Transition Metalsbijaya neupaneNo ratings yet
- 0 - D and F Block ElementsDocument16 pages0 - D and F Block ElementsPRITAM KumarNo ratings yet
- Transition Elements & Cordination Chemistry (NCUK)Document24 pagesTransition Elements & Cordination Chemistry (NCUK)phonepyaehtut2006No ratings yet
- D F Block ElementsDocument26 pagesD F Block ElementsAditi TiwariNo ratings yet
- English Grammer BoomDocument96 pagesEnglish Grammer BoomAbhi DebNo ratings yet
- Transition MetalsDocument20 pagesTransition Metalsdulalsushant3No ratings yet
- D and F Block Notes From ALLENDocument51 pagesD and F Block Notes From ALLENChristopher NolanNo ratings yet
- D and F BLOCKDocument31 pagesD and F BLOCKAmalnath SNo ratings yet
- D and F BlockDocument20 pagesD and F BlockRuler HellNo ratings yet
- 222dblock Filled PDFDocument38 pages222dblock Filled PDFSrini SundaravaradhanNo ratings yet
- THE D - AND f-BLOCK ELEMENTSDocument19 pagesTHE D - AND f-BLOCK ELEMENTSshivanshchaurasiya51No ratings yet
- D & F Block ElementsDocument51 pagesD & F Block ElementsVeankatapathy 613 Xl group B100% (1)
- D and F BlockDocument15 pagesD and F Blockthinkiit100% (1)
- The D-Block Elements-Transition ElementsDocument6 pagesThe D-Block Elements-Transition ElementsFabry OseNo ratings yet
- Transition MetalsDocument31 pagesTransition MetalsAigerim TurlanovaNo ratings yet
- D F Block ElementsDocument26 pagesD F Block ElementsVK GNo ratings yet
- Transition ElementsDocument2 pagesTransition ElementsThanni AkanbiNo ratings yet
- D&F Block ElementsDocument10 pagesD&F Block ElementsLovesh KashyapNo ratings yet
- D Block ElementsDocument16 pagesD Block ElementsSreejay BommineniNo ratings yet
- Transition MetalDocument3 pagesTransition MetalZain KhanNo ratings yet
- Che 410 ................... Transition Metal ChemistryDocument13 pagesChe 410 ................... Transition Metal ChemistryElizabeth AnyangoNo ratings yet
- CHEM 252 Lecture 1Document18 pagesCHEM 252 Lecture 1Adjei DanielNo ratings yet
- The D-And F-Block Revision NotesDocument4 pagesThe D-And F-Block Revision NotesMayank Choudhary100% (1)
- CHE 410 - Transistion Metal Chemistry Powerpoint Presentation 11102022Document94 pagesCHE 410 - Transistion Metal Chemistry Powerpoint Presentation 11102022Mwalimu Rashid RashooNo ratings yet
- Electronic Configuration: Variable Oxidation StatesDocument6 pagesElectronic Configuration: Variable Oxidation StatesSonu SahilNo ratings yet
- New Fou 1&2 Nagratoli S - BlockDocument19 pagesNew Fou 1&2 Nagratoli S - BlockAnamikaNo ratings yet
- D and F BlockDocument12 pagesD and F BlockJinal VadodariyaNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Keypoints Revision Questions Chapter 8Document15 pages12 Chemistry Keypoints Revision Questions Chapter 8Sarif AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Endurance Race 5070Document29 pagesChemistry Endurance Race 507024avesh.kumarNo ratings yet
- 24 D F Block Elements Formula Sheets QuizrrDocument17 pages24 D F Block Elements Formula Sheets QuizrrShubhanshu ChandraNo ratings yet
- Unit: 8 - D-& F - Block Elements: Position in The Periodic TableDocument18 pagesUnit: 8 - D-& F - Block Elements: Position in The Periodic TablebhumikaNo ratings yet
- Properties of Metals G LudhianaDocument7 pagesProperties of Metals G Ludhianaapi-3731257No ratings yet
- S-Block Elements: Earth Metals. These Are So Called Because Their Oxides and Hydroxides Are Alkaline in NatureDocument8 pagesS-Block Elements: Earth Metals. These Are So Called Because Their Oxides and Hydroxides Are Alkaline in NatureAgamGoelNo ratings yet
- Metal and Oon - Metals: 4.1 ElementsDocument28 pagesMetal and Oon - Metals: 4.1 ElementsJ. MariappanNo ratings yet
- Metal and Oon - Metals: 4.1 ElementsDocument28 pagesMetal and Oon - Metals: 4.1 ElementsKrishan Lohan0% (1)
- Metal and Oon - Metals: 4.1 ElementsDocument28 pagesMetal and Oon - Metals: 4.1 ElementsGeneric nameNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Formula D and F Block ElementsDocument6 pagesChemistry Formula D and F Block Elementsom popalghatNo ratings yet
- Unit-8 D - and F - Block ElementsDocument2 pagesUnit-8 D - and F - Block ElementsSaurabhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20: Transition Metals and Coordination ChemistryDocument17 pagesChapter 20: Transition Metals and Coordination ChemistryChandra Vinoth SenthilnathanNo ratings yet
- F334 - The Steel StoryDocument11 pagesF334 - The Steel StoryBecky TenneyNo ratings yet
- CH 6 TRANSITION ELEMENTSDocument4 pagesCH 6 TRANSITION ELEMENTSRana Hassan TariqNo ratings yet
- CHP 18 Transition Metals (E)Document6 pagesCHP 18 Transition Metals (E)Khe ManshuNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Imp The Dandf Block Elements MixDocument14 pages12 Chemistry Imp The Dandf Block Elements MixPrinceNo ratings yet
- D and F BlockDocument30 pagesD and F BlockTS SPORTZNo ratings yet
- Reasioning Ques 12 2023Document55 pagesReasioning Ques 12 2023TANISHK YADAVNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 PDFDocument4 pagesChapter 8 PDFChristeena HenryNo ratings yet
- D and F Block ElementsDocument18 pagesD and F Block ElementsLakshmi SinghNo ratings yet
- Transition MetalsDocument2 pagesTransition MetalsJohn Carlo V. ElchicoNo ratings yet
- Selected Topics in Chemistry For Non-Major 1: Dr. Adebisi, A. A. Department of Chemistry, Covenant University, OtaDocument25 pagesSelected Topics in Chemistry For Non-Major 1: Dr. Adebisi, A. A. Department of Chemistry, Covenant University, OtaIfiok UsoroNo ratings yet
- Dandfblockelements 151025054903 Lva1 App6892Document21 pagesDandfblockelements 151025054903 Lva1 App6892Keshav PanchalNo ratings yet
- D and F Block ElementsDocument4 pagesD and F Block Elementsishu010.comNo ratings yet
- XII Chem Ch8 Thed&f-blockElements ChapterNotesDocument5 pagesXII Chem Ch8 Thed&f-blockElements ChapterNotesPrashant ChawlaNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Hydrides: The Commonwealth and International Library: Chemistry DivisionFrom EverandInorganic Hydrides: The Commonwealth and International Library: Chemistry DivisionNo ratings yet
- Step Growth PolymerizationDocument50 pagesStep Growth Polymerizationtemesgen abebeNo ratings yet
- Aromatic Hydrocarbo N Type of Organic Compound Iupac Name Common Name Chemical Formula / Structure UsesDocument17 pagesAromatic Hydrocarbo N Type of Organic Compound Iupac Name Common Name Chemical Formula / Structure UsessoujirosettaNo ratings yet
- Theory of Ion Chromatography From MetrohmDocument40 pagesTheory of Ion Chromatography From Metrohmopenid_mUOZbS9i88% (8)
- Precipitation Reaction (Sodium Hydroxide and Barium Nitrate)Document3 pagesPrecipitation Reaction (Sodium Hydroxide and Barium Nitrate)Kim BuguinaNo ratings yet
- L - 01 - Question Discussion - 12th NEET - Ramesh Sir - ShaniDocument33 pagesL - 01 - Question Discussion - 12th NEET - Ramesh Sir - Shanihunterrems18No ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Biochemistry A Short Course 3rd by TymoczkoDocument36 pagesSolution Manual For Biochemistry A Short Course 3rd by Tymoczkocabecadrawable.sxfi2c100% (44)
- Cracking Hydrocarbons Practice QuestionDocument1 pageCracking Hydrocarbons Practice QuestionZhering RodulfoNo ratings yet
- Skin and HideDocument7 pagesSkin and HideJabed AktarNo ratings yet
- Wa0013Document5 pagesWa0013falgunsanadhyaNo ratings yet
- Project: Determine The Quantity of Casein Present in Different Samples of MilkDocument12 pagesProject: Determine The Quantity of Casein Present in Different Samples of MilkYashashv MohanNo ratings yet
- Elliot Prest - Criterion B - NeutralizationDocument7 pagesElliot Prest - Criterion B - NeutralizationElliot PrestNo ratings yet
- Final HairdryerDocument22 pagesFinal HairdryerRodrigo Soria0% (1)
- Vanders Human Physiology 12th Edition Widmaier Test BankDocument22 pagesVanders Human Physiology 12th Edition Widmaier Test BankDanielleHawkinsnamtg100% (15)
- FX6-400 230V 50Hz Leaflet EN COX 2935087040 Ed00Document2 pagesFX6-400 230V 50Hz Leaflet EN COX 2935087040 Ed00minhmaiphuocNo ratings yet
- Mock 2 Unit 1 BiologyDocument20 pagesMock 2 Unit 1 BiologycrudecadaverNo ratings yet
- Biochar Ammonia 2014Document8 pagesBiochar Ammonia 2014Khaled Abou AlfaNo ratings yet
- B.sc. ChemistryDocument66 pagesB.sc. ChemistryDr. Dinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Urea SynthesisDocument25 pagesUrea SynthesisMuhammad YasirNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument17 pagesChemical Reactions and EquationsRajesh Kumar RoushanNo ratings yet
- Catalogo KomibrightDocument5 pagesCatalogo KomibrightJonathan BedoyaNo ratings yet
- Continuous Hydrogen Production by SequenDocument10 pagesContinuous Hydrogen Production by SequenwameathNo ratings yet
- Propolis: An Update On Its Chemistry and Pharmacological ApplicationsDocument60 pagesPropolis: An Update On Its Chemistry and Pharmacological ApplicationsSAM KNo ratings yet
- Elements and CompoundsDocument8 pagesElements and CompoundsJerry De Leon TaayNo ratings yet
- Science Worksheet Grade - 7Document4 pagesScience Worksheet Grade - 7Srinivas_3181No ratings yet
- Technical Data Sheet For Hdpe Pe 100, 315.0 MM X 28.6 MM DuctDocument1 pageTechnical Data Sheet For Hdpe Pe 100, 315.0 MM X 28.6 MM DuctJohn BenzNo ratings yet
- Lithium Cobalt Oxide (LCO) : 1.2.4: Positive Electrodes For Lithium-Ion CellsDocument2 pagesLithium Cobalt Oxide (LCO) : 1.2.4: Positive Electrodes For Lithium-Ion CellsSurbhi SumanNo ratings yet
- Xi Chemistry PracticalDocument37 pagesXi Chemistry PracticalKOOL KIDZ Hindi Songs For kidsNo ratings yet
- Biobased Acrylate Photocurable Resin Formulation For Stereolithography 3D PrintingDocument6 pagesBiobased Acrylate Photocurable Resin Formulation For Stereolithography 3D PrintingDaniel RamosNo ratings yet
- Chicken LitterDocument29 pagesChicken LitterPrashanth ChinthallapallyNo ratings yet