Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ian Desert
Uploaded by
Naee AndrewsOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ian Desert
Uploaded by
Naee AndrewsCopyright:
Available Formats
Patagonian Desert
Antonaeshia A. Biology p.2 Janurary 21, 2011
The Patagonia Desert is the largest desert in the USA. It is also the 7th largest in the whole world. It is located in Argentina as well as in some parts of Chile. It lies between the Andes Mountains, which is to the west of it, and the Atlantic Ocean, which is to the east of it. The Andes Mountains is the cause for the rain shadow that is responsible for the deserts formation and the reason why it is such a large desert in that area. The deserts temperatures exceed to 53oF and averages to 37oF. Patagonians winters last for seven months and its summers last for five. Patagonia is composed mainly of plains, plateaus, and sandstone canyons. All of those futures are formed by the deserts wind. The wind is caused by the rain shadow and because of it being so windy it is one of the largest dust sources in the world. The desert has many diverse futures such as temporary rivers and lakes. It also has a temporary drainage deposit from the Andes Mountains spring. Glacial and volcanic deposits are also found in the area; therefore, the deserts climate is radically affected over time. Species/Pl ant Adaptation Niche Autotr Visuals ophs/ Heter troph s Heter otrop hic
Jaguarundi
Their whiskers help them adapt. They have acute sight, hearing, and sense of smell. It is nocturnal.
Found in lowland habitats found mostly close to water. Great at catching fish. It hunts alone. It climbs well in trees but is terrestrial in hunting. They have 1-4 kittens. Reach maturity at 22-24 months.
Guanaco
They can go days without water.
Balaenidae
They have no teeth but have large plates that are used to pull food from the water. Some of them have strong hind claws, which help them dig. Their forefeet have four toes, which are used for grasping. It is mainly nocturnal.
Chinchilla
Found in small herds. They share a warning call to the herd when they feel they are in danger. One of the largest Feed on mostly plankton and krill, Found near land in most waters. Feed near the surface. Live I small groups of 3-4 individuals. Found in foothill habitats. They can climb and jump. Found grouped together with 100 individuals. They fight. Life span is 10 years. They breed seasons last from May to November. One or two offspring is produced in a litter and
Heter otrop hic
Heter otrop hic
Heter otrop hic
there are two litters per season.
Puma
They have claws that they hide when they walk but use them when grasping prey. They have to adapt to the lack of water as well as all the other species/animals in the desert.
Heter otrop hic
Copihue
Autotr ophic
Lenga
It is able to grow high in the mountains and also as trees in lower places.
Autotr ophic
The Balaendidae also know as the Right Whale has bumps on their face and on their head. These bumps are where organisms live. These organisms are called whale lice. They are parasites; however, they dont affect the whale. This is a commensalism relationship; therefore, one is benefited and the other is not affected. The one being benefited is the whale lice because it has a place to live. The whale is being unaffected though because the lice does not harm it in any way.
Puma Population-N/A Birth Rate-41% July-September Death Rate-N/A Ecological Status-Endangered Balaendidae Population- About 10,000 Birth Rate- 0.37 Death Rate-N/A Ecological Status-Endangered
During the 1980s and early 1990s was an oil spill. This oil spill affected the penguins in my biome. Because they get in the water everyday they are still being affected by this oil spill. This oil spill is an abiotic factor. Also these penguins have been declining in population size so much that they have become threatened. Being threatened means they are very close to being extinct. The animals such as puma and Red Foxes are being poisoned and killed for their fur. This is a biotic factor that is affecting my biome. The more they are killed and poison the closer they could get to being threatened; however, the puma is already endangered because of this. They have been getting killed for their fur for years, but now it needs to come to and end. Because of the killings, as the years go by the population of these animals decline, for the population should be staying stable and not declining every year. Before they become extinct the killers should think about how it would mess up the food web. The most important limiting factor in Patagonian is indirect rain through plants. This limiting factor means that precipitation doesnt hit directly on the plants. Because the rain doesnt hit the plants directly doesnt mean they are harmed. The indirect precipitation actually increases their richness. Although the canopy closure has a negative impact on herbs and shrubs richness it doesnt affect any other plants. I have learned that the most human interaction with my biome is hunting. From my research the hunters hunt mostly Chinchillas, Pumas, and Red Foxes. They are the most animals killed by hunters. The hunters usually kill them for their fur. Because of their hunting the populations of those animals have declined. Also people travel there for vacations. Reference http://uncoma.academia.edu/AdrianaRuggiero/Papers/194301/ORIGINAL_ARTICLE_ Plant_species_richnessenvironment_relationships_across_the_Subantarctic_Patagonian_tra nsition_zonehttp://web.hcsps.sa.edu.au/projects/deserts/projects/group17/index.htm http://mesh.biology.washington.edu/penguinProject/Magellanic http://www.mundoandino.com/Argentina/Patagonian-Desert http://www.environment.gov.au/biodiversity/abrs/publications/fauna-ofaustralia/pubs/volume1b/52-ind.pdf http://www.conservapedia.com/Right_whale#Ecological_Status http://www.arkive.org/long-tailed-chinchilla/chinchilla-lanigera/#text=Threats http://www.iucnredlist.org/apps/redlist/details/18868/0 http://ecos.fws.gov/speciesProfile/profile/speciesProfile.action?spcode=A046
http://www.chinformation.com/taxonomy.html
You might also like
- Biology Investigatory Project (Recovered)Document25 pagesBiology Investigatory Project (Recovered)shubham25% (4)
- FC Sem IiiDocument4 pagesFC Sem IiiDhritika SanghviNo ratings yet
- Remay Berhane - Stem Cafe - Alex Coburn - FgasaDocument4 pagesRemay Berhane - Stem Cafe - Alex Coburn - Fgasaapi-550790092No ratings yet
- PRESENTATIONenglishDocument2 pagesPRESENTATIONenglishNahomy BardalesNo ratings yet
- Science and EnglishDocument11 pagesScience and EnglishGillian Grace ReyesNo ratings yet
- Endangered AnimalsDocument7 pagesEndangered AnimalsCatalin IacobNo ratings yet
- El Nino Affects Otters and Whales: Journal Article Meteorological OrganizationDocument9 pagesEl Nino Affects Otters and Whales: Journal Article Meteorological Organizationapi-302665119No ratings yet
- Research: An Endangered Animal.: Worked By: Rei Metko Accepted By: Rovena Mihali ObjectivesDocument11 pagesResearch: An Endangered Animal.: Worked By: Rei Metko Accepted By: Rovena Mihali ObjectivesRei MetkoNo ratings yet
- LPRYouth FINALDocument3 pagesLPRYouth FINALversloeildhorusNo ratings yet
- Species at Risk: e Most Critically Endangered Animals in The PhilippinesDocument9 pagesSpecies at Risk: e Most Critically Endangered Animals in The PhilippinesKyle OyaoNo ratings yet
- Saving Animals E-Award PresentationDocument74 pagesSaving Animals E-Award PresentationNaphton ProjectsNo ratings yet
- kayshaXD 22Document1 pagekayshaXD 22hunninghake_chelseyNo ratings yet
- Biomes of The Forest Elephant and LifeDocument5 pagesBiomes of The Forest Elephant and LifeGood ChannelNo ratings yet
- Laguna State Polytechnic University: College of EngineeringDocument26 pagesLaguna State Polytechnic University: College of EngineeringJirah LacbayNo ratings yet
- Argumentative EssayDocument2 pagesArgumentative EssayAnasol Amparo ReyesNo ratings yet
- Criticalyy Endangered Species Negros Fruit Dove (Ptilinopus Arcanus)Document3 pagesCriticalyy Endangered Species Negros Fruit Dove (Ptilinopus Arcanus)Elysa Jana LasapNo ratings yet
- Research EssayDocument12 pagesResearch Essayapi-549216833No ratings yet
- Future of Life Reading GuideDocument4 pagesFuture of Life Reading GuideJalen JonesNo ratings yet
- Peruvian Amazonia and Its BiodiversityDocument13 pagesPeruvian Amazonia and Its BiodiversityGerard PalaciosNo ratings yet
- Destruction of Habitat - The Link To Extinction - PrintDocument13 pagesDestruction of Habitat - The Link To Extinction - Printsoundsof stringsNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity NotesDocument31 pagesBiodiversity NotesSiddhanthJainNo ratings yet
- Importance of BiodiversityDocument26 pagesImportance of BiodiversityDayan EsparteroNo ratings yet
- What Is A UNESCO Global GeoparkDocument5 pagesWhat Is A UNESCO Global GeoparktivaaNo ratings yet
- What Is A Keystone Species?Document14 pagesWhat Is A Keystone Species?Abeniezer WendimuNo ratings yet
- MyClass PC Adv 77Document5 pagesMyClass PC Adv 77rebecaNo ratings yet
- Biology Lseeon 8Document5 pagesBiology Lseeon 8Laurie WadkinsNo ratings yet
- BiodiversityDocument8 pagesBiodiversityapi-423260675No ratings yet
- Endangered SpeciesDocument6 pagesEndangered Speciescalvinday180No ratings yet
- The Wild Life of Today and How To Help INFORMATIVE SpeechDocument3 pagesThe Wild Life of Today and How To Help INFORMATIVE SpeechKenneth ValNo ratings yet
- Global Perspectives ReportDocument5 pagesGlobal Perspectives ReportAzka UsmanNo ratings yet
- BiodiversityDocument3 pagesBiodiversityKetty Dávila DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Exotic AnimalsDocument5 pagesIntroduction of Exotic Animalsmadipalmer_No ratings yet
- What Is A Tropical RainforestDocument4 pagesWhat Is A Tropical Rainforestapi-269405494No ratings yet
- Casting para Pre-IntermediateDocument19 pagesCasting para Pre-IntermediateRildo Haro VargasNo ratings yet
- What Are Endangered Species?Document9 pagesWhat Are Endangered Species?malvikaNo ratings yet
- THE Extinction: Plants and AnimalsDocument15 pagesTHE Extinction: Plants and AnimalsKaren Baltazar BelarminoNo ratings yet
- Types of Biomes - CompiledDocument7 pagesTypes of Biomes - CompiledToni GutzNo ratings yet
- BrochureDocument2 pagesBrochureapi-264090303No ratings yet
- "Extinct" Amphibians Rediscovered After Nearly Half A CenturyDocument3 pages"Extinct" Amphibians Rediscovered After Nearly Half A CenturyCHRISTIAN SORIANONo ratings yet
- Endangered Animals - MarineDocument3 pagesEndangered Animals - MarineJoan JohnNo ratings yet
- The Tropical RainforestDocument14 pagesThe Tropical RainforestMylesNo ratings yet
- IE2 Course Pack: Essential Reading MaterialDocument15 pagesIE2 Course Pack: Essential Reading MaterialKim Hoang TaNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 FINALDocument1 pageActivity 2 FINALBrenndale SusasNo ratings yet
- Endangered Species Face ExtinctionDocument30 pagesEndangered Species Face ExtinctionGeetha SmileyNo ratings yet
- Endangered SpeciesDocument6 pagesEndangered SpeciesMelli MelloNo ratings yet
- Noting DetailsDocument16 pagesNoting DetailsleslieNo ratings yet
- Noting DetailsDocument16 pagesNoting Detailsleslie100% (1)
- Aireya - Lenguaje Animal - English Version - Parte6Document11 pagesAireya - Lenguaje Animal - English Version - Parte6Oswaldo FloresNo ratings yet
- The Status of Philippine Endemic Animal Species in 2020Document4 pagesThe Status of Philippine Endemic Animal Species in 2020Chacha Ortega NaquilaNo ratings yet
- Extincion de Animales InglesDocument3 pagesExtincion de Animales IngleslailagalicuaNo ratings yet
- Philippine Biodiversity Declining Due to Habitat Loss and OverexploitationDocument23 pagesPhilippine Biodiversity Declining Due to Habitat Loss and OverexploitationKyle OyaoNo ratings yet
- Save Endangered AnimalsDocument4 pagesSave Endangered AnimalsKatherine GarciaNo ratings yet
- The Mountain gorilla is a subspecies of the eastern gorillaDocument1 pageThe Mountain gorilla is a subspecies of the eastern gorillalunildaNo ratings yet
- Rare Species Vulnerability to ExtinctionDocument25 pagesRare Species Vulnerability to ExtinctionSoh Yi HanNo ratings yet
- Australian Tropical Savanna: A Unique Home for Marsupials and Eucalyptus TreesDocument15 pagesAustralian Tropical Savanna: A Unique Home for Marsupials and Eucalyptus TreesHaide Haspela HamorNo ratings yet
- Animal Extinction and Preservation - Animal Books | Children's Animal BooksFrom EverandAnimal Extinction and Preservation - Animal Books | Children's Animal BooksNo ratings yet
- Wildlife in the Oceans and Seas for Kids (Aquatic & Marine Life) | 2nd Grade Science Edition Vol 6From EverandWildlife in the Oceans and Seas for Kids (Aquatic & Marine Life) | 2nd Grade Science Edition Vol 6No ratings yet
- Checking Fixture STDDocument12 pagesChecking Fixture STDSandip PatilNo ratings yet
- Question and Answer Set of System Analysis andDocument209 pagesQuestion and Answer Set of System Analysis andpriyanka_kabra6No ratings yet
- E1224Document3 pagesE1224Alejandro Garcia FloresNo ratings yet
- DLPDocument10 pagesDLPPalaming Jerico MelegritoNo ratings yet
- Impact of Hazards on Women and Children in South AsiaDocument10 pagesImpact of Hazards on Women and Children in South AsiaBepul HossenNo ratings yet
- Prana Astrology in Kalacakra TantraDocument7 pagesPrana Astrology in Kalacakra TantraNiraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Car ParkingDocument65 pagesCar Parkingmaniblp100% (1)
- NewsNWSARReportWEB PDFDocument117 pagesNewsNWSARReportWEB PDFAnonymous NbMQ9YmqNo ratings yet
- Writing Assignment 3Document5 pagesWriting Assignment 3api-454037345No ratings yet
- Hacking Database ServersDocument7 pagesHacking Database ServersPuspala ManojkumarNo ratings yet
- Kyocera FS-C5350DN Kyocera Command Center Operation Guide Rev. 6.3 (Manual)Document66 pagesKyocera FS-C5350DN Kyocera Command Center Operation Guide Rev. 6.3 (Manual)Anonymous pp0zmS2oNo ratings yet
- Soal English Usbn 19Document8 pagesSoal English Usbn 19Gina Inayatul MaulaNo ratings yet
- IIA Los Angeles SAP Security PresentationDocument36 pagesIIA Los Angeles SAP Security PresentationCarol0% (1)
- Oracle Session Traffic LightsDocument13 pagesOracle Session Traffic Lightspiciul7001No ratings yet
- Online Examination System For AndroidDocument7 pagesOnline Examination System For AndroidSri Sai UniversityNo ratings yet
- UNDSZXCNCVXZDocument14 pagesUNDSZXCNCVXZPao Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- International Body Psychotherapy Journal Issue 2Document75 pagesInternational Body Psychotherapy Journal Issue 2Corina Tengher100% (2)
- Loop Fold Structure of Proteins: Resolution of Levinthal's ParadoxDocument24 pagesLoop Fold Structure of Proteins: Resolution of Levinthal's ParadoxJpds JoyantaNo ratings yet
- Diverse Narrative Structures in Contemporary Picturebooks: Opportunities For Children's Meaning-MakingDocument11 pagesDiverse Narrative Structures in Contemporary Picturebooks: Opportunities For Children's Meaning-MakingBlanca HernándezNo ratings yet
- Studies in Canadian Military History. Andrew B. Godefroy - Defence and Discovery Canada Military Space Program, 1945 Press (2011)Document257 pagesStudies in Canadian Military History. Andrew B. Godefroy - Defence and Discovery Canada Military Space Program, 1945 Press (2011)Rahmi KarayolNo ratings yet
- 4PH0 1P Que 20140515Document28 pages4PH0 1P Que 20140515ramexistsNo ratings yet
- Journal Review ChecklistsDocument7 pagesJournal Review ChecklistsAnkur ChopraNo ratings yet
- International Journal of English Language and Literature StudiesDocument9 pagesInternational Journal of English Language and Literature StudiesZara NurNo ratings yet
- 12 Computer Science Notes ch4D Arrays and Structures PDFDocument19 pages12 Computer Science Notes ch4D Arrays and Structures PDFSarathChelath100% (1)
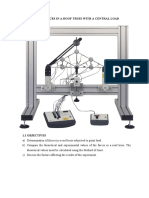
- Experiment 6 Forces in A Roof TrussDocument5 pagesExperiment 6 Forces in A Roof Trusshafiey89No ratings yet
- CATIA - Mold Tooling CreationDocument2 pagesCATIA - Mold Tooling CreationPlabsput Toin ToingNo ratings yet
- Esthetician Cover LetterDocument4 pagesEsthetician Cover Letterzys0vemap0m3100% (2)
- Girl UndergroundDocument52 pagesGirl UndergroundJuan Alberto GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Split-Up Syllabus For Class Ix 2020-21Document7 pagesSplit-Up Syllabus For Class Ix 2020-21fire gamerNo ratings yet
- 0 Chhavi Gupta Resume PDFDocument3 pages0 Chhavi Gupta Resume PDFanon_630797665No ratings yet