Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Important Concepts For Case Studies: Partial Compliance With AFRF Is Not Allowed E.G. "Financial Statements Are in Substantial Compliance With I FRS"
Uploaded by
Raees aliOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Important Concepts For Case Studies: Partial Compliance With AFRF Is Not Allowed E.G. "Financial Statements Are in Substantial Compliance With I FRS"
Uploaded by
Raees aliCopyright:
Available Formats
Outlines:
CFAP 06: Advanced Audit & Related Services
This standard discusses:
ISA 200: Oveall Objectives of Auditor
1. Overall objective of auditor.
Secret Sheet for Quick Revision
2. Key requirements for performing an audit i.e. Professional Judgment, Professional Skepticism, Premium Content
(For students of Muhammad Asif, FCA)
Compliance with Code of Ethics, Compliance with ISAs. (For Summer 2023)
3.Various terms frequently used in ISA e.g. Applicable Financial Reporting Framework, Reasonable
Assurance, Material Misstatement, Audit Risk, Sufficient appropriate evidence.
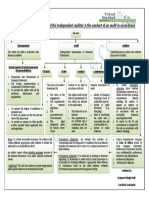
Framework
General Purpose Framework Special Purpose Framework Fair Presentation Framework Compliance Framework
To meet needs of wide range of users To meet needs of specific users e.g. Allows additional disclosure or Does not allow additional
e.g. 1. Regulatory Basis departure from AFRF to achieve disclosure or departure.
1. IFRS 2. Tax Basis fair presentation.
2. IFRS for SMEs 3. Cash Basis
3. National Framework e.g. US GAAP 4. Contractual Basis Opinion:
4. XYZ Law of Jurisdiction X Opinion: “financial statements are prepared, in all
“financial statements give true and fair view material respects, in accordance with the
Implications on Report: in accordance with the framework”, or framework”.
Implication on Report: EOM (to explain basis of accounting) “financial statements are presented fairly, If framework is misleading/unacceptable,
If AFRF is other than IFRS, jurisdiction shall also OM (if distribution of report is restricted) in all material respects, in accordance with the engagement is not accepted.
be mentioned in opinion. framework”. (Both phrases are equivalent)
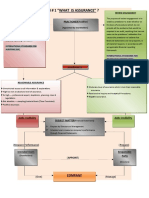
Audit Risk (AR)
There are 03 Parties involved in an audit (risk of misstatement after audit)
Auditor Management (e.g. CFO, CEO) Stakeholders (Existing Shareholders, Risk of Material Misstatement (RMM) Detection Risk (DR)
& TCWG (e.g. Directors) Prospective investors, A holding company, (risk of misstatement prior to audit) (risk that auditor does not
Lenders, Donors, Tax Authorities.) detect misstatement)
Overall Objectives of Auditor:
To obtain reasonable assurance, and report on F/S. Responsibilities of Management: At F/S Level At Assertion Level
To communicate certain matters to internal/ Preparation of F/S. Expectation Gap: (which affects many (which affects
external parties when required by ISA/local laws. Internal controls. 1. Auditor prepares financial statements. assertions/areas) specific assertion)
(Opinions on internal control, future viability, To provide information to auditor. 2. Auditor checks 100% transactions.
efficiency/effectiveness of management are NOT 3. Auditor provides absolute assurance.
auditor’s objectives.) 4. Auditor is responsible to detect fraud. Inherent Risk (IR) Control Risk (CR)
5. EOM, OM, Going Concern Uncertainty are (risk due to nature of transactions) (risk due to weaknesses in internal control)
modified opinions.
Important Concepts for Case Studies:
Partial compliance with AFRF is not allowed e.g. “Financial statements are in substantial
compliance with I FRS”.
Outlines:
CFAP 06: Advanced Audit & Related Services
This standard discusses:
ISA 200: Oveall Objectives of Auditor
1. Overall objective of auditor.
Secret Sheet for Quick Revision Premium Content
2. Key requirements for performing an audit i.e. Professional Judgment, Professional Skepticism, Compliance with
(For students of Muhammad Asif, FCA) (For Summer 2023)
Code of Ethics, Compliance with ISAs.
3.Various terms frequently used in ISA e.g. Applicable Financial Reporting Framework, Reasonable Assurance,
Material Misstatement, Audit Risk, Sufficient appropriate evidence.
KEY REQUIREMENTS FOR PERFORMING
AN AUDIT Evidence
Professional Judgment Professional Skepticism Compliance with ISAs Compliance with Code of Ethics Characteristics: Sources:
Sufficient (measure of Quantity) 1. Previous audits.
Appropriate (measure of Quality) 2. A & C Procedures
Application of knowledge and Being alert to conditions which Structure of ISAs: A CA shall comply with requirements of 3. During the audit (inside or outside the entity)
experience to reach an appropriate indicate possible misstatements. Introductory Material, Objectives, Definition. Code of Ethics in every engagement. 4. Using Others (e.g. Predecessor Auditor,
course of action. (e.g. procedures (See list of conditions below) However, Independence is required only Component Auditor, Internal Auditor, Service
Requirements.
when guidance is not available in ISas) for assurance engagements. Auditor, Expert, Quality Control Reviewer)
Application and Other Explanatory Material (including
Appendices).
Auditor has to comply with all ISAs and their all
requirements, except when requirement is not relevant
or not practicable.
When Requirement is not relevant: When Requirement is not
1. ISA 610 not relevant if no internal audit function. practicable/not effective:
2. ISA 705 not relevant if auditor expresses unmodified opinion. Auditor shall perform
3. ISA 265 not relevant, if no significance deficiency in internal control. alternative procedures
4. Requirements relating to segment information ISA 501 not relevant performed to obtain
if no segments. evidence/assurance.
Levels of Assurance
Application of Professional Skepticism in Case Studies:
Read the following events/conditions carefully, and think misstatement which may occur in each case in financial statements. This list is very important to solve case studies in exam. Limited Assurance. Reasonable Assurance: Absolute Assurance:
Moderate level of assurance expressed in High, but not absolute, level of Not provided, due to Inherent Limitations.
negative form. assurance expressed in positive form. 1. Nature of financial statements (estimates,
Sales: Unusual increase in sales, Unusual decrease in sales, Income is received (or expense is paid) in advance “Nothing has come to our attention that “Financial statements give true and judgments and uncertainties are involved)
Inventory: Decrease in sales/demand (due to change in fashion/technology or launch of new products), Long-standing inventory/increase in inventory turnover ratio, Defective goods causes us to believe that financial fair view in accordance with the 2. Nature of audit procedures (Not complete
in inventory, Cost of production increases, or Sale price decreases, If product is malfunctioning, New products are launched by company or competitor, Contract of specialized inventory statements do not give true and fair view”. framework”. information, No legal powers, Fraud)
is cancelled or customer goes bankrupt, Defective goods returned by customers. Inventory is held at various locations, or Inventory is held with third party. 3. Time and Cost limitation
4. Other difficult matters/assertions (Related
Fixed Assets: Major fixed assets purchased during the year, Significant capital expenditures incurred during the year, Revaluation Policy, Change in life, Decrease in sales/demand of Parties, NOCLAR, Going Concern)
inventory, Faults in production process (e.g. increase in scrap/wastage of inventory during production), Destroyed or Unused or Under-utilized Fixed Assets, Closure of a factory
Debtors: Increase in Debtors (or turnover ratio), Dispute with debtors, FCY receivables/payables.
Creditors: Decrease in creditors (or turnover ratio)
Provisions: Provision for Warranty (Company provides warranty to its customers, Increase in warranty period/complains, Malfunctioning of products, Not in alignment with sales),
Provision for Restructuring (closure of a factory), Provision for Onerous contracts (Loss making non-cancellable contracts), Provision for Legal Cases (unfair dismissal of staff, serious
accident damaging environment or injuring people, malfunctioning of product)
Intangible Assets: Goodwill (Business purchased during the year), Development Cost (Product developed/launched during the year).
Going Concern Uncertainty: Loss during the year, Bankruptcy of major customer. Adverse key financial ratios (e.g. Current ratio, Quick-asset ratio, Debt-equity ratio), Ceased
substantial manufacturing activities, Serious accident damaging environment or injuring people.
Risk at F/S level: Issue of Shares is planned, Sale of business is planned, Contingent remuneration of CFO/CEO, Other fraud risk factors
Tax: Pending tax litigations, Deferred tax,
Other Risks: You are appointed this year, Non-compliance with Laws and Regulations (fines/bribery paid), Implementation of New IT system, Related Party Transactions, Reduction in
staff, Company deals in large number of products, Recording contingent asset as receivable, Weak internal controls: e.g. Reconciliations not being prepared (in bank, debtors, creditors,
inventory), Predecessor auditor did not wish to be reappointed, or expressed modified opinion, Restricted time schedule for audit, Predecessor auditor expressed modified opinion.
You might also like
- Chapter 2 MindMapDocument1 pageChapter 2 MindMapArslan Ahmad100% (1)
- Resumen Capitulo 2Document4 pagesResumen Capitulo 2Lucho EnriqueNo ratings yet
- 3 Financial Reporting and Analysis MMDocument29 pages3 Financial Reporting and Analysis MMAishwarya BansalNo ratings yet
- MSME Draft LetterDocument1 pageMSME Draft LetterRoshanjit ThakurNo ratings yet
- Auditing and Assurance 1Document247 pagesAuditing and Assurance 1All FreeNo ratings yet
- Professional Standards: Chapter Welcome To Econ 132-AuditDocument4 pagesProfessional Standards: Chapter Welcome To Econ 132-Audityea okayNo ratings yet
- Caf-8 Mindmaps-69Document19 pagesCaf-8 Mindmaps-69Muhammad ImranNo ratings yet
- Auditing and AccountingDocument38 pagesAuditing and Accountingberihun admassuNo ratings yet
- BABE1 Reviewer 1Document13 pagesBABE1 Reviewer 1James Ryan AlzonaNo ratings yet
- Ifrs Framework PDFDocument23 pagesIfrs Framework PDFMohammad Delowar HossainNo ratings yet
- 2nd Lecture-Ch. 2Document37 pages2nd Lecture-Ch. 2otaku25488No ratings yet
- FAR 001 Conceptual FrameworkDocument4 pagesFAR 001 Conceptual FrameworkdreianyanmaraNo ratings yet
- Definition of AuditingDocument7 pagesDefinition of AuditingChristen HerceNo ratings yet
- 07 Part-6Document5 pages07 Part-6Mary Joy RarangNo ratings yet
- Far 02 Conceptual Framework For Financial Reporting CompressDocument11 pagesFar 02 Conceptual Framework For Financial Reporting CompressDaphnie Loise CalderonNo ratings yet
- G10473 EC Students Experience Verification Factsheet enDocument21 pagesG10473 EC Students Experience Verification Factsheet ensvvankeshwaramNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Framework and Accounting Standards: OutlineDocument6 pagesConceptual Framework and Accounting Standards: OutlineMichael TorresNo ratings yet
- Assurance Services: Regulatory Framework and FundamentalsDocument32 pagesAssurance Services: Regulatory Framework and FundamentalsTADRNo ratings yet
- Pillar 3 USB Disclosure 6-30-17Document33 pagesPillar 3 USB Disclosure 6-30-17Siva RenjithNo ratings yet
- Standards and The Conceptual Framework Underlying Financial AccountingDocument26 pagesStandards and The Conceptual Framework Underlying Financial AccountingLodovicus LasdiNo ratings yet
- AT - Materiality and RisksDocument7 pagesAT - Materiality and RisksRey Joyce AbuelNo ratings yet
- ISA 200 Overall Objectives of The Independent AuditorDocument9 pagesISA 200 Overall Objectives of The Independent AuditorBilal RazaNo ratings yet
- FAR 02 Conceptual Framework For Financial ReportingDocument11 pagesFAR 02 Conceptual Framework For Financial ReportingKimberly NuñezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Lesson Outline - StudentDocument9 pagesChapter 1 - Lesson Outline - StudentKim Heok ChuaNo ratings yet
- Special Stds Comparison Chart PDFDocument3 pagesSpecial Stds Comparison Chart PDFyfarhana2002No ratings yet
- CH#1Document2 pagesCH#1Tariq IqbalNo ratings yet
- Acctg 330 Ch1Document2 pagesAcctg 330 Ch1agm25No ratings yet
- Audit Materiality: Session 10Document16 pagesAudit Materiality: Session 10Abdullah EjazNo ratings yet
- The Implementation of Accounting Objectives - An Application To Extraordinary ItemsDocument12 pagesThe Implementation of Accounting Objectives - An Application To Extraordinary ItemsNguyệt MinhNo ratings yet
- Basel 2 - DeloitteDocument29 pagesBasel 2 - DeloitteSENTHIL KUMARNo ratings yet
- Framework of Preparation and Presentation of Financial Statements What Is A Conceptual Framework?Document6 pagesFramework of Preparation and Presentation of Financial Statements What Is A Conceptual Framework?Dhanushika SamarawickramaNo ratings yet
- Crci L1Document6 pagesCrci L1Law KanasaiNo ratings yet
- Conceptual and Regulatory FrameworkDocument8 pagesConceptual and Regulatory FrameworkJaylan A ElwailyNo ratings yet
- Planning Kaplan Chapter 6: Acca Paper F8 Int Audit and AssuranceDocument38 pagesPlanning Kaplan Chapter 6: Acca Paper F8 Int Audit and Assurancehaddad2020No ratings yet
- Lecture 21 - Standards On Auditing (SA 320 and 402) PDFDocument6 pagesLecture 21 - Standards On Auditing (SA 320 and 402) PDFAruna RajappaNo ratings yet
- Credit Analysis and Framewok - MODULE 1Document9 pagesCredit Analysis and Framewok - MODULE 1Boci & Company Services LimitedNo ratings yet
- IAASB ISA 315 Revised 2019Document16 pagesIAASB ISA 315 Revised 2019Bianca Marie PedrozoNo ratings yet
- 1.RISK CompediumDocument95 pages1.RISK CompediumyogeshthakkerNo ratings yet
- F8-30 The Auditor's Report On Financial StatementsDocument18 pagesF8-30 The Auditor's Report On Financial StatementsReever RiverNo ratings yet
- 2016 Aura Risk MatesDocument30 pages2016 Aura Risk Matesikhwan ahmad prayogoNo ratings yet
- FrameworkDocument3 pagesFrameworkVola AriNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Famework FASB IASBDocument36 pagesConceptual Famework FASB IASBMusab AhmedNo ratings yet
- NSA 320 (Revised) "Materiality in Planning and Performing An Audit"Document1 pageNSA 320 (Revised) "Materiality in Planning and Performing An Audit"Roshan AddhikariNo ratings yet
- Basel II Capital Accord SlidesDocument25 pagesBasel II Capital Accord SlidesAamir RazaNo ratings yet
- Far 1-2Document3 pagesFar 1-2Marjorie UrbinoNo ratings yet
- Professional Competence For Engagement Partners Responsible For Audits of Financial Statements (Revised)Document17 pagesProfessional Competence For Engagement Partners Responsible For Audits of Financial Statements (Revised)Paula MilenaNo ratings yet
- 004 - Chapter 02 - Financial Reporting FrameworksDocument10 pages004 - Chapter 02 - Financial Reporting FrameworksHaris ButtNo ratings yet
- 2 Financial Reporting Theory UpdatedDocument52 pages2 Financial Reporting Theory UpdatedSiham OsmanNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Frame Work-CAP IIDocument9 pagesConceptual Frame Work-CAP IIbinuNo ratings yet
- Isa 200Document9 pagesIsa 200Muhammad Abid QaziNo ratings yet
- Isa 810 - PreciDocument1 pageIsa 810 - PreciJennifer GaiteNo ratings yet
- Illustrative KAMs - Aviation IndustryDocument5 pagesIllustrative KAMs - Aviation IndustryBilal AhmedNo ratings yet
- Acc Cap1 PresentationDocument30 pagesAcc Cap1 PresentationtafsirmhinNo ratings yet
- Course Code: COM-405 Course Title: Credit Hours: 3 (3-0) : Introduction To Business FinanceDocument15 pagesCourse Code: COM-405 Course Title: Credit Hours: 3 (3-0) : Introduction To Business FinanceSajjad AhmadNo ratings yet
- CFA1 FRA Revision HHD 2020.10.23Document62 pagesCFA1 FRA Revision HHD 2020.10.23Hà Thúy VyNo ratings yet
- CH 02Document59 pagesCH 02abdullah.h.aloibiNo ratings yet
- UNEC FrlessonDocument22 pagesUNEC FrlessonTaKo TaKoNo ratings yet
- FAR 02 - Conceptual Framework For Financial ReportingDocument11 pagesFAR 02 - Conceptual Framework For Financial ReportingJohn Bohmer Arcillas PilapilNo ratings yet
- Information Systems Auditing: The IS Audit Reporting ProcessFrom EverandInformation Systems Auditing: The IS Audit Reporting ProcessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Depreciation Reports in British Columbia: The Strata Lot Owners Guide to Selecting Your Provider and Understanding Your ReportFrom EverandDepreciation Reports in British Columbia: The Strata Lot Owners Guide to Selecting Your Provider and Understanding Your ReportNo ratings yet
- University of National and World EconomyDocument11 pagesUniversity of National and World EconomyIva YarmovaNo ratings yet
- Process Identification Part 2Document16 pagesProcess Identification Part 2hover.dragon16No ratings yet
- Procurement WorkDocument8 pagesProcurement WorkbagumaNo ratings yet
- Class 10th - The Great DepressionDocument12 pagesClass 10th - The Great DepressionT A N Y A T I W A R INo ratings yet
- Sales Executive Business Development in Boston MA Resume Martin LairdDocument2 pagesSales Executive Business Development in Boston MA Resume Martin LairdMartinLairdNo ratings yet
- Heritage Tourism: Submitted By, Krishna Dev A.JDocument5 pagesHeritage Tourism: Submitted By, Krishna Dev A.JkdboygeniusNo ratings yet
- Tanglewood CasebookDocument96 pagesTanglewood CasebookPayasam AbhilashNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Global EconomyDocument18 pagesLesson 2 Global EconomyEngr. Kimberly Shawn Nicole SantosNo ratings yet
- Letter HeadDocument1 pageLetter Headmelvin bautistaNo ratings yet
- Auto Rickshaw - Business PlanDocument28 pagesAuto Rickshaw - Business PlanAbhishek1881100% (1)
- Three Years Performance Report MoDPDocument15 pagesThree Years Performance Report MoDPUswa ShabbirNo ratings yet
- Coal Import ProcessDocument5 pagesCoal Import Processsmyns.bwNo ratings yet
- Mawb LR 749-30816310Document1 pageMawb LR 749-30816310Hemant PrakashNo ratings yet
- ZARA Case Study 2 ZARA THE WORLD S LARGEST FASHION RETAILERDocument6 pagesZARA Case Study 2 ZARA THE WORLD S LARGEST FASHION RETAILERSinem DüdenNo ratings yet
- Invoice 41071Document2 pagesInvoice 41071Zinhle MpofuNo ratings yet
- AU Small Finance Bank - Research InsightDocument6 pagesAU Small Finance Bank - Research InsightDickson KulluNo ratings yet
- HW 2-SolnDocument9 pagesHW 2-SolnZhaohui ChenNo ratings yet
- Econometric Study On Malaysia's Palm Oil Position in TheDocument8 pagesEconometric Study On Malaysia's Palm Oil Position in TheBagasNurWibowowNo ratings yet
- S AshfaqDocument45 pagesS AshfaqCMA-1013 V.NAVEENNo ratings yet
- sportstuff.comDocument3 pagessportstuff.comRanjitha KumaranNo ratings yet
- To Download The Complete and Accurate Content Document, Go ToDocument27 pagesTo Download The Complete and Accurate Content Document, Go Topamelarandallptjxncmkyr100% (45)
- Assignment 1 WorkingDocument9 pagesAssignment 1 WorkingUroosa VayaniNo ratings yet
- Banking System Is Composed of Universal and Commercial Banks, Thrift Banks, Rural andDocument10 pagesBanking System Is Composed of Universal and Commercial Banks, Thrift Banks, Rural andgalilleagalillee100% (1)
- Private Equity AsiaDocument12 pagesPrivate Equity AsiaGiovanni Graziano100% (1)
- The Impact of Food Quality On Customer Satisfaction and Behavioural Intentions: A Study On Madurai RestaurantDocument5 pagesThe Impact of Food Quality On Customer Satisfaction and Behavioural Intentions: A Study On Madurai RestaurantJohn Francis SegarraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 ReviseDocument4 pagesChapter 2 ReviseFroy Joe Laroga Barrera IINo ratings yet
- MBA Class of 2019: Full-Time Employment StatisticsDocument4 pagesMBA Class of 2019: Full-Time Employment StatisticsakshatmalhotraNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle Assessment: Applied To The Case Study of A Lawn Mower TractorDocument76 pagesLife Cycle Assessment: Applied To The Case Study of A Lawn Mower TractorTest CasaNo ratings yet
- G11 Organization Management Q1 L4Document4 pagesG11 Organization Management Q1 L4Cherry CieloNo ratings yet