Professional Documents
Culture Documents
English SL Cirriculum
Uploaded by
Vansh RajaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
English SL Cirriculum
Uploaded by
Vansh RajaCopyright:
Available Formats
International Baccalaureate
Diploma Programme Subject Brief
Language A: literature
First assessments for SL and HL—2021
The Diploma Programme (DP) is a rigorous pre-university course of study designed for students in the 16 to 19 age
range. It is a broad-based two-year course that aims to encourage students to be knowledgeable and inquiring,
but also caring and compassionate. There is a strong emphasis on encouraging students to develop
intercultural understanding, open-mindedness, and the attitudes necessary for them to respect LOMA PROGRAM
and evaluate a range of points of view. B DIP ME
I DIES IN LANGUA
STU D LITERATUR GE
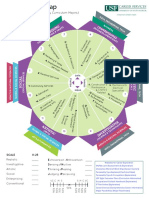
The course is presented as six academic areas enclosing a central core. Students study two AN E
modern languages (or a modern language and a classical language), a humanities or social ED G E
A
IN SO
UIS GE
WL
ON
EX
DI CIE
ND
science subject, an experimental science, mathematics and one of the creative arts.
ACQ GUA
T
NO
VID TIE
ITI
CHES TO TEAC
EN
UAL S
LAN
Instead of an arts subject, students can choose two subjects from another area. It is this
K
OA HI
OF
DE
PR
S
comprehensive range of subjects that makes the Diploma Programme a demanding
NG
D ES
THEORY
AP
course of study designed to prepare students effectively for university entrance. In
SAY
each of the academic areas students have flexibility in making their choices, which
means they can choose subjects that particularly interest them and that they may wish
AP
PR
NG
CS
OA NI
CHES O LE AR
to study further at university.
S CI
ATI
EA T
CR
CE
I
TIV RV
EM
EN
I T Y, SE
A C T I V I T Y,
CE
H
Normally, three subjects (and not more than four) are taken at higher level (HL), and
AT
S
M
the others are taken at standard level (SL). The IB recommends 240 teaching hours
IN
for HL subjects and 150 hours for SL. Subjects at HL are studied in greater depth and TE T H E A R TS
E SS
RN DN
breadth than at SL. AT I O E
N A L– M I N D
In addition, three core elements—the extended essay, theory of knowledge and creativity,
activity, service—are compulsory and central to the philosophy of the programme.
This IB DP subject brief has three key components:
I. Course description and aims II. Curriculum model overview III. Assessment model
I. Course description and aims
The language A: literature aims at exploring the various manifesta- zz develop an understanding of relationships between texts and a
tions of literature as a particularly powerful mode of writing across variety of perspectives, cultural contexts, and local and global issues,
cultures and throughout history. The course aims at developing and an appreciation of how they contribute to diverse responses and
an understanding of factors that contribute to the production open up multiple meanings
and reception of literature—the creativity of writers and readers, zz develop an understanding of the relationships between studies in
the nature of their interaction with their respective contexts and language and literature and other disciplines
with literary tradition, the ways in which language can give rise to
zz communicate and collaborate in a confident and creative way
meaning and/or effect, and the performative and transformative
potential of literary creation and response. Through close analysis zz foster a lifelong interest in and enjoyment of language and literature.
of a range of literary texts in a number of literary forms and from
different times and places, students will consider their own inter-
pretations as well as the critical perspectives of others, to explore II. Curriculum model overview
how such positions are shaped by cultural belief systems and to
negotiate meanings for texts. Recommended
teaching hours
The aims of studies in language and literature courses are to enable
Syllabus component SL HL
students to:
zz engage with a range of texts, in a variety of media and forms, from Readers, writers and texts 50 80
different periods, styles and cultures
Time and space 50 80
zz develop skills in listening, speaking, reading, writing, viewing,
presenting and performing Intertextuality: connecting texts 50 80
zz develop skills in interpretation, analysis and evaluation Total teaching hours 150 240
zz develop sensitivity to the formal and aesthetic qualities of texts and
an appreciation of how they contribute to diverse responses and
open up multiple meanings
© International Baccalaureate Organization 2019
International Baccalaureate® | Baccalauréat International® | Bachillerato Internacional®
III. Assessment model Assessment at a glance
It is the intention of this course that students are able to fulfill the Weighting
following assessment objectives: Time of final
(hours) grade (%)
1. Know, understand and interpret: Type of
zz a range of texts, works and/or performances, and their meanings assessment Format of assessment SL HL SL HL
and implications
zz contexts in which texts are written and/or received
External
zz elements of literary, stylistic, rhetorical, visual and/or performance Paper 1: Guided analysis of 1.25 2.25 35 35
craft Guided unseen literary passage/
zz features of particular text types and literary forms. literary passages from different
2. Analyse and evaluate: analysis text types.
zz ways in which the use of language creates meaning
Paper 2: Comparative essay 1.75 1.75 35 25
zz uses and effects of literary, stylistic, rhetorical, visual or theatrical Comparative based on two literary
techniques essay works written in
zz relationships among different texts response to a choice
zz ways in which texts may offer perspectives on human concerns.
of one out of four
questions.
3. Communicate:
zz ideas in clear, logical and persuasive ways HL essay Written coursework 20
zz in a range of styles, registers and for a variety of purposes and component: 1,200–1,500
situations word essay on one work
zz (for literature and performance only) ideas, emotion, character
studied.
and atmosphere through performance. Internal
Individual Prepared oral response 30 20
oral on the way that one
work originally written
in the language studied
and one work studied
in translation have
approached a common
global issue.
About the IB: For over 50 years, the IB has built a reputation for high-quality, challenging programmes of education that develop internationally
minded young people who are well prepared for the challenges of life in the 21st century and are able to contribute to creating a better, more
peaceful world.
For further information on the IB Diploma Programme, visit: www.ibo.org/en/programmes/diploma-programme/.
Complete subject guides can be accessed through the programme resource centre or purchased through the IB store: store.ibo.org.
For more on how the DP prepares students for success at university, visit: www.ibo.org/en/university-admission.
You might also like
- Reading Critically, Writing Well - A Reader and Guide, Sixth Edition PDFDocument660 pagesReading Critically, Writing Well - A Reader and Guide, Sixth Edition PDFNgô Thị Cẩm Thùy83% (6)
- State of The Global Workplace 2022 DownloadDocument170 pagesState of The Global Workplace 2022 DownloadSeth Bautista0% (1)
- IBDP Business Management Subject Guide (First Assessment 2024)Document77 pagesIBDP Business Management Subject Guide (First Assessment 2024)jadenNo ratings yet
- 717023-Dantes Guide To Hell - Monster ManualDocument124 pages717023-Dantes Guide To Hell - Monster Manualtaylor valery Grenier100% (1)
- Beth Moore Support Studies PosterpdfDocument1 pageBeth Moore Support Studies PosterpdfLIDERAZGO ACTIVONo ratings yet
- Bco Grade 8 English First Quarter PDFDocument4 pagesBco Grade 8 English First Quarter PDFAudhrey BravoNo ratings yet
- IU Vascular Sample SeptDocument21 pagesIU Vascular Sample SeptAlexander Edo Tondas67% (3)
- Daniel Tiffany - My Silver Planet A Secret History of Poetry and KitschDocument312 pagesDaniel Tiffany - My Silver Planet A Secret History of Poetry and KitschJuan José Guerra100% (3)
- Subject Brief MergedDocument55 pagesSubject Brief Mergedmadiyar.zhNo ratings yet
- International Baccalaureate Diploma Programme Subject Brief: Individuals and Societies: PsychologyDocument2 pagesInternational Baccalaureate Diploma Programme Subject Brief: Individuals and Societies: PsychologyCarola ValdésNo ratings yet
- IB Language Ab Initio Guide First Assessment in 2020Document2 pagesIB Language Ab Initio Guide First Assessment in 2020Susan SharkeyNo ratings yet
- HL Economics enDocument2 pagesHL Economics enTrúc HồNo ratings yet
- History HL 2020 EngDocument2 pagesHistory HL 2020 Engapi-678513549No ratings yet
- IB Diploma Programme Information and Subject Briefs June 2021Document7 pagesIB Diploma Programme Information and Subject Briefs June 2021chloe.paleoNo ratings yet
- Diploma Programme Core: Theory of Knowledge: I. Course Description and AimsDocument3 pagesDiploma Programme Core: Theory of Knowledge: I. Course Description and AimsViki KumarNo ratings yet
- Geography SL HL 2017 enDocument2 pagesGeography SL HL 2017 enAryan ShahNo ratings yet
- Social & Cultural AnthropologyDocument2 pagesSocial & Cultural Anthropologylorrain hussainNo ratings yet
- 11-HUMSS: SUMMARY OF GRADES (1st Quarter, 1st Semester 2020-2021)Document11 pages11-HUMSS: SUMMARY OF GRADES (1st Quarter, 1st Semester 2020-2021)Giancarla Maria Lorenzo DingleNo ratings yet
- Site Dev - Lingion R1aDocument1 pageSite Dev - Lingion R1aEphrem Marx AparicioNo ratings yet
- May, Tim Perry Beth. Social Research Issues, Methods and Process (2022)Document338 pagesMay, Tim Perry Beth. Social Research Issues, Methods and Process (2022)jpinedad2300No ratings yet
- Final SDPDocument1 pageFinal SDPMaehely Jelle AdolfoNo ratings yet
- Bil. Nama Murid: I I& K ES IH AT AN LDocument57 pagesBil. Nama Murid: I I& K ES IH AT AN LROHINAH BT YULO KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- Pastoralist Resilience PortraitDocument1 pagePastoralist Resilience PortraitBenny YosephNo ratings yet
- Abingdon: N G H AMDocument33 pagesAbingdon: N G H AMdaggerpressNo ratings yet
- Copper Testing - Quick Reference Guide 1-5Document4 pagesCopper Testing - Quick Reference Guide 1-5Daniel PiresNo ratings yet
- Nawinna House - Electrical PDFDocument1 pageNawinna House - Electrical PDFShyama WijesingheNo ratings yet
- 1 Ground Floor Plan: Existing Boundary WallDocument1 page1 Ground Floor Plan: Existing Boundary WallShyama WijesingheNo ratings yet
- Isometric View 2/F Water Supply System B: DN Exit DNDocument1 pageIsometric View 2/F Water Supply System B: DN Exit DNJesson Diaz VicenteNo ratings yet
- Projector Manual 3842Document67 pagesProjector Manual 3842Amit NandiNo ratings yet
- 17041aa108 DWG PDF-modeldDocument1 page17041aa108 DWG PDF-modeldVishnu ThipparthiNo ratings yet
- Vadacha Mala L SectionDocument1 pageVadacha Mala L SectionPrashant GaradNo ratings yet
- A Brief History of Clinical Airway ManagementDocument4 pagesA Brief History of Clinical Airway ManagementJames Lemuel Bato AquinoNo ratings yet
- ArDOT Roundabout Checklist (08-01-18) PDFDocument2 pagesArDOT Roundabout Checklist (08-01-18) PDFJames trippNo ratings yet
- 2023 09 08 08 16 12 - 0aba523cDocument8 pages2023 09 08 08 16 12 - 0aba523cnouhailamessaoudyNo ratings yet
- Moog MinitaurDocument19 pagesMoog Minitaurjake_spurgeon_2No ratings yet
- Summary-Of-Grade-Quarter 1 2022-2023Document1 pageSummary-Of-Grade-Quarter 1 2022-2023Mariel rendonNo ratings yet
- Pianist - October-November 2016Document91 pagesPianist - October-November 2016Nick Papas100% (8)
- 11-HUMSS: Top Performing StudentsDocument8 pages11-HUMSS: Top Performing StudentsGiancarla Maria Lorenzo DingleNo ratings yet
- DENAH GEREJA IMANUEL BAUTASIK-ModelDocument1 pageDENAH GEREJA IMANUEL BAUTASIK-ModelVia YunusNo ratings yet
- Thought Circle Worksheet: Theme: Class: StudentDocument1 pageThought Circle Worksheet: Theme: Class: StudentMichelle MagbanuaNo ratings yet
- Landscape Architecture PortfolioDocument25 pagesLandscape Architecture PortfolioAnna PauletteNo ratings yet
- Gig Car Share Home Zone 2017-3-16 PDFDocument1 pageGig Car Share Home Zone 2017-3-16 PDFRecordTrac - City of OaklandNo ratings yet
- Selasar Dakwah: Kebun RakyatDocument1 pageSelasar Dakwah: Kebun RakyatMuhammad Irhash MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Figure 1: The Feeling Wheel: Remo RsefulDocument1 pageFigure 1: The Feeling Wheel: Remo RsefulMohammad Faiz AkbarNo ratings yet
- The Feeling WheelDocument1 pageThe Feeling Wheelbell assaddinNo ratings yet
- KKKKKDocument17 pagesKKKKKkukoyigbemigaNo ratings yet
- World of Work Map 2016bDocument1 pageWorld of Work Map 2016bLluís Marrugat ViñaNo ratings yet
- Tos Ptest1 G11 Applied-EconomicsDocument1 pageTos Ptest1 G11 Applied-EconomicsMa. Galil VarcaNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Site Plan of Maynard High SchoolDocument1 pagePreliminary Site Plan of Maynard High SchoolbeaconvillagerNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Unit9 Extrapractice BeDocument2 pagesIntermediate Unit9 Extrapractice BeAnastasiia GorodniaNo ratings yet
- Socialized Duplex: Water TankDocument1 pageSocialized Duplex: Water TankJEAN-YVES TRONCONo ratings yet
- Academic Map EnglishDocument1 pageAcademic Map Englishapi-363392618No ratings yet
- 2008 Webster MO Precinct Vote CanvassDocument1 page2008 Webster MO Precinct Vote CanvassJohn MNo ratings yet
- Graficos Circulares de BachDocument1 pageGraficos Circulares de BachStellaEstel100% (1)
- Tridhaatu VihaanDocument9 pagesTridhaatu VihaanTridhaatu NakshaktraNo ratings yet
- Stu - Ge Stu - Ge: Listes Des EtudiantsDocument1 pageStu - Ge Stu - Ge: Listes Des EtudiantsSimohamed BenmoussaNo ratings yet
- THE Vall EY: TH E HIL LSDocument2 pagesTHE Vall EY: TH E HIL LSAlexis SauvageotNo ratings yet
- Topic School Rules: Da y Remark SDocument4 pagesTopic School Rules: Da y Remark SKayè Sy PiansayNo ratings yet
- Golf Club: Multi Puropse Hall Roof DeckDocument1 pageGolf Club: Multi Puropse Hall Roof DeckRaphael AustriaNo ratings yet
- Zonificacion CorelDocument1 pageZonificacion CorelJafet GonzalesNo ratings yet
- ERO 15569 Effective School Evaluation June16 FULL WEB 002Document44 pagesERO 15569 Effective School Evaluation June16 FULL WEB 002William J ElliottNo ratings yet
- Strange Case of DR Jekyll and MR HydeDocument158 pagesStrange Case of DR Jekyll and MR HydePrince Taiwo Oluwaseun Gods powerNo ratings yet
- Distances Table (In Nautical Miles)Document1 pageDistances Table (In Nautical Miles)muhammad rizalNo ratings yet
- Ibdp Learner ProfilDocument2 pagesIbdp Learner ProfilVansh RajaNo ratings yet
- Computer ScineceDocument3 pagesComputer ScineceVansh RajaNo ratings yet
- Ess SL CirriculumDocument2 pagesEss SL CirriculumVansh RajaNo ratings yet
- 4 ComputerhlDocument2 pages4 ComputerhlVansh RajaNo ratings yet
- BusinessDocument6 pagesBusinessVansh RajaNo ratings yet
- Economics FM 22Document5 pagesEconomics FM 22Vansh RajaNo ratings yet
- Cas BriefingDocument2 pagesCas BriefingholyshakeNo ratings yet
- Is Childrens Literature Dead ExtractDocument2 pagesIs Childrens Literature Dead ExtractKRISHNANo ratings yet
- 1-5 Chapter QuestionsDocument4 pages1-5 Chapter QuestionsAnnalicia LopezNo ratings yet
- Selections From Contemporary American Novel II Schedule 2022-2023 II NDocument28 pagesSelections From Contemporary American Novel II Schedule 2022-2023 II NFırat KaplanNo ratings yet
- A Literature of Their Own - Elaine ShowalterDocument3 pagesA Literature of Their Own - Elaine ShowalterMidiã Ellen100% (1)
- The Kite by William Summerset MaughamDocument2 pagesThe Kite by William Summerset MaughamLeider David Garnica VargasNo ratings yet
- Audun Engelstad - Playing The Producers Game Adaptation and FidelityDocument15 pagesAudun Engelstad - Playing The Producers Game Adaptation and FidelityJimmy NewlinNo ratings yet
- Descripción de La Reina Madre Del Oeste. Desde El Periodo Han.Document1 pageDescripción de La Reina Madre Del Oeste. Desde El Periodo Han.ABCNo ratings yet
- R.L StineDocument7 pagesR.L StineMilanjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- 1D Oracle 1DDocument2 pages1D Oracle 1DLiubartas Aleksiejus0% (1)
- Philsin College Rizal Inc.: Poem WritingDocument4 pagesPhilsin College Rizal Inc.: Poem WritingGlaiza QuingNo ratings yet
- Twelfth Night:Act 1 and 2 (Abridged Version)Document13 pagesTwelfth Night:Act 1 and 2 (Abridged Version)KatherineNo ratings yet
- Turnitin Skripsi Ramli, BismillahDocument46 pagesTurnitin Skripsi Ramli, Bismillahryza mauryzNo ratings yet
- Movie Comparison HP V LotrDocument4 pagesMovie Comparison HP V LotrNicoleBarryNo ratings yet
- English Literature (Life Sketch of Ferdinand)Document8 pagesEnglish Literature (Life Sketch of Ferdinand)paulabishek799No ratings yet
- Bewitched: Form and Female Agency in Madeline Miller's "Circe"Document40 pagesBewitched: Form and Female Agency in Madeline Miller's "Circe"Marko PejoskiNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2,040 pagesUntitledinacrapNo ratings yet
- Present Simple or Present ContinuousDocument4 pagesPresent Simple or Present ContinuousGaraNo ratings yet
- The Home and The World (Rabindranath Tagore)Document357 pagesThe Home and The World (Rabindranath Tagore)visionNo ratings yet
- Hamlet ReviewDocument1 pageHamlet ReviewAlexandra DxNo ratings yet
- Verdins - JBS, 52.2, 179-191Document14 pagesVerdins - JBS, 52.2, 179-191Kārlis VērdiņšNo ratings yet
- MemoirDocument3 pagesMemoirMia ManayagaNo ratings yet
- Test 1 1. Mark The Letter A, B, C or D To Indicate The Underlined Part That Needs Correction in Each of The Following QuestionsDocument7 pagesTest 1 1. Mark The Letter A, B, C or D To Indicate The Underlined Part That Needs Correction in Each of The Following QuestionsTuyết NhưNo ratings yet
- European Literature BackgroundDocument2 pagesEuropean Literature BackgroundRichlyNo ratings yet
- Troy-WPS OfficeDocument2 pagesTroy-WPS OfficeMuheedatNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ArabicDocument15 pagesIntroduction To ArabicShobe LeeNo ratings yet
- Framing Pictures A Reader-Response Criticism of Rob Cham's and Harry Monzon's Selected Wordless BooksDocument26 pagesFraming Pictures A Reader-Response Criticism of Rob Cham's and Harry Monzon's Selected Wordless BooksBeiya ClaveriaNo ratings yet
- DEL NEVO, Matthew. Baudelaire's AestheticDocument11 pagesDEL NEVO, Matthew. Baudelaire's AestheticRafaelDoValleNo ratings yet