Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Working Plan of Care Portfolio
Uploaded by
api-583124801Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Working Plan of Care Portfolio
Uploaded by
api-583124801Copyright:
Available Formats
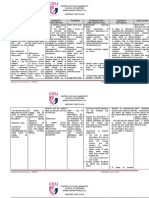
WORKING PLAN OF CARE
Subjective Findings: bizarre, catatonic behavior, not medication compliant, flat affect; was found staring at buildings
wearing inappropriate apparel for the weather; “They follow me around, watching me”. . He refused to communicate
with me when I interacted with Text
him. He stayed in his room for a majority of the clinical day.
Legal Status: PC2 Age: 66… Sex:Text M Employment ………………
Status: unemployed
DSM-5 Diagnosis Current Stressors/Reason For Hospitalization
Pt was found standing outside of businesses staring at them. He
Paranoid Schizophrenia was dressed in apparel that was not appropriate for the weather
conditions. He was also displaying bizarre, catatonic behavior. He
is not compliant with care plan or meds.
Assessment Tools Utilized Relevant Medications Cultural Needs
1. Therapeutic communication 1. lorazepam (Ativan) No cultural needs that affect
2. Information from chart 2. melatonin care
I was not able to utilize assessment tools that required the 3. NicoDerm CQ transdermal
client to speak with me because he was choosing not to patch
verbally communicate with me. 4. nicotine polarcrilex
(Nicorette)
5. acetaminophen (Tylenol)
1. NURSING DIAGNOSIS R/T AEB
Impaired verbal communication r/t psychological barriers as evidenced by refusal to speak.
INTERVENTIONS RATIONALES
1. Use therapeutic communication techniques: speak in a well- 1. Effective communication entails involving clients, being
modulated voice, use simple communication, maintain eye sensitive to client needs, and ensuring client understanding (
contact at the client's level, get the client's attention before O'Hagan et al, 2014 ).
speaking, and show concern for the client.
2. Ignoring clients was found to be a negative communication
2. Avoid ignoring the client with verbal impairment; be strategy ( O'Hagan et al, 2014 ).
engaged and provide meaningful responses to client concerns.
Place call light within reach of client who cannot verbally call 3. Viewing patients with communicative difficulties in a
for help. holistic manner cultivates empowering communication (
Parsloe & Carroll, 2018 )
3. Validate clients’ feelings, focus on their strengths, and assist
them in gaining confidence in identifying needs.
EVALUATION/CLIENT RESPONSE/PROGRESS
During clinical hours, the client did not verbally communicate with me. I utilized therapeutic communication techniques while
interacting with the client, I did not ignore him while he walked past me in the hallway, and I told him to let me know if he
needed anything. He had no verbal response to any interventions. What did work from these interventions was that the client
made eye contact with me as I spoke therapeutically to him.
2. NURSING DIAGNOSIS R/T AEB
Social Isolation r/t neurobehavioral manifestations as evidenced by isolation from others while on the unit.
INTERVENTIONS RATIONALES
1. Establish a therapeutic relationship with the client. 1. In her study, Skingley (2013) suggested that many of the
circumstances that contribute to social isolation are amendable
2. Promote social interactions. and that the community nurse is in the position to affect
changes.
3. Assist the client in identifying activities that encourage
socialization. 2. Positive social interactions may act as a basis for the client
to establish new social group relationships ( Cruwys et al, 2014
).
3. According to this study, the sooner the older client is
supported in mobility and social participation, the sooner he or
she will be able to experience a sense of well-being and
lessening of the feelings of social isolation ( Elbasan et al,
2013 ).
EVALUATION/CLIENT RESPONSE/PROGRESS
While on the unit with this client, I established a therapeutic relationship by introducing myself and why I was on the unit that
day. I told him about the groups that day and encouraged him to join the spirituality group that was currently happening. He did
not verbally respond to any of my interactions/suggestions, and he continued to pace the hallways and eventually went back into
his room. What did work from these interventions was that the client expressed a look of dissatisfaction when I told him about
the group that was currently happening.
3. NURSING DIAGNOSIS R/T AEB
Ineffective Health maintenance Behaviors r/t cognitive dysfunction as evidenced by medication and care plan noncompliance.
INTERVENTIONS RATIONALES
1. Assess the client's perception of health and health 1. A study of 681 older clients with diabetes or metabolic
maintenance. syndrome found that they often underestimate their
cardiovascular risk, with as many as 42% perceiving
2. Provide information that supports informed decision- themselves to be in good or excellent health ( Martell-Claros
making. et al, 2013 ).
3. Assess the client's feelings, values, and reasons for not 2. In a modified grounded theory study (N = 59), participants
following the prescribed plan of care. endorsed the elements of informed decision-making, including
discussion of the role of the client, the clinical issue, the
alternatives, and benefits/risks/uncertainties; assessment of
client understanding and preference; soliciting input from
trusted others; and discussion of the effect on clients’ daily
lives ( Price et al, 2012 ).
3. A systematic review of 80 studies determined that personal
beliefs and values, decisional control preferences, and
perception of the decision-making process affect treatment
decision-making in older adults diagnosed with cancer (
Tariman et al, 2012 ).
EVALUATION/CLIENT RESPONSE/PROGRESS
I was not able to perform these interventions with the client, but I gathered my information from his chart to create this
intervention. If I were to implement these interventions, the client should be able to make more informed decisions on how to
properly manage his health to promote his health status. Revisions that I would make for next time would be to implement
interventions that did not require the client to speak so often.
You might also like
- Psychiatric Nursing Skills Lab Treatment ModalitiesDocument2 pagesPsychiatric Nursing Skills Lab Treatment ModalitiesMeryville JacildoNo ratings yet
- Callo, Dimple C. (Case Scenario 2)Document4 pagesCallo, Dimple C. (Case Scenario 2)Dimple Castañeto CalloNo ratings yet
- Case Study SchizophreniaDocument3 pagesCase Study SchizophreniaCHRISANTO ARZANANNo ratings yet
- Pre-Orientation Phase: Anisa A. JamitoDocument23 pagesPre-Orientation Phase: Anisa A. JamitoBella DonnaNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment (Rle) : Interview Techniques Biographic DataDocument3 pagesHealth Assessment (Rle) : Interview Techniques Biographic DataLile RajabaNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument10 pagesDocumentNylia AtibiNo ratings yet
- NCP Adolescent - CunadaDocument4 pagesNCP Adolescent - CunadaGamer TimeNo ratings yet
- Doctor - Patient RelationshipDocument32 pagesDoctor - Patient RelationshipRushdaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlansDocument10 pagesNursing Care PlansGracie S. Vergara100% (1)
- Not Just For Soos .: Soo Prep Guide and Review of The Patient Centred Clinical Method (PCCM)Document7 pagesNot Just For Soos .: Soo Prep Guide and Review of The Patient Centred Clinical Method (PCCM)Peterpeter AndrewNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation ObjectivesDocument2 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation ObjectivesElaine dadaNo ratings yet
- Essential Elements of CommunicationDocument11 pagesEssential Elements of CommunicationMeriele AndreaNo ratings yet
- Perry 2020Document14 pagesPerry 2020Oliver CRNo ratings yet
- Conducting A Nurse Consultation: ClinicalDocument6 pagesConducting A Nurse Consultation: ClinicalAlif Akbar HasyimiNo ratings yet
- Boa Comunicação (BMJ02) PDFDocument4 pagesBoa Comunicação (BMJ02) PDFJonas NascimentoNo ratings yet
- Conflict PaperDocument10 pagesConflict PapermahnumaNo ratings yet
- 02章(30 89)物理治疗转诊筛查Document60 pages02章(30 89)物理治疗转诊筛查zhangpengNo ratings yet
- Con Ict Management: Difficult Conversations With Dif Ficult PeopleDocument6 pagesCon Ict Management: Difficult Conversations With Dif Ficult PeoplePricopi VictorNo ratings yet
- Heidi 467Document3 pagesHeidi 467Medicina UFU 92No ratings yet
- Cancer Nursing Care PlansDocument26 pagesCancer Nursing Care PlansMildred AlidonNo ratings yet
- MMHDocument8 pagesMMHClaudineNo ratings yet
- Principles of Palliative Care 2nd PartDocument26 pagesPrinciples of Palliative Care 2nd PartDisala Ranaweera100% (1)
- Cabanis Dynamic Model NotesDocument13 pagesCabanis Dynamic Model NotesDisha ToshniwalNo ratings yet
- CAAR Example 2021Document9 pagesCAAR Example 2021KashaNo ratings yet
- The Doctor-Patient Relationship and Interviewing TechniquesDocument50 pagesThe Doctor-Patient Relationship and Interviewing TechniquesPranay KumarNo ratings yet
- Running Head: Effectiveness of Dementia Inteventions 1Document17 pagesRunning Head: Effectiveness of Dementia Inteventions 1John Mureithi NjugunaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Health (2nd Quarter)Document13 pagesLesson 6 Health (2nd Quarter)Anonymous b6TnI2No ratings yet
- Communication: Communication Is A Process of Sharing Information and Meaning, of Sending and Receiving MessagesDocument5 pagesCommunication: Communication Is A Process of Sharing Information and Meaning, of Sending and Receiving MessagesNina OaipNo ratings yet
- PX Assesment: Assessment Diagnosis Planning ImplementationDocument23 pagesPX Assesment: Assessment Diagnosis Planning ImplementationDNAANo ratings yet
- De-Escalation in Health Care. Quick Safety. The Joint Commission, Division of Healthcare Improvement Issue 47 - January 2019Document4 pagesDe-Escalation in Health Care. Quick Safety. The Joint Commission, Division of Healthcare Improvement Issue 47 - January 2019Urgencias HorwitzNo ratings yet
- Psychotherapy with Adolescents and Their Families: Essential Treatment StrategiesFrom EverandPsychotherapy with Adolescents and Their Families: Essential Treatment StrategiesNo ratings yet
- Clark SAD Assessment CHPTDocument16 pagesClark SAD Assessment CHPTMavis BeaconNo ratings yet
- 1.introduction To Behavioral SciencesDocument18 pages1.introduction To Behavioral SciencesFaisal Mehboob100% (1)
- Managing Adolescents With Chronic Illness - Part 2 (Final)Document35 pagesManaging Adolescents With Chronic Illness - Part 2 (Final)mohdfaidhiNo ratings yet
- PSYCH-CRISIS-MSE-SELFAWARENESS-NOTESDocument10 pagesPSYCH-CRISIS-MSE-SELFAWARENESS-NOTESAmirrah LaurenteNo ratings yet
- Cap 8 WeineirDocument8 pagesCap 8 WeineirAitana ParrillaNo ratings yet
- Ease of Screening For Depression and DeliriumDocument6 pagesEase of Screening For Depression and DeliriumThaísa NogueiraNo ratings yet
- Communication Skills in MedicineDocument5 pagesCommunication Skills in MedicineSGD blima semlimanamNo ratings yet
- PrinciplesofSkillsAssessmentinDBT SwalesDunkleyDocument13 pagesPrinciplesofSkillsAssessmentinDBT SwalesDunkleyPaula TrindadeNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Clinical Assessment GuideDocument10 pagesModule 2 Clinical Assessment GuideBins AgaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Patient with Ineffective CopingDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for Patient with Ineffective Copinglouie john abilaNo ratings yet
- Getting The Most Out of The Clinical Encounter: The Four Habits ModelDocument10 pagesGetting The Most Out of The Clinical Encounter: The Four Habits Modelliao01No ratings yet
- Care Plans: o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o oDocument12 pagesCare Plans: o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o oNylia AtibiNo ratings yet
- professional reflection paper revised for eportfolioDocument5 pagesprofessional reflection paper revised for eportfolioapi-739232245No ratings yet
- Delirium: Section I: Scenario DemographicsDocument6 pagesDelirium: Section I: Scenario DemographicsNikey LimNo ratings yet
- Descriptive StatisticsDocument16 pagesDescriptive StatisticsSaadia TalibNo ratings yet
- Social Mktg Ppt 3Document17 pagesSocial Mktg Ppt 3abdelamuzemil8No ratings yet
- Running Head: Effectiveness of Dementia Inteventions 1Document12 pagesRunning Head: Effectiveness of Dementia Inteventions 1John Mureithi NjugunaNo ratings yet
- SPIKES ProtocolDocument4 pagesSPIKES ProtocolKassem Gharaibeh100% (1)
- Delivering Bad News Sensitively Using the SPIKES ProtocolDocument4 pagesDelivering Bad News Sensitively Using the SPIKES ProtocolHussam KabakbjiNo ratings yet
- ReflectionDocument14 pagesReflectionJosef AgyemanNo ratings yet
- Module 4a NCM 114Document84 pagesModule 4a NCM 114SONZA JENNEFERNo ratings yet
- Restraint in NursingDocument6 pagesRestraint in Nursingbabayao35No ratings yet
- Van Scoyoc, S. (2017) - The Use and Misuse of Psychometrics in Clinical Settings. in B. Cripps (Ed.)Document17 pagesVan Scoyoc, S. (2017) - The Use and Misuse of Psychometrics in Clinical Settings. in B. Cripps (Ed.)susanvanscoyoc9870No ratings yet
- Topical Questions + AnswerDocument40 pagesTopical Questions + AnswerThenaamutan AmuthanNo ratings yet
- A Case of Anxiety Related To Unprotected SexualDocument22 pagesA Case of Anxiety Related To Unprotected SexualAlyssa Mae AzarconNo ratings yet
- Assessment and Intervention Short AnswersDocument15 pagesAssessment and Intervention Short AnswersPrecious Winlove LumagbasNo ratings yet
- HA WK4aDocument10 pagesHA WK4aMARY ROSE FAJUTINANo ratings yet
- NCP IneffectiveHealthMaintenanceDM2Document3 pagesNCP IneffectiveHealthMaintenanceDM2Arone SebastianNo ratings yet
- Arguments in English text on benefits of studying abroadDocument2 pagesArguments in English text on benefits of studying abroadNarcos Ben100% (1)
- MODULE 9 VygotskyDocument4 pagesMODULE 9 VygotskyTricia Morga83% (12)
- Understanding Rhetorical SituationsDocument5 pagesUnderstanding Rhetorical SituationsMICHAELINA MARCUSNo ratings yet
- Making Sense of Art HistoryDocument114 pagesMaking Sense of Art HistoryKenneth PlasaNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Smartphone Addiction On Academic Performance of Higher Education StudentsDocument44 pagesThe Impact of Smartphone Addiction On Academic Performance of Higher Education Studentscareer pathNo ratings yet
- Telenor en BangladeshDocument74 pagesTelenor en BangladeshrenteivanNo ratings yet
- Apo 27Document12 pagesApo 27Elena Alexa100% (1)
- 10 1001@jamapediatrics 2018 5056Document7 pages10 1001@jamapediatrics 2018 5056Aris BayuNo ratings yet
- DELIVERING MY LESSON PLANDocument13 pagesDELIVERING MY LESSON PLANJayrel Fabrero100% (1)
- Classroom ManagementDocument25 pagesClassroom ManagementAye Pyae SoneNo ratings yet
- Decisions and Desire: - by Group 4Document46 pagesDecisions and Desire: - by Group 4Adarsh BansalNo ratings yet
- DIASS Project SemicolonDocument6 pagesDIASS Project SemicolonRomano Felizar BenzulaNo ratings yet
- A Literary Analysis: I. TitleDocument3 pagesA Literary Analysis: I. TitleSuico, Agnes Catherine100% (1)
- Written Assignment Unit 2Document6 pagesWritten Assignment Unit 2Francis Desoliviers Winner-BluheartNo ratings yet
- Complacency - Safety Toolbox Talks Meeting TopicsDocument2 pagesComplacency - Safety Toolbox Talks Meeting Topicsshadow21No ratings yet
- HTW 8-3-5 - Upgrade Model Course 1.21 On Personal Safety and Social Responsibilities (Dominica)Document3 pagesHTW 8-3-5 - Upgrade Model Course 1.21 On Personal Safety and Social Responsibilities (Dominica)PETER RAFANo ratings yet
- MR Know AllDocument4 pagesMR Know AllIdinz Seband100% (3)
- Unit 16: Goals and Accomplishments: Nivel B1Document4 pagesUnit 16: Goals and Accomplishments: Nivel B1Marcela BlandonNo ratings yet
- The List of Millennial CharacteristicsDocument13 pagesThe List of Millennial CharacteristicsLem Eruel MabutasNo ratings yet
- English12 Q4 W2 DebbiedelossantosDocument37 pagesEnglish12 Q4 W2 DebbiedelossantosJuliusSarmientoNo ratings yet
- Iago Character Analysis EssayDocument4 pagesIago Character Analysis EssayAsha Forsyth100% (11)
- 17 Tips Taking Initiative at WorkDocument16 pages17 Tips Taking Initiative at WorkHarshraj Salvitthal100% (1)
- 2018 A Level French C1 Oral CardsDocument26 pages2018 A Level French C1 Oral CardselisNo ratings yet
- Unit - 2 Oral Communication - Meaning, Advantages and LimitationsDocument15 pagesUnit - 2 Oral Communication - Meaning, Advantages and LimitationsTavishNo ratings yet
- CRT Campus Recruitment Test GuideDocument2 pagesCRT Campus Recruitment Test GuidePriyanshu SinghNo ratings yet
- DoshiDocument64 pagesDoshiDivya maniNo ratings yet
- Dan Lok - The Perfect Closing Script - Part 1 - The Agenda StepDocument4 pagesDan Lok - The Perfect Closing Script - Part 1 - The Agenda StepAries SattiNo ratings yet
- 30 Years Ago Opinion in Modern WayDocument3 pages30 Years Ago Opinion in Modern WayAngelo BananNo ratings yet
- Review: Mental Illness and RecoveryDocument6 pagesReview: Mental Illness and Recoveryantonio de diaNo ratings yet
- Advanced 2 - WorkbookDocument151 pagesAdvanced 2 - WorkbookMOYRA LORENA HUANCA OROSCONo ratings yet