Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Untitled
Uploaded by
Lubomira Suchecki0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views8 pagesThe document discusses why learning about the brain is important and provides key information about brain development and function. It notes that understanding how the brain develops allows us to better comprehend human growth and theories of development. It also explains that the brain develops based on stimuli received, outlines the eight neural pathways, and discusses how exercise and stimulating environments positively impact brain development while deprivation and abuse can hamper it.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses why learning about the brain is important and provides key information about brain development and function. It notes that understanding how the brain develops allows us to better comprehend human growth and theories of development. It also explains that the brain develops based on stimuli received, outlines the eight neural pathways, and discusses how exercise and stimulating environments positively impact brain development while deprivation and abuse can hamper it.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views8 pagesUntitled
Uploaded by
Lubomira SucheckiThe document discusses why learning about the brain is important and provides key information about brain development and function. It notes that understanding how the brain develops allows us to better comprehend human growth and theories of development. It also explains that the brain develops based on stimuli received, outlines the eight neural pathways, and discusses how exercise and stimulating environments positively impact brain development while deprivation and abuse can hamper it.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 8
Q: Why do we need to learn about the brain?
A: A basic knowledge about how the human
brain functions will allow us to better
understand the stages of human
development and the theories which
describe them.
` The brain develops according to the quantity and
quality of the stimuli it receives.
` There are eight neural pathways: touch, sight, sound,
taste, smell, temperature, pain and positioning.
` Daily exercise increases nerve connections in the
brain. This makes it easier for children to learn.
` The brain develops most strongly when all pathways
are being stimulated. (A child read to on her parents lap
learns more than language – she is developing emotional
responses, such as the ability to trust and a sense of safety).
` Brain development is hampered when
children are deprived, neglected, poorly fed
or abused.
` Negative environments in the early years can
impact ones ability to learn, provide for ones
self, form relationships, be healthy and
behave in socially acceptable ways.
` As a result of such findings…
x information on how to parent well is now available to
families.
` Researchers have also discovered…
x that the presence of just one caring committed adult in
early childhood and the adolescent years can produce
resiliency in adulthood.
= the ability to overcome problems and manage life effectively.
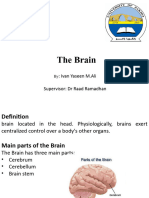
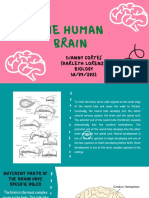
` The human brain is connected via the
nervous system to every part of the body.
` Medulla oblongata –controls vital processes of
heart rate, respiration, blood pressure, and
swallowing
` Pons controls of vital processes of respiration,
cardiovascular functions, coordination of eye
movements and balance
` Hypothalamus – links the nervous system to the
endocrine system
` Pituitary Gland - a gland that secretes 8
regulatory hormones
` Thalamus –relay station between the senses and
the cortex
` Cerebral Cortex – the outer layer of the brain consisting of
the parietal, occipital, frontal and temporal lobes
◦ Parietal Lobe - the middle lobe of each cerebral hemisphere
(located at the upper rear of the head); it contains important
sensory centers.
◦ Occipital lobe – helps process visual information.
◦ Temporal lobe – processes hearing, memory and language
functions.
◦ Frontal lobe – helps control voluntary movement, emotions,
reasoning, judgment, planning and goal setting
` Cerebellum – governs movement.
` Spinal Cord - a thick bundle of nerve fibers that runs from
the base of the brain to the hip area, running through the
spine (vertebrae).
` Hippocampus – spatial navigation and the consolidation of
short term to long term memory.
` Corpus Collosum – communication between brain
hemispheres.
` Using the textbook (page 218) and the
following diagram, label the brain on the back
of your notes (you will have to add extra
arrows!)
You might also like
- 03 ATA-24,33 E190 369pg PDFDocument369 pages03 ATA-24,33 E190 369pg PDFVolodymyrNo ratings yet
- Haroon a. Khan (Auth.)- Globalization and the Challenges of Public Administration_ Governance, Human Resources Management, Leadership, Ethics, E-Governance and Sustainability in the 21st Century-PalgrDocument216 pagesHaroon a. Khan (Auth.)- Globalization and the Challenges of Public Administration_ Governance, Human Resources Management, Leadership, Ethics, E-Governance and Sustainability in the 21st Century-PalgrGraham Herrick50% (2)
- Detailed Collection of All Synonyms From Cambridge IELTS BooksDocument78 pagesDetailed Collection of All Synonyms From Cambridge IELTS BooksAli Mehdi Maknojia92% (13)
- Educ2181 PP WeeblyDocument4 pagesEduc2181 PP Weeblyapi-363014935No ratings yet
- Negotiation and Diplomacy Term PaperDocument37 pagesNegotiation and Diplomacy Term PaperManifa OsmanNo ratings yet
- The Four Hinges Are The Four Cardinal Virtues: Gec 108: EthicsDocument7 pagesThe Four Hinges Are The Four Cardinal Virtues: Gec 108: EthicsDaniela Kian AyalaNo ratings yet
- Hular, Diane S. Physiological Psychology: Reaction Paper On Nervous SystemDocument2 pagesHular, Diane S. Physiological Psychology: Reaction Paper On Nervous SystemViola HastingsNo ratings yet
- Draft Case Study Traumatic Brain InjuryDocument47 pagesDraft Case Study Traumatic Brain InjuryTrixia Joy R NachorNo ratings yet
- Brain Structures and Their Functions PDFDocument26 pagesBrain Structures and Their Functions PDFNur Nashran Mahran100% (4)
- Nervous System Reaction PaperDocument3 pagesNervous System Reaction PaperJohn Ruel Sanchez IINo ratings yet
- The Human MindDocument15 pagesThe Human MindTEODORA SERAFIMNo ratings yet
- PerDev Powers of The Mind Lesson ActivitiesDocument9 pagesPerDev Powers of The Mind Lesson Activitieskath santiagoNo ratings yet
- The Power To ActDocument38 pagesThe Power To ActRed Lopez100% (1)
- Brain BasedDocument33 pagesBrain BasedDeshpande Shilpa100% (1)
- Central Nervous SystemDocument24 pagesCentral Nervous SystemanushkaNo ratings yet
- MHNDocument26 pagesMHNGopika SNo ratings yet
- Human BrainDocument12 pagesHuman BrainJashwanthNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesNervous Systemkitkat22phNo ratings yet
- CNP Module 2 - Brain and Spinal CordDocument13 pagesCNP Module 2 - Brain and Spinal CordTerrin ManjilaNo ratings yet
- The Cns Portfolio EditionDocument9 pagesThe Cns Portfolio Editionapi-438492450No ratings yet
- Brain and Nervous SystemDocument13 pagesBrain and Nervous SystemBrenda LizarragaNo ratings yet
- BrainDocument35 pagesBrainRonaleen mislang100% (1)
- Nervous System Reaction PaperDocument3 pagesNervous System Reaction PaperJohn Ruel Sanchez IINo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 The Mental SelfDocument12 pagesChapter 8 The Mental Selfbulcasejohn21No ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Brain: Brain DivisionsDocument3 pagesAnatomy of The Brain: Brain DivisionsUsagi TsukinoNo ratings yet
- Personal Development Lesson 6Document30 pagesPersonal Development Lesson 6Nikka Irah CamaristaNo ratings yet
- Brain Structure Psychology Chapter2 PDFDocument6 pagesBrain Structure Psychology Chapter2 PDFjosephttubogNo ratings yet
- RBEtrainingDocument16 pagesRBEtrainingChoco ByumNo ratings yet
- The Power of Mind NotesDocument8 pagesThe Power of Mind Notestrizzia acostaNo ratings yet
- Neuro Ppt. Lec. 1Document49 pagesNeuro Ppt. Lec. 1Jay successNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BrainDocument3 pagesIntroduction To BrainrgdevikaNo ratings yet
- Anatomia e Sistema NerosoDocument8 pagesAnatomia e Sistema NerosoChloe BujuoirNo ratings yet
- Neuro Case PresentationDocument52 pagesNeuro Case PresentationjisarafaelNo ratings yet
- Anaphy SemifinalsDocument5 pagesAnaphy SemifinalsRej CosainNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 19 Neurological SystemDocument38 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Chapter 19 Neurological SystemBrantNo ratings yet
- Neurologic AssessmentDocument56 pagesNeurologic AssessmentkeithlyndNo ratings yet
- The Brain. The Nervous SystemDocument13 pagesThe Brain. The Nervous SystemИрина КривошеяNo ratings yet
- Handout 2.4 - Science - Grade - 4Document5 pagesHandout 2.4 - Science - Grade - 4Syed Asim RazaNo ratings yet
- Ms - Angeline M.SC (N) Previous Year Psychiatric Nursing Choithram College of NursingDocument79 pagesMs - Angeline M.SC (N) Previous Year Psychiatric Nursing Choithram College of NursingPankaj TirkeyNo ratings yet
- Brain Devl On Middle ChildhoodDocument1 pageBrain Devl On Middle ChildhoodAntonette TaytayonNo ratings yet
- The Human BrainDocument6 pagesThe Human BraindamanzurNo ratings yet
- Personality Development Weeks 7-8 Lecture NoteDocument8 pagesPersonality Development Weeks 7-8 Lecture NoteCzarina Ciara AndresNo ratings yet
- Brain Structures and Their Functions 1 PDFDocument3 pagesBrain Structures and Their Functions 1 PDFAndrea RamirezNo ratings yet
- How To Keep Your Brain Young Prof Kerryn Phelps Full ChapterDocument67 pagesHow To Keep Your Brain Young Prof Kerryn Phelps Full Chapteranna.bryant691100% (10)
- Nervous SystemDocument22 pagesNervous Systemnirvashah1201No ratings yet
- The BrainDocument2 pagesThe BrainFernanda TéllezNo ratings yet
- Brainbased Learning 1207071173838260 5Document18 pagesBrainbased Learning 1207071173838260 5tanveer_techNo ratings yet
- Human BrainDocument13 pagesHuman BrainAaniya AsadNo ratings yet
- The BrainDocument12 pagesThe BrainSaadNo ratings yet
- 6.the Powers of The MindDocument61 pages6.the Powers of The MindClarisse LealNo ratings yet
- Biological Bases, AssignmentDocument6 pagesBiological Bases, AssignmentBenjii CarlosNo ratings yet
- OUR BODY Chapter - I (Science Class IV)Document4 pagesOUR BODY Chapter - I (Science Class IV)doultaniskNo ratings yet
- Brain System: Parts and FunctionsDocument9 pagesBrain System: Parts and FunctionsChristhoper John Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Group 5 Output 2 PDFDocument56 pagesNervous System Group 5 Output 2 PDFNicole Victorino LigutanNo ratings yet
- Nervous System ReportDocument11 pagesNervous System ReportsharkNo ratings yet
- Wk. 3 - Brain N Endocrine SystemDocument47 pagesWk. 3 - Brain N Endocrine SystemShayyy JacksonNo ratings yet
- Nervous System EditedDocument36 pagesNervous System EditedMellida Kate Winslet T.No ratings yet
- Nervous System Lesson Plan Grades 3 51Document12 pagesNervous System Lesson Plan Grades 3 51Alle LunagNo ratings yet
- NAME: - : Prepared By: Mitchell L. Rodriguez, Grade 4 TeacherDocument3 pagesNAME: - : Prepared By: Mitchell L. Rodriguez, Grade 4 TeacherRhiza PintoNo ratings yet
- HNP - Predisposing FDocument42 pagesHNP - Predisposing FLady Jean Milan ColataNo ratings yet
- The Central Nervous SystemDocument24 pagesThe Central Nervous SystemBlanche Mascarinas LaborteNo ratings yet
- Neuroscience in The Workplace How Understanding The Brain Can Transform Your Business e BookDocument34 pagesNeuroscience in The Workplace How Understanding The Brain Can Transform Your Business e BookHarish C NNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 2 - Module 2: Nervous SystemDocument20 pagesScience: Quarter 2 - Module 2: Nervous SystemHans Festin-DiazNo ratings yet
- The Human BrainDocument27 pagesThe Human BrainManuel Colindres 2.0No ratings yet
- Brain Health - How to Have a Healthy Memory and a Healthy BrainFrom EverandBrain Health - How to Have a Healthy Memory and a Healthy BrainNo ratings yet
- The Brain Is Composed of The,, andDocument23 pagesThe Brain Is Composed of The,, andMohd NizamNo ratings yet
- HHG4M - Lifespan Development Textbook Lesson On IdentityDocument10 pagesHHG4M - Lifespan Development Textbook Lesson On IdentityLubomira SucheckiNo ratings yet
- HHG4M - Lifespan Development Textbook Lesson 4Document88 pagesHHG4M - Lifespan Development Textbook Lesson 4Lubomira SucheckiNo ratings yet
- HHG4M - Lifespan Development Textbook Lesson 3Document68 pagesHHG4M - Lifespan Development Textbook Lesson 3Lubomira Suchecki100% (1)
- HHG4M - Lifespan Development Textbook Lesson 1Document24 pagesHHG4M - Lifespan Development Textbook Lesson 1Lubomira Suchecki100% (1)
- Socialization and Human Development: The Influence of Family, School, Media, CultureDocument37 pagesSocialization and Human Development: The Influence of Family, School, Media, CultureLubomira SucheckiNo ratings yet
- The Human Brain: Critical Periods of Brain DevelopmentDocument13 pagesThe Human Brain: Critical Periods of Brain DevelopmentLubomira SucheckiNo ratings yet
- Geo5 Fem Theoretical GuideDocument113 pagesGeo5 Fem Theoretical GuideAnonymous 87xpkIJ6CFNo ratings yet
- Aperin TOS Entrepreneurship Grade12Document2 pagesAperin TOS Entrepreneurship Grade12Arvin Austria AperinNo ratings yet
- Critical Analysis of Sonnet 18Document9 pagesCritical Analysis of Sonnet 18Shaina Eleccion50% (4)
- Karnataka HC Adoption 1 448484Document19 pagesKarnataka HC Adoption 1 448484Winston MenezesNo ratings yet
- Interference Fields: in Healing Chronic IllnessDocument7 pagesInterference Fields: in Healing Chronic IllnessPoorni ShivaramNo ratings yet
- 50 Examples of Complex SentencesDocument2 pages50 Examples of Complex Sentencestoreena99No ratings yet
- Unveiling The Factors Shaping Financial Choices Among Women in The Professional Sphere: An Analytical Framework Utilizing Structural Equation Modeling in Behavioral Finance.Document17 pagesUnveiling The Factors Shaping Financial Choices Among Women in The Professional Sphere: An Analytical Framework Utilizing Structural Equation Modeling in Behavioral Finance.International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Automata TheoryDocument6 pagesAutomata TheoryNilesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Example: 3: 6314 Square and Cube Numbers Page 1Document4 pagesExample: 3: 6314 Square and Cube Numbers Page 1Anonymous OlT7WTNo ratings yet
- Interview Feedback FormDocument4 pagesInterview Feedback FormRohit HNo ratings yet
- Mathematics in The Modern WorldDocument6 pagesMathematics in The Modern WorldDaniel ManimtimNo ratings yet
- The Role of Knowledge Management and Internal CommDocument9 pagesThe Role of Knowledge Management and Internal CommsamNo ratings yet
- Pubch 03Document111 pagesPubch 03Edwin Okoampa BoaduNo ratings yet
- EG Lagging Students 2016Document30 pagesEG Lagging Students 2016arickNo ratings yet
- ME 261 Numerical Analysis: System of Linear EquationsDocument15 pagesME 261 Numerical Analysis: System of Linear EquationsTahmeed HossainNo ratings yet
- NP9 VISVAS 9am 3avarthies 24th NovDocument1 pageNP9 VISVAS 9am 3avarthies 24th Novkomala2447_157422965No ratings yet
- Fact TablesDocument3 pagesFact TablesbashamscNo ratings yet
- Project Rahul (Internal Resistance)Document13 pagesProject Rahul (Internal Resistance)Ricky Kumar72% (18)
- Important Portions For End Term Exams (Section B)Document2 pagesImportant Portions For End Term Exams (Section B)Nayana RajeshNo ratings yet
- Asaba FSE Site Distribution - Week 20 FY12Document115 pagesAsaba FSE Site Distribution - Week 20 FY12Adetayo OnanugaNo ratings yet
- Tourist Behaviour Unit I & IIDocument83 pagesTourist Behaviour Unit I & IIRashmiranjanNo ratings yet
- Logit ProbitDocument17 pagesLogit ProbitGKGEANo ratings yet
- College Thesis. - BSED - 2022Document201 pagesCollege Thesis. - BSED - 2022Justin MirandoNo ratings yet
- 2015 Don C. Benjamin - Social World of Deuteronomy A New Feminist CommentaryDocument108 pages2015 Don C. Benjamin - Social World of Deuteronomy A New Feminist CommentaryPedro RamirezNo ratings yet