Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lower Extemity
Uploaded by
Eric SalinasCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lower Extemity
Uploaded by
Eric SalinasCopyright:
Available Formats
Lower Extremity 1. Hip Bone (Os Coxae) ilium, ischium, Pubis a. Ilium major part Os Coxae i.
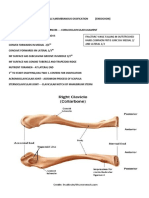
Superior part acetabulum ii. Posterolateral (ala/wing) landmarks: 1. Posterior Gluteal Line (Gluteus Maximus m.) 2. Anterior Gluteal Line (Gluteus Medius m) 3. Inferior Gluteal Line (Gluteus Minimus m) iii. Illiac Spines 1. ASIS 2. AIIS 3. PSIS 4. PIIS iv. Greater Sciatic Notch located here b. Ischium Posterior Inferior part hip bone Posterior part of acetabulum i. Forms inferiomedial boundary Obturator Foramen ii. Structures: 1. Ischipubic Ramus 2. Ischial Tuberosity 3. Ischial Spine 4. Lesser Sciatic Notch c. Pubis Anteromedial part of hip bone Anterior part of Acetabulum i. Structures: 1. Superior Ramus (Pectin Pubis- Pectineal line) 2. Inferior Ramus d. Obturator Foramen i. Oval shaped ii. Formed pubis and ischium iii. Covered by obturator membrane except for obturator canal (artery & nerve) e. Acetabulum- Cup of Vinegar i. Formed by three parts of coxae ilium, ischium, pubis ii. Structures: 1. Acetabular fossa 2. Lunate Surface 3. Acetabular notch (Transverse Acetabular Ligament) 2. Cutaneous nerves associated with Gluteal region (Diagram A) Anterior Iliphypogastric L1 Lat Femoral Cutaneous L2 Sapheous L3, L4 Superficial Branch of Peroneal L5 Posterior Med Cluneal S4 (3) dorsal rami S1, S2, S3 Sup Cluneal (3) dorsal rami L1,L2,L3 Lat Femoral cutaneous L2 Post Femoral Cutaneous S2 S1, S2, S3 Lat Sural Cutaneous (Common Peroneal) L5 Medial Sural (tibial) S1 Lat Plantar S1 Med Plantar L5
3. Musculature of Gluteal region (see excel) 4. Posterior Thigh Hamstring area a. Cutaneous innervations and its fascia i. Posterior femoral cutaneous covering posterior thigh down to popliteal fossa 1. From tibal portion sciatic n. extis greater sciatic foramen with sciatic n. 2. Contains S1-S3 nerve fibers ii. Lateral femoral cutaneous supplying lateral aspect thigh 1. From posterior abdominal wall passes deep to inguinal ligament, medial to ASIS 2. Contain L2 & L3 3. Tensor fascia covers posterior thigh musculature 5. Femur a. Head and its fovea (Teres Ligament attachment of hip) b. Structures: i. Neck (anatomical) ii. Intertrochanteric Line (anterior) iii. Intertrochanteric Crest (posterior) iv. Gluteal tuberosity (third trochanter) v. Pectineal line posterior vi. Linea Aspera Posterior (medial and lateral) vii. Medial and lateral epicondyle (medially Adductor tubercle) viii. Medial and lateral condyle ix. Intercondylar fossa posterior x. Patellar - anterior and Popliteal fossa posterior 6. Musculatur of Hamstring see excel 7. Anterior region of Thigh a. Cutaneous nerve and fascia and other associated structures i. Fascia deep thigh fascia (fascia Lata) ii. Cutaneous innervations of thigh 1. Lateral femoral Cutaneous n. (L2 & L3) supplying anterior thigh to knee 2. Genitofemoral n. (L2 & L3) femoral portion, supplying skin over femoral triangle 3. Femoral n. (L2, L3, & L4) some branches innervated skin at medioanterior thigh b. Superficial blood vessels of anterior thigh 1. Great Saphenous Vein starts 4 fingers from medial aspect patella a. Goes up medial margin thigh b. Enters femoral triangle empty femoral vein this pt goes through Saphenous opening 6cm inferior pubic tubercle i. Opeining 4cm long 2cm wide ii. Medial margin smooth edge iii. Infra-lateral and superior (Falciform) margin sharp iv. Here half a dozen superficial lymph nodes communicate deep inguinal nodes c. Femoral Triangle i. Boundaries 1. Lateral Sartorius m 2. Medial Adductor Longus m
3. Superior Inguinal ligament (aponeuroses external oblique m) 4. Floor pectineus muscle (medially) iliopsas tendon (laterally) 5. Roof tensor fascia lata m a. Contents i. femoral artery & vein (w/in femoral sheath), femoral n ii. femoral artery gives rise to Deep Artery of Thigh d. Hip Joint i. Diarthrotic jt, ball and socket, synovial jt ii. Capsular ligament of hip joint 1. Iliofemoral ligament - anterior (Y shaped) Ligament of Bigelow strength of jt extension 2. Pubofemoral ligament anterior - abduction 3. Ischiofemoral ligament posterior - extension iii. Internal Structures of hip joint 1. Acetabular Labium 2. Teres ligament 3. Transverse Ligament (allows passage for Acetabular branch of obturator artery iv. Blood Supply to hip 1. Deep artery of thigh giving two branches a. Medial and Lateral Circumflex Femoral Arteries 2. Obturator Artery, giving rise Acetabular Artery to Teres Ligament of hip joint e. Blood Vessels of Anterior Thigh i. Femoral artery in femoral triangle, gives rise to following blood vessels: 1. External Pudendal Artery 2. Medial Circumflex Femoral Artery 3. Lateral Circumflex Femoral Artery 4. Deep Artery of Thigh (hamstring) giving many branches. Perforating arteries 5. Descending artery (anterior thigh) from lateral circumflex femoral artery ii. Femoral Vein iii. Great Saphenous Vein f. Adducctor Canal (Hunter s Canal/Subsartorial Canal) i. Formed adductor magnus m. Superior and medial to adductor tubercle of femur ii. 15 cm long iii. Boundaries 1. Medially Sartorius m. 2. Laterally/Anterior Vastus Medialis m. 3. Posteriorly Adductor Longus and Magnus m 4. Contains Femoral Artery and Vein g. Popliteal Fossa i. Apex toward adductor canal ii. Located posterior aspect of knee, diamond shaped area iii. Boundaries, Roof and Floor 1. Superior lateral Biceps Femoris m 2. Superior medial Semimembranosus m 3. Inferior lateral Lateral head of Gastrocnemius m 4. Inferior Medial Medial head of Gastrocnemius m
5. Roof Fascia of popiteal foss and skin. Contains small Saphenous Vein and Sural n. 6. Floor/Anterior- Popliteal m, Oblique ligament of knee jt 7. Contains: a. Popiteal blood vessels b. Small saphenous vein c. Tibial and Common Peroneal nerves d. This area Tibial nerve gives rise to Medial Sural Cutaneous nerve, Common Peroneal Nerve rise to Lateral Sural Cutaneous nerve h. Knee Joint Patella i. Synovial hinge joint. Atriculation between femur, patella, and tibia bones ii. Weak joint due to structure. Enforced for stability by strong ligaments and muscles iii. Articular capsule posterior aspect allows passage for Popliteus muscle via Arcuate Popliteal Ligament 1. Posterior aspect Oblique Popliteal Ligament which extension of Semimebranosus muscle 2. Articular capsule strengthen by Medial Collateral Ligament/ tibial collateral and Lateral collateral Ligament/ fibular collateral 3. Patellar ligament strengthen joint at anterior aspect iv. Synovial membrane extensive attaching to Patella, Menisci internally v. Many internal folds, forming following structure: 1. Infrapatellar Folds/Fat Pads between patella and Tibia 2. Infrapatellar Synovial Fold to intercondylar fossa of femur forming Alar Folds at either side a. Articularis Genus muscle located in synovial membrane superiorly at patellar fossa of femur- pulls membrane superiorly at time of extension of knee. i. Part of vastus intermedialis muscle vi. Intra Articular Ligaments of Knee Joint 1. Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) anterior intercondlyar fossa of tibia to lateral and posterior aspect intercondlyar foss of femur a. Limits excessive posterior movement of knee b. Taught during extension 2. Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL), posterior intercondlyar fossa of tibia to medial and anterior aspect of intercondlyar fossa of femur a. Stronger than ACL b. Limits excessive anterior movement of knee c. Taught during flexion of knee and prevents hyperflexion of knee joint 3. Medial and Lateral Menisci a. Medial meniscus is larger and C-shaped i. Attached to tibial collateral ligament b. Lateral meniscus more circular in shape i. Contribution to posterior cruciate ligament known Posterior Meniscofemoral Ligament (ligament of Weisberg) 4. Transverse Ligament anterior aspect of intercondylar foss of tibia connecting two menisci at anterior aspect 5. Patella sesmoid bone acting as pully of knee joint 6. Blood supply knee via Femoral and Popliteal Arteries
a. Genicular arteries from: i. Femoral artery ii. Popliteal artery iii. Anterior and Posterior recurrent arteries from Tibial Recurrent artery iv. Middle Genicular from popliteal supplies internal aspect of jt. i. Leg i. Three compartments Anterior, Posterior, Lateral, Formed by Anterior and Posterior intermuscular septum, and Interosseous membrane. Fascia provide Anterior, Lateral, and Posterior compartments ii. Blood vessels and Nerves - Anterior compartment of Leg 1. Anterior Tibial Artery anterior to interosseous membrane a. Deep between tibialis anterior and extensor digitorum longus muscle b. Artery end at dorsal aspect of foot as Dorsal Pedis Artery 2. Deep peroneal (fibular) nerve, passing through extensor digitorum longus muscle a. End at dorsum of foot to supply muscles of dorsum of foot and skin over great toe iii. Blood vessels and nerves Lateral Compartment of Leg 1. Blood via Anterior Tibial Artery 2. Superficial Peroneal (fibular) nerve from common peroneal a. Enters compartment and eventually all skin of dorsum of foot iv. Blood vessels and Nerve Posterior Aspect of Leg 1. Tibial Nerve larger branch of sciatic nerve a. Popliteal fossa passes through 2 heads of gastrocnemius, then through soleus, descend deep to superficial compartment of posterior leg. Passes posterior to medial malleolus of ankle 2. Posterior Tibial Artery Larger branch of popliteal artery. Through soleus muscle gives off anterior tibial artery. At head of Tibialis Posterior muscle divides into peroneal (fibular) artery (larger of 2). Posterior Tibial artery (smaller) descend down with tibial nerve to posterior aspect of medial malleolus j. Bones of Leg i. Tibia 1. Anterior border, medial and lateral anterior surface and posterior surface 2. Anterior and Posterior Intercondylar Fossa 3. Medial and Lateral Condyle 4. Tibial Tuberosity 5. Oblique Line anterior lateral of tibia and Soleal Line - posterior 6. Medial Malleolus 7. Fibular notch (distal aspect) 8. Gerdy s tubercle (lateral tibia) iliotibial tract tensor fascia latae m ii. Fibula 1. Apex, Head, and neck 2. Medial Crest, Anterior border, posterior border, and interosseous crest - anterior 3. Lateral, medial and Posterior surface 4. Lateral malleolus 5. Digital fossa k. Blood supply and Nerve of foot
l.
i. Dorsum of Foot 1. Saphenous nerve medial side of foot (great toe) 2. Deep (toe) and Superficial Peroneal (fibular) nerve skin of dorsum ii. Plantar of Foot 1. Tibial and Sural nerve skin at heel 2. Sural nerve lateral aspect of foot 3. Medial and lateral plantar nerves skin over sole of foot iii. Dorsal Artery of Foot 1. Anterior Tibial Artery major blood supply 2. At talus bone gives following arteries: a. Medial Tarsal Artery b. Lateral Tarsal Artery c. Arcuate Artery i. Rise to Dorsal Metatarsal Arteries 1. Gives Digital Arteries d. Deep plantar artery (base 1st dorsal interosseous muscle) iv. Sole of Foot arteries 1. Posterior Tibial artery rise to Lateral and Medial Plantar Arteries 2. Deep Plantar Arch from Dorsal Pedis Artery Foot Bones i. Talus 1. Trochlea 2. Neck 3. Head 4. Medial and lateral tubercle (posterior) ii. Calcaneus 1. Body 2. Posterior medial and Anterior Talar articular surfaces 3. Peroneal Tubercle - lateral 4. Calcaneal Tuberosity 5. Plantar tubercles (medial, lateral, and anterior) 6. Sustentaculum tali and groove for tendon of flexor hallucis longus m. 7. Articular surface of Cuboid bone iii. Navicular 1. Tuberosity iv. Cuboid 1. Tuberosity 2. Groove for tendon of Peroneus Longus m. v. Cuneiform 1. Medial (1st) intermediate (2nd) smallest, and Lateral (3rd) largest vi. Metatarsal 1. Five 2. 5th metatarsal tuberosity for Peroneus Brevis and Peroneus Tertius muscles vii. Phalanx 1. Great toe tow (Proximal and Distal) 2. 2nd 5th toes has three (Proximal, medial, Distal)
m. Joints of Ankle and foot i. Tibiofibular Joint 1. Distal Tibiofibular Joint a. Syndesmosis b. Anterior and Posterior tibiofibular ligaments c. Strong interosseous ligament d. Blood Malleolar bracnch Anterior and Posterior tibial arteries and fibular artery ii. Ankle Joint 1. Diarthrotic 2. Medially formed by Tibia and Talus bones 3. Deltoid ligament (medial) 4 parts a. Anterior Tibiotalar b. Posterior Tibiotalar c. Tibionavicular d. Tibiocalcaneal 4. Lateral formed by Fibula and Talus bones 5. Lateral Collateral Ligament 3 parts a. Anterior Talofibular b. Posterior Talofibular c. Calcaneofibular iii. Important ligaments of Foot 1. Interosseous Talocalcaneal ligament 2. Dorsal Talonavicular ligament 3. Dorsal calcaneocuboid ligament 4. Bifurcate ligament 2 parts a. Calcaneonavicular b. Calcaneocuboid iv. Plantar ligaments of Foot 1. Long Plantar ligament 2. Short Plantar (plantar calcaneocuboid) ligament 3. Plantar Calcaneonavicular (Spring) ligament 4. Plantar cuboidnavicular ligament 5. Note tendons of the a. Peroneus Longus Muscle b. Tibialis Posterior Muscle
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Grade-7 Joints and Muscles NotesDocument3 pagesGrade-7 Joints and Muscles NotesSahithi PNo ratings yet
- TendonitisDocument3 pagesTendonitisJingyi Xie0% (1)
- Muscle TissueDocument20 pagesMuscle TissueDheeraj MenezesNo ratings yet
- One Shot ANATOMY Revision by DR Ashwani KumarDocument94 pagesOne Shot ANATOMY Revision by DR Ashwani KumarTauqueer AlamNo ratings yet
- Retaining Ligaments of The Face: Review of Anatomy and Clinical ApplicationsDocument14 pagesRetaining Ligaments of The Face: Review of Anatomy and Clinical ApplicationsMariel IslasNo ratings yet
- 23 - Glutes, Adductors & Hip FlexorsDocument40 pages23 - Glutes, Adductors & Hip Flexorsbreinfout fotosNo ratings yet
- Lecture Module #7: Articulation Part-II: Maureen Costello MS CCC/SLPDocument48 pagesLecture Module #7: Articulation Part-II: Maureen Costello MS CCC/SLPChristina DoughertyNo ratings yet
- Locomotion and MovementDocument58 pagesLocomotion and MovementdddNo ratings yet
- Muscular System Notes 16 17Document66 pagesMuscular System Notes 16 17api-305436791100% (3)
- Imaging Anatomy Musculoskeletal 2nd Ed PDFDocument1,194 pagesImaging Anatomy Musculoskeletal 2nd Ed PDFTuttiNo ratings yet
- Muscles NamingDocument17 pagesMuscles NamingAbraham MendezNo ratings yet
- OIA-SA-H Cat Muscles MegatableDocument6 pagesOIA-SA-H Cat Muscles MegatablePerseus Evangelio100% (2)
- Chapter 19Document10 pagesChapter 19poNo ratings yet
- Clavicle: Fracture While Falling in Outstreched and Lateral 1/3Document9 pagesClavicle: Fracture While Falling in Outstreched and Lateral 1/3hyyjNo ratings yet
- Rabbit (Oryctolagus Cuniculus) Muscular System: I. Dermal/IntegumentaryDocument9 pagesRabbit (Oryctolagus Cuniculus) Muscular System: I. Dermal/IntegumentaryAnnray Justine T. GlipaNo ratings yet
- Visual Anatomy and Physiology 3rd Edition Martini Test BankDocument55 pagesVisual Anatomy and Physiology 3rd Edition Martini Test Bankconvenerlollwctta96% (28)
- Lesson 1o Head MusclesDocument19 pagesLesson 1o Head MusclesAdam LallanaNo ratings yet
- Exercises Target Muscles Number of Sets Number of Repetition Warm UpDocument2 pagesExercises Target Muscles Number of Sets Number of Repetition Warm UpJake CasipleNo ratings yet
- PNF in Practice: An Illustrated Guide Von Susan S Adler, Dominiek Beckers, Math BuckDocument12 pagesPNF in Practice: An Illustrated Guide Von Susan S Adler, Dominiek Beckers, Math BuckLuisaBernalNo ratings yet
- Kinesiology: Chapter 2 (An Introduction To Movement) : DR: Iqra KaramatDocument14 pagesKinesiology: Chapter 2 (An Introduction To Movement) : DR: Iqra KaramatNimra TariqNo ratings yet
- Muscle Strength and Muscle ActionDocument54 pagesMuscle Strength and Muscle ActionFarrukh Shahzad100% (6)
- Muscular System 20222023Document29 pagesMuscular System 20222023Danny Mel ManglaylayNo ratings yet
- Acl Knee Brace - Google SearchDocument1 pageAcl Knee Brace - Google SearchmauniiNo ratings yet
- Overhead Throwing: Biomechanics and PathologyDocument7 pagesOverhead Throwing: Biomechanics and Pathologyrapannika100% (1)
- Human Anatomy Study Guide: Chapter 10: Muscle Tissue and OrganizationDocument5 pagesHuman Anatomy Study Guide: Chapter 10: Muscle Tissue and OrganizationSuperjunior8No ratings yet
- Lec 9 Trick MovementsDocument19 pagesLec 9 Trick MovementsBhargav69% (13)
- Anatomy of HipDocument44 pagesAnatomy of Hipvijaykrishna59No ratings yet
- Lab 6 Appendicular Muscles WorksheetDocument8 pagesLab 6 Appendicular Muscles WorksheetMareline MendietaNo ratings yet
- Clinical SymposiaDocument54 pagesClinical Symposiamarikos82No ratings yet
- The Shoulder JointDocument17 pagesThe Shoulder JointBhargavNo ratings yet