Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is Climate Change and Global Heating and How Does It Work To Affect Us
Uploaded by
Neodymium-Juan Rico Malazzab0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageClimate change refers to long-term shifts in temperatures and weather patterns that are primarily caused by human activities like burning fossil fuels since the 1800s. Burning fossil fuels generates greenhouse gas emissions like carbon dioxide and methane that trap heat in the atmosphere like a blanket, raising global temperatures. Examples of major sources of these greenhouse gases are using gasoline for transportation, coal for heating, clearing forests, and landfills. Global warming occurs when these greenhouse gases collect in the atmosphere and absorb and trap heat that would otherwise escape into space, causing the planet to get hotter over long periods of time. Though natural fluctuations have caused climate changes in the past, the current era of global warming is directly caused by human activities like burning fossil fuels
Original Description:
Original Title
Untitled
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentClimate change refers to long-term shifts in temperatures and weather patterns that are primarily caused by human activities like burning fossil fuels since the 1800s. Burning fossil fuels generates greenhouse gas emissions like carbon dioxide and methane that trap heat in the atmosphere like a blanket, raising global temperatures. Examples of major sources of these greenhouse gases are using gasoline for transportation, coal for heating, clearing forests, and landfills. Global warming occurs when these greenhouse gases collect in the atmosphere and absorb and trap heat that would otherwise escape into space, causing the planet to get hotter over long periods of time. Though natural fluctuations have caused climate changes in the past, the current era of global warming is directly caused by human activities like burning fossil fuels
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageWhat Is Climate Change and Global Heating and How Does It Work To Affect Us
Uploaded by
Neodymium-Juan Rico MalazzabClimate change refers to long-term shifts in temperatures and weather patterns that are primarily caused by human activities like burning fossil fuels since the 1800s. Burning fossil fuels generates greenhouse gas emissions like carbon dioxide and methane that trap heat in the atmosphere like a blanket, raising global temperatures. Examples of major sources of these greenhouse gases are using gasoline for transportation, coal for heating, clearing forests, and landfills. Global warming occurs when these greenhouse gases collect in the atmosphere and absorb and trap heat that would otherwise escape into space, causing the planet to get hotter over long periods of time. Though natural fluctuations have caused climate changes in the past, the current era of global warming is directly caused by human activities like burning fossil fuels
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
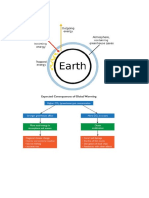
What is Climate Change and Global
Heating and How Does it Work to Affect
Us
Climate change refers to long-term shifts in temperatures and weather patterns. These shifts may be
natural, such as through variations in the solar cycle. But since the 1800s, human activities have been the
main driver of climate change, primarily due to burning fossil fuels like coal, oil, and gas.
Burning fossil fuels generates greenhouse gas emissions that act like a blanket wrapped around the Earth,
trapping the sun’s heat, and raising temperatures.
Examples of greenhouse gas emissions that are causing climate change include carbon dioxide and
methane. These come from using gasoline for driving a car or coal for heating a building, for example.
Clearing land and forests can also release carbon dioxide. Landfills for garbage are a major source of
methane emissions. Energy, industry, transport, buildings, agriculture, and land use are among the main
emitters
How is global warming created?
Global warming occurs when carbon dioxide (CO 2) and other
air pollutants collect in the atmosphere and absorb sunlight
and solar radiation that have bounced off the earth’s surface.
Normally this radiation would escape into space, but these
pollutants, which can last for years to centuries in the
atmosphere, trap the heat and cause the planet to get hotter.
These heat-trapping pollutants—specifically carbon dioxide,
methane, nitrous oxide, water vapor, and synthetic
fluorinated gases—are known as greenhouse gases, and their
impact is called the greenhouse effects
Though natural cycles and fluctuations have caused the
earth’s climate to change several times over the last 800,000 years, our current era of global
warming is directly attributable to human activity—specifically to our burning of fossil fuels such as
coal, oil, gasoline, and natural gas, which results in the greenhouse effect. In the United States, the
largest source of greenhouse gases is transportation (29 percent), followed closely by electricity
production (28 percent) and industrial activity (22 percent). Learn about the natural and human
causes of climate change.
You might also like
- Climate Change EssayDocument4 pagesClimate Change Essayyaz100% (4)
- Global Warming Assignment (Final)Document8 pagesGlobal Warming Assignment (Final)Howard How100% (4)
- Global WarmingDocument12 pagesGlobal Warmingshoeb100% (1)
- Arjela Jatax6Document2 pagesArjela Jatax6Gertty JataNo ratings yet
- Climate Cha Nge (Eng)Document1 pageClimate Cha Nge (Eng)Amina BrahimiNo ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument1 pageClimate ChangeGeorgia BuenavidesNo ratings yet
- Page 2 Causes of Global WarmingDocument1 pagePage 2 Causes of Global Warmingdikoha1833No ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument1 pageClimate ChangeMinister Peace ShalomNo ratings yet
- Natural ScienceDocument1 pageNatural Scienceiamshi229No ratings yet
- Causes of Climate ChangeDocument6 pagesCauses of Climate ChangeAkhilesh AjayanNo ratings yet
- Climate Change and Its EffectsDocument7 pagesClimate Change and Its EffectsHassan ImamNo ratings yet
- Fossil Fuel's: Consequences of Using Fossil FuelsDocument4 pagesFossil Fuel's: Consequences of Using Fossil FuelsDaniel FloresNo ratings yet
- Global Warming: Causes, Effects, and SolutionsDocument2 pagesGlobal Warming: Causes, Effects, and SolutionsTinu AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Greenhouse Effect and GasesDocument4 pagesGreenhouse Effect and Gasespradeep aggarwalNo ratings yet
- Causes of Climate ChangeDocument4 pagesCauses of Climate ChangeShuqrie KieNo ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument1 pageClimate ChangeWendy JeannetteNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary "Climate Change"Document5 pagesVocabulary "Climate Change"КатяNo ratings yet
- Climate Change EssayDocument3 pagesClimate Change EssayKd123No ratings yet
- Bono, Leo Joselito E. EH406Document4 pagesBono, Leo Joselito E. EH406Rash Ibno PundingNo ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument11 pagesClimate ChangeAa CcNo ratings yet
- Impact of Climate Change On The Environment: Quarter 3-Lesson 3Document19 pagesImpact of Climate Change On The Environment: Quarter 3-Lesson 3Rod P. Cabico Jr.No ratings yet
- Global Warming: Expected To Become More IntenseDocument4 pagesGlobal Warming: Expected To Become More IntenseKomal VernekarNo ratings yet
- Climate Change EssayDocument2 pagesClimate Change EssaySammNo ratings yet
- Climate Change-WPS OfficeDocument2 pagesClimate Change-WPS OfficeHansNo ratings yet
- Greenhouse Gases: Climate Change Is Real - Causes and Impacts of Climate ChangeDocument15 pagesGreenhouse Gases: Climate Change Is Real - Causes and Impacts of Climate ChangeAhmad Hassan ChathaNo ratings yet
- Science ArgumentDocument5 pagesScience Argumentapi-449126920No ratings yet
- PBL (Second Grading) - Climate Change and Global Warming What Is Climate Change? (Alazar)Document2 pagesPBL (Second Grading) - Climate Change and Global Warming What Is Climate Change? (Alazar)shokoy akoNo ratings yet
- Global Warming: Tania Milagros Delgado ChoqqueDocument15 pagesGlobal Warming: Tania Milagros Delgado ChoqqueTANIA MILAGROS DELGADO CHOQQUENo ratings yet
- Climate Change Is The Defining Issue of Our Time and We Are at A Defining MomentDocument3 pagesClimate Change Is The Defining Issue of Our Time and We Are at A Defining MomentApril Francesca LuaNo ratings yet
- Where The World Is Heading: Project Realised by Chitac Alexia-AnamariaDocument10 pagesWhere The World Is Heading: Project Realised by Chitac Alexia-Anamariaalexia aaNo ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument1 pageClimate ChangeGHZ CoolzNo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument33 pagesGlobal WarmingAnup DasNo ratings yet
- NG NGOC QUYNH - Week 4Document2 pagesNG NGOC QUYNH - Week 4tuan anhNo ratings yet
- HeyDocument7 pagesHeyHASHIM TRUNKWALANo ratings yet
- Geo Essay (10 Marks)Document3 pagesGeo Essay (10 Marks)Ari 05No ratings yet
- Chemistry Project Isc 12Document8 pagesChemistry Project Isc 12wrickm19No ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument7 pagesGlobal WarmingHardik TankNo ratings yet
- This Is A Project On Talecommunication.: Climate Change Includes Both The Global Warming Driven by Human EmissionsDocument1 pageThis Is A Project On Talecommunication.: Climate Change Includes Both The Global Warming Driven by Human EmissionsArushiNo ratings yet
- Iqbal Bau TaiDocument4 pagesIqbal Bau TaiAdeliaNo ratings yet
- Iqbal Bau TaiDocument4 pagesIqbal Bau TaiDellaNurAfifahNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ProjectDocument3 pagesChemistry ProjectSounak ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Human Activities Causing Climate Change 1Document2 pagesHuman Activities Causing Climate Change 1zschairail balanzaNo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument2 pagesGlobal WarmingMiftaqul OrsyaNo ratings yet
- Climate Change 9-St - Dominic ScienceDocument11 pagesClimate Change 9-St - Dominic ScienceGabriel AquiNo ratings yet
- How To Curb Global Warming? by Prerna PandeyDocument2 pagesHow To Curb Global Warming? by Prerna PandeyRitik PandeyNo ratings yet
- PH M Thu Trang E7-Week 4Document2 pagesPH M Thu Trang E7-Week 4tuan anhNo ratings yet
- 5Document1 page5nakofi4653No ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument6 pagesGlobal WarmingJehad C. AsiriaNo ratings yet
- Colegio Tecnológico Cristiano Prof. Justo Gonzales Carrasco: Teacher: Subject: StudentsDocument6 pagesColegio Tecnológico Cristiano Prof. Justo Gonzales Carrasco: Teacher: Subject: StudentsDaniel FloresNo ratings yet
- Global Warming Essay 7Document3 pagesGlobal Warming Essay 7mohsinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Climate ChangeDocument12 pagesChapter 9 Climate Changejieeniola1No ratings yet
- Global Warming ThesisDocument15 pagesGlobal Warming ThesisSaira Caritan100% (1)
- Causes of Climate ChangeDocument11 pagesCauses of Climate ChangeMary Rose Agullo FataganiNo ratings yet
- Climate Change EssayDocument5 pagesClimate Change Essayyaz100% (4)
- Global WarmingDocument8 pagesGlobal WarmingsamanNo ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument4 pagesClimate ChangeDee-Kay JoricNo ratings yet
- STS Notes On Climate ChangeDocument2 pagesSTS Notes On Climate Changetabeb chanNo ratings yet
- What Is Climate ChangeDocument5 pagesWhat Is Climate Changecrv747hriNo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument13 pagesGlobal WarmingYagnik Mhatre50% (4)
- The Earth Remembers: A Story of Warming, Damage, and HopeFrom EverandThe Earth Remembers: A Story of Warming, Damage, and HopeNo ratings yet