Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MEAEmod 02 Slide 04
Uploaded by
D-2009 Saswat Pritam Baruah0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views17 pagesApplied electronics part
Original Title
MEAEmod02slide04
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentApplied electronics part
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views17 pagesMEAEmod 02 Slide 04
Uploaded by
D-2009 Saswat Pritam BaruahApplied electronics part
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 17
APPLIED
ELECTRONICS
ASSAM SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY UNIVERSITY
B.Tech : 4thSemester: Mechanical Engineering
Sub code : ECE181407
Module 2: DIODES
ZENER DIODES
INTRODUCTION…
A heavily doped semiconductor diode which
is designed to operate in reverse direction is
known as the Zener diode.
In other words, the diode which is specially
designed for optimising the breakdown region
is known as the Zener diode.
A Zener diode not only allows current to
flow from anode to cathode but also, in the
reverse direction on reaching the Zener
voltage. Due to this functionality, Zener
diodes are the most commonly used
semiconductor diodes.
Zener Diode Circuit
Diagram
The circuit diagram of the Zener diode is
shown above.
The Zener diode is employed in reverse
biasing. The reverse biasing means the n-type
material of the diode is connected to the
positive terminal of the supply and the P-type
material is connected to the negative
terminal of the supply. The depletion region
of the diode is very thin because it is made of
the heavily doped semiconductor material.
Working of Zener Diode
The Zener diode is made up of heavily
doped semiconductor material. The heavily
doped means the high-level impurities is
added to the material for making it more
conductive. The depletion region of the
Zener diode is very thin because of the
impurities. The heavily doping material
increases the intensity of the electric field
across the depletion region of the Zener
diode even for the small reverse voltage.
Working:
When no biasing is applied across the
Zener diode, the electrons remains in the
valence band of the p-type material and
no current flow through the diode.
The electrons of the valence band easily
move from one band to another when
the external energy is applied across it.
Working:
When the reverse bias applies across the diode and
the supply voltage is equal to the Zener voltage then
it starts conducting in the reverse bias direction. The
Zener voltage is the voltage at which the depletion
region completely vanish.
The reverse bias applies across the diode increases
the intensity of electric field across the depletion
region. Thus, it allows the electrons to move from the
valence band of P-type material to the conduction
band of N-type material. This transferring of valence
band electrons to the conduction band reduces the
barrier between the p and n-type material. When the
depletion region become completely vanish the diode
starts conducting in the reverse biased.
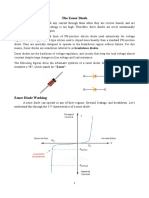
V-I Characteristics of Zener Diode
The VI characteristic graph of the Zener diode
is shown .
This curve shows that the Zener diode, when
connected in forwarding bias, behaves like an
ordinary diode. But when the reverse voltage
applies across it and the reverse voltage rises
beyond the predetermined rating, the Zener
breakdown occurs in the diode.
At Zener breakdown voltage the current
starts flowing in the reverse direction. The
graph of the Zener breakdown is not exactly
vertical as shown which shows that the Zener
diode has resistance.
The voltage across the Zener is represented
by the equation shown below.
V = VZ + IZRZ
VI Characteristics:
Application of Zener Diode:
Zener diode as a voltage regulator
Zener diode in over voltage protection
Zener diode in clipping circuits
Zener Diode as a Voltage Regulator
Zener Diode as a Voltage Regulator
Zener diode is used as a Shunt voltage
regulator for regulating voltage across small
loads.
The breakdown voltage of Zener diodes
will be constant for a wide range of current.
Zener diode is connected parallel to the
load to make it reverse bias and once the
Zener diode exceeds knee voltage, the
voltage across the load will become
constant.
Voltage Regulator:
There is a series resistor connected to the circuit in
order to limit the current into the diode. It is
connected to the positive terminal of the d.c. It works
in such a way the reverse-biased can also work in
breakdown conditions. Here ordinary junction diode is
used because the low power rating diode can get
damaged when we apply reverse bias above its
breakdown voltage. When the minimum input voltage
and the maximum load current is applied, the Zener
diode current should always be minimum.
Since the input voltage and the required output voltage
is known, it is easier to choose a Zener diode with a
voltage approximately equal to the load voltage, i.e.
VZ = VL.
Voltage Regulator:
The value of the series resistor is written as
RS = (VL − VZ)IL
Current through the diode increases when
the voltage across the diode tends to
increase which results in the voltage drop
across the resistor.
Similarly, the current through the diode
decreases when the voltage across the diode
tends to decrease. Here, the voltage drop
across the resistor is very less, and the
output voltage results normally.
You might also like
- DiodeDocument13 pagesDiodeKarla MaalihanNo ratings yet
- Automatic Battery Charger Using SCRDocument36 pagesAutomatic Battery Charger Using SCRAurea May Sabater67% (3)
- Function DescriptionDocument14 pagesFunction DescriptionAndres Torres100% (2)
- 200080157-00 Manual Instalacion SMART OLT TGMS v1.4.0 Rev0Document14 pages200080157-00 Manual Instalacion SMART OLT TGMS v1.4.0 Rev0Moises AntonioNo ratings yet
- AUDI A6 Q5 ESL ELV Module J518 Repair Solution Repair KitDocument5 pagesAUDI A6 Q5 ESL ELV Module J518 Repair Solution Repair Kitt77No ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument13 pagesZener DiodePhenoमिनल IdiotsNo ratings yet
- Arduino Based Collision Detection Warning SystemDocument51 pagesArduino Based Collision Detection Warning Systemanil kumarNo ratings yet
- Variable-Frequency Drive - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument14 pagesVariable-Frequency Drive - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaBala SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode Characteristics and ApplicationsDocument3 pagesZener Diode Characteristics and ApplicationsANIL KUMAR YARAMALANo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Diode in Reverse Bias Condition: Basic Types of DiodesDocument7 pagesSemiconductor Diode in Reverse Bias Condition: Basic Types of DiodesrahulNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode Characteristics and ApplicationsDocument3 pagesZener Diode Characteristics and ApplicationsANIL KUMAR YARAMALANo ratings yet
- Diode - Definition, VI Characteristics, and Breakdown in Zener Diode - DiodeDocument8 pagesDiode - Definition, VI Characteristics, and Breakdown in Zener Diode - DiodehavejsnjNo ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument3 pagesZener Diodekanak-825262No ratings yet
- AE Unit - 1Document12 pagesAE Unit - 1aamirnasirNo ratings yet
- Light Emitting DiodeDocument27 pagesLight Emitting DiodeTesfaye DemeNo ratings yet
- BE UNIT-IIDocument12 pagesBE UNIT-IIhenryhorrid384No ratings yet
- Zener Diode As A WaveshaperDocument15 pagesZener Diode As A WaveshaperpriyaNo ratings yet
- U-1 (Boe 8-18)Document11 pagesU-1 (Boe 8-18)Tisha SetiaNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode Applications 1. Zener Diode As A VoltageDocument3 pagesZener Diode Applications 1. Zener Diode As A VoltageSaravananNo ratings yet
- DiodeDocument36 pagesDiodeJacobNo ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument1 pageZener DiodeArasu LoganathanNo ratings yet
- How Zener Diodes Regulate VoltageDocument22 pagesHow Zener Diodes Regulate VoltageRafath UmaimathNo ratings yet
- Active Electronic Components 1Document43 pagesActive Electronic Components 1Kanchana SenadheeraNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode Guide: Construction, Working & ApplicationsDocument29 pagesZener Diode Guide: Construction, Working & ApplicationsVarsha PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument14 pagesZener DiodeTanya SoodNo ratings yet
- DiodeDocument20 pagesDiodehabtemariam mollaNo ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument7 pagesZener DiodeMuhammad AsgharNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode Guide - Construction, Working, Applications & Breakdown CharacteristicsDocument16 pagesZener Diode Guide - Construction, Working, Applications & Breakdown CharacteristicsJsmBhanot83% (6)
- Ece20l 07Document7 pagesEce20l 07Diane Carina MendozaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1e PHY125Document19 pagesUnit 1e PHY1252023275863.rishiNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode Voltage RegulatorDocument27 pagesZener Diode Voltage Regulatorمحمد رافد حميد B/23No ratings yet
- Zener Diode ExplanationDocument6 pagesZener Diode ExplanationShubham SwamiNo ratings yet
- Theejaswini PhyDocument22 pagesTheejaswini Phyindianaashika72No ratings yet
- Basic Analog Electrnics PPT IN PDFDocument67 pagesBasic Analog Electrnics PPT IN PDFMusa KunrooNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument4 pagesZener Diode - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaManitNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 NotesDocument54 pagesUnit 3 Notesakhilyadavjerri488No ratings yet
- University Kuala Lumpur Malaysian Institute of Aviation TechnologyDocument6 pagesUniversity Kuala Lumpur Malaysian Institute of Aviation Technologyvishnu ramaNo ratings yet
- Edu Expansion Presentation (Circuits)Document16 pagesEdu Expansion Presentation (Circuits)nandinigupta613No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document32 pagesChapter 3api-394738731No ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument14 pagesZener DiodePrasanth. SNo ratings yet
- Project Title: Fabrication of An Automatic Battery Charger Using "SCR"Document36 pagesProject Title: Fabrication of An Automatic Battery Charger Using "SCR"Marsu HardionoNo ratings yet
- Zenner DiodeDocument23 pagesZenner DiodeKrishanu NaskarNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document81 pagesUnit 1Eswar suryaNo ratings yet
- What Is A Diode?Document48 pagesWhat Is A Diode?B SaiNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode - WikipediaDocument29 pagesZener Diode - WikipediaLupu DanielNo ratings yet
- The Zener Diode: Voltage RegulationDocument3 pagesThe Zener Diode: Voltage RegulationAMIT KUMAR SINGHNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode TheoryDocument7 pagesZener Diode TheoryCarlos IbaNo ratings yet
- Physics Project File: MADE BY: - CLASS-12 SectionDocument12 pagesPhysics Project File: MADE BY: - CLASS-12 SectionAryan JindalNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument38 pagesPhysics ProjectRitu FalwariaNo ratings yet
- The Zener DiodeDocument4 pagesThe Zener DiodeKeshav JhaNo ratings yet
- 3 Zener DiodeDocument16 pages3 Zener DiodeGurudevNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument3 pagesZener Diode: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaApri ZaldyNo ratings yet
- D IODESDocument62 pagesD IODESCllyan Reyes0% (1)
- Electronics-Tutorials - Ws-The Zener DiodeDocument10 pagesElectronics-Tutorials - Ws-The Zener DiodeVenki EdeNo ratings yet
- Zener diode basics for voltage regulationDocument4 pagesZener diode basics for voltage regulationLalita KumariNo ratings yet
- Aim of Experiment: To Plot Forward & Reverse Biased Characteristics ofDocument4 pagesAim of Experiment: To Plot Forward & Reverse Biased Characteristics ofTapobroto ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode 1Document8 pagesZener Diode 1tamjeedahmad1581947No ratings yet
- ElectronicsDocument4 pagesElectronicsAYUSHKA NANDANo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics UNIT1Document74 pagesBasic Electronics UNIT1AnoushkaNo ratings yet
- Soumyadip Kalsa, Roll - 33, Sub - BiologyDocument13 pagesSoumyadip Kalsa, Roll - 33, Sub - BiologySMOKER GAMINGNo ratings yet
- PN Junction Diode FundamentalsDocument8 pagesPN Junction Diode FundamentalsJames KamandaNo ratings yet
- Zener PracticalDocument6 pagesZener PracticalAzim KhanNo ratings yet
- ZM-R5860-BGA Rework Station: Shenzhen Zhuomao Technology Co., LTDDocument2 pagesZM-R5860-BGA Rework Station: Shenzhen Zhuomao Technology Co., LTDRecon G BonillaNo ratings yet
- MMIC Processing Techniques and Design ConsiderationsDocument23 pagesMMIC Processing Techniques and Design ConsiderationsVishal IyerNo ratings yet
- fork() System Call in CDocument8 pagesfork() System Call in CAbdul WahabNo ratings yet
- Internetworking With ATMDocument21 pagesInternetworking With ATMoureducation.in100% (2)
- 7N90Document6 pages7N90ttnaingNo ratings yet
- Fs2311001 Autopulse AP 100 Product Overview Us DigitalDocument2 pagesFs2311001 Autopulse AP 100 Product Overview Us DigitalengrjameschanNo ratings yet
- CSEAnnexDocument6 pagesCSEAnnexaripermana002No ratings yet
- Omni 400Document96 pagesOmni 400JoséOrdóñezCedeñoNo ratings yet
- MAX86160 Integrated Heart-Rate Sensor For In-Ear ApplicationsDocument42 pagesMAX86160 Integrated Heart-Rate Sensor For In-Ear Applicationsmaria jose rodriguez lopezNo ratings yet
- Flyckt Marmonier PDFDocument311 pagesFlyckt Marmonier PDFArifRachmanNo ratings yet
- TCL CON DAÑ OS L32D10 MT23LA Service Manual PDFDocument43 pagesTCL CON DAÑ OS L32D10 MT23LA Service Manual PDFAxl MendozaNo ratings yet
- DatasheetDocument4 pagesDatasheetcendrezNo ratings yet
- PG 2V1000Document2 pagesPG 2V1000Juan EsNo ratings yet
- HP ColorLJ9500 MFP SMDocument574 pagesHP ColorLJ9500 MFP SMcwalters7No ratings yet
- TESDA-Approved Dressmaking Tools and SuppliesDocument72 pagesTESDA-Approved Dressmaking Tools and SuppliesElonah Jean ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- ZXGD3005E6: 25V 10A Gate Driver in Sot26Document8 pagesZXGD3005E6: 25V 10A Gate Driver in Sot26Manoel BonfimNo ratings yet
- DMX Patch ChartDocument4 pagesDMX Patch Chartjuris francisNo ratings yet
- HV10 Serisi Klavuz V5.0Document67 pagesHV10 Serisi Klavuz V5.0daniel hughesNo ratings yet
- Online Booking System For Car ParkingDocument4 pagesOnline Booking System For Car Parkingkalanakal9669No ratings yet
- Introduction To Computers (BBA)Document27 pagesIntroduction To Computers (BBA)Sam Singh100% (1)
- Polycrystalline Solar Module: An Everexceed High-Power Residential Solar Module Isan Aesthetic To Most Roofs AdditionDocument2 pagesPolycrystalline Solar Module: An Everexceed High-Power Residential Solar Module Isan Aesthetic To Most Roofs AdditionAmrina RosyadaNo ratings yet
- Blackbody Radiation Derivation of Planck S Radiation LawDocument20 pagesBlackbody Radiation Derivation of Planck S Radiation Lawpauljkt1No ratings yet
- Interference and Capacity in Cellular SystemsDocument19 pagesInterference and Capacity in Cellular SystemsAyo OlaNo ratings yet
- Parallel Generators Don't Divide Reactive KVAR Load Equally - Electrical Engineering Stack ExchangeDocument3 pagesParallel Generators Don't Divide Reactive KVAR Load Equally - Electrical Engineering Stack ExchangeLohidas PailaNo ratings yet
- Electrical System PDFDocument2 pagesElectrical System PDFKent WaiNo ratings yet