Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ABB Hospital 48
Uploaded by
pitigoi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageABB hospital
Original Title
ABB hospital 48
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentABB hospital
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageABB Hospital 48
Uploaded by
pitigoiABB hospital
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
thers ty meane of
3.3.3 Ducts
In group 2 medical locations the ducts installed
inside the room must be purposed excl
the power supply of the electrical devices and
their accessories present in the same room; in
practice, ducts that supply power to equipment
located in other rooms cannot pass through these
group 2 medical locations.
y for
The clrcults branching from a medical IT system
‘must necessarily be separated trom the electrical
circuits powered by other systems, and must,
therefore, be installed in separate pipingor ducts
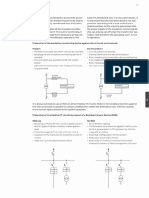
and boxes. The use of shared ducts and koxes is
also allowed provided that the separation is im-
plemented with an insulating separator (fig. 3.13).
The circuits of the Medical iT system can also be
implemented using unipolar cables (cords) of the
type NO7V-K (with the warning not to use navy,
blue or ight blue conductors, since amedical IT
system never has Neutral).
If it is impossible to implement a physical separa-
ton of two electrical systems, and the Medical IT
circuit runs through a duct "shared" with the con-
ductors of another system, double insulation ca~
bles with a non-metallic sheath must be used.
Inaddition, if the leakage current is due toa ca-
pacitive effect, it is recommended that the pro-
tection conductor be separated from the phase
conductors and then inserted in its own protec
tive tube,
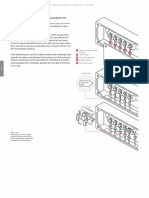
In group 2 medical locations where electromedi-
‘cal devices are used in order to monitor and sup-
port vital parameters, such as those of intensive
‘care, resuscitation and similar, the devices should
bbe powered using conductors that are shielded or
inserted in metallic piping asa precaution against
‘lectrical fields, Both the shieldings of the cables.
{as well as the metal piping must be equipoten-
tialised on the nearest node or sub-node.
For radiology and CAT rooms and rooms with
‘equipment that emits ionising radiation, the
power supply conductors shauld nat intarrupt tha
radiation shieldings present.
‘The protection of the ducts against overcurrents
must be implemented using omnipolar automatic,
miniature circuit breakers, Also in Medical T sys-
tems, the circuits branched to the secondary
must be protected with fuses or thermomagnetic
automatic miniature circuit breakers, but not with
RCDs because the RCD would not be effective in
this particular “medical insulation” system.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- ABB Hospital 58Document1 pageABB Hospital 58pitigoiNo ratings yet
- ABB Hospital 66Document1 pageABB Hospital 66pitigoiNo ratings yet
- ABB Hospital 61Document1 pageABB Hospital 61pitigoiNo ratings yet
- ABB Hospital 53Document1 pageABB Hospital 53pitigoiNo ratings yet
- ABB Hospital 64Document1 pageABB Hospital 64pitigoiNo ratings yet
- ABB Hospital 52Document1 pageABB Hospital 52pitigoiNo ratings yet
- ABB Hospital 54Document1 pageABB Hospital 54pitigoiNo ratings yet
- ABB Hospital 46Document1 pageABB Hospital 46pitigoiNo ratings yet
- ABB Hospital 67Document1 pageABB Hospital 67pitigoiNo ratings yet
- ABB Hospital 56Document1 pageABB Hospital 56pitigoiNo ratings yet
- ABB Hospital 39Document1 pageABB Hospital 39pitigoiNo ratings yet
- ABB Hospital 49Document1 pageABB Hospital 49pitigoiNo ratings yet
- ABB Hospital 43Document1 pageABB Hospital 43pitigoiNo ratings yet
- ABB Hospital 44Document1 pageABB Hospital 44pitigoiNo ratings yet
- ABB Hospital 55Document1 pageABB Hospital 55pitigoiNo ratings yet
- ABB Hospital 41Document1 pageABB Hospital 41pitigoiNo ratings yet
- ABB Hospital 30Document1 pageABB Hospital 30pitigoiNo ratings yet
- ABB Hospital 60Document1 pageABB Hospital 60pitigoiNo ratings yet
- ABB Hospital 45Document1 pageABB Hospital 45pitigoiNo ratings yet
- ABB Hospital 35Document1 pageABB Hospital 35pitigoiNo ratings yet
- ABB Hospital 42Document1 pageABB Hospital 42pitigoiNo ratings yet
- ABB Hospital 32Document1 pageABB Hospital 32pitigoiNo ratings yet
- ABB Hospital 26Document1 pageABB Hospital 26pitigoiNo ratings yet
- ABB Hospital 24Document1 pageABB Hospital 24pitigoiNo ratings yet
- ABB Hospital 37Document1 pageABB Hospital 37pitigoiNo ratings yet
- ABB Hospital 36Document1 pageABB Hospital 36pitigoiNo ratings yet
- ABB Hospital 25Document1 pageABB Hospital 25pitigoiNo ratings yet
- ABB Hospital 33Document1 pageABB Hospital 33pitigoiNo ratings yet
- ABB Hospital 31Document1 pageABB Hospital 31pitigoiNo ratings yet