Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Scabies
Uploaded by
syemi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
39 views14 pagesOriginal Title
Scabies PPT
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
39 views14 pagesScabies
Uploaded by
syemiCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 14
SCABIES
WHAT ARE SCABIES
Scabies is a skin condition caused by an
infestation of the human itch mite
called Sarcoptes scabiei. These microscopic
mites burrow into the skin and cause
symptoms of itching and rash
HOW DO WE GET SCABIES
Anyone can get scabies.
It is found all over the world and the mite is
transmitted by direct and prolonged skin-to-skin
contact with a person who has scabies.
Sexual contact is the most common way scabies
is transmitted.
Transmission can also happen from parents
to children, particularly mother-to-infant.
The mite can only survive about 48 to 72
hours without human contact, so it is
uncommon, though possible, for scabies to
spread through infested bedding or furniture.
HOW LONG DOES SCABIES LAST
Scabies mites can only live about 72 hours
without human contact, but once on a person,
the mites can live up to two months.
Mites survive longer in colder conditions with
higher humidity.
Once on a person, mites can burrow into the
skin, and symptoms usually begin three to six
weeks after infestation.
What Are the Signs and Symptoms of
Scabies?
Symptoms of scabies are usually itching (which tends to be
more intense at night), and a pimple-like rash.
Scabies rash can appear on any part of the body, but the most
common sites are wrists, elbows, armpits, the skin between the
fingers and toes and around the nails, and skin usually covered
by clothing such as the buttocks, belt line, nipples, and penis.
Infants and young children may have scabies rash on their
head, face, neck, palms, and soles.
In some patients with weakened immune systems, scabies
rash may become crusted.
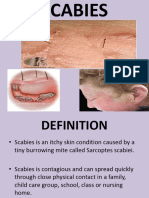
What Do Scabies Look Like?
Scabies often looks like small red pimple-like bumps
on the skin. The bumps may be crusty.
They may also be accompanied by "burrows," or thin
gray, brown, or red lines that radiate from the bumps.
They may be hard to see, and can look like scratch
marks
How Is Scabies Tested and Diagnosed?
Scabies is usually diagnosed by the patient's
history and a physical examination of the
lesions (bumps). Other tests that may be done
include:
Skin scraping to identify the mites or eggs
Dermoscopy, which uses a handheld
dermoscope to allow closer visual examination
of the skin to look for mites
Adhesive tape test in which a doctor uses
strong adhesive tape applied to the skin
lesions
HOW CAN SCABIES BE TREATED
Scabies Treatment: Cream Applications
permethrin (Elimite), which is applied directly to the
skin, from the neck to the soles of the feet. It should
be left on overnight and then washed off 8 to 14
hours later. Usually a second application after 1 to 2
weeks is recommended.
Other topical scabies treatments include crotamiton
(Crotan, Eurax) cream or lotion, lindane (not usually
used as a first-line treatment due to risk of seizures),
sulfur ointment, and benzyl benzoate.
HOW CAN SCABIES BE PREVENTED
• Clean all clothes and linen. Use hot, soapy water
to wash all clothing, towels and bedding used at
least three days before treatment. Dry with high
heat. Dry-clean items that can't be washed at
home.
• Starve the mites. Consider placing items can't be
washed, in a sealed plastic bag and leaving it in an
out-of-the-way place, such as in garage, for a couple
of weeks. Mites die if they don't eat for a week.
• Itching may persist for some time after you apply
medication to kill the mites. These steps may help
you find relief from itching:
• Cool and soak skin. Soaking in cool water or
applying a cool, wet washcloth to irritated areas of
skin may minimize itching.
• Apply soothing lotion. Calamine lotion, available
without a prescription, can effectively relieve the
pain and itching of minor skin irritations.
• Take antihistamines. At doctor's suggestion, the
person may find that over-the-counter
antihistamines relieve the allergic symptoms
caused by scabies
Are Cases of Scabies Often
Misdiagnosed?
Scabies can often resemble other skin
conditions. It may look like small pimples, or
mosquito bites. It may also look like eczema
or tinea (ringworm, athlete's foot, and jock
itch). It is important to see a doctor to receive
the correct diagnosis and treatment
What Is “Norwegian Scabies”?
"Norwegian scabies" is another name for
crusted scabies
occur more often in patients with compromised
immune systems due to conditions such as
HIV/AIDS or cancer, or in the elderly, and in
patients with Down's syndrome.
Patients with crusted scabies have large
numbers of scabies mites and are very
contagious.
The scales become warty, with crusts and
fissures. Lesions may have an unpleasant odor
You might also like
- Scabies: General InformationDocument3 pagesScabies: General InformationAbiNo ratings yet
- Itchy skin condition caused by human itch miteDocument10 pagesItchy skin condition caused by human itch mitepmNo ratings yet
- ScabiesDocument5 pagesScabiesSashi MehNo ratings yet
- ScabiesDocument4 pagesScabiesNuradin JemalNo ratings yet
- Kerry-Ann Williams, Tahirah Williams & David WilliamsDocument10 pagesKerry-Ann Williams, Tahirah Williams & David WilliamsKerry-Ann WilliamsNo ratings yet
- ScabiesDocument4 pagesScabiesBrix ValdrizNo ratings yet
- General Information About ScabiesDocument16 pagesGeneral Information About ScabiesPramesti DarojahNo ratings yet
- Scabies Symptoms, Causes, TreatmentDocument6 pagesScabies Symptoms, Causes, TreatmentKathy SuazoNo ratings yet
- ScabiesfactsheetDocument2 pagesScabiesfactsheetpepe perezNo ratings yet
- The Best Home Remedies for Scabies, No More Complicated MedicationsFrom EverandThe Best Home Remedies for Scabies, No More Complicated MedicationsNo ratings yet
- Scabies Bites FactsDocument5 pagesScabies Bites FactsnisircNo ratings yet
- Scabies: Muhammad Fahmy Septian RIO LisaDocument24 pagesScabies: Muhammad Fahmy Septian RIO LisaFahmy SeptianNo ratings yet
- Report SCABIESDocument4 pagesReport SCABIESMary Rose VitoNo ratings yet
- ScabiesDocument15 pagesScabiesAbdullah Mascardo BarabagNo ratings yet
- What Is ScabiesDocument7 pagesWhat Is ScabiesKenNo ratings yet
- Vorwick ScabiesDocument3 pagesVorwick ScabiesTio Norman WicaksonoNo ratings yet
- What Are The Symptoms of Scabies?: Rash 130 MillionDocument2 pagesWhat Are The Symptoms of Scabies?: Rash 130 Millionrachel mariamNo ratings yet
- Scabies: Signs and SymptomsDocument8 pagesScabies: Signs and Symptomspragna novaNo ratings yet
- ArthropodsDocument42 pagesArthropodsKateNo ratings yet
- Scabies Research Penelope Dean 09 14 2011 1Document6 pagesScabies Research Penelope Dean 09 14 2011 1api-28066963No ratings yet
- HTP ScabiesDocument3 pagesHTP ScabiesShyrra Edades PinderNo ratings yet
- ScabiesDocument2 pagesScabiesPRINTDESK by DanNo ratings yet
- Skin Infestation PDFDocument30 pagesSkin Infestation PDFHampson MalekanoNo ratings yet
- Makita Ra Ang Slide??????????????Document19 pagesMakita Ra Ang Slide??????????????Renato AbellaNo ratings yet
- ScabiesDocument18 pagesScabiesMueez BalochNo ratings yet
- Scabies 160908065024Document12 pagesScabies 160908065024Syed NoorNo ratings yet
- Scabies-Tadulako Dec 2012Document40 pagesScabies-Tadulako Dec 2012Hasnapasuloi NanhaNo ratings yet
- Scabies Signs, Symptoms & TreatmentDocument4 pagesScabies Signs, Symptoms & TreatmentFerreze AnnNo ratings yet
- 336 ScabiesDocument2 pages336 ScabiesrozanfikriNo ratings yet
- Document From BenjaminfjodDocument21 pagesDocument From BenjaminfjodBenjamin VanlaltlansangaNo ratings yet
- SCABIESDocument5 pagesSCABIESMenna GomaaNo ratings yet
- ScabiesDocument12 pagesScabiesVeeliz VaksNo ratings yet
- Scabies (Calaustro Kyla)Document22 pagesScabies (Calaustro Kyla)Carlojay IniegoNo ratings yet
- Relieve Itchy Scabies with Proper TreatmentDocument25 pagesRelieve Itchy Scabies with Proper TreatmentpmNo ratings yet
- Fox Scabies EncyclopediaDocument10 pagesFox Scabies EncyclopediaNimfa Christina R WibowoNo ratings yet
- Scabies: Signs and SymptomsDocument4 pagesScabies: Signs and SymptomsIbrahim AbdullahNo ratings yet
- UNIT III (Health)Document47 pagesUNIT III (Health)Lyn MontebonNo ratings yet
- How to Treat and Prevent Spread of ScabiesDocument3 pagesHow to Treat and Prevent Spread of ScabiesRicherson YovannlimNo ratings yet
- Scabies Epi308eDocument2 pagesScabies Epi308eReechel mae BremnerNo ratings yet
- Scabies Diagnosis and ManagementDocument5 pagesScabies Diagnosis and ManagementAbdul Rauf ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Scabies.: Vanessa ChelimoDocument19 pagesScabies.: Vanessa ChelimoAlvin OmondiNo ratings yet
- ECZEMADocument5 pagesECZEMApragna novaNo ratings yet
- ECZEMADocument5 pagesECZEMApragna novaNo ratings yet
- SCABIES: CAUSES, SYMPTOMS AND TREATMENTDocument17 pagesSCABIES: CAUSES, SYMPTOMS AND TREATMENTDr.M HanifNo ratings yet
- Skin ConditionsDocument43 pagesSkin ConditionspdladvaNo ratings yet
- Scabies Presentation EnglishDocument35 pagesScabies Presentation EnglishAipzulman RozaliNo ratings yet
- SCABIES FACTS: CAUSES, SYMPTOMS AND TREATMENTDocument5 pagesSCABIES FACTS: CAUSES, SYMPTOMS AND TREATMENTpakemainmainNo ratings yet
- SCABIESDocument14 pagesSCABIESNom Kumar Naik Rathod100% (1)
- Lesson: Lagonoy High School Quarter 3 Module 3Document3 pagesLesson: Lagonoy High School Quarter 3 Module 3John Mark PrestozaNo ratings yet
- Scabies SRU Rev 06Document31 pagesScabies SRU Rev 06Dwika HerdykiawanNo ratings yet
- Home Cure Fungal Infections of The SkinDocument8 pagesHome Cure Fungal Infections of The SkinvijaykaruaNo ratings yet
- DD 01Document2 pagesDD 01Yuanita FaradibaNo ratings yet
- Scabies - NarraDocument2 pagesScabies - NarraBryan De HopeNo ratings yet
- ScabiesDocument18 pagesScabiesRashidul IslamNo ratings yet
- ImpetigoDocument2 pagesImpetigoAMOS MELINo ratings yet
- Scabies NotesDocument9 pagesScabies NotesAvi eNo ratings yet
- Vpe 321 ZooDocument23 pagesVpe 321 ZooransinghNo ratings yet
- Basic Science EnglishDocument63 pagesBasic Science EnglishShajana ShahulNo ratings yet
- PhlebotomyDocument20 pagesPhlebotomyaguilarsuzette20No ratings yet
- Kingdoms BacteriaDocument22 pagesKingdoms Bacteriaapi-267309851No ratings yet
- Aquatabs MPADocument2 pagesAquatabs MPADavid SalasNo ratings yet
- Causes and Management of Vomiting and Diarrhea in ChildrenDocument5 pagesCauses and Management of Vomiting and Diarrhea in ChildrenHakim MiswanNo ratings yet
- A.18 Hypochlorous-AcidDocument57 pagesA.18 Hypochlorous-AcidHervian LanangNo ratings yet
- Yogesh Garg PPT On Disposal of WasteDocument48 pagesYogesh Garg PPT On Disposal of WasteSonia GhulatiNo ratings yet
- Sharp Injury PreventionDocument12 pagesSharp Injury Preventionsimmi2768No ratings yet
- ENG8 Q4 MOD4Document29 pagesENG8 Q4 MOD4Janine Loresco-FernandezNo ratings yet
- Thessaly's perpetual relationship with medicineDocument7 pagesThessaly's perpetual relationship with medicineAngelica StöehrNo ratings yet
- Chen Et Al 2021Document17 pagesChen Et Al 2021WoogyuNo ratings yet
- Medip,+667 2199 1 CEDocument4 pagesMedip,+667 2199 1 CEGSPNo ratings yet
- Presentation URTI& LRTI - G1Document134 pagesPresentation URTI& LRTI - G1Aniq Zahran MasomNo ratings yet
- Infectious Dermatosis (Bacterial Skin Infections)Document31 pagesInfectious Dermatosis (Bacterial Skin Infections)Melch PintacNo ratings yet
- Protozoan Diseases in Farm RuminantsDocument29 pagesProtozoan Diseases in Farm Ruminantsqadir-qadisNo ratings yet
- Universal Safety (Health) PrecautionsDocument61 pagesUniversal Safety (Health) Precautionstummalapalli venkateswara rao100% (2)
- Japanese Encephalitis: OIE Terrestrial Manual 2008 231Document9 pagesJapanese Encephalitis: OIE Terrestrial Manual 2008 231Iin NovitaNo ratings yet
- المختص في الحشرات -Synopsis of Medical EntomologyاDocument63 pagesالمختص في الحشرات -Synopsis of Medical EntomologyاDrMohamedBenrashedNo ratings yet
- Namibia 2011 National Guidelines For The Management of TuberculosisDocument218 pagesNamibia 2011 National Guidelines For The Management of TuberculosisLaura Lopez GonzalezNo ratings yet
- 6 Campak 33Document19 pages6 Campak 33Sonata C'pahutarNo ratings yet
- Gram-Negative Bacteria Diseases and TreatmentsDocument4 pagesGram-Negative Bacteria Diseases and TreatmentswingNo ratings yet
- Chylous Ascites 3Document3 pagesChylous Ascites 3Nur atikaNo ratings yet
- NCM 220 RATIONALIZATION TITLEDocument3 pagesNCM 220 RATIONALIZATION TITLEJeralyn Delarosa GabagatNo ratings yet
- Skin DisordersDocument4 pagesSkin DisordersAj PotXzs Ü100% (2)
- Garlic As QSI Capsule ProposalDocument5 pagesGarlic As QSI Capsule ProposalZerElie DavidNo ratings yet
- Soil Transmitted Helminth Infections: The Nature, Causes and Burden of The ConditionDocument79 pagesSoil Transmitted Helminth Infections: The Nature, Causes and Burden of The ConditionYokaiCO100% (1)
- Rekomendasi KlinikDocument6 pagesRekomendasi KlinikPrasetya YudhaNo ratings yet
- Antibacterial Activities of Ethanol Extracts ofDocument9 pagesAntibacterial Activities of Ethanol Extracts ofGenesis JoseNo ratings yet
- TJC Self Study Handbook.8.1.2021Document33 pagesTJC Self Study Handbook.8.1.2021Andrew McGowanNo ratings yet