Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Funacc Rebyuwer
Uploaded by
Bea Manaloto0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views4 pagesThis document provides information about cash and cash management. It discusses:
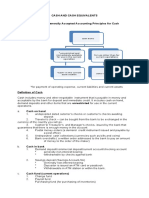
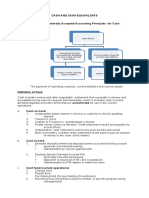
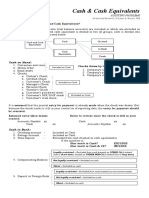
1) Types of cash and cash equivalents like checking accounts, petty cash funds, and bank accounts in foreign currencies. It notes that checks, money orders, and drafts are also considered cash.
2) Items that are not considered cash like receivables, prepaid expenses, temporary investments, and restricted assets.
3) Methods used by companies to protect and manage their cash, like segregating duties, using an imprest system, requiring vouchers, conducting internal audits, and reconciling bank statements.
4) The process of bank reconciliation to ensure no discrepancies exist between a company's book records and its
Original Description:
Original Title
FUNACC-REBYUWER (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides information about cash and cash management. It discusses:
1) Types of cash and cash equivalents like checking accounts, petty cash funds, and bank accounts in foreign currencies. It notes that checks, money orders, and drafts are also considered cash.
2) Items that are not considered cash like receivables, prepaid expenses, temporary investments, and restricted assets.
3) Methods used by companies to protect and manage their cash, like segregating duties, using an imprest system, requiring vouchers, conducting internal audits, and reconciling bank statements.
4) The process of bank reconciliation to ensure no discrepancies exist between a company's book records and its
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views4 pagesFunacc Rebyuwer
Uploaded by
Bea ManalotoThis document provides information about cash and cash management. It discusses:
1) Types of cash and cash equivalents like checking accounts, petty cash funds, and bank accounts in foreign currencies. It notes that checks, money orders, and drafts are also considered cash.
2) Items that are not considered cash like receivables, prepaid expenses, temporary investments, and restricted assets.
3) Methods used by companies to protect and manage their cash, like segregating duties, using an imprest system, requiring vouchers, conducting internal audits, and reconciling bank statements.
4) The process of bank reconciliation to ensure no discrepancies exist between a company's book records and its
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
LESSON 8 Checking account- used to issue
check paments to creditors. Safer
Cash- an example of financial asset because there is no need to carry
-usually at the first item in the statement of hugw amount of cash anymore. Do
financial position not usually earn interest income.
Bank accounts in foreign currency-
Before item presented as “Cash” cash items deposited in foreign
1. The item must be unrestricted as to its countries and denominated in
withdrawal. different countries
2. It must be immediately available for use in 3. Working funds- operation
the current operation of the company Petty cash fund- pay for small
expenses incurred by the company
Receivables- Cash Deposit in Banks on the daily basis
Specific Cash Items: items Classified as part of Change fund- used in the store by
Cash in SFP the cashier
Payroll fund- fund to pay the salaries
1. Cash on hand of the employees
a) Bills and Coins- issued by BSP Dividend fund- pay the dividends
b) Different Checks- received from that were declared by corporation to
other people their stockholders
Different kinds of checks: Interest fund- set aside to pay
interest that will become due from
Customer’s check- received from customers short and long term liabilitiesof the
Traveler’s check- check with a security entity
feature
Manager’s check- issued by bank managers Specific Non-Cash Items: Not Considered as cash
Cashier’s check- issued by bank cashiers in SFP
Company’s undelivered check- prepared by 1. Receivables
company thet will eventually be delivered Cash in closed banks/ banks having
to corporate creditors or suppliers financial difficulty- they no longer
Company’s postdated check- company meet one of the twin requirements
checks that were already delivered to needed
payees, but they cannot be encashed ot Customer’s post-dated checks-
dposited until the date on the check postdated check that was issued to
Company’s stale check- issued by the the company by a customer
company to suppliers and creditors and are Cutomer’s NSF( no sufficient fund)-
not encashed on time customers will issed check with
c) Bank drafts- documents issued by problems
banks as an evidence of money Classification:
deposited to them i. Drawn Against Insufficient
d) Postal money orders- cash items fund (DAIF) check
sent through the post office ii. Drawn Against unclear
2. Cash in Bank( unrestricted) deposits (DAUD) check
Savings Account- usual regular Customer’s stale check- received
savngs account that earns interest from the customer that was not
encashed by the company on Employed by a company to protect its cash:
time(expired)
1. Segregation of Duties
IOU( I owe you)- amounts borrowed
3 duties considered to be incompatible:
by employees from the company
Authorization- incharge of allowing
2. Prepaid Assets
the purchase requisition orders
Advances for employee travel- used
Custody- in charge of safekeeping
by employees while they are on a
the assets of the company. In charge
business trip
of releasing the cash to requesting
Postage stamps- they can no longer
employees
be used for a medium of exchange.
Recording- in charge of making the
Used for sending mails through the
necessary journal entries in the book
post office
of the company
Supplies- usual offices supplies being
used by the company Note: there will be a risk if the function is given to
3. Temporary Investments the same person
Trading securities- shares of the
2. Imprest system
stocks of other companies that were
2 important features
purchased by the company using
All cash receipts for today must
excess fund.
be deposited intact to their
Stocks are not considered as a
depository bank - to prevent
form cash because they are not
hugr amount of cash to be left in
the medium of exchange
the premises of the company
4. Non-current assets
All cash disbursements must be
Restricted foreign Bank accounts-
made through checks
cannot qualify as a cash item for
3. Voucher system- employees must first get
there is a restriction as to its
the approval of a higher level management
withdrawal
before cash disbursements can be made
Bond sinking fund- fund reserve for
4. Internal audit at irregular intervals- to
payment of the bonds payable that
prevent familiarization on the part of the
are about to mature
employees(only audit)
Plant expansion/ Acquisition fund-
5. Periodic bank reconciliation- records of the
reserved for the purchase of
bank company must be reconciled with the
additional non-cash assets like land
bank records
and building
Retirement fund- reserved for Bank Reconciliation
retirement benefits of employees
Done to show that there is no discrepancy
Pension fund- also instituted for the
between the cash balance per book records
benefit of managers and employees
and the cash balance per bank records.
Contingent Funds- prepare for the
worst case scenarios Credit for company
5. Expenses
Debit for bank
Expenses vouchers- represent the
expenses that were incurred by the 2 reciprocal accounts will be reconciled
company for the period
Cash in bank- pov of the company
Cash Management Deposits from ABC com- pov of the back
LESSON 9 1. Resident Citizen- a filipino that lives or
reside at the Philippines
Taxation- the process by which our government,
2. Non resident citizen- a filipino but does not
through our lawmakers, raises income to pay its
live or reside in the Philippines
necessary expenses.
3. Resident alien- a American but living in the
Purpose: Philippines
4. Non resident alien- American that does not
1. To provide proper funding needed to run
lives or reside in the Philippines
the government
2 classifications
2. a) by imposing high customs duties or taxes
1. Engaged in trade or business (NRA-ETB)-
on imported goods, local products would
stays for more than 180 days
remain
2. Not engaged in trade or business (NRA-
b) by imposing the progressive taxes, it will
NETB)
reduce the inequalities between the wealth
and income of our people Kinds of Income
c) by increasing taxes, the government may
1. Compensation income- received by
mitigate the effect of an impending inflation
employees working for different companies
Basic principles of a sound tax system 2. Business income- generated by the
entrepreneurs.( they do not work as
1. Fiscal Adequacy- government should make
employee)
sure that the amount of revenue collected
3. Passive income- generated by different
is enough to shoulder its different expenses
investments made by the individual
2. Theoretical Justice- burden of taxation
should be proportionate to the ability of the Gross income – Allowable deductions = taxable
taxpayer to pay it income
3. Administrative Feasibility- tax law being
promulgated by the government should be
capable of just and equitable administration
3 inherent powers of the government
1. Eminent domain- power of the government
to take private property, upon payment of
just compensation to be used for a public
purpose
2. Police power- power of government to
make law that will promote public health,
moral, safety and welfare of the people Note: Applicable only for residents, citizens, &
3. Taxation- power of government to collect NRA-ETB. NRA- NETB 25% final withholding. Tax
taxes that will be used to finance the passive income will be computed separately.
different projects needed by the people
Allowable Deductions
Income Taxation
-Deduction for qualified individuals would
- 2 biggest classifications of the income taxpayer depend one the income they earn
are individual and corporation
4 classification of individual
1. Earning purely compensation income
Basic personal exemptions(50,000) LESSON 6
Add basic personal Exemp
Statement of cash flow
(maximum 100,000)
Premium payments on health and -presents the sources and utilization of an
hospitalization insurance organization’s cash and cash equivalents.
2. Business / prof income
3 major section
Regular expenses incurred by the
1. Operating Activities- activitiea are related to
business
normal operating cycle
Interest expense
Cash receipts from sale of goods and
Tax expense
rendering of services (+)
Losses
Cash receipts from royalties, fees,
Bad dept expenses
commision, and other revenue (+)
Depreciation and depletion exp
Cash payments to suppliers of goods
Charitable contributions
and services(-)
Research and developmet exp
Cash payments to employees(-)
Basic personal exemp
Cash payments to income taxas(-)
Add personal exemp
Interest paid (-)
Premium payment on health and
Interest received (+)
hospitalization insurance(limit 2400
Dividends received (+)
per family or 200 per month)
2. Investing Activites- activities generally result
Note: from acquisition and disposal of non-
current
Basic Personal Exemption- (50,000 per year) all
Cash payments to acquire property,
kinds of individual except NRA-NETB. Applicable to
plant, and equipment (-)
single, married, or a widow/widower
Cash payments to acquire intangible
NRA-ETB is lower than 50,000.( reciprocity) assets (-)
Cash receipts from sale of property,
Add Personal Exemption- Maximum 100,000,
plant, and equipment (+)
25000 per dependent child. If married father is the
Cash receipts from solo intangible
proper claimant, if legally separated mother is the
assets (+)
claimant.
Cash receipts from sale of long-term
Allowance deduction for every individual: assels (+)
3. Financing Activities- activities usually arise
from changes in non-current liabilities and
owner’s equity of a business organization
Cash investments from owners (+)
Cash proceeds from bank loans (+)
Cash distributions to owners (-)
Repayment of bank loans (-)
Operating -Profit or Loss
Investing- Non-current Asset
Financing - Equity and Non-current Liability
You might also like
- Reviewer Fundamentals of Accounting 2Document3 pagesReviewer Fundamentals of Accounting 2Astro LunaNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Nature and Composition of CashDocument4 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Nature and Composition of CashJanna GunioNo ratings yet
- Nature and Composition of CashDocument4 pagesNature and Composition of CashJanna GunioNo ratings yet
- Summary of Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument4 pagesSummary of Cash and Cash EquivalentsMhico Mateo100% (1)
- Fabm 1 - Week 4Document3 pagesFabm 1 - Week 4FERNANDO TAMZ2003No ratings yet
- Las 3Document8 pagesLas 3Venus Abarico Banque-AbenionNo ratings yet
- Fabm Week 4 Study GuideDocument3 pagesFabm Week 4 Study GuideFERNANDO TAMZ2003No ratings yet
- Business Finance ReviewerDocument4 pagesBusiness Finance ReviewerJanna rae BionganNo ratings yet
- Audit of Cash Chapter 1Document8 pagesAudit of Cash Chapter 1SAN FELIPE Maria Czarina MontereseNo ratings yet
- INTACC - Chapter 1Document4 pagesINTACC - Chapter 1MeriiiNo ratings yet
- Current Assets:: What Is The Statement of Financial PositionDocument4 pagesCurrent Assets:: What Is The Statement of Financial PositionEmar KimNo ratings yet
- NU - Audit of Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument14 pagesNU - Audit of Cash and Cash EquivalentsDawn QuimatNo ratings yet
- FABM2 ReviewerDocument7 pagesFABM2 ReviewerMakmak NoblezaNo ratings yet
- Audit - Cash and Cash Equivalents PDFDocument15 pagesAudit - Cash and Cash Equivalents PDFSiena Farne100% (1)
- Accounting For Cash and Cash TransactionDocument63 pagesAccounting For Cash and Cash TransactionAura Angela SeradaNo ratings yet
- Chapters 8 9Document2 pagesChapters 8 9Rena Jocelle NalzaroNo ratings yet
- Cash & Cash Equivalents, LECTURE &EXERCISESDocument16 pagesCash & Cash Equivalents, LECTURE &EXERCISESNMCartNo ratings yet
- Cash & Cash Equivalents, Lecture &exercisesDocument16 pagesCash & Cash Equivalents, Lecture &exercisesNMCartNo ratings yet
- BF Reviewer LastDocument4 pagesBF Reviewer LastKarl JardinNo ratings yet
- Cash & Cash Equivalents: - For Ending BalanceDocument3 pagesCash & Cash Equivalents: - For Ending BalanceETTORE JOHN DE VERANo ratings yet
- Module 2A - ACCCOB2 Lecture 2 - Cash and Cash Equivalents - FHV T1AY2021Document6 pagesModule 2A - ACCCOB2 Lecture 2 - Cash and Cash Equivalents - FHV T1AY2021Cale Robert RascoNo ratings yet
- Accounting: Nature of Accounting Business OrganizationDocument2 pagesAccounting: Nature of Accounting Business OrganizationRochelle Joy CruzNo ratings yet
- Sta Clara - Summary Part 1Document49 pagesSta Clara - Summary Part 1Carms St ClaireNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Accounting 1: Cash and Cash EquivalentDocument17 pagesIntermediate Accounting 1: Cash and Cash EquivalentClar AgramonNo ratings yet
- Accounting Finals 1 ReviewerDocument5 pagesAccounting Finals 1 ReviewerlaurenNo ratings yet
- Government Accounting MidtermDocument10 pagesGovernment Accounting MidtermMina Myoui100% (1)
- Cash & Cash Equivalents, Lecture &exercisesDocument16 pagesCash & Cash Equivalents, Lecture &exercisesDessa GarongNo ratings yet
- L1 - Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument5 pagesL1 - Cash and Cash EquivalentsAshley BrevaNo ratings yet
- Five Accounting ElementsDocument2 pagesFive Accounting ElementsD AngelaNo ratings yet
- Acccob 2 Lecture 2 Cash and Cash Equivalents T2ay2021Document7 pagesAcccob 2 Lecture 2 Cash and Cash Equivalents T2ay2021Rey HandumonNo ratings yet
- Accounting NotesDocument6 pagesAccounting NotesD AngelaNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument12 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsbelliissiimmaaNo ratings yet
- Cash Items 1. Cash On HandDocument2 pagesCash Items 1. Cash On HandMarjorie PagsinuhinNo ratings yet
- Handouts 51Document20 pagesHandouts 51Ziyeon SongNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - Substantive Test of CashDocument6 pagesModule 5 - Substantive Test of CashJesievelle Villafuerte NapaoNo ratings yet
- Arief Taufiqqurrakhman (C1B018115) Cash and Marketable Securities Management and Working Capital and Short-Term Financing PDFDocument6 pagesArief Taufiqqurrakhman (C1B018115) Cash and Marketable Securities Management and Working Capital and Short-Term Financing PDFBikin RelaxNo ratings yet
- Cash & Cash EquivalentsDocument20 pagesCash & Cash Equivalentsalexis prada100% (2)
- Handout - Intro To Financial StatementsDocument2 pagesHandout - Intro To Financial StatementsApril SasamNo ratings yet
- INTERMEDIATE ACCOUNTING 1 (Module)Document2 pagesINTERMEDIATE ACCOUNTING 1 (Module)April GumiranNo ratings yet
- Accounting C2 Lesson 3 PDFDocument5 pagesAccounting C2 Lesson 3 PDFJake ShimNo ratings yet
- Pre 2 Auditing Concepts and Applications Module 1 and 2Document3 pagesPre 2 Auditing Concepts and Applications Module 1 and 2Anjilla Amor RubiaNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Cash and Cash Equivalents - PDF Filename UTF-8''AccountingDocument2 pagesAccounting For Cash and Cash Equivalents - PDF Filename UTF-8''AccountingFrancis RaagasNo ratings yet
- LECTURE NOTES - Aud ProbDocument15 pagesLECTURE NOTES - Aud ProbJean Ysrael Marquez100% (1)
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument5 pagesCash and Cash Equivalentsco230435No ratings yet
- Current Vs Non-Current AssetsDocument3 pagesCurrent Vs Non-Current AssetsTrisha GarciaNo ratings yet
- Ia1 Mod 1Document9 pagesIa1 Mod 1omssheshNo ratings yet
- Receivables Are Financial Assets That Represent A Contractual Right To Receive Cash or Another Financial Asset FromDocument3 pagesReceivables Are Financial Assets That Represent A Contractual Right To Receive Cash or Another Financial Asset FromMjhayeNo ratings yet
- ACCO 20053 Lecture Notes 1 - Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument3 pagesACCO 20053 Lecture Notes 1 - Cash and Cash EquivalentsVincent Luigil AlceraNo ratings yet
- Intermediate AccountingDocument4 pagesIntermediate AccountingjenNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EDocument3 pagesCash and Cash EShaira BugayongNo ratings yet
- LeaP FABM2 Q3 Week4 Day 12Document7 pagesLeaP FABM2 Q3 Week4 Day 12Danna Marie EscalaNo ratings yet
- Audit Problems FinalDocument48 pagesAudit Problems FinalShane TabunggaoNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash Equivalents Lecture NotesDocument2 pagesCash and Cash Equivalents Lecture Notesyna kyleneNo ratings yet
- PAS 7 - Statement of Cash Flows: Operating Activities Investing Activities Financing ActivitiesDocument1 pagePAS 7 - Statement of Cash Flows: Operating Activities Investing Activities Financing ActivitiesDora the ExplorerNo ratings yet
- Fraud NotesDocument10 pagesFraud Notes유우No ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument3 pagesCash and Cash Equivalentsshe lacks wordsNo ratings yet
- Types of Accounts and The Account Titles: AssetsDocument90 pagesTypes of Accounts and The Account Titles: AssetsNichole Balao-asNo ratings yet
- Audit of Receivables Lecture NotesDocument10 pagesAudit of Receivables Lecture NotesDebs Fanoga100% (1)
- D.M. Academy Classes: Accountancy & Business Studies by - Legacy GuptaDocument12 pagesD.M. Academy Classes: Accountancy & Business Studies by - Legacy Guptalegacy guptaNo ratings yet
- Reading and WritingDocument2 pagesReading and WritingBea ManalotoNo ratings yet
- Eapp Q2 RebyuwerDocument5 pagesEapp Q2 RebyuwerBea ManalotoNo ratings yet
- 11 Intro To Philo As v1.0Document21 pages11 Intro To Philo As v1.0jerielseguido-187% (15)
- Business ProposalDocument2 pagesBusiness ProposalBea ManalotoNo ratings yet
- Trading Stocks: QES Group Eversafe RubberDocument5 pagesTrading Stocks: QES Group Eversafe RubberAmir HasridzNo ratings yet
- Euro Zone Crisis QDocument70 pagesEuro Zone Crisis Qtarungupta2001No ratings yet
- Assignment On Dhaka Bank LimitedDocument23 pagesAssignment On Dhaka Bank LimitedMd Wasiq DayemNo ratings yet
- Financial Administration and Audit Act (FAA) - INSTRUDocument78 pagesFinancial Administration and Audit Act (FAA) - INSTRURohan Wright100% (7)
- SAP ERP Financials User's Guide: Heinz Forsthuber, Jörg SiebertDocument80 pagesSAP ERP Financials User's Guide: Heinz Forsthuber, Jörg SiebertTeja SaiNo ratings yet
- Scotiabank StatementDocument3 pagesScotiabank StatementЮлия П100% (2)
- IDFC FIRST Bank Limited Sixth Annual Report FY 2019 20Document273 pagesIDFC FIRST Bank Limited Sixth Annual Report FY 2019 20Sourabh PorwalNo ratings yet
- Summer Training Report On Standard Chartered BankDocument97 pagesSummer Training Report On Standard Chartered BankAbhay KumarNo ratings yet
- Form No. 16 Part A (2020)Document2 pagesForm No. 16 Part A (2020)Dharmendra ParmarNo ratings yet
- State Finance Act 31 of 1991Document21 pagesState Finance Act 31 of 1991André Le RouxNo ratings yet
- Recruitment Selection Placement PlanDocument6 pagesRecruitment Selection Placement PlanJaypee EchanoNo ratings yet
- BOQ Video Conference EquipmentsDocument10 pagesBOQ Video Conference Equipmentsamhosny64No ratings yet
- 1 - Nikhara 15 Days Notice 24 12 2019Document3 pages1 - Nikhara 15 Days Notice 24 12 2019Don RedbrookNo ratings yet
- Far East Bank and Trust Co. vs. Gold Palace Jewellery Co.Document3 pagesFar East Bank and Trust Co. vs. Gold Palace Jewellery Co.Juna Aimee FranciscoNo ratings yet
- National State Bank, Elizabeth, N. J. v. LongDocument9 pagesNational State Bank, Elizabeth, N. J. v. LongSamuel RichardsonNo ratings yet
- Sir Onde Loospam EconDocument5 pagesSir Onde Loospam EconGleb De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Burgundy Fees and Charges As On 2019 09Document7 pagesBurgundy Fees and Charges As On 2019 09Shivanshu SinghNo ratings yet
- FinTech RegTech and SupTech - What They Mean For Financial Supervision FINALDocument19 pagesFinTech RegTech and SupTech - What They Mean For Financial Supervision FINALirvandi syahputraNo ratings yet
- Meta Title: EMI For Personal Loan of Rs 10 Lakh Meta Description: A Personal Loan Obtained From A Bank or NBFC Can BeDocument4 pagesMeta Title: EMI For Personal Loan of Rs 10 Lakh Meta Description: A Personal Loan Obtained From A Bank or NBFC Can BeParag ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- The Bombay Stamp ActDocument69 pagesThe Bombay Stamp ActsunnyggggNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Banks in Pakistan As Per Their Market ShareDocument5 pagesComparison of Banks in Pakistan As Per Their Market ShareBahria noty100% (1)
- INFOLINK UNIVERSITY COLLEG1 Reaserch Paper ProposlDocument7 pagesINFOLINK UNIVERSITY COLLEG1 Reaserch Paper ProposlGulilat lemi100% (1)
- The Cash Account For Collegiate Sports Co On November 1Document1 pageThe Cash Account For Collegiate Sports Co On November 1Miroslav GegoskiNo ratings yet
- Punjab Bus BrandingDocument12 pagesPunjab Bus BrandingMohit ChhabriaNo ratings yet
- Chilaw Finance Limited Intro..Document115 pagesChilaw Finance Limited Intro..Ebony West100% (1)
- Ambrian Gold Book - 2011Document56 pagesAmbrian Gold Book - 2011gpperkNo ratings yet
- Cost of A Security BreachDocument16 pagesCost of A Security BreachAayush GargNo ratings yet
- Customers Satisfaction Towards CRM Practices Adhered by Public Sector Banks in E-Banking EraDocument6 pagesCustomers Satisfaction Towards CRM Practices Adhered by Public Sector Banks in E-Banking EraIAEME PublicationNo ratings yet
- Nmims Mba Distance DetailsDocument9 pagesNmims Mba Distance DetailsGanapathy VigneshNo ratings yet
- Mobile Banking ServicesDocument11 pagesMobile Banking ServicesDiksha SadanaNo ratings yet