Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Scabies
Scabies
Uploaded by
Abhay SagarOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Scabies
Scabies
Uploaded by
Abhay SagarCopyright:
Available Formats
Phramacotherapeutics Notes
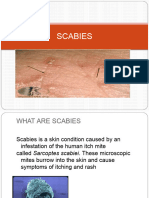
Scabies
Scabies is an itchy skin rash caused by a tiny burrowing mite called Sarcoptes scabiei.
Intense itching occurs in the area where the mite burrows.
The need to scratch may be stronger at night
Etiopathogenesis:
Scabies is caused by the Sarcoptes scabiei mite, which burrows into the skin and lays
eggs.
The infestation spreads through close skin-to-skin contact with an infected person,
including sexual contact.
The mite can also be spread through contact with contaminated clothing, bedding, or
furniture.
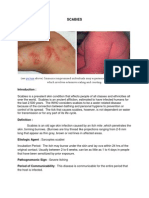
Clinical Manifestations:
The main symptom of scabies is intense itching, which can be worse at night.
Other symptoms may be seen particularly in areas where the mite burrows,include:-
Between the fingers,
On the wrists and elbows,
Around the waistline and
Genitals, and under the arms.
And under the arms.
Non-pharmacological management:
The following non-pharmacological measures can be taken to prevent the spread of scabies:
1-Wash all clothes, towels, and bedding in hot water and dry them in a hot dryer.
2-Vacuum carpets, furniture, and car seats regularly.
3-Do not share personal items such as clothing, towels, and bedding.
4-Avoid close contact with anyone who has scabies.
Pharmacological management:
Treatment for scabies involves the use of prescription medications to kill the mites and their
eggs.
The following medications are commonly used:
1-Topical scabicides: These are creams, lotions, or ointments that are applied to the skin.
Examples include permethrin, benzyl benzoate, and sulfur ointment.
2-Oral medications: Ivermectin is an oral medication that can be used to treat scabies.
Notes by Abhay Sagar (Lecturer RCCCOP,Basti)
Phramacotherapeutics Notes
3-Antihistamines: These medications can help relieve itching.
Notes by Abhay Sagar (Lecturer RCCCOP,Basti)
You might also like
- Teaching Plan Scabies 11Document4 pagesTeaching Plan Scabies 11umar khan0% (1)
- The Best Home Remedies for Scabies, No More Complicated MedicationsFrom EverandThe Best Home Remedies for Scabies, No More Complicated MedicationsNo ratings yet
- ScabiesDocument14 pagesScabiessyemiNo ratings yet
- ScabiesDocument18 pagesScabiesMueez BalochNo ratings yet
- Document From BenjaminfjodDocument21 pagesDocument From BenjaminfjodBenjamin VanlaltlansangaNo ratings yet
- Scabies: General InformationDocument3 pagesScabies: General InformationAbiNo ratings yet
- Scabies 1Document25 pagesScabies 1pmNo ratings yet
- Scabies: Muhammad Fahmy Septian RIO LisaDocument24 pagesScabies: Muhammad Fahmy Septian RIO LisaFahmy SeptianNo ratings yet
- General Information About ScabiesDocument16 pagesGeneral Information About ScabiesPramesti DarojahNo ratings yet
- ScabiesfactsheetDocument2 pagesScabiesfactsheetpepe perezNo ratings yet
- ScabiesDocument4 pagesScabiesBrix ValdrizNo ratings yet
- Scabies SRU Rev 06Document31 pagesScabies SRU Rev 06Dwika HerdykiawanNo ratings yet
- Scabies OET Reading Material Part-A - SCABIES PART A Scabies Is A Skin Infestation Caused by A Mite - StudocuDocument1 pageScabies OET Reading Material Part-A - SCABIES PART A Scabies Is A Skin Infestation Caused by A Mite - StudocuMoneka GrgNo ratings yet
- Kerry-Ann Williams, Tahirah Williams & David WilliamsDocument10 pagesKerry-Ann Williams, Tahirah Williams & David WilliamsKerry-Ann WilliamsNo ratings yet
- RingwormDocument7 pagesRingwormSAMSON, MAXZENE ANICKANo ratings yet
- ArthropodsDocument42 pagesArthropodsKateNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Plan - NSTP1Document3 pagesDaily Lesson Plan - NSTP1Charity Mae DoradoNo ratings yet
- ScabiesDocument5 pagesScabiesSashi MehNo ratings yet
- SCABIESDocument14 pagesSCABIESNom Kumar Naik Rathod100% (1)
- Skin Infestation PDFDocument30 pagesSkin Infestation PDFHampson MalekanoNo ratings yet
- Background of The StudyDocument4 pagesBackground of The StudyFerreze AnnNo ratings yet
- Ticks: Ixodidae - Hard Ticks Argasidae - Soft TicksDocument20 pagesTicks: Ixodidae - Hard Ticks Argasidae - Soft TickssanthiyasandyNo ratings yet
- ScabiesDocument8 pagesScabiesrimshajafar10No ratings yet
- Fox Scabies EncyclopediaDocument10 pagesFox Scabies EncyclopediaNimfa Christina R WibowoNo ratings yet
- What Are The Symptoms of Scabies?: Rash 130 MillionDocument2 pagesWhat Are The Symptoms of Scabies?: Rash 130 Millionrachel mariamNo ratings yet
- ScabiesDocument2 pagesScabiesPRINTDESK by DanNo ratings yet
- Home Cure Fungal Infections of The SkinDocument8 pagesHome Cure Fungal Infections of The SkinvijaykaruaNo ratings yet
- Homework of Basic Communication Skills Lecture 1Document2 pagesHomework of Basic Communication Skills Lecture 1Cypher Soth ViNo ratings yet
- SCABIESDocument5 pagesSCABIESMenna GomaaNo ratings yet
- SCABIES by DR Pavan PatilDocument5 pagesSCABIES by DR Pavan PatilDr. Pavan PatilNo ratings yet
- Scabies (Montealto, Matidios, Manlangit)Document2 pagesScabies (Montealto, Matidios, Manlangit)larne manlangitNo ratings yet
- Scabies (Calaustro Kyla)Document22 pagesScabies (Calaustro Kyla)Carlojay IniegoNo ratings yet
- Scabies Bites FactsDocument5 pagesScabies Bites FactsnisircNo ratings yet
- Jock ItchDocument4 pagesJock ItchFranzelle Estrella ÜNo ratings yet
- Scabies Cont.: How Can The Spread of This Disease Be Prevented?Document2 pagesScabies Cont.: How Can The Spread of This Disease Be Prevented?Austine OsaweNo ratings yet
- What Is ScabiesDocument7 pagesWhat Is ScabiesKenNo ratings yet
- ScabiesDocument14 pagesScabiesBenjamin VanlaltlansangaNo ratings yet
- Ntagious-Skin-Diseases/scabies ScabiesDocument10 pagesNtagious-Skin-Diseases/scabies ScabiespmNo ratings yet
- ScabiesDocument8 pagesScabiesJessica Dumayas Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Scabies SRUDocument20 pagesScabies SRUHesti Prihastuti DewiNo ratings yet
- MOH Guidelines For Scabies Prevention and Control in Healthcare SettingsDocument11 pagesMOH Guidelines For Scabies Prevention and Control in Healthcare Settingsrazan alamriNo ratings yet
- Infestation and InfectionDocument60 pagesInfestation and InfectionJam AhmadNo ratings yet
- Scabies: Signs and SymptomsDocument8 pagesScabies: Signs and Symptomspragna novaNo ratings yet
- ScabiesDocument5 pagesScabiesKeilah MarieNo ratings yet
- Jeevan 2210013 ScabiesDocument3 pagesJeevan 2210013 ScabiesJeevanKarthiresanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management of Skin and Parasitic DiseasesDocument14 pagesNursing Management of Skin and Parasitic Diseasesyer tagalajNo ratings yet
- Vorwick ScabiesDocument3 pagesVorwick ScabiesTio Norman WicaksonoNo ratings yet
- Scabies-Tadulako Dec 2012Document40 pagesScabies-Tadulako Dec 2012Hasnapasuloi NanhaNo ratings yet
- HTP ScabiesDocument3 pagesHTP ScabiesShyrra Edades PinderNo ratings yet
- Scabies - Topic Overview: Mites Skin Scabies ScabiesDocument6 pagesScabies - Topic Overview: Mites Skin Scabies ScabiesKathy SuazoNo ratings yet
- Important Diseases1 - Skin and EyeDocument40 pagesImportant Diseases1 - Skin and EyePeiyong TanNo ratings yet
- P.S Very Nice!! May Pa-Picture Si Mayora!:D: FolliculitisDocument7 pagesP.S Very Nice!! May Pa-Picture Si Mayora!:D: FolliculitisBea SartoNo ratings yet
- Infestation: ScabiesDocument16 pagesInfestation: ScabiesBrix ValdrizNo ratings yet
- ScabiesDocument15 pagesScabiesAbdullah Mascardo BarabagNo ratings yet
- Scabies Life Cycle Diagnosis, Treatment and Control: Said AdanDocument16 pagesScabies Life Cycle Diagnosis, Treatment and Control: Said AdanochaNo ratings yet
- Scabies MITEDocument16 pagesScabies MITEIrul AnwarNo ratings yet
- Scabies Life Cycle Diagnosis, Treatment and Control: Said AdanDocument16 pagesScabies Life Cycle Diagnosis, Treatment and Control: Said AdanResti FadyaNo ratings yet
- Scabies Diagnosis and ManagementDocument5 pagesScabies Diagnosis and ManagementAbdul Rauf ZakariaNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Skin Fungal Infections, (Updated 2023) Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Skin Fungal Infections, (Updated 2023) Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- EVS Question D.Pharm 2nd 2nd SesionalDocument1 pageEVS Question D.Pharm 2nd 2nd SesionalAbhay SagarNo ratings yet
- Drug Name /synonyms Biological Source Chemical Constituents Therapeutic UsesDocument1 pageDrug Name /synonyms Biological Source Chemical Constituents Therapeutic UsesAbhay SagarNo ratings yet
- Time Table Time Activity Should Be DoneDocument1 pageTime Table Time Activity Should Be DoneAbhay SagarNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutics 15 00038 v2Document21 pagesPharmaceutics 15 00038 v2Abhay SagarNo ratings yet
- TerpenoidsDocument3 pagesTerpenoidsAbhay SagarNo ratings yet
- Time Table !!1Document1 pageTime Table !!1Abhay SagarNo ratings yet
- Conjunctivitis (Bacterial and Viral)Document2 pagesConjunctivitis (Bacterial and Viral)Abhay SagarNo ratings yet
- Pharmacognosy Question Paper Set 2 Second SesionalDocument1 pagePharmacognosy Question Paper Set 2 Second SesionalAbhay SagarNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapeutics Question Second SessionalDocument1 pagePharmacotherapeutics Question Second SessionalAbhay SagarNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapeutics Question Paper Set - 1Document3 pagesPharmacotherapeutics Question Paper Set - 1Abhay Sagar100% (1)
- Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) PT NotesDocument2 pagesAntimicrobial Resistance (AMR) PT NotesAbhay SagarNo ratings yet
- HIV and Opportunistic Infections PTDocument2 pagesHIV and Opportunistic Infections PTAbhay SagarNo ratings yet
- Opioids AnalgesicDocument1 pageOpioids AnalgesicAbhay SagarNo ratings yet
- Payment RecieptRahul Carry PDFDocument1 pagePayment RecieptRahul Carry PDFAbhay SagarNo ratings yet
- Common Diseases and Disorders Along With Their Normal Biochemical ValuesDocument1 pageCommon Diseases and Disorders Along With Their Normal Biochemical ValuesAbhay SagarNo ratings yet
- Payment RecieptRahul CarryDocument1 pagePayment RecieptRahul CarryAbhay SagarNo ratings yet